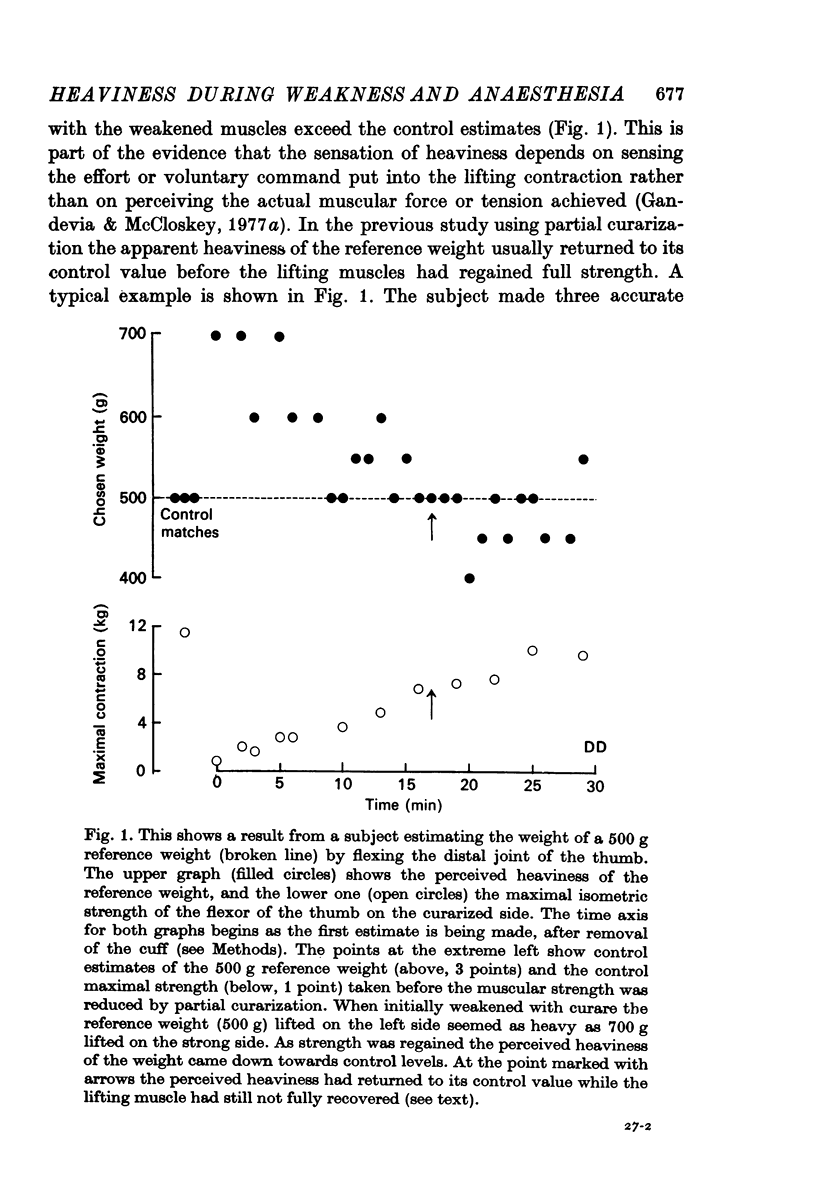
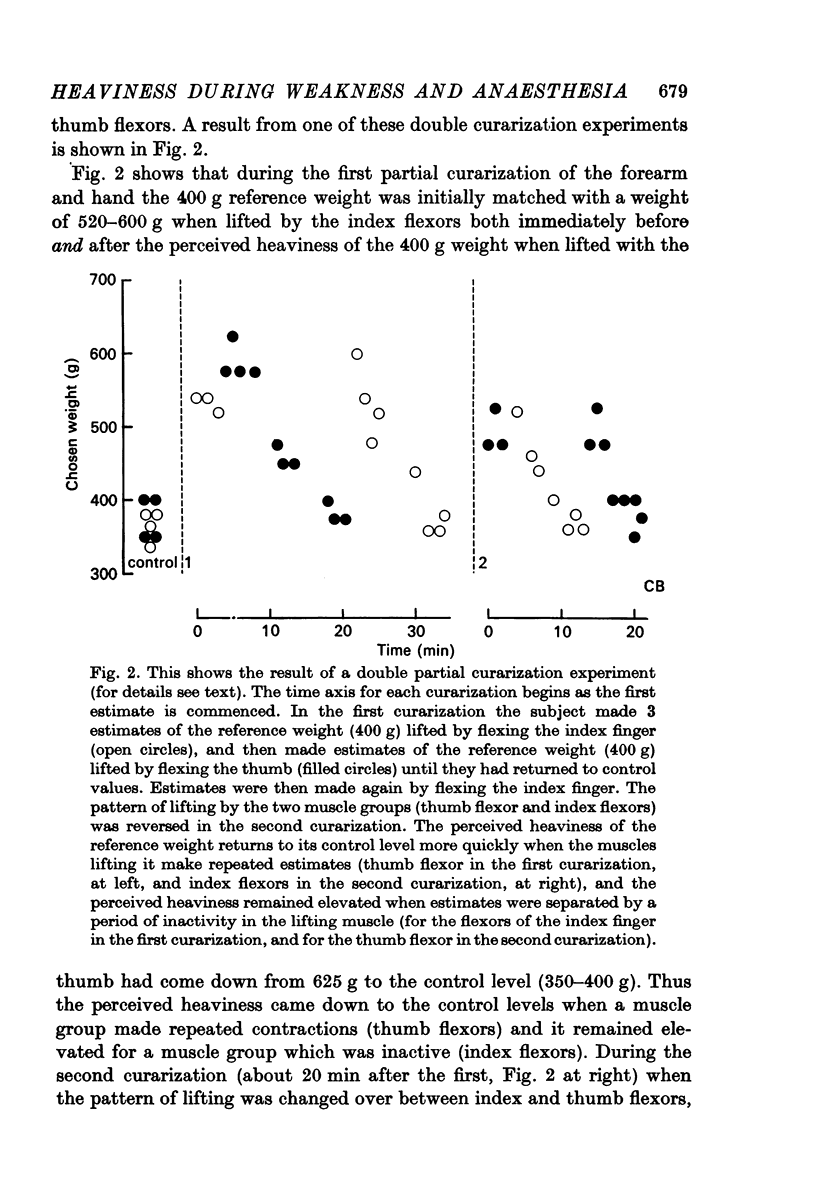
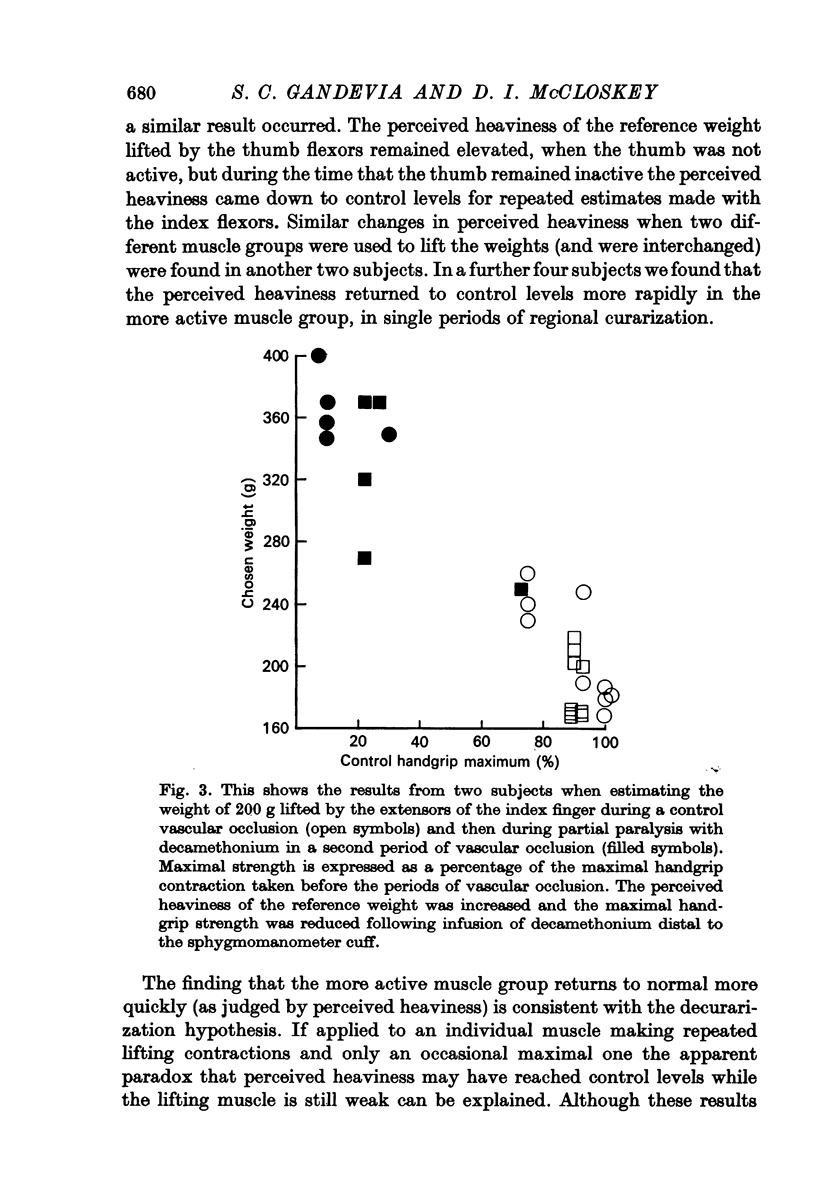
Abstract
1. The centrally generated `effort' or direct voluntary command to motoneurones required to lift a weight was studied using a simple