Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADRIAN R. H. Internal chloride concentration and chloride efflux of frog muscle. J Physiol. 1961 May;156:623–632. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ADRIAN R. H. The effect of internal and external potassium concentration on the membrane potential of frog muscle. J Physiol. 1956 Sep 27;133(3):631–658. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Freygang W. H. The potassium and chloride conductance of frog muscle membrane. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;163(1):61–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
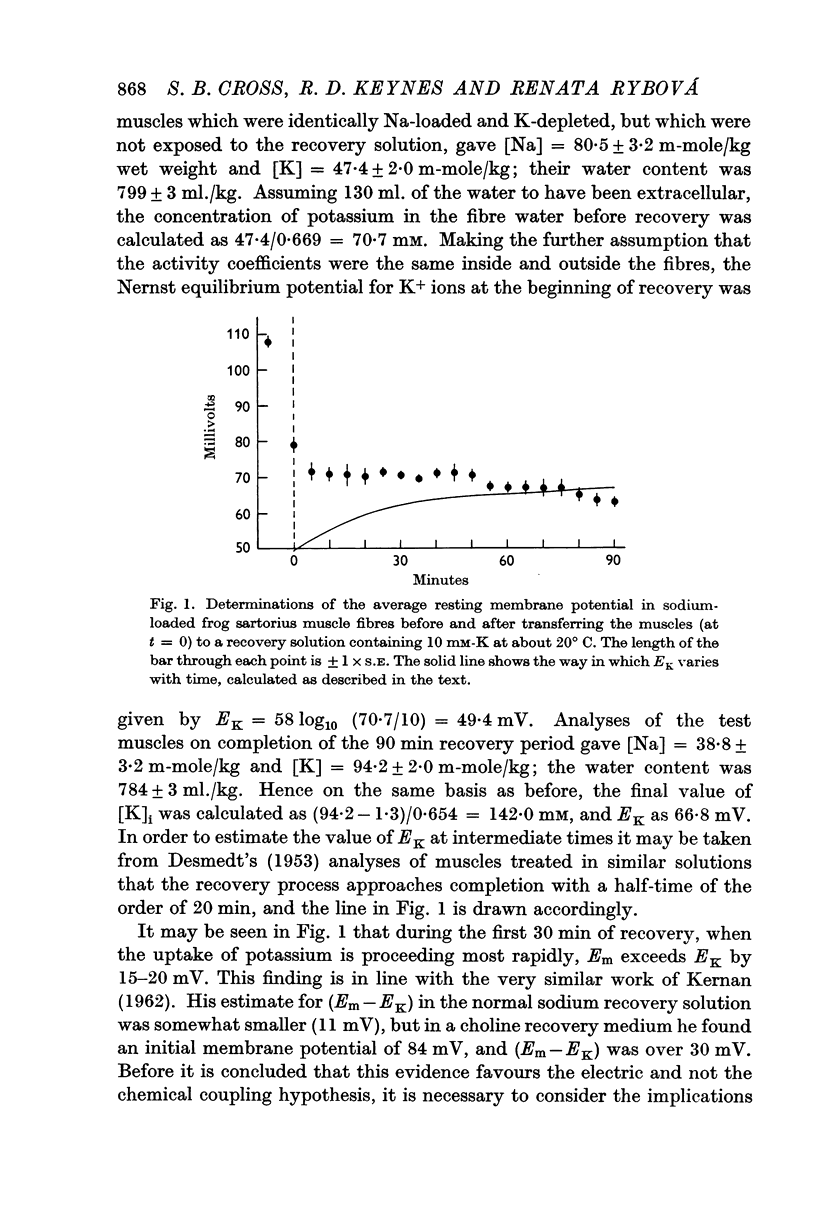
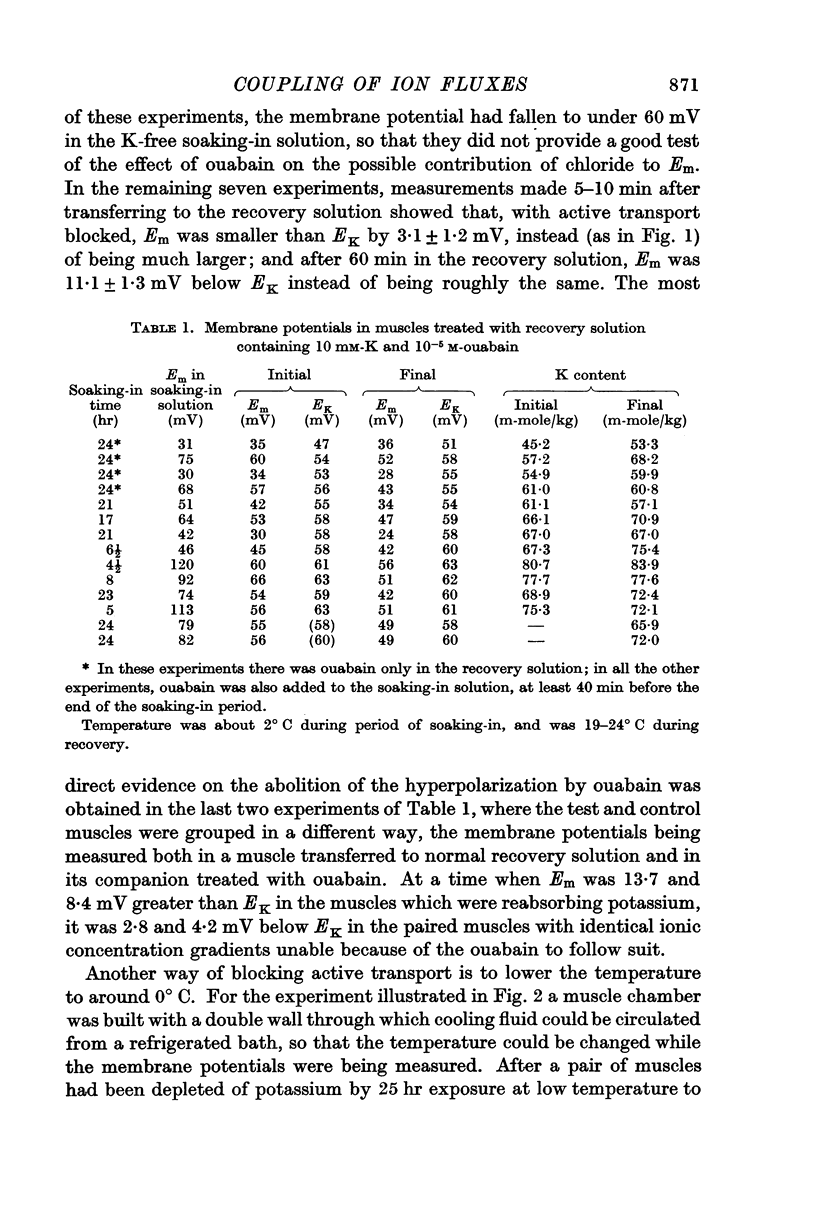
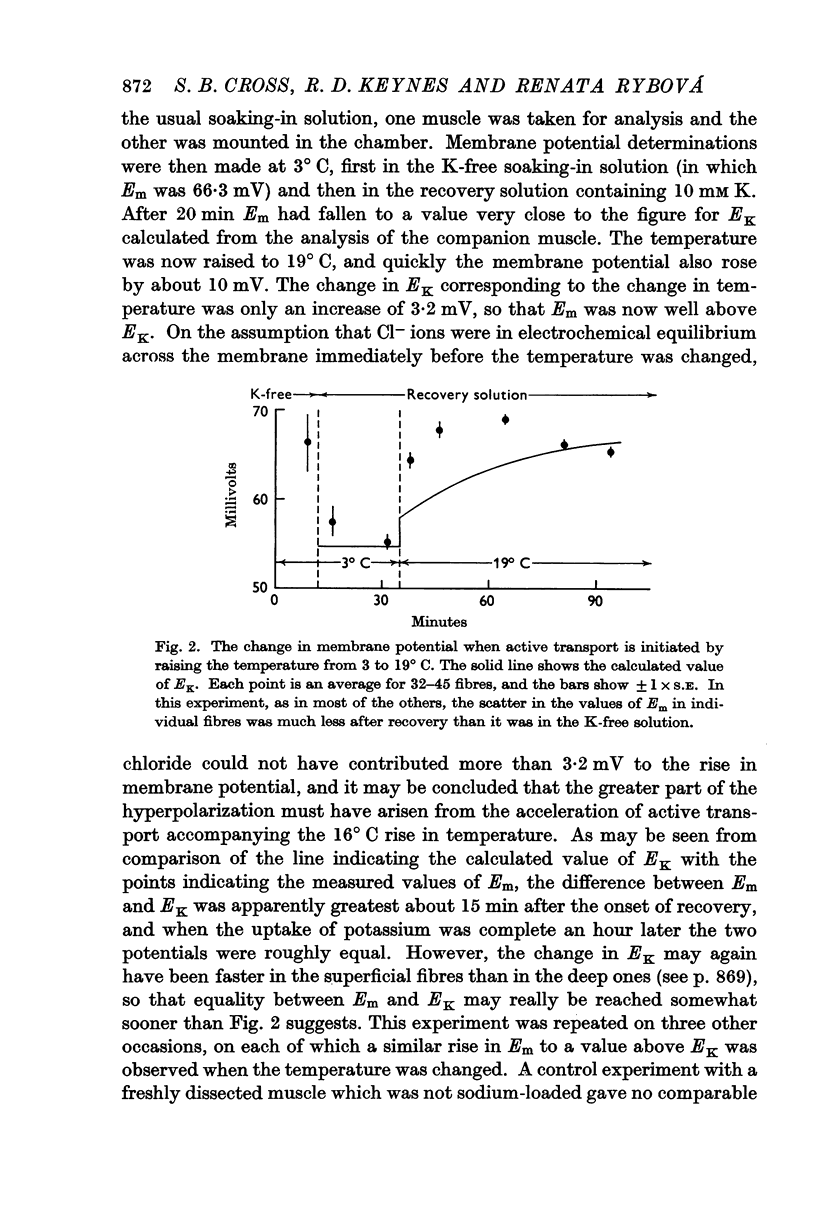
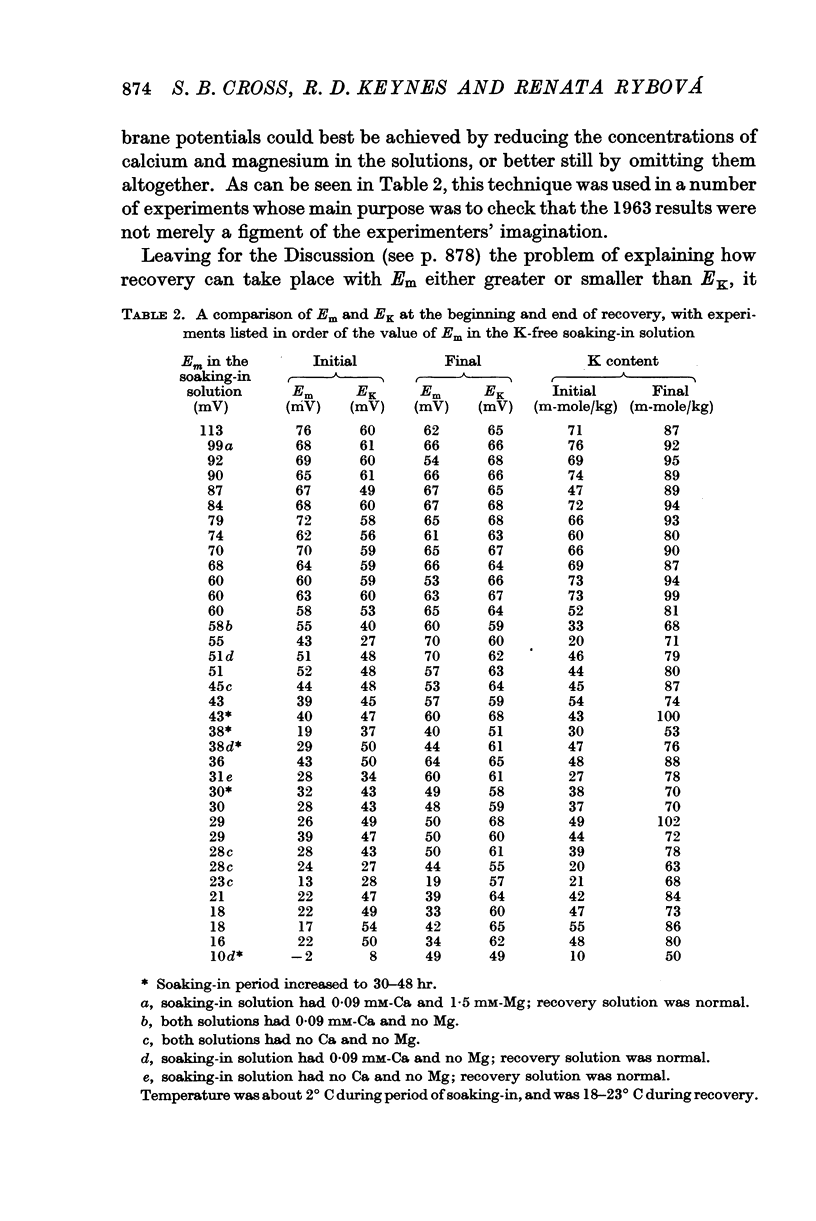
