Abstract
1. The effect of stimulation or inhibition of active Na—K transport on [3H]ouabain binding has been investigated in isolated soleus muscles and adipocytes.
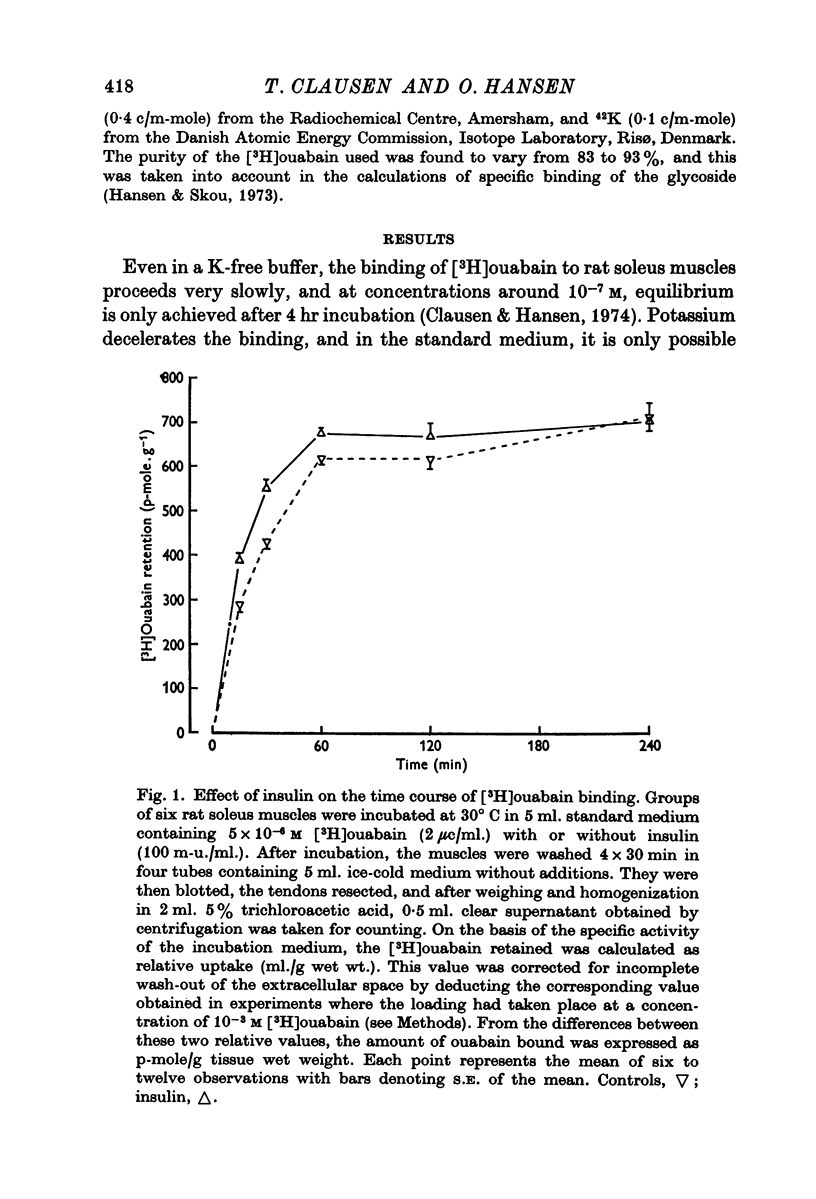
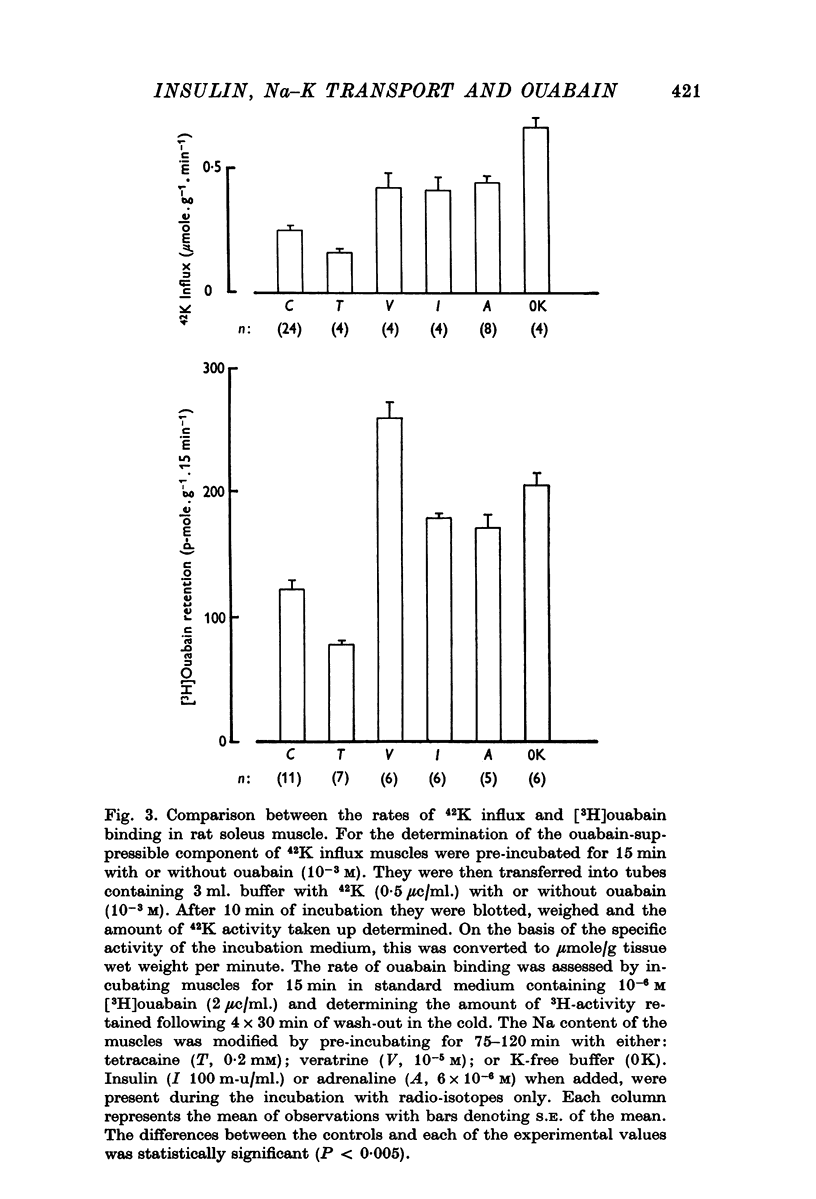
2. In rat soleus muscle, the ouabain-sensitive component of 42K influx was stimulated by insulin (100 m-u/ml.), adrenaline (6 × 10-6 M), and by pre-incubation with veratrine (10-5 M) or in a K-free buffer. In all of these instances, the rate of ouabain binding was increased by 41-113%. Conversely, pre-treatment with tetracaine (0·2 mM) decreased the 42K-influx and diminished the rate of [3H]ouabain binding by 36%.