weight-matching task when the muscles lifting a reference weight were weakened. This centrally generated input to motoneurones was increased when the lifting muscles were partially paralysed with curare or decamethonium as judged by the increased perceived heaviness of a reference weight lifted by the weakened muscles.
2. If subjects were asked simply to make matching isometric contractions when the lifting muscles were weakened the isometric tension produced by a weakened muscle was over-estimated.
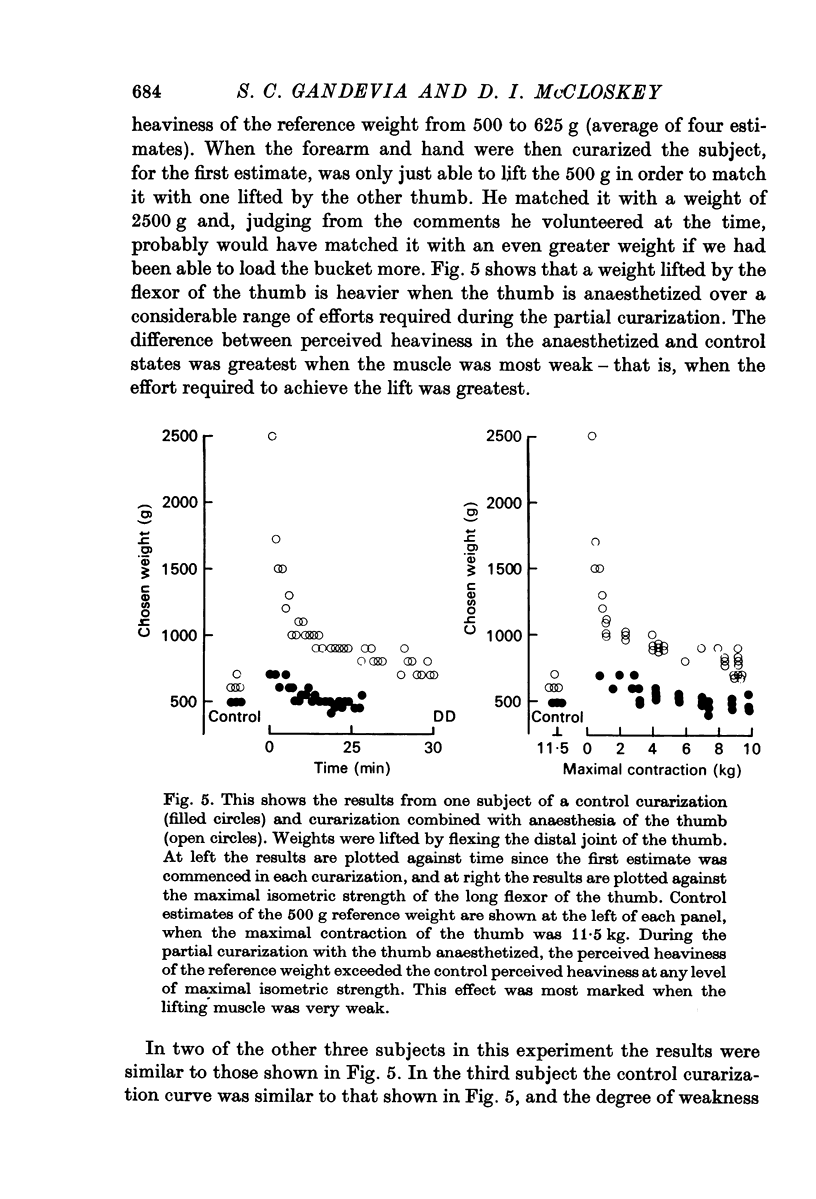
