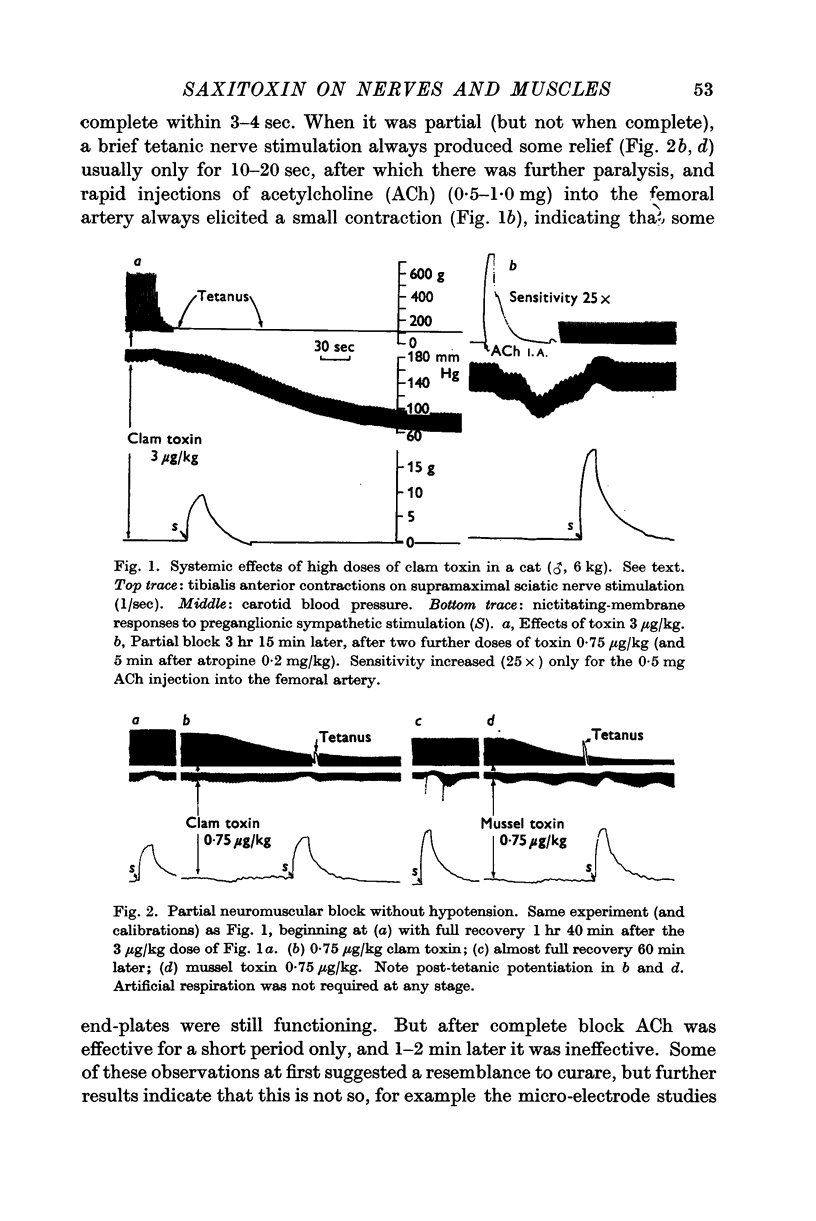
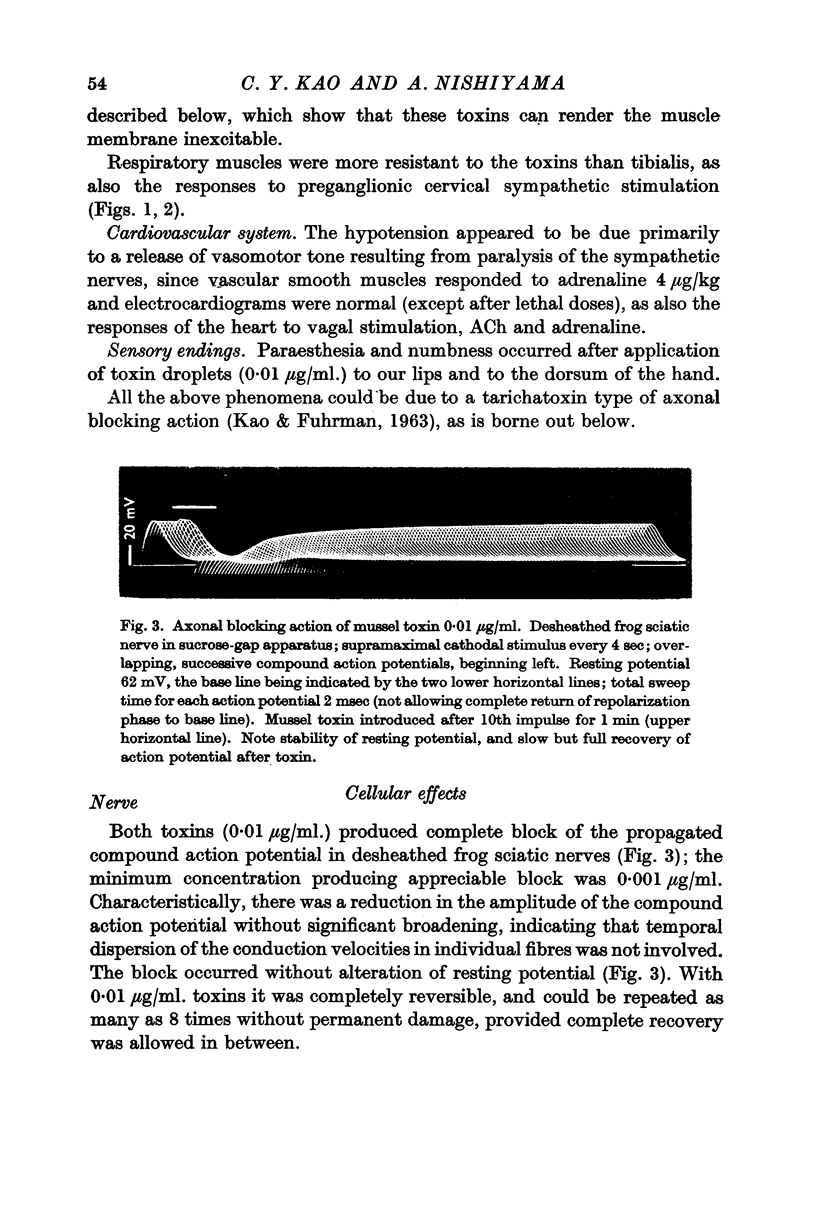
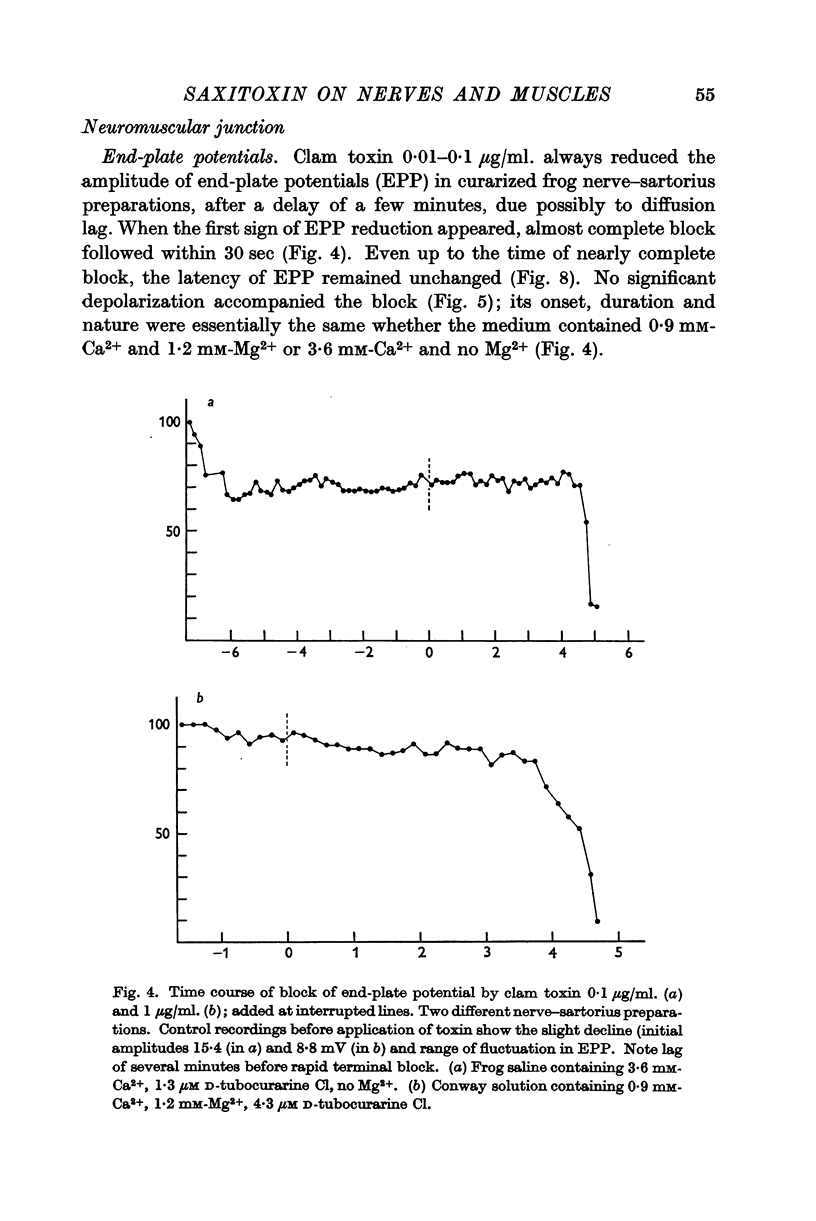
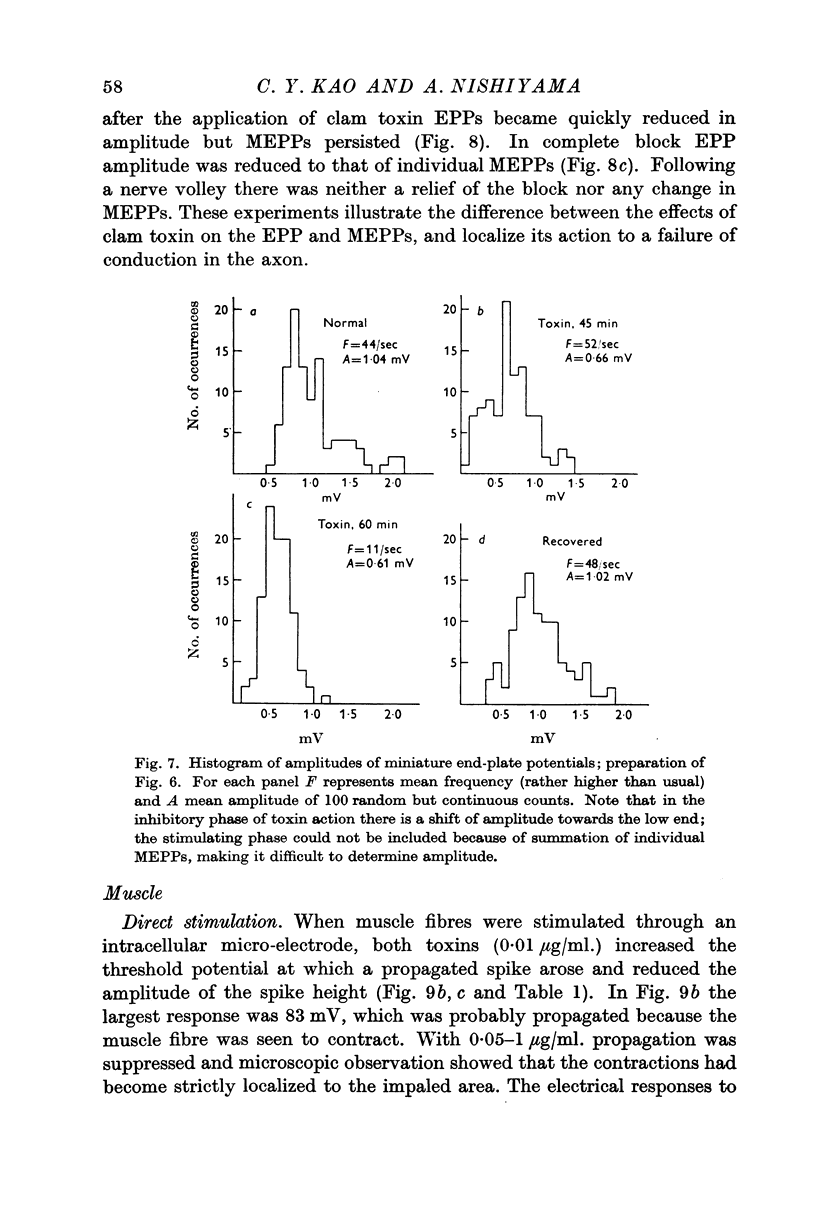
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Freygang W. H. The potassium and chloride conductance of frog muscle membrane. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;163(1):61–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOLTON B. L., BERGNER A. D., O'NEILL J. J., WAGLEY P. F. Effect of a shell-fish poison on end-plate potentials. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1959 Oct;105:233–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCHWALD H. D., DURHAM L., FISCHER H. G., HARADA R., MOSHER H. S., KAO C. Y., FUHRMAN F. A. IDENTITY OF TARICHATOXIN AND TETRODOTOXIN. Science. 1964 Jan 31;143(3605):474–475. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3605.474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle P. J., Conway E. J. Potassium accumulation in muscle and associated changes. J Physiol. 1941 Aug 11;100(1):1–63. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1941.sp003922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DECK K. A. Uber die Wirkung des Guanidinhydrochlorids und anderer Substanzen auf das Aktionspotential der Nerveneinzelfaser. Pflugers Arch. 