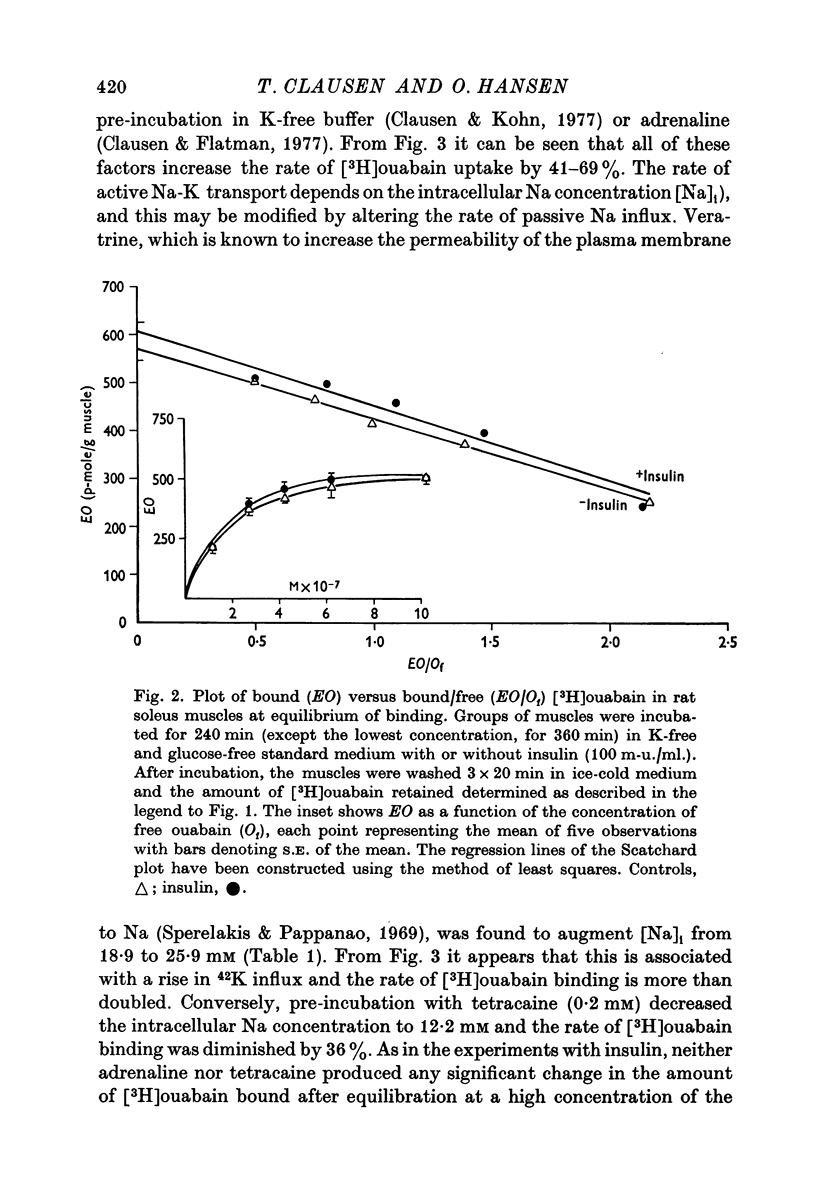
3. Neither insulin, adrenaline or tetracaine produced any detectable change in the total number of ouabain-binding sites (as measured under equilibrium conditions) in rat soleus muscle.
