Abstract
1. Ambiguities and discrepancies in the published descriptions of the patterns of breathing in man have been re-investigated.
Steady-state hyperpnoea during rest was induced in normal subjects of both sexes by means of CO2 inhalation, usually in high O2, but sometimes in low (PA, O2 ∼ 200 and 55 torr respectively).
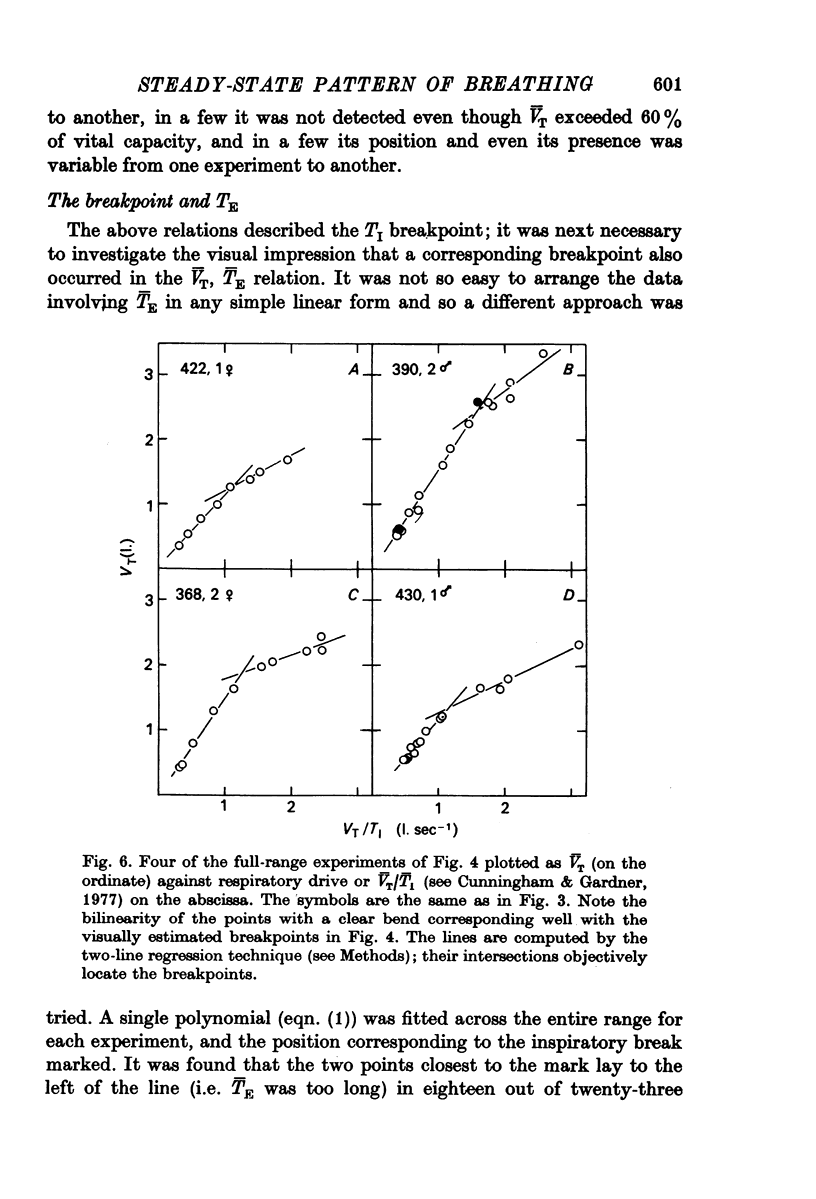
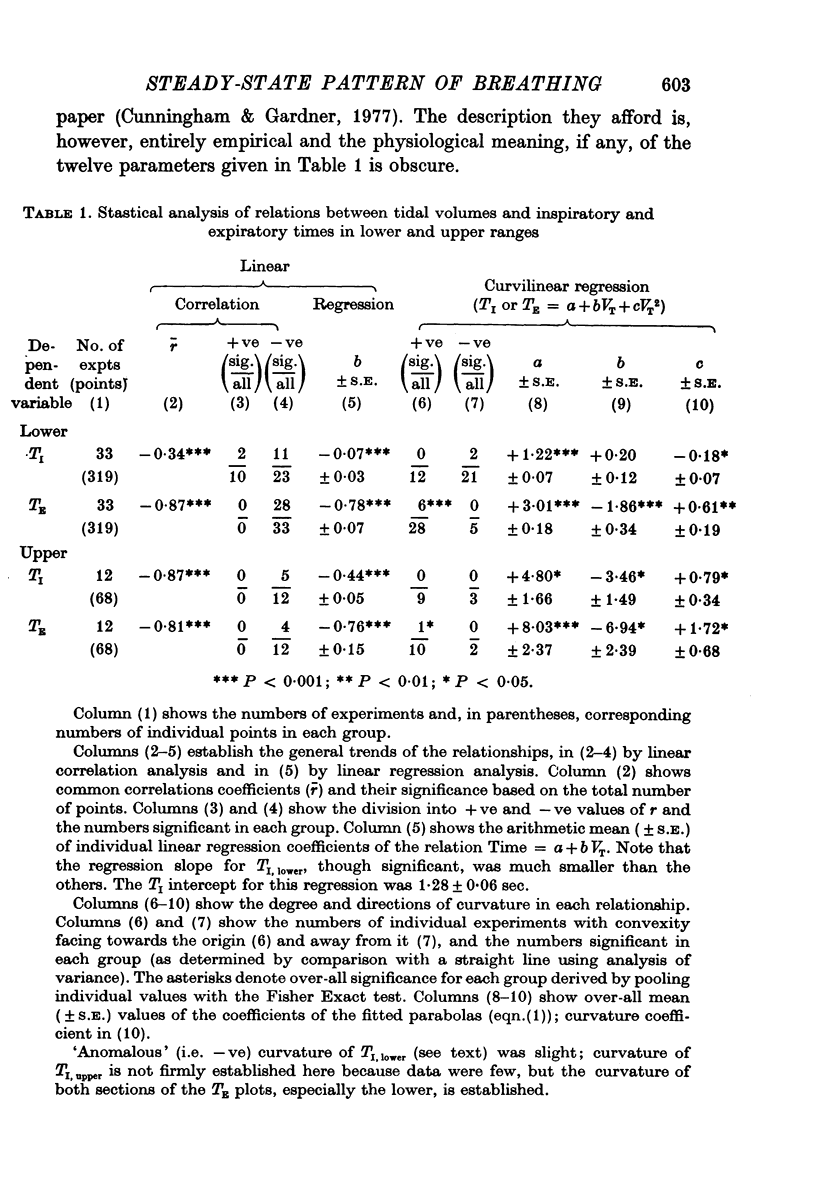
2. The relations between mean tidal volume V̄T and mean times for inspiration T̄I and expiration T̄E were satisfactorily divided into lower and upper parts (ranges 1 and 2) in nineteen out of thirty-three experiments using an objective least-squares method, and polynomials were fitted separately to each of the following pairs of variables V̄T,lower, T̄I; V̄T,lower, T̄E; V̄T,upper, T̄I; V̄T,upper, T̄E.
3. The breakpoints occurred when V̄T was about one third of vital capacity, but there was much variation between subjects.
