Abstract
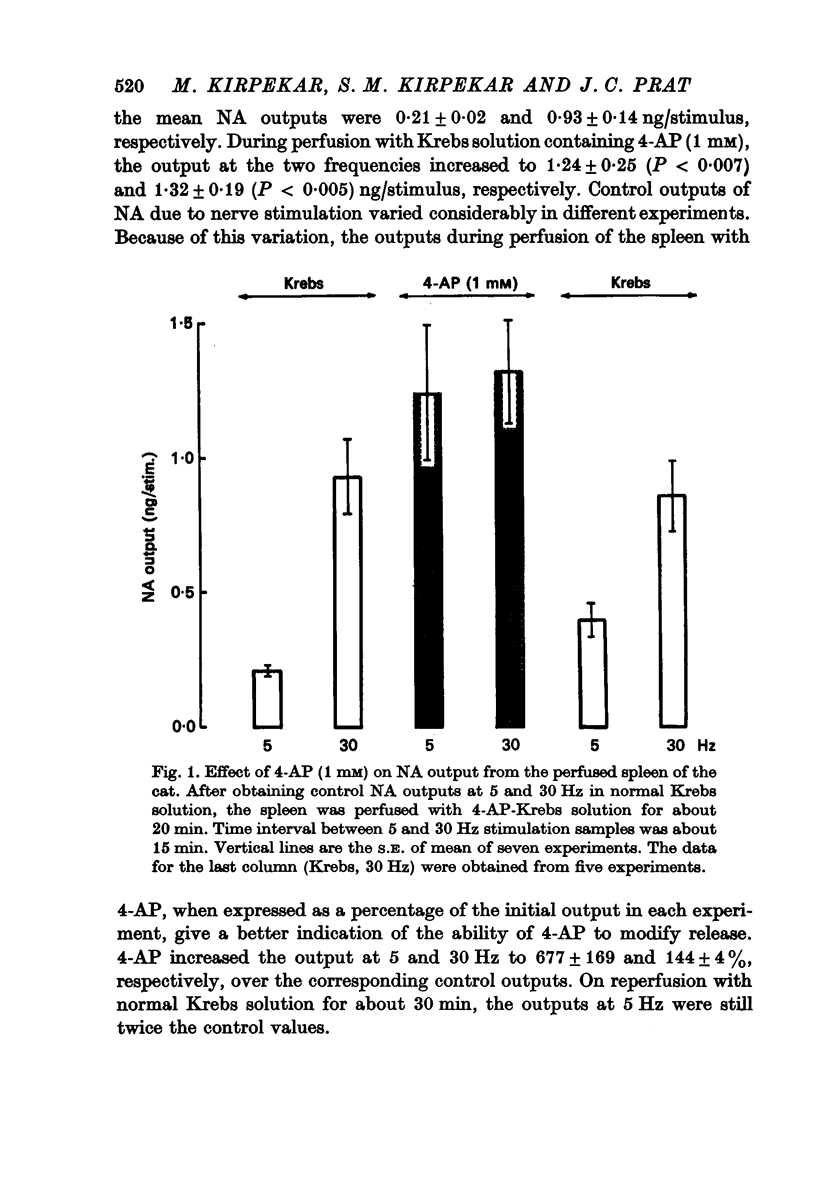
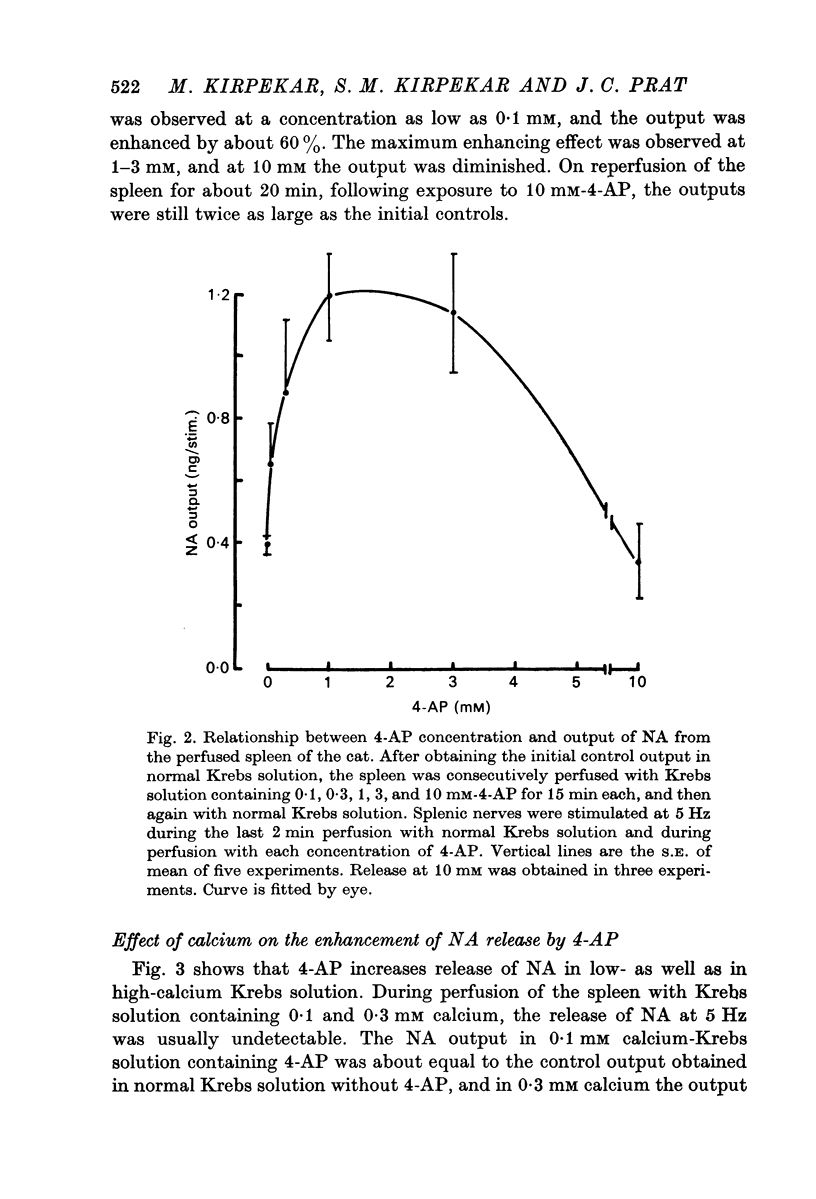
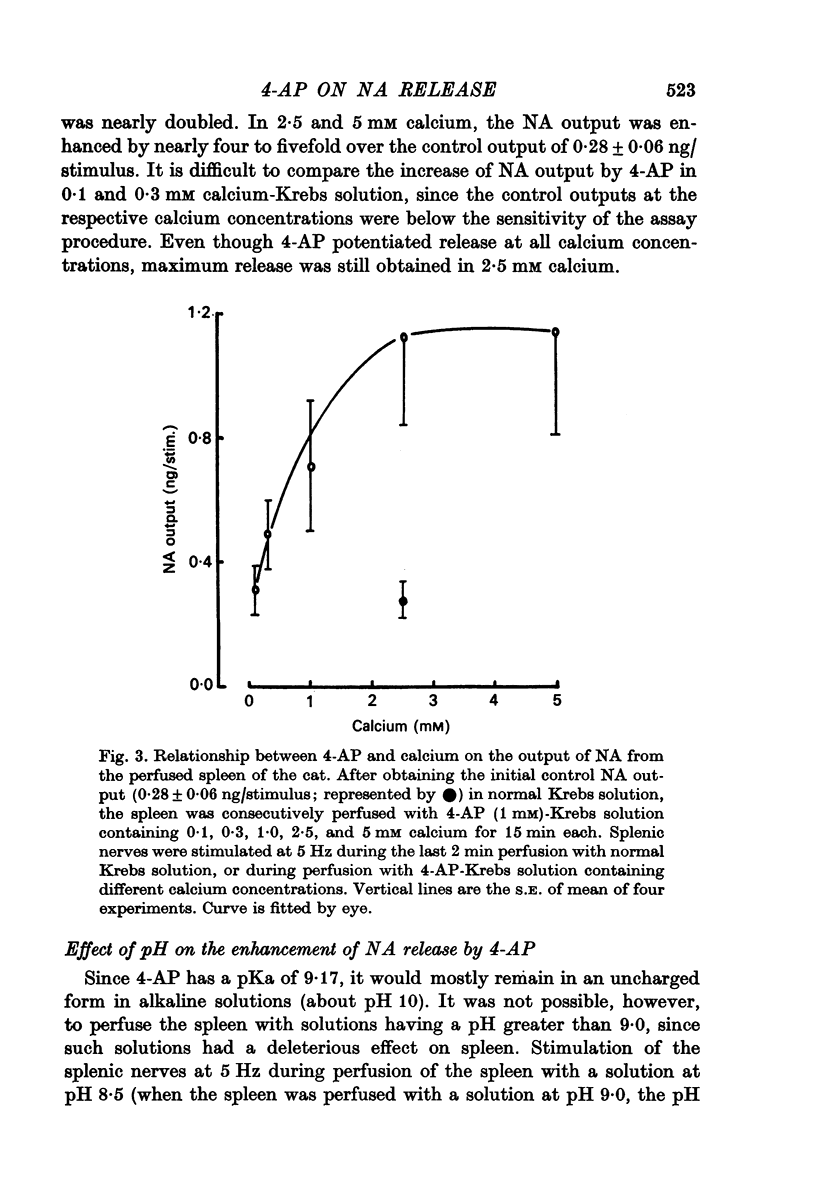
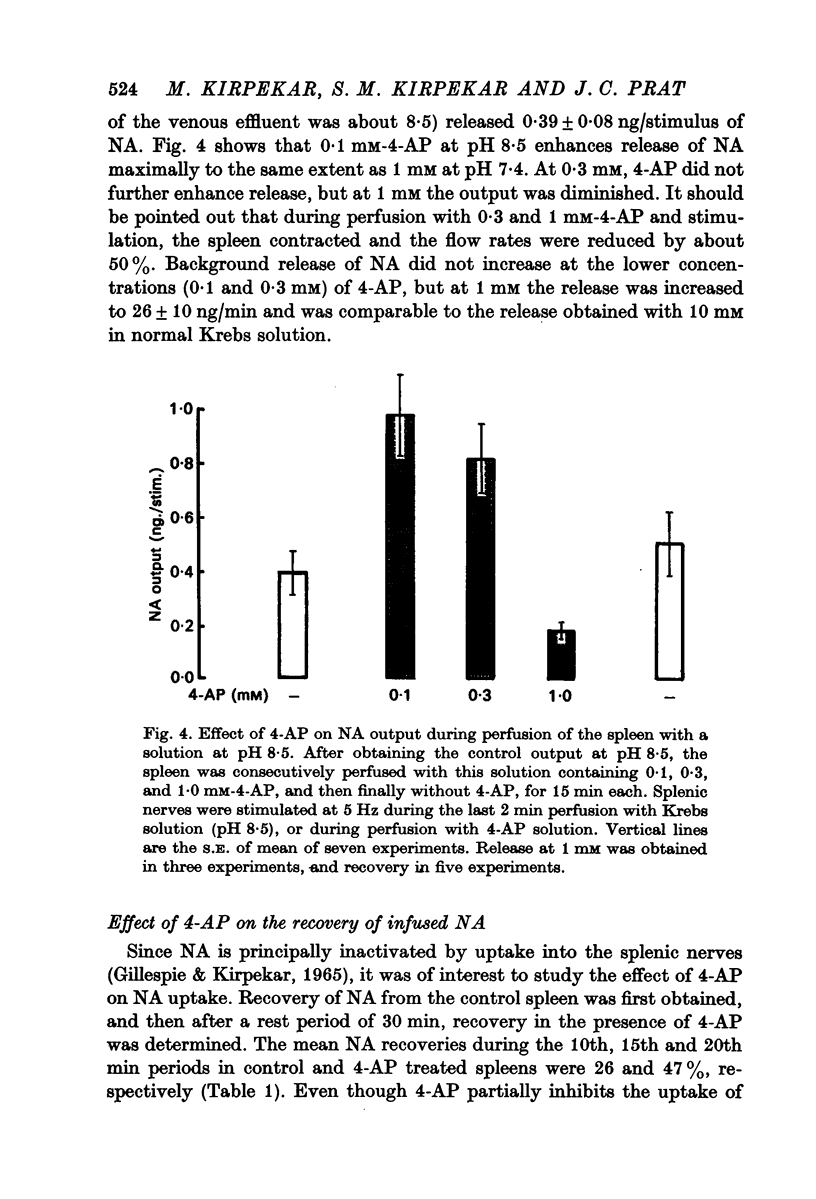
1. 4-aminopyridine (4-AP, 1 mM) increased noradrenaline (NA) output from the perfused cat spleen at 5 Hz by about fivefold. Enhancement of NA release by 4-AP was reversible. Output of NA induced by potassium was not affected. 2. NA output was doubled at low concentrations (0.1--0.3 mM) of 4-AP, but maximal effect was obtained at 1--3 mM. At 10 mM, it induced spontaneous release of NA which was insensitive to calcium. 3. Insignificant outputs obtained at 5 Hz in 0.1 and 0.3 mM calcium-Krebs solution were markedly enhanced by 4-AP. 4-AP enhanced release at all calcium concentrations up to 5 mM, but maximum output was obtained at 2.5 mM. 4. 4-AP at pH 8.5 was more effective in enhancing NA release than at pH 7.4. 5. 4-AP increased the recovery of intra-arterially infused NA from the control 26 to 47%. 6. 4-AP did not affect release of catecholamines (CA) from the perfused cat adrenal gland by acetylcholine (ACh). 7. It is suggested that 4-AP inactivates potassium current in sympathetic nerves and prolongs the duration of the action potential, thereby allowing a greater influx of calcium ions into the neurone to enhance release of NA.