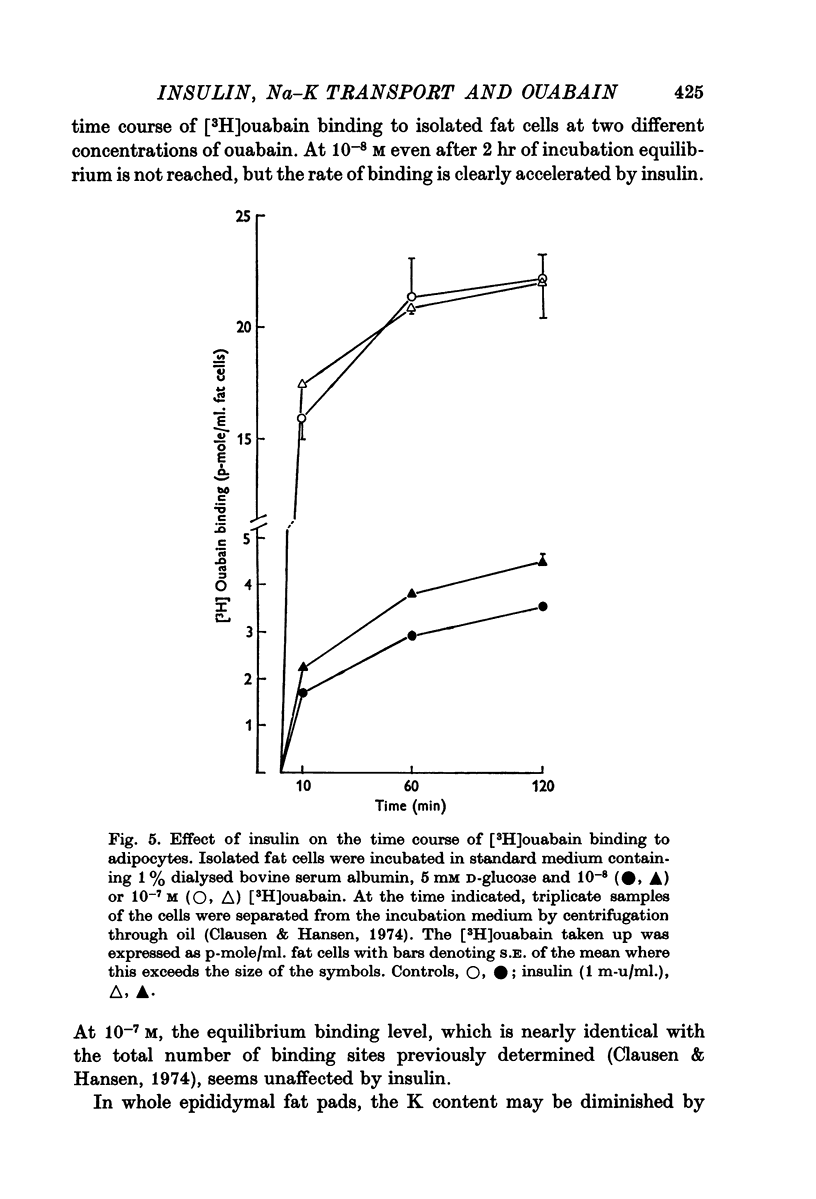
4. In mouse and guinea-pig soleus muscle and in fat cells isolated from rats, insulin also increased the rate of [3H]ouabain binding without producing any significant change in the total number of ouabain-binding sites.
