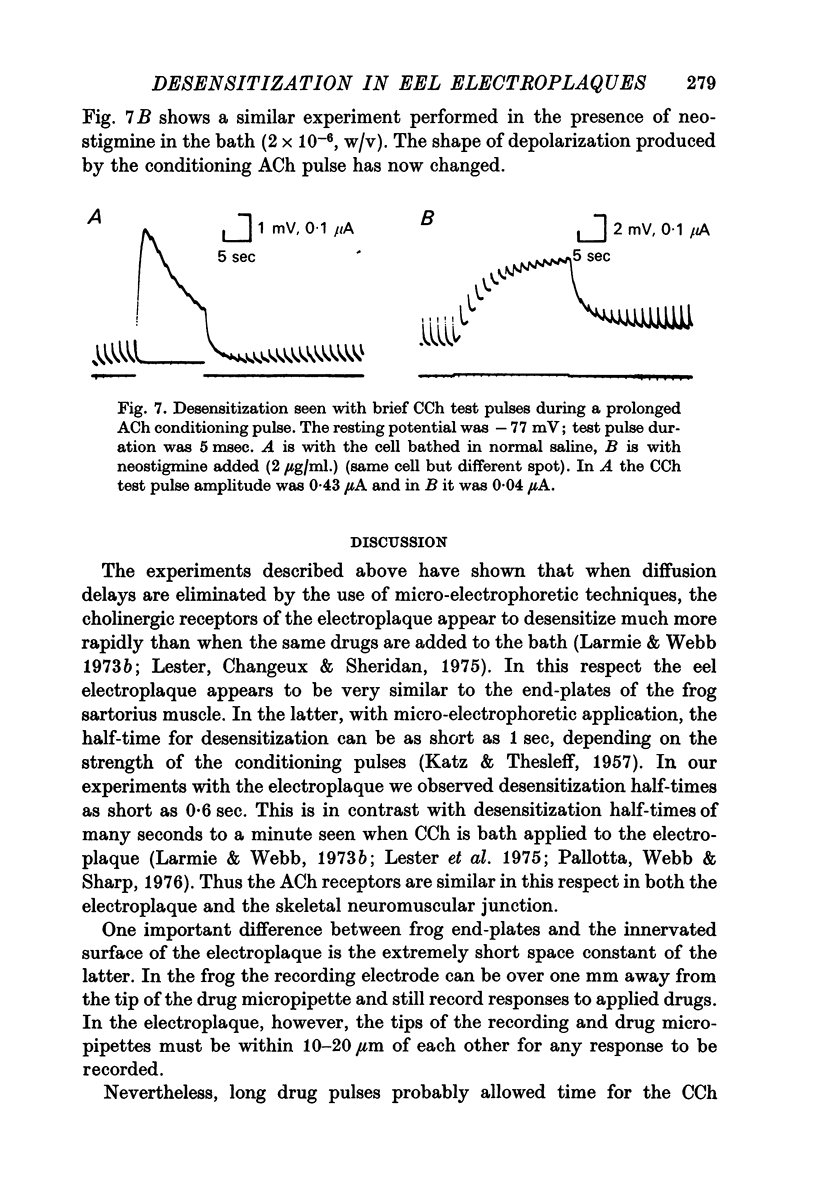
Abstract
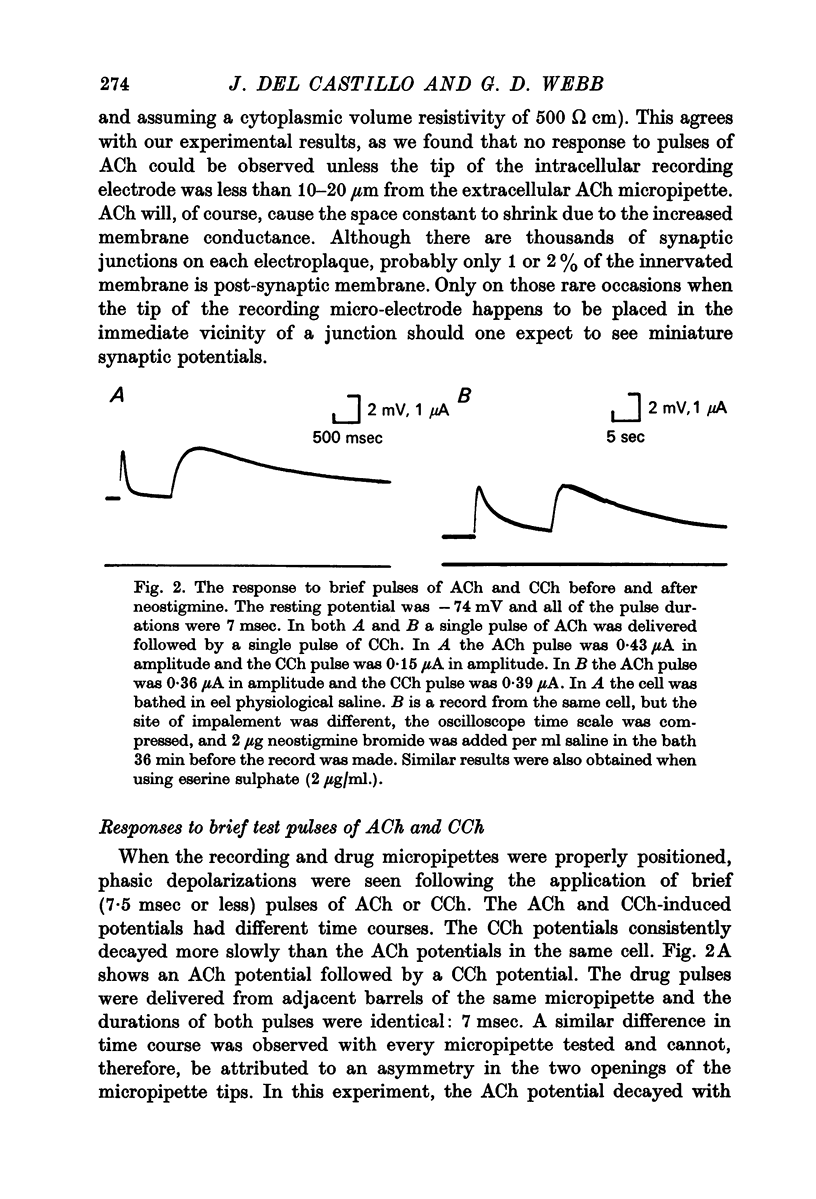
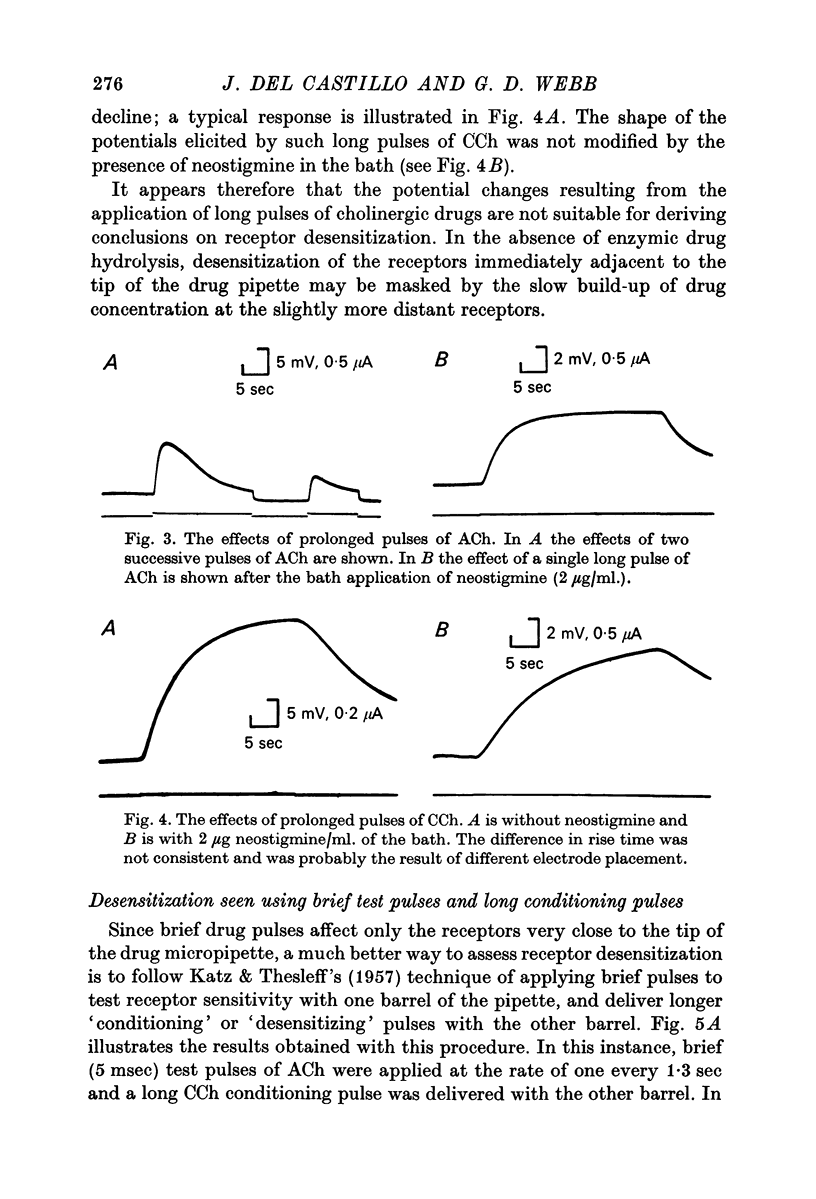
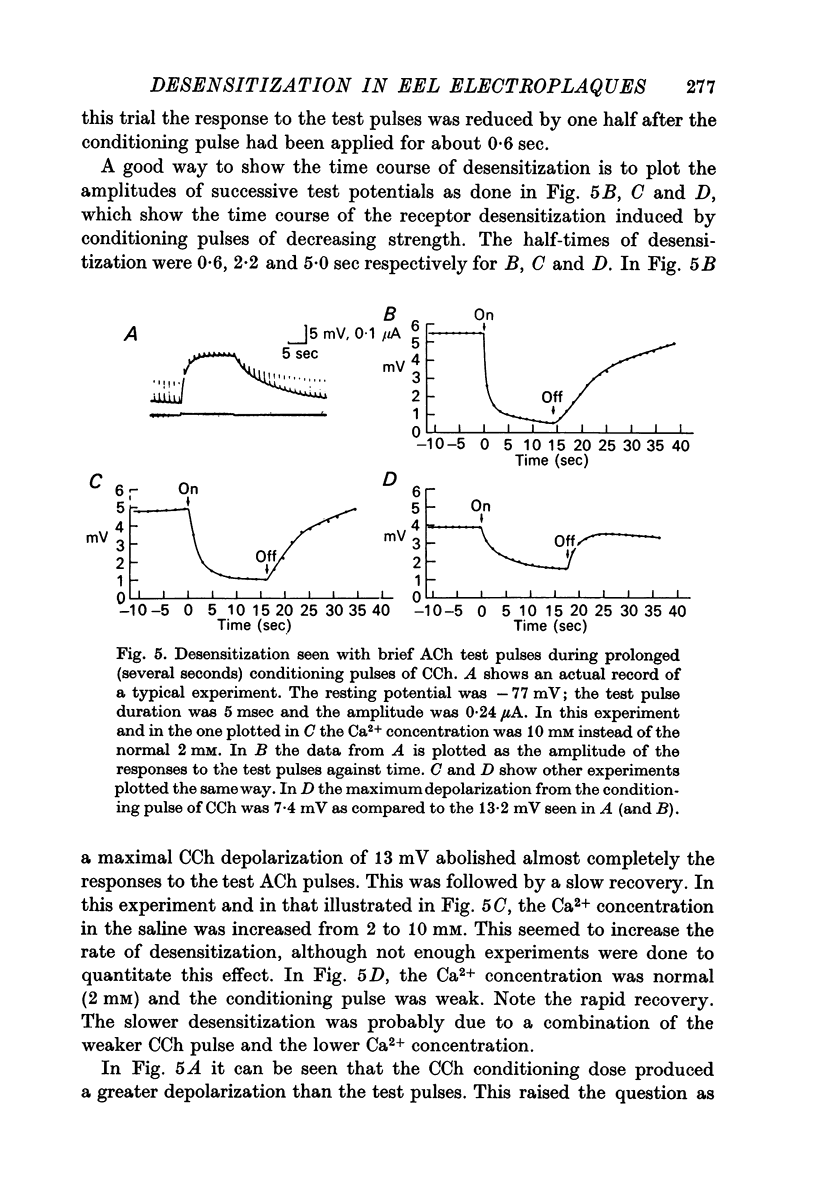
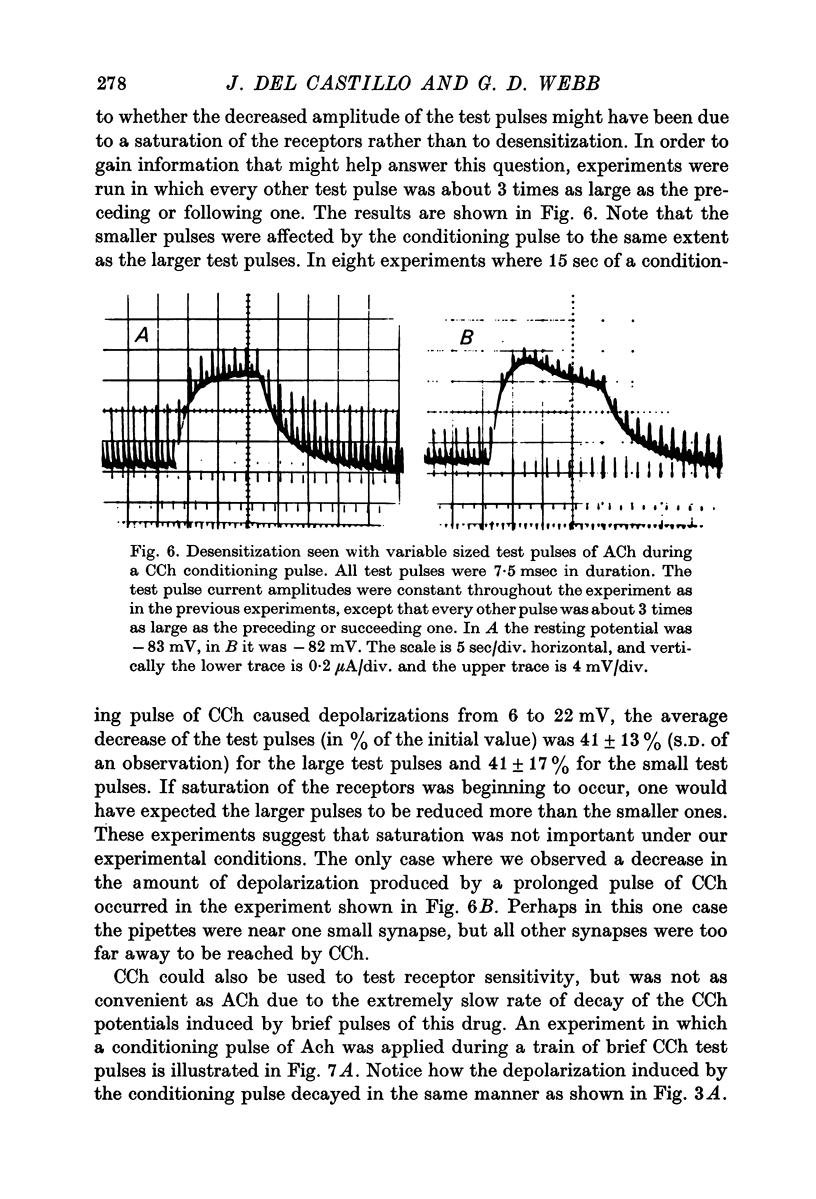
1. The electrical potential difference across the innervated membrane of the electroplaque of Electrophorus electricus was measured with an intracellular micro-electrode while an extracellular double-barrelled micropipette was used to apply acetylcholine and carbamylcholine iontophoretically very close to the point of insertion of the recording electrode. 2. The average depolarizing response to brief (several msec) pulses of carbamylcholine decayed 22 times more slowly than the response to acetylcholine. Treatment of the electroplaque with eserine or neostigmine prolonged the acetylcholine responses. 3. When a steady current of acetylcholine was applied for several seconds, the membrane first depolarized, then partially repolarized. Usually no repolarization was seen during long pulses of carbamylcholine or long pulses of acetylcholine in the presence of eserine or neostigmine. 