1958;266(3):249–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00416776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Biophysical aspects of neuro-muscular transmission. Prog Biophys Biophys Chem. 1956;6:121–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Quantal components of the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):560–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DETTBARN W. D., HIGMAN H., ROSENBERG P., NACHMANSOHN D. Rapid and reversible block of electrical activity by powerful marine biotoxins. Science. 1960 Jul 29;132(3422):300–301. doi: 10.1126/science.132.3422.300-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS M. H. PARALYTIC EFFECTS OF "PARALYTIC SHELLFISH POISON" ON FROG NERVE AND MUSCLE. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Jun;22:478–485. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb01702.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. An analysis of the end-plate potential recorded with an intracellular electrode. J Physiol. 1951 Nov 28;115(3):320–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINGERMAN M., FORESTER R. H., STOVER J. H., Jr Action of shellfish poison on peripheral nerve and skeletal muscle. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Dec;84(3):643–646. doi: 10.3181/00379727-84-20739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENERICK H. The control of membrane ionic currents by the membrane potential of muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1959 May 20;42(5):923–930. doi: 10.1085/jgp.42.5.923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAO C. Y., HOFFMAN B. F. Graded and decremental response in heart muscle fibers. Am J Physiol. 1958 Jul;194(1):187–196. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.194.1.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARRAMENDI L. M., LORENTE DE NO R., VIDAL F. Restoration of sodium-deficient frog nerve fibres by an isotonic solution of guanidinium chloride. Nature. 1956 Aug 11;178(4528):316–317. doi: 10.1038/178316a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUTTGAU H. C. Die Wirkung von Guanidinhydrochlorid auf die Erregungsprozesse an isolierten markhaltigen Nervenfasern. Pflugers Arch. 1958;267(4):331–343. doi: 10.1007/BF00362893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER K. F. Food poisoning (concluded). N Engl J Med. 1953 Nov 19;249(21):843–concl. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195311192492105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSHER H. S., FUHRMAN F. A., BUCHWALD H. D., FISCHER H. G. TARICHATOXIN--TETRODOTOXIN: A POTENT NEUROTOXIN. Science. 1964 May 29;144(3622):1100–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3622.1100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURTHA E. F. Pharmacological study of poisons from shellfish and puffer fish. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Nov 17;90:820–836. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb26425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NARAHASHI T., DEGUCHI T., URAKAWA N., OHKUBO Y. Stabilization and rectification of muscle fiber membrane by tetrodotoxin. Am J Physiol. 1960 May;198:934–938. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.5.934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NARAHASHI T., MOORE J. W., SCOTT W. R. TETRODOTOXIN BLOCKAGE OF SODIUM CONDUCTANCE INCREASE IN LOBSTER GIANT AXONS. J Gen Physiol. 1964 May;47:965–974. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.5.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHANTZ E. J. Biochemical studies on paralytic shellfish poisons. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Nov 17;90:843–855. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb26427.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIBERG G. S., STEPHENSON N. R. Toxicologic studies on paralytic shellfish poison. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1960 Nov;2:607–615. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(60)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