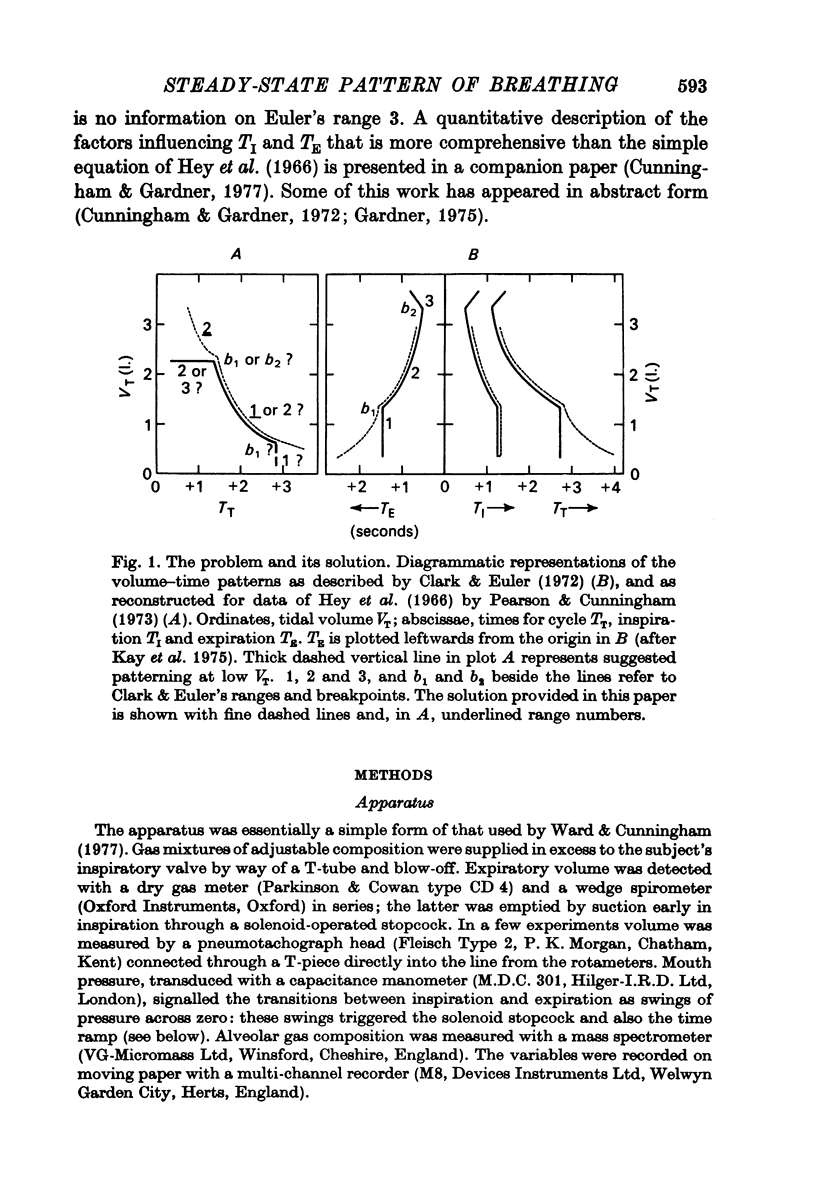
4. In range 2, V̄T was inversely related to both T̄I and T̄E and there appeared to be linkage between T̄I and T̄E, all as described by Clark & Euler (1972). The relation suggested by Hey, Lloyd, Cunningham, Jukes & Bolton (1966) over range 2 was not confirmed.
