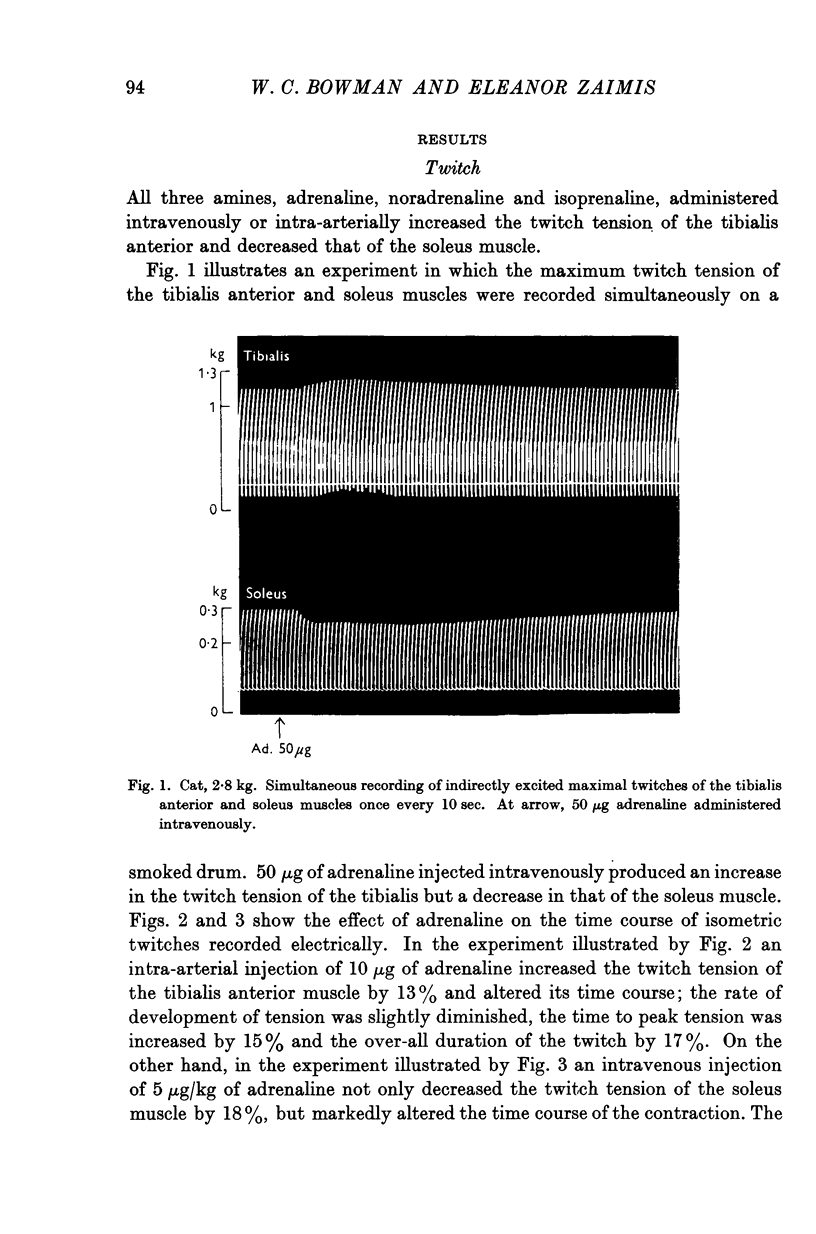
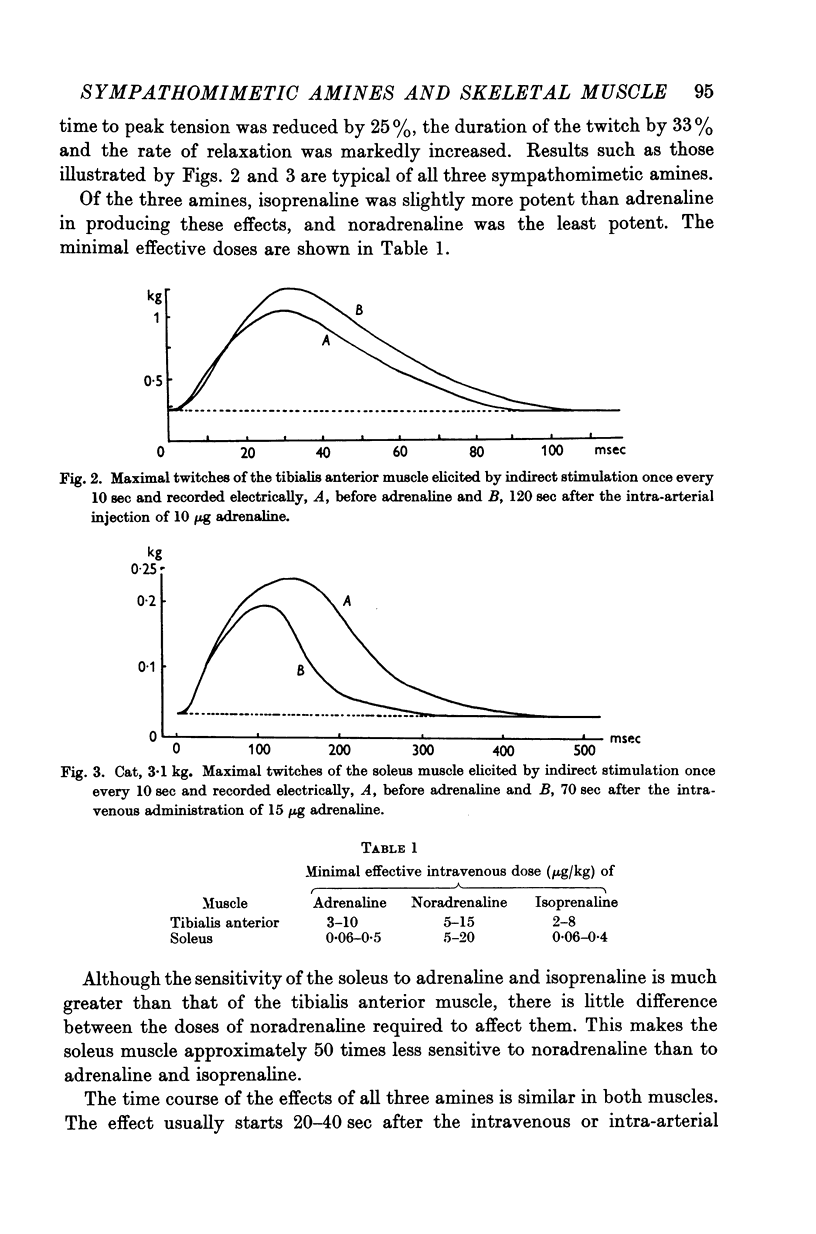
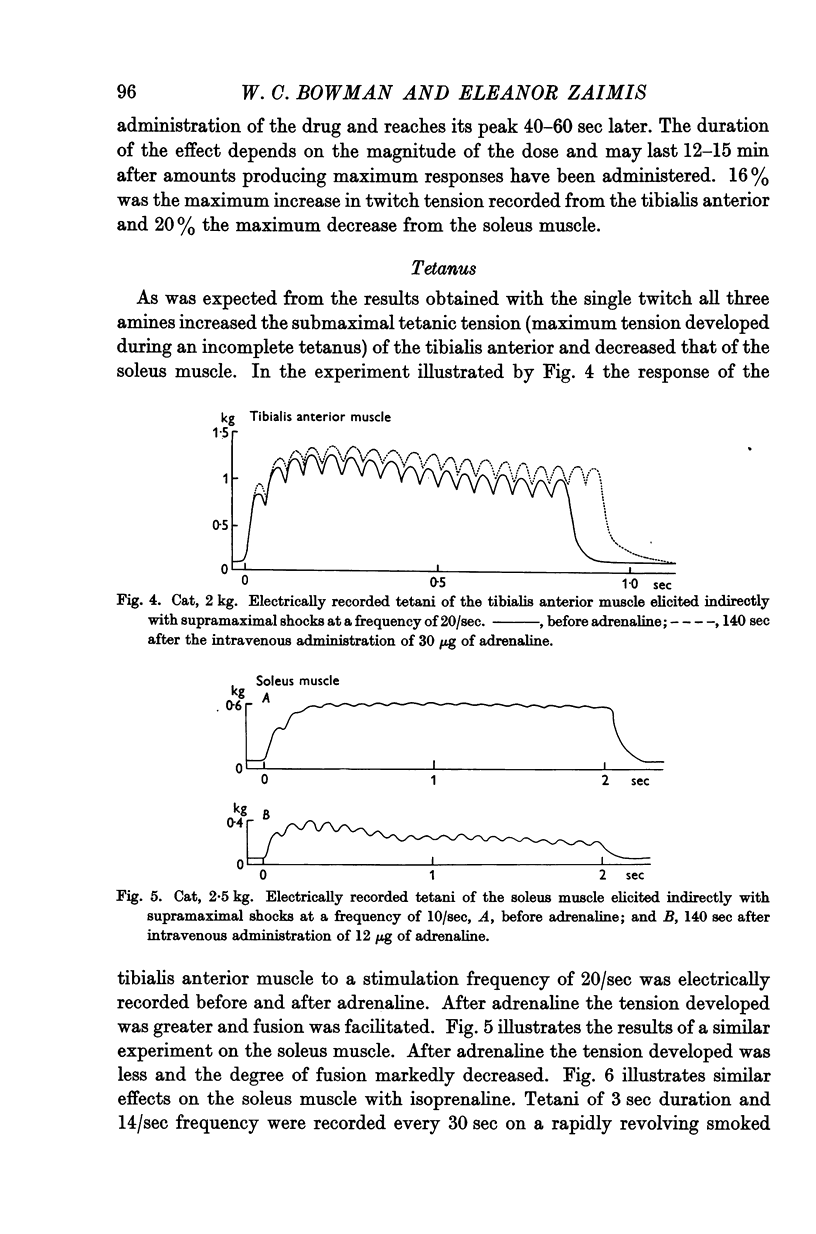
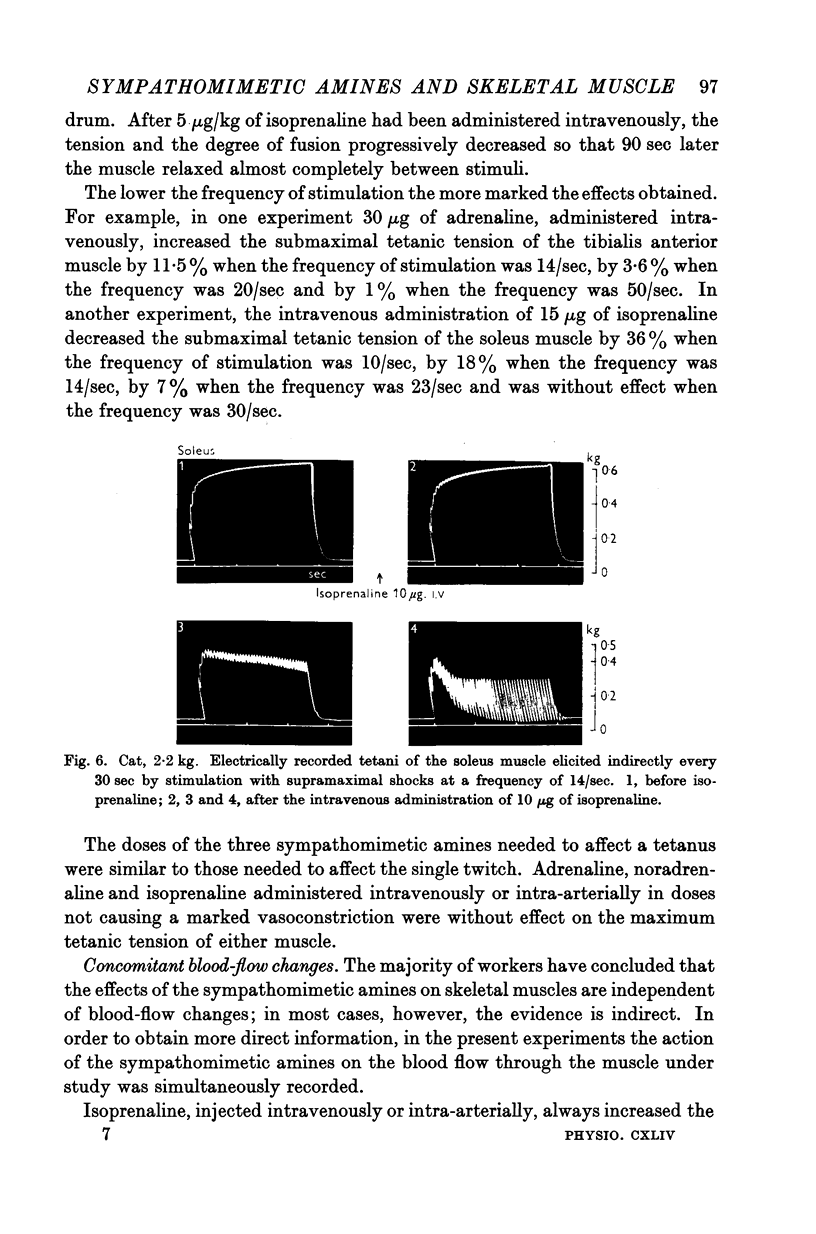
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown G. L., Goffart M., Dias M. V. The effects of adrenaline and of sympathetic stimulation on the demarcation potential of mammalian skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1950 Apr 15;111(1-2):184–194. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1950.sp004473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülbring E., Burn J. H. Blood flow during muscle contraction and the orbeli phenomenon in the dog. J Physiol. 1939 Feb 14;95(1):203–225. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1939.sp003720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUTTING W., NEWMAN H., YEE J. Effect of dosage on the rate of disappearance of ethanol from the blood of dogs. J Physiol. 1949 Dec 15;110(1-2):18–25. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLKOW B. Impulse frequency in sympathetic vasomotor fibres correlated to the release and elimination of the transmitter. Acta Physiol Scand. 1952;25(1):49–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1952.tb00858.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLKOW B. Nervous control of the blood vessels. Physiol Rev. 1955 Jul;35(3):629–663. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1955.35.3.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLKOW B., VON EULER U. S. Selective activation of noradrenaline and adrenaline producing cells in the cat's adrenal gland by hypothalamic stimulation. Circ Res. 1954 May;2(3):191–195. doi: 10.1161/01.res.2.3.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOFFART M., RITCHIE J. M. The effect of adrenaline on the contraction of mammalian skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1952 Mar;116(3):357–371. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOFFART M. Recherches relatives à l'action de l'adrénaline sur le muscle strié de mammifère. I. Potentiation par l'adrénaline de la contraction maximale du muscle non fatigué. Arch Int Physiol. 1952 Sep;60(3):318–349. doi: 10.3109/13813455209145098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOFFART M. The action of 1-noradrenaline and adrenochrome on unfatigued mammalian muscle. Pharmacol Rev. 1954 Mar;6(1):33–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILTON S. M. Experiments on the post contraction hyperaemia of skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1953 Apr 28;120(1-2):230–245. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUIDOBRO F., CUBILLOS L., EYZAGUIRRE C. Effect of aromatic amines on neuromuscular function. Acta Physiol Lat Am. 1952 Jul;2(2):107–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAINDL F., von EULER U. S. Liberation of nor-adrenaline and adrenaline from the suprarenals of the cat during carotid occlusion. Am J Physiol. 1951 Aug;166(2):284–288. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.166.2.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITCHFIELD J. W., PEART W. S. Phaeochromocytoma with normal excretion of adrenaline and noradrenaline. Lancet. 1956 Dec 22;271(6956):1283–1284. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(56)91435-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONTAGU K. A. On the mechanism of action of adrenaline in skeletal nerve-muscle. J Physiol. 1955 Jun 28;128(3):619–628. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver G., Schäfer E. A. The Physiological Effects of Extracts of the Suprarenal Capsules. J Physiol. 1895 Jul 18;18(3):230–276. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1895.sp000564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON EULER U. S., FOLKOW B. Einfluss verschiedener afferenter Nervenreize auf die Zusammensetzung des Nebennierenmarkinkretes bei der Katze. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1953;219(3):242–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