- DESMEDT J. E. Electrical activity and intracellular sodium concentration in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1953 Jul;121(1):191–205. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARDS C., HARRIS E. J. Factors influencing the sodium movement in frog muscle with a discussion of the mechanism of sodium movement. J Physiol. 1957 Mar 11;135(3):567–580. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRUMENTO A. S. SODIUM PUMP: ITS ELECTRICAL EFFECTS IN SKELETAL MUSCLE. Science. 1965 Mar 19;147(3664):1442–1443. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3664.1442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:127–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOROWICZ P., GERBER C. J. EFFECTS OF EXTERNAL POTASSIUM AND STROPHANTHIDIN ON SODIUM FLUXES IN FROG STRIATED MUSCLE. J Gen Physiol. 1965 Jan;48:489–514. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.3.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON J. A. Influence of ouabain, strophanthidin and dihydrostrophanthidin on sodium and potassium transport in frog sartorii. Am J Physiol. 1956 Nov;187(2):328–332. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.187.2.328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERNAN R. P. Membrane potential changes during sodium transport in frog sartorius muscle. Nature. 1962 Mar 10;193:986–987. doi: 10.1038/193986a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D. SOME FURTHER OBSERVATIONS ON THE SODIUM EFFLUX IN FROG MUSCLE. J Physiol. 1965 May;178:305–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D., SWAN R. C. The effect of external sodium concentration on the sodium fluxes in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;147:591–625. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D., SWAN R. C. The permeability of frog muscle fibres to lithium ions. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;147:626–638. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEV A. A. DETERMINATION OF ACTIVITY AND ACTIVITY COEFFICIENTS OF POTASSIUM AND SODIUM IONS IN FROG MUSCLE FIBRES. Nature. 1964 Mar 14;201:1132–1134. doi: 10.1038/2011132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RITCHIE J. M., STRAUB R. W. The hyperpolarization which follows activity in mammalian non-medullated fibres. J Physiol. 1957 Apr 3;136(1):80–97. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