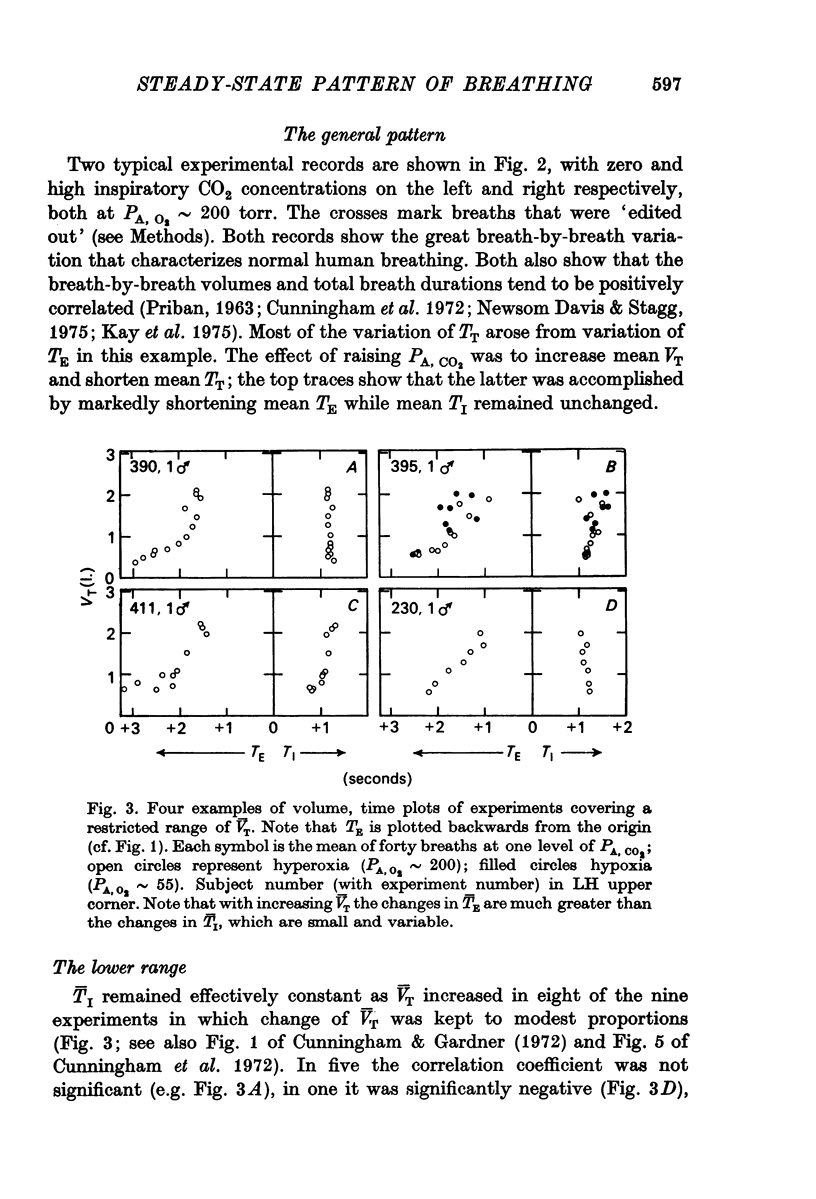
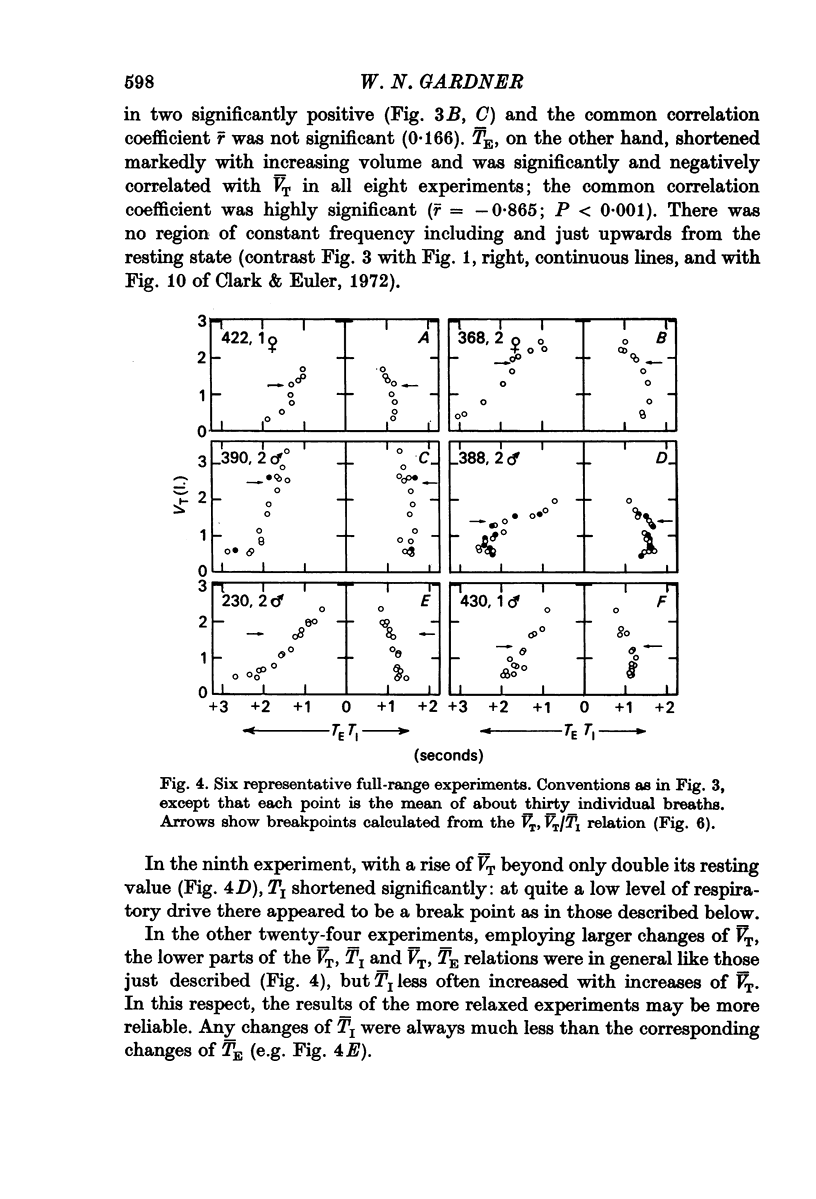
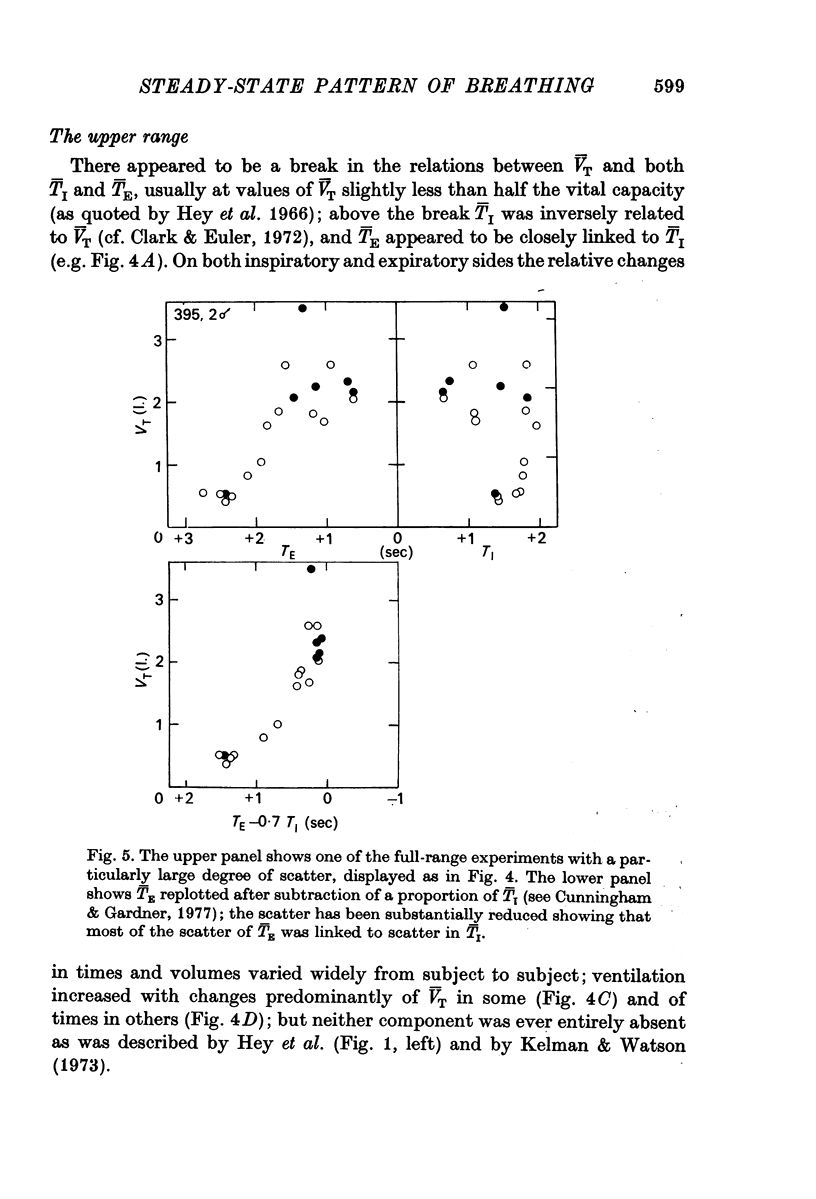
5. The main part of the relation described by Hey et al. (1966) is concerned with range 1. Here the relation between V̄T and T̄I was variable; slight, but significant negative correlation predominated. V̄T was, on the other hand, strongly and inversely related to T̄E, and plots of (T̄E — T̄I) against V̄T over both ranges showed even less scatter. Hence (a) T̄E is probably related to V̄T through two mechanisms, one involving a link with TI and another prominent one being quite independent of TI, (b) most changes of respiratory frequency in normal man are brought about by change of TE rather than of TI, and (c) there is no region of constant frequency as implied by Clark & Euler (1972).