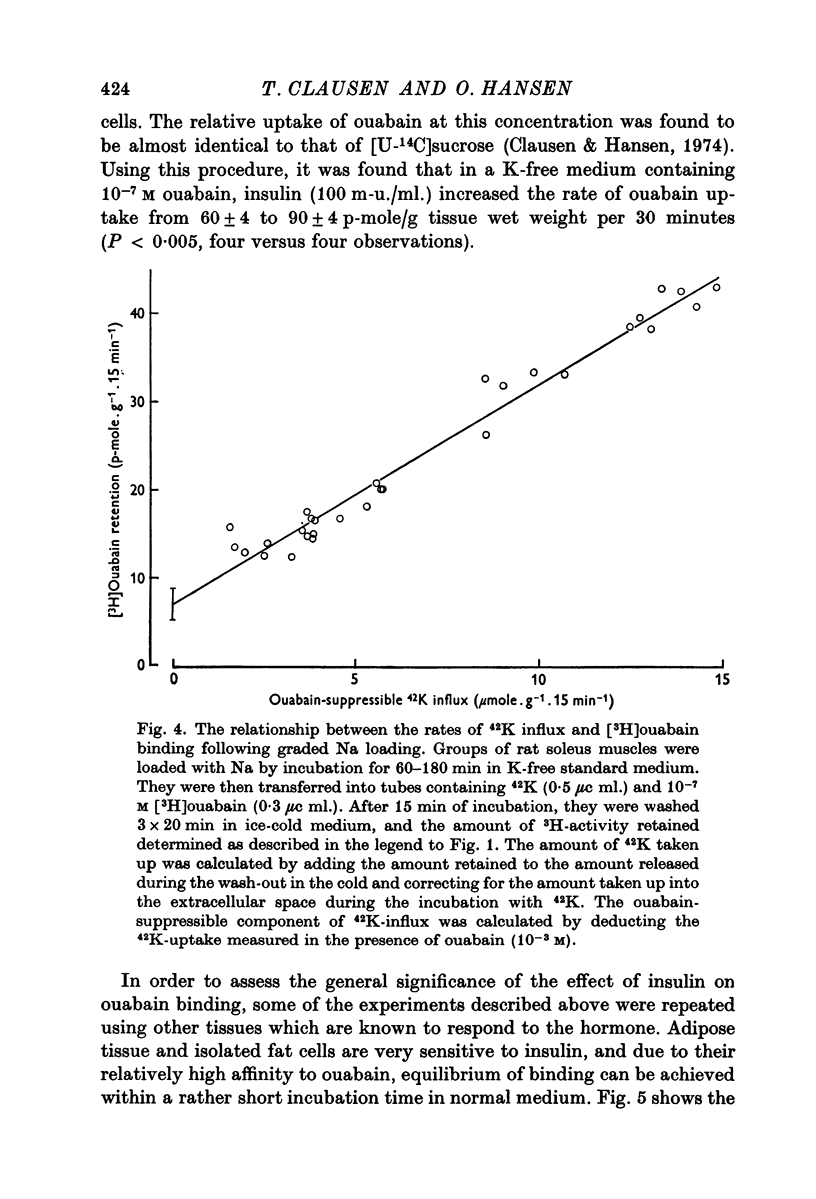
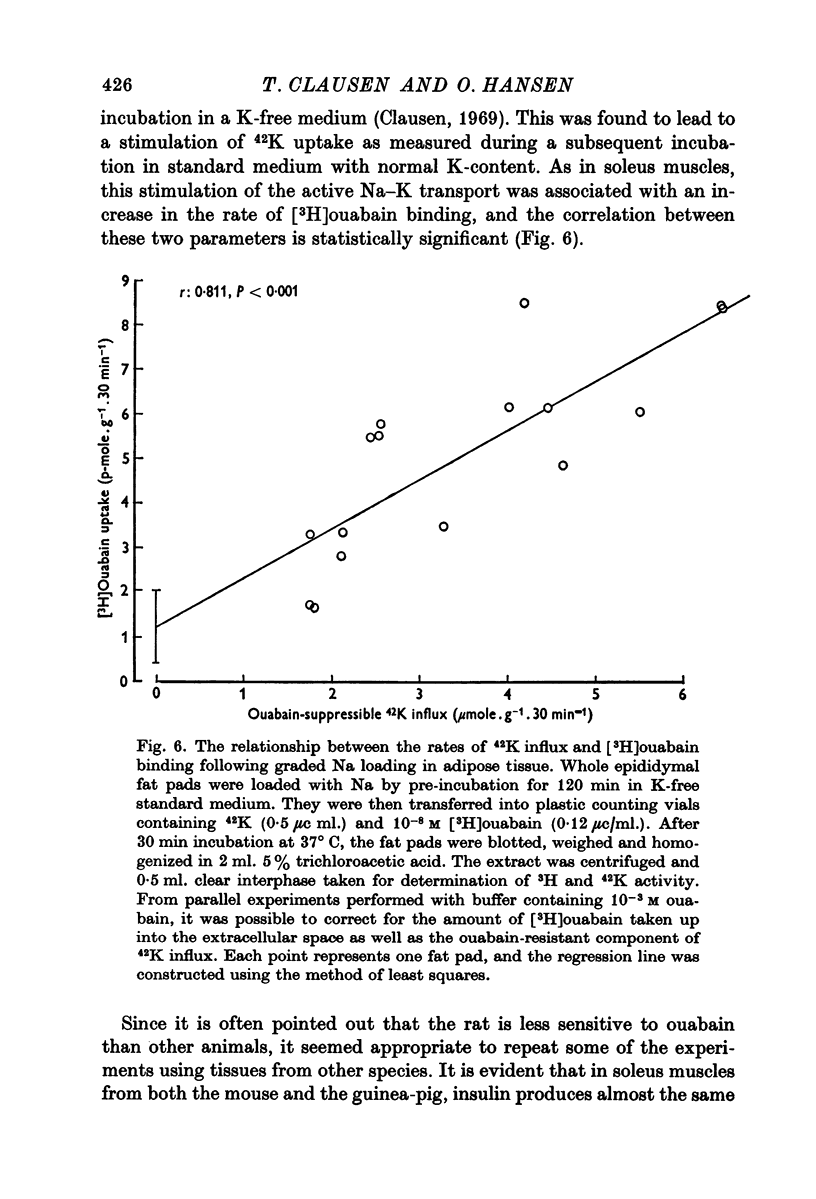
5. Both in soleus muscle and the epididymal fat pad of the rat, there was a linear correlation between 42K influx and the initial rate of [3H]ouabain binding.
