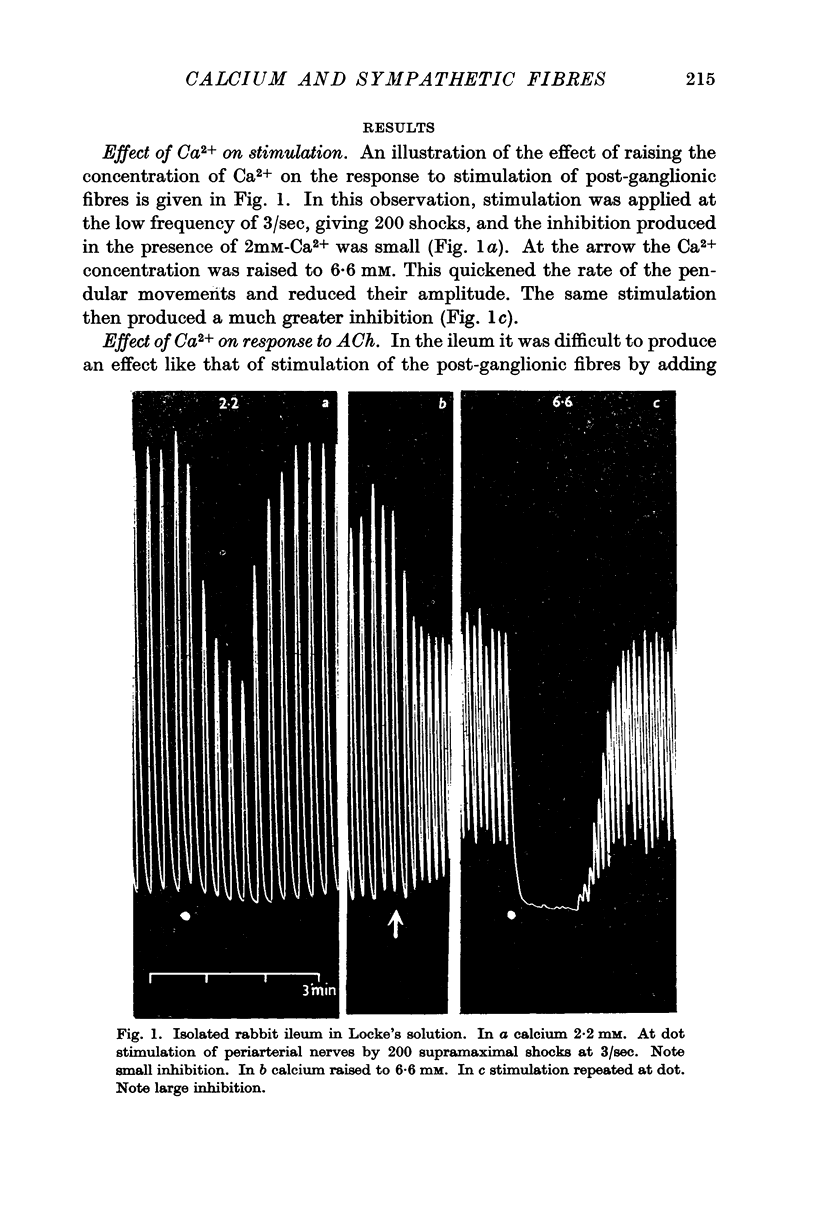
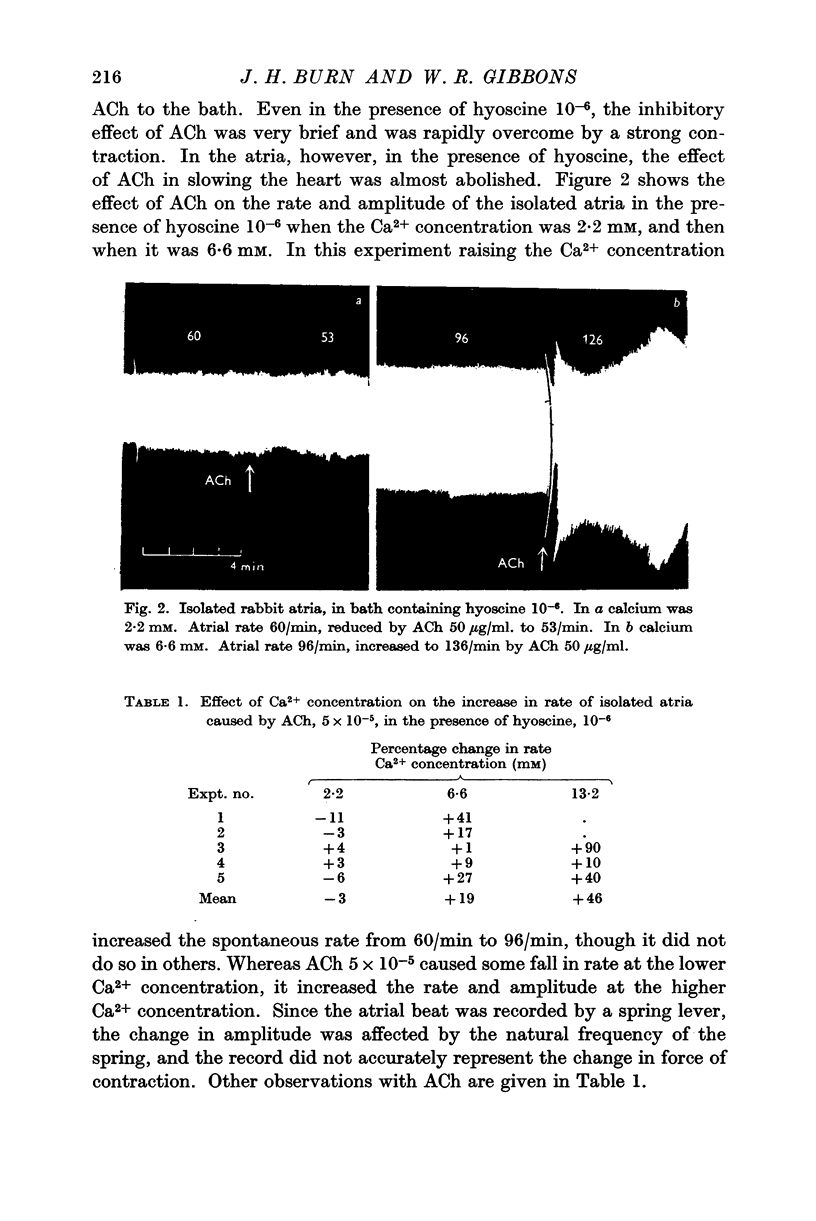
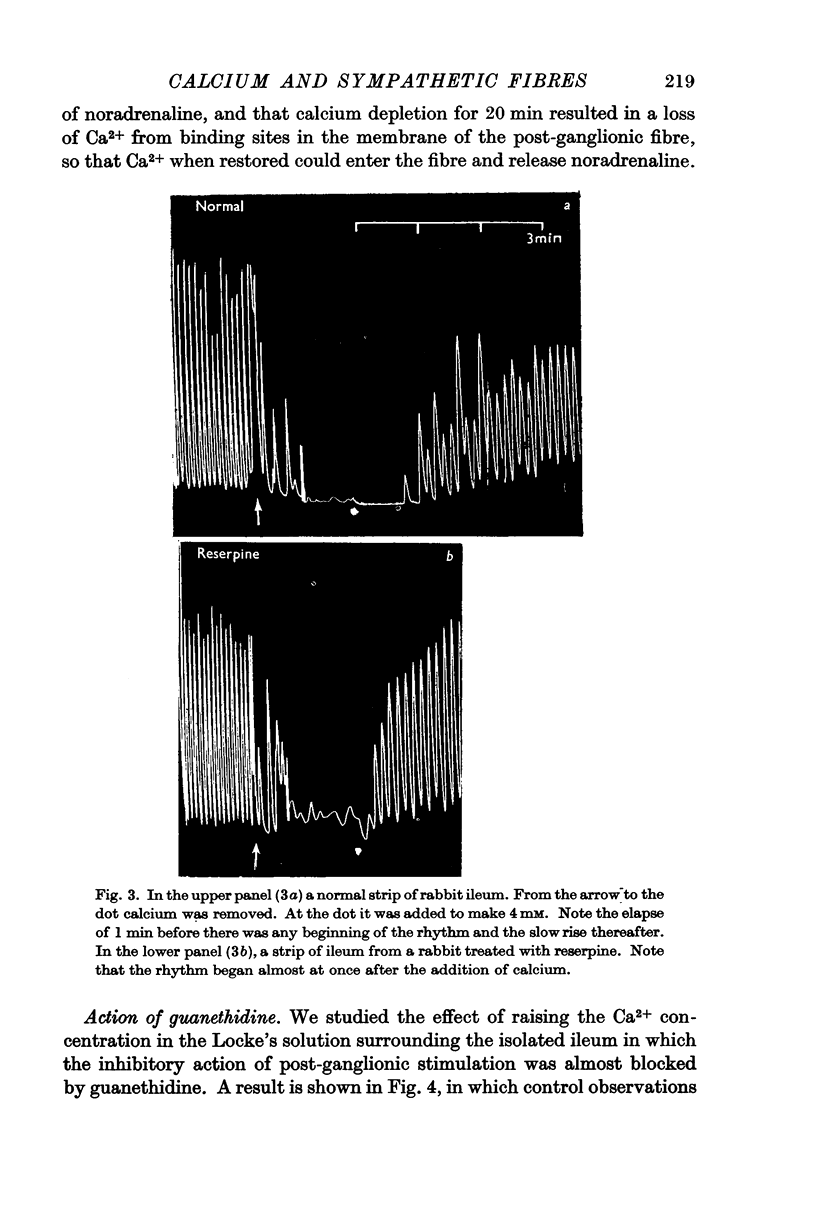
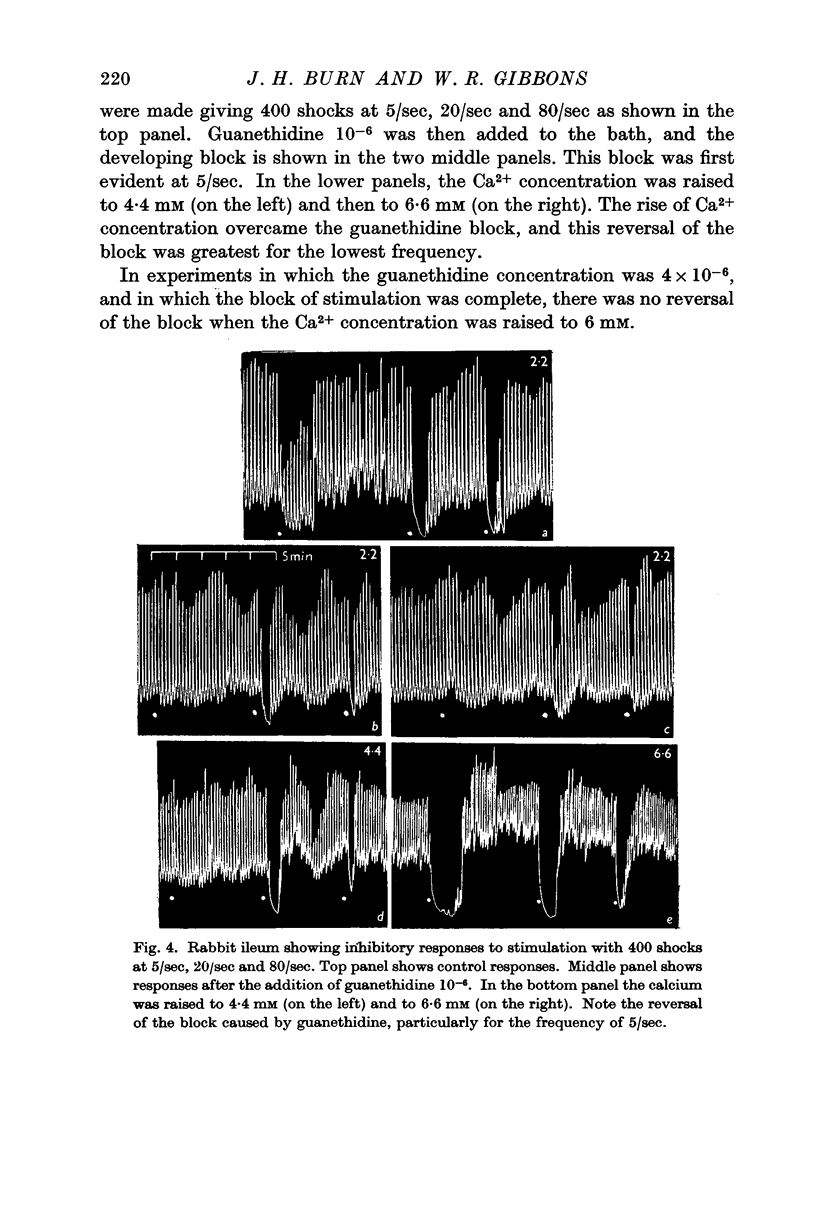
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURN J. H., GIBBONS W. R. THE PART PLAYED BY CALCIUM IN DETERMINING THE RESPONSE TO STIMULATION OF SYMPATHETIC POSTGANGLIONIC FIBRES. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Jun;22:540–548. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb01708.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURN J. H., RAND M. J. Action of nicotine on the heart. Br Med J. 1958 Jan 18;1(5063):137–139. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5063.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W., Rubin R. P. The mechanism of catecholamine release from the adrenal medulla and the role of calcium in stimulus-secretion coupling. J Physiol. 1963 Jul;167(2):288–310. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERRY C. B. The synpathomimetic effect of acetylcholine on the spleen of the cat. J Physiol. 1963 Jul;167:487–504. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkleman B. On the nature of inhibition in the intestine. J Physiol. 1930 Sep 18;70(2):145–157. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1930.sp002683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