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANTON A. H., SAYRE D. F. A study of the factors affecting the aluminum oxide-trihydroxyindole procedure for the analysis of catecholamines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1962 Dec;138:360–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLIER B., EXLEY K. A. MECHANISM OF THE ANTAGONISM BY TETRAETHYLAMMONIUM OF NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCK DUE TO D-TUBOCURARINE OR CALCIUM DEFICIENCY. Nature. 1963 Aug 17;199:702–703. doi: 10.1038/199702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS W. W., RUBIN R. P. The role of calcium in the secretory response of the adrenal medulla to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1961 Nov;159:40–57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLESPIE J. S., KIRPEKAR S. M. THE INACTIVATION OF INFUSED NORADRENALINE BY THE CAT SPLEEN. J Physiol. 1965 Jan;176:205–227. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., Tilmisany A. K. The action of tetraethyl-ammonium chloride on the response of the rat anococcygeus muscle to motor and inhibitory nerve stimulation and to some drugs. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Sep;58(1):47–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb07692.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRPEKAR S. M., CERVONI P. EFFECT OF COCAINE, PHENOXYBENZAMINE AND PHENTOLAMINE ON THE CATECHOLAMINE OUTPUT FROM SPLEEN AND ADRENAL MEDULLA. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Oct;142:59–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOKETSU K. Action of tetraethylammonium chloride on neuromuscular transmission in frogs. Am J Physiol. 1958 Apr;193(1):213–218. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.193.1.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpekar S. M., Misu Y. Release of noradrenaline by splenic nerve stimulation and its dependence on calcium. J Physiol. 1967 Jan;188(2):219–234. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpekar S. M., Prat J. C., Puig M., Wakade A. R. Modification of the evoked release of noradrenaline from the perfused cat spleen by various ions and agents. J Physiol. 1972 Mar;221(3):601–615. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpekar S. M., Wakade A. R., Prat J. C. Effect of tetraethylammonium and barium on the release of noradrenaline from the perfused cat spleen by nerve stimulation and potassium. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1976 Jul;294(1):23–29. doi: 10.1007/BF00692781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Walton K., Bohr V. Synaptic transmission in squid giant synapse after potassium conductance blockage with external 3- and 4-aminopyridine. Biophys J. 1976 Jan;16(1):83–86. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85664-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meves H., Pichon Y. Proceedings: Effects of 4-aminopyridine on the potassium current in internally perfused giant axons of the squid. J Physiol. 1975 Sep;251(1):60P–62P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelhate M., Pichon Y. Proceedings: Selective inhibition of potassium current in the giant axon of the cockroach. J Physiol. 1974 Oct;242(2):90P–91P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Haefely W., Staehelin H. Potentiation by tetraethylammonium of the response of the cat spleen to postganglionic sympathetic nerve stimulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1967 Sep;157(3):532–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh J. Z., Oxford G. S., Wu C. H., Narahashi T. Interactions of aminopyridines with potassium channels of squid axon membranes. Biophys J. 1976 Jan;16(1):77–81. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85663-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