6. It is concluded that the rate of ouabain binding is determined significantly by the rate of active Na—K transport, but within the time intervals studied (4-6 hr) stimulation or inhibition of the Na pump does not lead to any appreciable change in the total number of Na pumps. It seems unlikely that the stimulation of active Na—K transport by insulin or adrenaline is due to unmasking or de novo synthesis of Na pumps.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akera T., Brody T. M. Membrane adenosine triphosphatase. The effect of potassium on the formation and dissociation of the ouabain-enzyme complex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Mar;176(3):545–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Willis J. S. Binding of the cardiac glycoside ouabain to intact cells. J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(2):441–462. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodemann H. H., Hoffman J. F. Side-dependent effects of internal versus external Na and K on ouabain binding to reconstituted human red blood cell ghosts. J Gen Physiol. 1976 May;67(5):497–525. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.5.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caswell A. H., Lau Y. H., Brunschwig J. P. Ouabain-binding vesicles from skeletal muscle. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Oct;176(2):417–430. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90184-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen T., Flatman J. A. The effect of catecholamines on Na-K transport and membrane potential in rat soleus muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(2):383–414. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen T., Kohn P. G. The effect of insulin on the transport of sodium and potassium in rat soleus muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(1):19–42. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen T. The relationship between the transport of glucose and cations across cell membranes in isolated tissues. V. Stimulating effect of ouabain, K+-free medium and insulin on efflux of 3-O-methylglucose from epidimal adipose tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;183(3):625–634. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann E., Philipp G., Tanner Ouabain-receptor interactions in (Na+ + K+)-ATPase preparations. A contribution to the problem of nonlinear Scatchard plots. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 2;455(2):287–296. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90305-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlij D., Grinstein S. The number of sodium ion pumping sites in skeletal muscle and its modification by insulin. J Physiol. 1976 Jul;259(1):13–31. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen O., Skou J. C. A study on the influence of the concentration of Mg 2+ , P i , K + , Na + , and Tris on (Mg 2+ + P i )-supported g-strophanthin binding to (Na + = K + )activated ATPase from ox brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 7;311(1):51–66. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90254-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen O. The relationship between G-strophanthin-binding capacity and ATPase activity in plasma-membrane fragments from ox brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 9;233(1):122–132. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90364-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner C. H., Lauf P. K. The effect of anti-L on ouabain binding to sheep erythrocytes. J Membr Biol. 1975 Apr 23;21(1-2):99–112. doi: 10.1007/BF01941064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. L. Purification and characterization of (Na+ plus K+ )-ATPase. IV. Estimation of the purity and of the molecular weight and polypeptide content per enzyme unit in preparations from the outer medulla of rabbit kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 12;356(1):53–67. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90293-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn P. G., Clausen T. The relationship between the transport of glucose and cations across cell membranes in isolated tissues. VI. The effect of insulin, ouabain, and metabolic inhibitors on the transport of 3-O-methylglucose and glucose in rat soleus muscles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 2;225(2):277–290. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90221-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A., Lindenmayer G. E., Allen J. C. The sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphatase: pharmacological, physiological and biochemical aspects. Pharmacol Rev. 1975 Mar;27(01):3–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperelakis N., Pappano A. J. Increase in PNa and PK of cultured heart cells produced by veratridine. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Jan;53(1):97–114. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin T., Sen A. K. Stability and ligand sensitivity of (3H)ouabain binding to (Na+ + K+)ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jan 14;198(1):120–131. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


