Full text
PDF
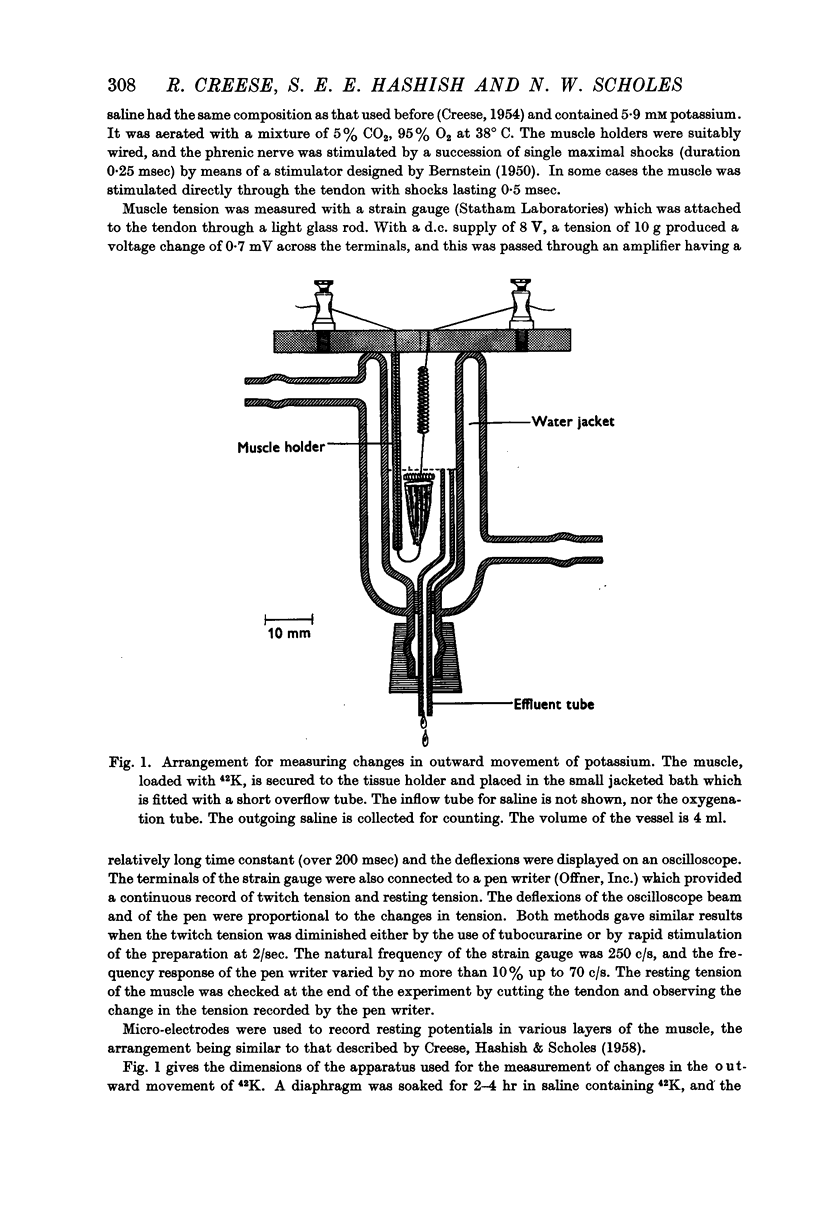

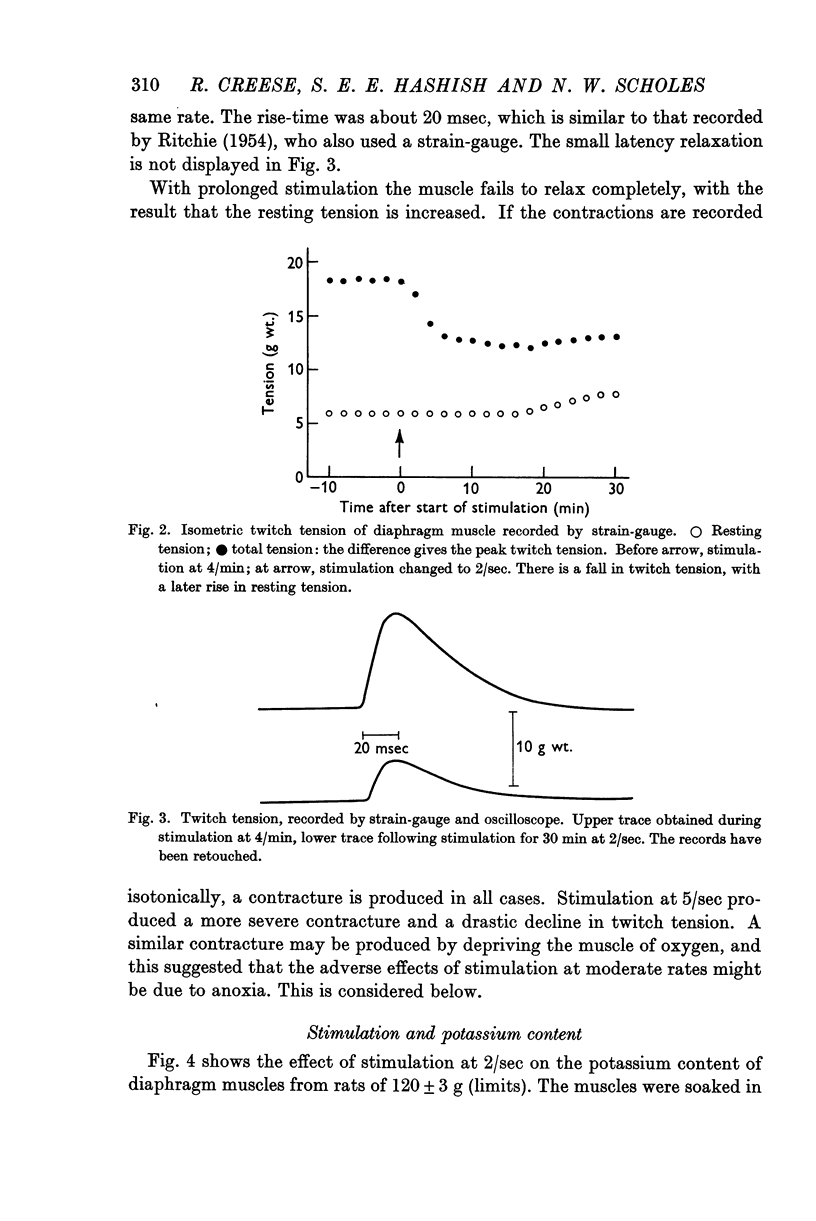
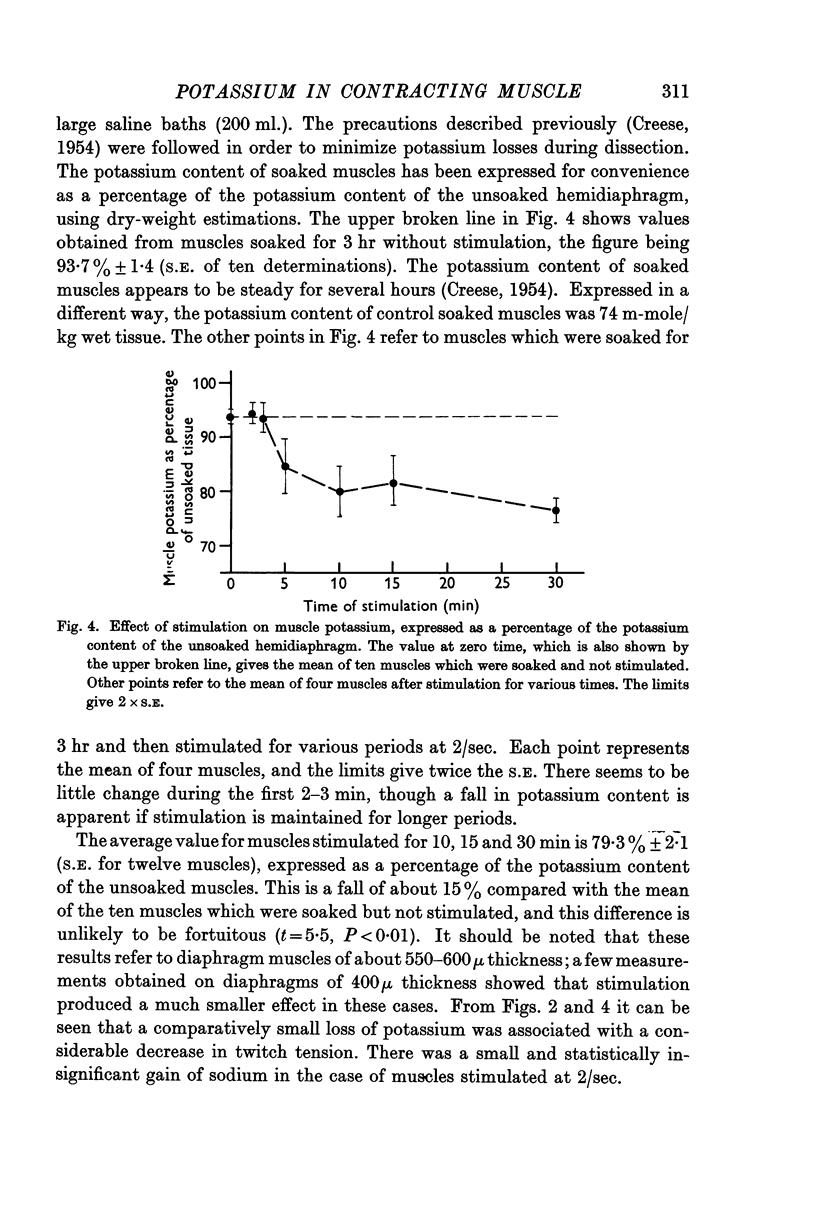
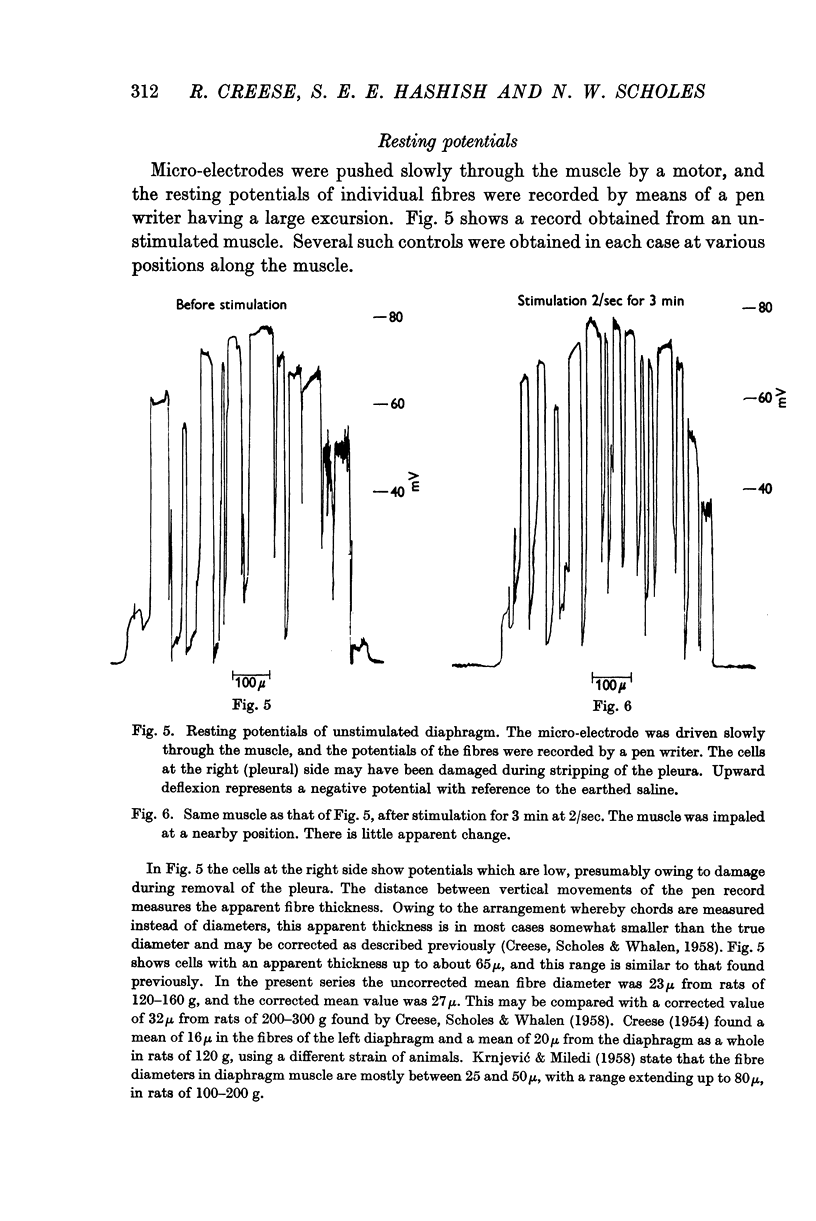









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERNSTEIN L. An electronic square wave stimulator. J Physiol. 1950 Apr;111(1-2):34p–36p. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. L., Bülbring E., Burns B. D. The action of adrenaline on mammalian skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1948 Jan 1;107(1):115–128. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1948.sp004255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALKINS E., TAYLOR I. M., HASTINGS A. B. Potassium exchange in the isolated diaphragm; effect of anoxia and cold. Am J Physiol. 1954 May;177(2):211–218. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.177.2.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREESE R. Measurement of cation fluxes in rat diaphragm. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1954 Sep 27;142(909):497–513. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1954.0039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREESE R., SCHOLES N. W., WHALEN W. J. Resting potentials of diaphragm muscle after prolonged anoxia. J Physiol. 