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartlett D., Jr, Remmers J. E., Gautier H. Laryngeal regulation of respiratory airflow. Respir Physiol. 1973 Jul;18(2):194–204. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(73)90050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartoli A., Bystrzycka E., Guz A., Jain S. K., Noble M. I., Trenchard D. Studies of the pulmonary vagal control of central respiratory rhythm in the absence of breathing movements. J Physiol. 1973 Apr;230(2):449–465. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartoli A., Cross B. A., Guz A., Huszczuk A., Jeffries R. The effect of varying tidal volume on the associated phrenic motoneurone output:studies of vagal and chemical feedback. Respir Physiol. 1975 Nov;25(2):135–155. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(75)90093-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartoli A., Cross B. A., Guz A., Jain S. K., Noble M. I., Trenchard D. W. The effect of carbon dioxide in the airways and alveoli on ventilation; a vagal reflex studied in the dog. J Physiol. 1974 Jul;240(1):91–109. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley G. W., Noble M. I., Trenchard D. The direct effect on pulmonary stretch receptor discharge produced by changing lung carbon dioxide concentration in dogs on cardiopulmonary bypass and its action on breathing. J Physiol. 1976 Oct;261(2):359–373. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark F. J., von Euler C. On the regulation of depth and rate of breathing. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(2):267–295. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross B. A., Guz A., Jain S. K., Archer S., Stevens J., Reynolds F. The effect of anaesthesia of the airway in dog and man: a study of respiratory reflexes, sensations and lung mechanics. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1976 Jun;50(6):439–454. doi: 10.1042/cs0500439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham D. J., Drysdale D. B., Gardner W. N., Jensen J. I., Petersen E. S., Whipp B. J. Very small, very short-latency changes in human breathing induced by step changes of alveolar gas composition. J Physiol. 1977 Apr;266(2):411–421. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham D. J., Gardner W. N. A quantitative description of the pattern of breathing during steady-state CO2 inhalation in man, with special emphasis on expiration. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(3):613–632. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham D. J., Gardner W. N. The relation between tidal volume and inspiratory and expiratory times during steady-state CO2 inhalation in man. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(2):50P–51P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham D. J., Ward S. A. Proceedings: The separate effects of alternate-breath oscillations of PA,CO2 during hypoxia on inspiration and expiration. J Physiol. 1975 Nov;252(2):33P–34P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. N., Stagg D. Interrelationships of the volume and time components of individual breaths in resting man. J Physiol. 1975 Feb;245(2):481–498. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drysdale D. B., Ward S. A. The reflex latency of inspiratory and expiratory responses to an alternate-breath oscillation of alveolar PCO2 in man [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1976 Sep;260(2):41P–42P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman S., Dalton K. J., Holland D., Patton J. M. The effects of added elastic loads on the respiratory response to CO 2 in man. Respir Physiol. 1972 Apr;14(3):237–250. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(72)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner W. N. Proceedings: The pattern of breathing following step changes of alveolar PCO2 in man. J Physiol. 1974 Oct;242(2):75P–76P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrard C. S., Lane D. J. Proceedings: The pattern of stimulated breathing in man during non-elastic expiratory loading. J Physiol. 1975 Sep;251(1):40P–41P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier H., Remmers J. E., Bartlett D., Jr Control of the duration of expiration. Respir Physiol. 1973 Jul;18(2):205–221. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(73)90051-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert R., Auchincloss J. H., Jr, Baule G., Peppi D., Long D. Breathing pattern during CO 2 inhalation obtained from motion of the chest and abdomen. Respir Physiol. 1971 Nov;13(2):238–252. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(71)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M. M., Younes M., Milic-Emili J. Control of tidal volume and respiratory frequency in anesthetized cats. J Appl Physiol. 1973 Oct;35(4):463–476. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1973.35.4.463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldane J. S., Meakins J. C., Priestley J. G. The respiratory response to anoxaemia. J Physiol. 1919 May 20;52(6):420–432. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1919.sp001841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hey E. N., Lloyd B. B., Cunningham D. J., Jukes M. G., Bolton D. P. Effects of various respiratory stimuli on the depth and frequency of breathing in man. Respir Physiol. 1966;1(2):193–205. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(66)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hlastala M. P., Wranne B., Lenfant C. J. Cyclical variations in FRC and other respiratory variables in resting man. J Appl Physiol. 1973 May;34(5):670–676. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1973.34.5.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennett S., Russell T., Warnock K. A. Proceedings: The duration of inspiration during changing states of ventilation in man. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(1):54P–55P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J. D., Petersen E. S., Vejby-Christensen H. Mean and breath-by-breath pattern of breathing in man during steady-state exercise. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(3):657–669. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelman G. R., Watson A. W. Effect of added dead-space on pulmonary ventilation during sub-maximal, steady-state exercise. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1973 Oct;58(4):305–313. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1973.sp002224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LLOYD B. B., JUKES M. G., CUNNINGHAM D. J. The relation between alveolar oxygen pressure and the respiratory response to carbon dioxide in man. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1958 Apr;43(2):214–227. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1958.sp001319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILIC-EMILI G., CAJANI F. La frequenza dei respiri in funzione della ventilazione, polmonare durante il ristoro. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1957 Jun;33(6):821–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadel J. A., Phillipson E. A., Fishman N. H., Hickey R. F. Regulation of respiration by bronchopulmonary receptors in conscious dogs. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 1973;33(1):33–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRIBAN I. P. An analysis of some short-term patterns of breathing in man at rest. J Physiol. 1963 May;166:425–434. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick J. M., Howard A. The influence of age, sex, body size and lung size on the control and pattern of breathing during CO 2 inhalation in Caucasians. Respir Physiol. 1972 Dec;16(3):337–350. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(72)90063-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson S. B., Cunningham D. J. Some observations on the relation between ventilation, tidal volume and frequency in man in various steady and transient states. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 1973;33(1):177–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebuck A. S., Rigg J. R., Saunders N. A. Respiratory frequency response to progressive isocapnic hypoxia. J Physiol. 1976 Jun;258(1):19–31. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIDDICOMBE J. G. Respiratory reflexes in man and other mammalian species. Clin Sci. 1961 Oct;21:163–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward S. A., Cunningham D. J. Separation of the inspiratory and expiratory reflex effects of alternate-breath oscillation of PACO2 during hypoxia. Respir Physiol. 1977 May;29(3):379–390. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(77)90011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdicombe J. G., Winning A. Effects of hypoxia, hypercapnia and changes in body temperature on the pattern of breathing in cats. Respir Physiol. 1974 Aug;21(2):203–221. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(74)90095-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Euler C., Wexler I., Herrero F. Control mechanisms determining rate and depth of respiratory movements. Respir Physiol. 1970 Jul;10(1):93–108. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(70)90030-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