4. During long conditioning pulses of acetylcholine or carbamylcholine, the responses to brief test pulses of acetylcholine showed a progressive decline in amplitude, but recovered after termination of the conditioning pulse. Desensitization half-times as short as 0-6 sec were observed, making these results similar to those obtained in the frog motor end-plate.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartels E. Reactions of acetylcholine receptor and esterase studied on the electroplax. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 Jun;17(6):945–966. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90353-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. A comparison of acetylcholine and stable depolarizing agents. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957 May 7;146(924):362–368. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1957.0017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Castillo J., Bartels E., Sobrino J. A. Microelectrophoretic application of cholinergic compounds, protein oxidizing agents, and mercurials to the chemically excitable membrane of the electroplax. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2081–2085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P. The electromotive action of acetylcholine at the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1950 Oct 16;111(3-4):408–422. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1950.sp004492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. A study of the desensitization produced by acetylcholine at the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):63–80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassignal N. L., Martin A. R. Reversal of acetylcholine potentials in eel electroplaque. Science. 1976 Feb 6;191(4226):464–466. doi: 10.1126/science.1246628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester H. A., Changeux J. P., Sheridan R. E. Conductance increases produced by bath application of cholinergic agonists to Electrophorus electroplaques. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Jun;65(6):797–816. doi: 10.1085/jgp.65.6.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Nakajima S., Grundfest H. Analysis of Spike Electrogenesis and Depolarizing K Inactivation in Electroplaques of Electrophorus electricus, L. J Gen Physiol. 1965 Nov 1;49(2):321–349. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nastuk W. L., Parsons R. L. Factors in the inactivation of postjunctional membrane receptors of frog skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Aug;56(2):218–249. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.2.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Manresa F., Grundfest H. Synaptic electrogenesis in eel electroplaques. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Jan;57(1):71–92. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb G. D., Hamrell B. B., Farquharson D. A., Niemi W. D. Studies of the blood chemistry of Electrophorus electricus and a new physiological saline solution based thereon. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 28;297(2):313–316. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