1958 Feb 17;140(2):301–317. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CSAPO A., WILKIE D. R. The dynamics of the effect of potassium on frog's muscle. J Physiol. 1956 Dec 28;134(3):497–514. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAJDU S. Behaviour of frog and rat muscle at higher temperatures. Enzymologia. 1950 Nov 15;14(4):187–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS E. J. The exchangeability of the potassium of frog muscle, studied in phosphate media. J Physiol. 1952 Jul;117(3):278–288. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL A. V., MACPHERSON L. The effect of nitrate, iodide and bromide on the duration of the active state in skeletal muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1954 Dec 15;143(910):81–102. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1954.0055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. The potassium permeability of a giant nerve fibre. J Physiol. 1955 Apr 28;128(1):61–88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D. The ionic fluxes in frog muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1954 May 27;142(908):359–382. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1954.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D. The ionic movements during nervous activity. J Physiol. 1951 Jun;114(1-2):119–150. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., MILEDI R. Motor units in the rat diaphragm. J Physiol. 1958 Mar 11;140(3):427–439. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogh A. The number and distribution of capillaries in muscles with calculations of the oxygen pressure head necessary for supplying the tissue. J Physiol. 1919 May 20;52(6):409–415. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1919.sp001839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogh A. The supply of oxygen to the tissues and the regulation of the capillary circulation. J Physiol. 1919 May 20;52(6):457–474. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1919.sp001844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCLENNAN H. The diffusion of potassium, inulin, and thiocyanate in the extracellular spaces of mammalian muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Sep;21(3):472–481. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90184-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERTON P. A. Voluntary strength and fatigue. J Physiol. 1954 Mar 29;123(3):553–564. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLENNAN H. The transfer of potassium between mammalian muscle and the surrounding medium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Jan;16(1):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RITCHIE J. M. The relation between force and velocity of shortening in rat muscle. J Physiol. 1954 Mar 29;123(3):633–639. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEEKS J. R., CHENOWETH M. B. A stationary manometric respirometer for isolated rat diaphragm allowing simultaneous direct registration of mechanical activity; observations with sodium azide and dinitrophenol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1952 Feb;104(2):187–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHALEN W. J. Oxygen consumption and tension of isolated heart muscle during rest and activity using a new technic. Circ Res. 1957 Sep;5(5):556–561. doi: 10.1161/01.res.5.5.556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