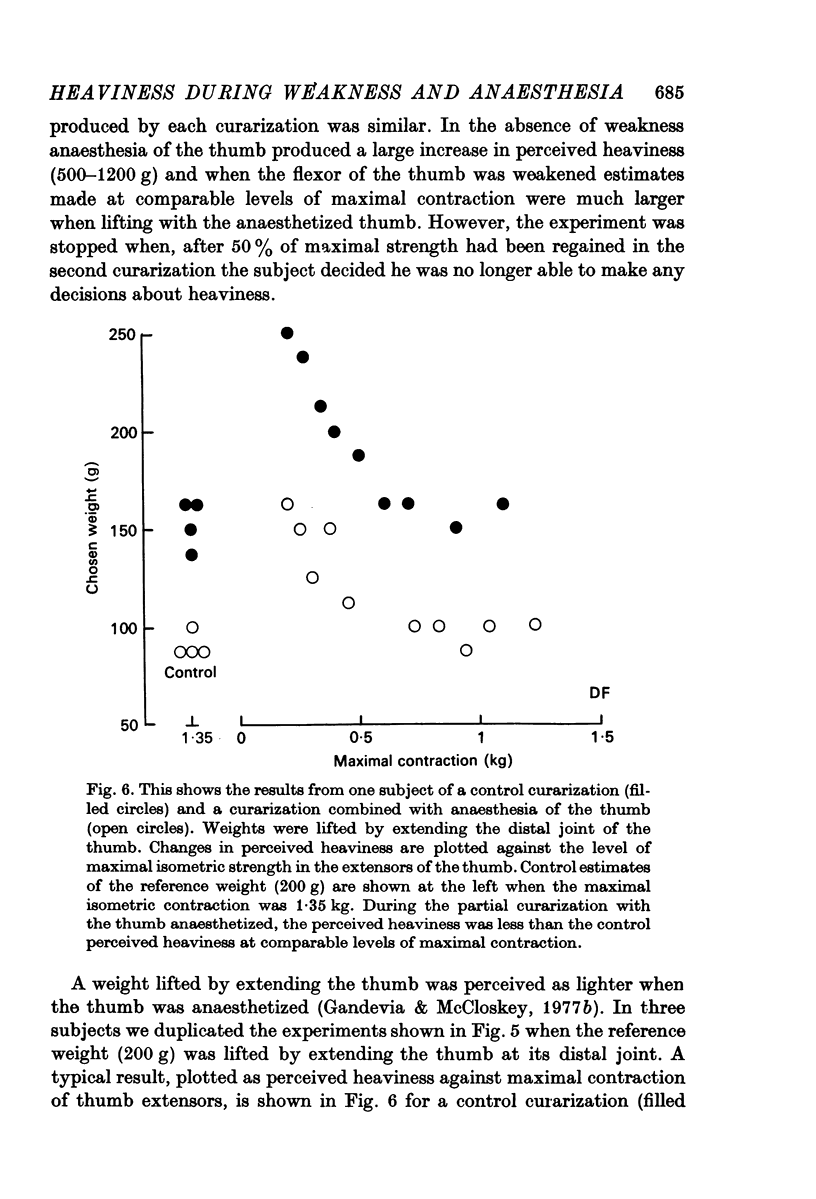
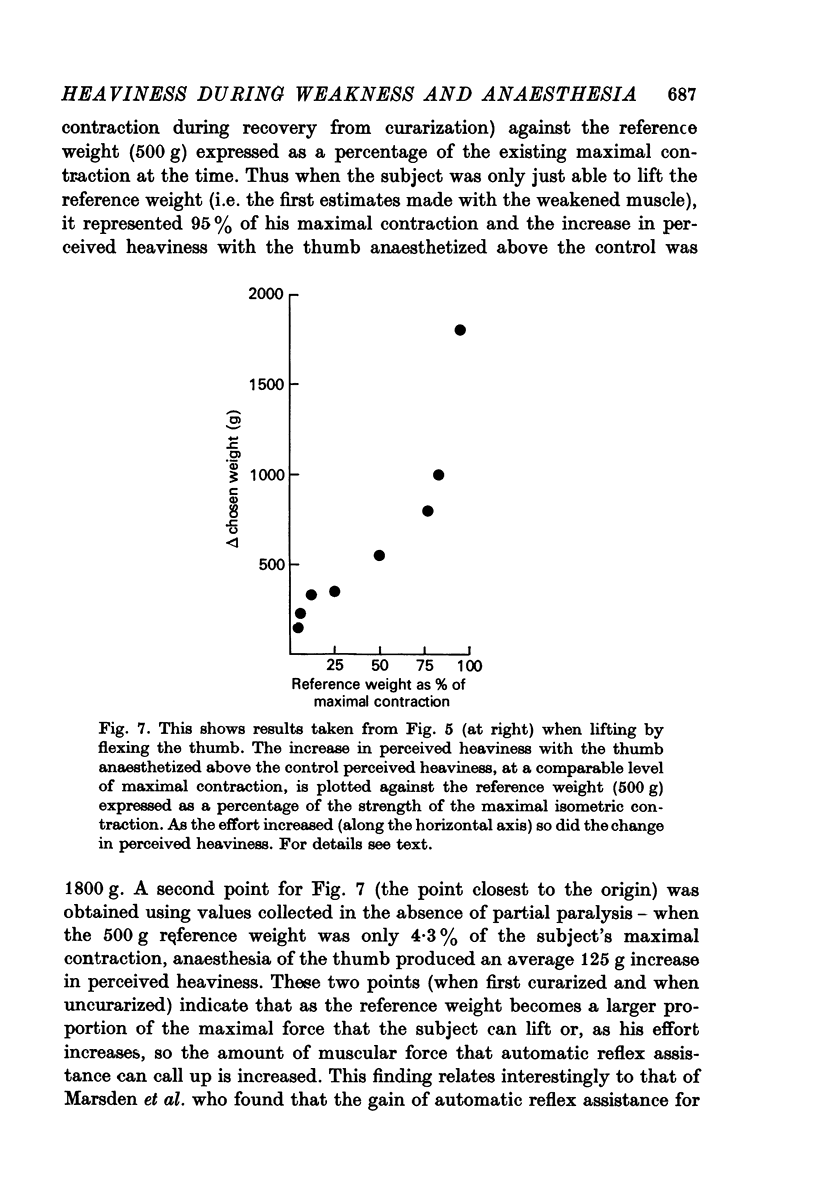
3. When subjects matched weights by flexing the distal joint of the thumb the perceived heaviness of a reference weight during a control partial curarization was compared with its perceived heaviness during a similar partial curarization when the thumb was also anaesthetized. At any level of maximal strength during curarization the perceived heaviness (which reflects the motor command to lifting motoneurones) was increased when the thumb was anaesthetized.
4. This increased voluntary command to lifting motoneurones may be required because automatic reflex assistance provided by apparent servo action from the long flexor of the thumb is suppressed by anaesthesia of the thumb (Marsden, Merton & Morton, 1971, 1973, 1976a; Dyhre-Poulsen & Djørup, 1976).
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam J., Hallett M., Marsden C. D., Merton P. A., Morton H. B. Absence of the first component of the long-latency human stretch reflex in a thumb muscle when it is used as an antagonist [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1976 Sep;260(2):67P–68P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. N., Sears T. A. The proprioceptive reflex control of the intercostal muscles during their voluntary activation. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(3):711–738. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evarts E. V. Motor cortex reflexes associated with learned movement. Science. 1973 Feb 2;179(4072):501–503. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4072.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evarts E. V., Tanji J. Gating of motor cortex reflexes by prior instruction. Brain Res. 1974 May 17;71(2-3):479–494. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90992-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman S. A., Tyrrell M. F. A new theory of the termination of action of the muscle relaxants. Proc R Soc Med. 1970 Jul;63(7):692–695. doi: 10.1177/003591577006300716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandevia S. C., McCloskey D. I. Effects of related sensory inputs on motor performances in man studied through changes in perceived heaviness. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(3):653–672. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandevia S. C., McCloskey D. I. Perceived heaviness of lifted objects and effects of sensory inputs from related, non-lifting parts. Brain Res. 1976 Jun 11;109(2):399–401. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90542-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandevia S. C., McCloskey D. I. Sensations of heaviness. Brain. 1977 Jun;100(2):345–354. doi: 10.1093/brain/100.2.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMMOND P. H. Involuntary activity in biceps following the sudden application of velocity to the abducted forearm. J Physiol. 1955 Feb 28;127(2):23–5P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iles J. F. Reflex responses in human pretibial muscles [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1976 Sep;260(2):54P–55P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. M., Watt D. G. Observations on the control of stepping and hopping movements in man. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(3):709–727. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyce G. C., Rack P. M. The effects of load and force on tremor at the normal human elbow joint. J Physiol. 1974 Jul;240(2):375–396. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Merton P. A., Morton H. B. Is the human stretch reflex cortical rather than spinal? Lancet. 1973 Apr 7;1(7806):759–761. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Merton P. A., Morton H. B. Servo action and stretch reflex in human muscle and its apparent dependence on peripheral sensation. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;216(1):21P–22P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Merton P. A., Morton H. B. Servo action in the human thumb. J Physiol. 1976 May;257(1):1–44. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Merton P. A., Morton H. B. Stretch reflex and servo action in a variety of human muscles. J Physiol. 1976 Jul;259(2):531–560. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCloskey D. I., Ebeling P., Goodwin G. M. Estimation of weights and tensions and apparent involvement of a "sense of effort". Exp Neurol. 1974 Jan;42(1):220–232. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(74)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCloskey D. I., Torda T. A. Corollary motor discharges and kinaesthesia. Brain Res. 1975 Dec 19;100(2):467–470. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90503-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips C. G. The Ferrier lecture, 1968. Motor apparatus of the baboon's hand. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1969 May 20;173(1031):141–174. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1969.0044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears T. A. The afferent regulation of learnt movements. Brain Res. 1974 May 17;71(2-3):465–473. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90990-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torda T. A., Klonymus D. H. Regional neuromuscular block. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand Suppl. 1966;24:177–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1966.tb01121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallbo A. B. Human muscle spindle discharge during isometric voluntary contractions. Amplitude relations between spindle frequency and torque. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Feb;90(2):319–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05594.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallbo A. B. Muscle spindle response at the onset of isometric voluntary contractions in man. Time difference between fusimotor and skeletomotor effects. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(2):405–431. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh E. G. Stretch reflexes in forearm muscles [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1976 Dec;263(2):263P–264P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


