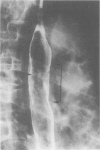
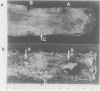
Abstract
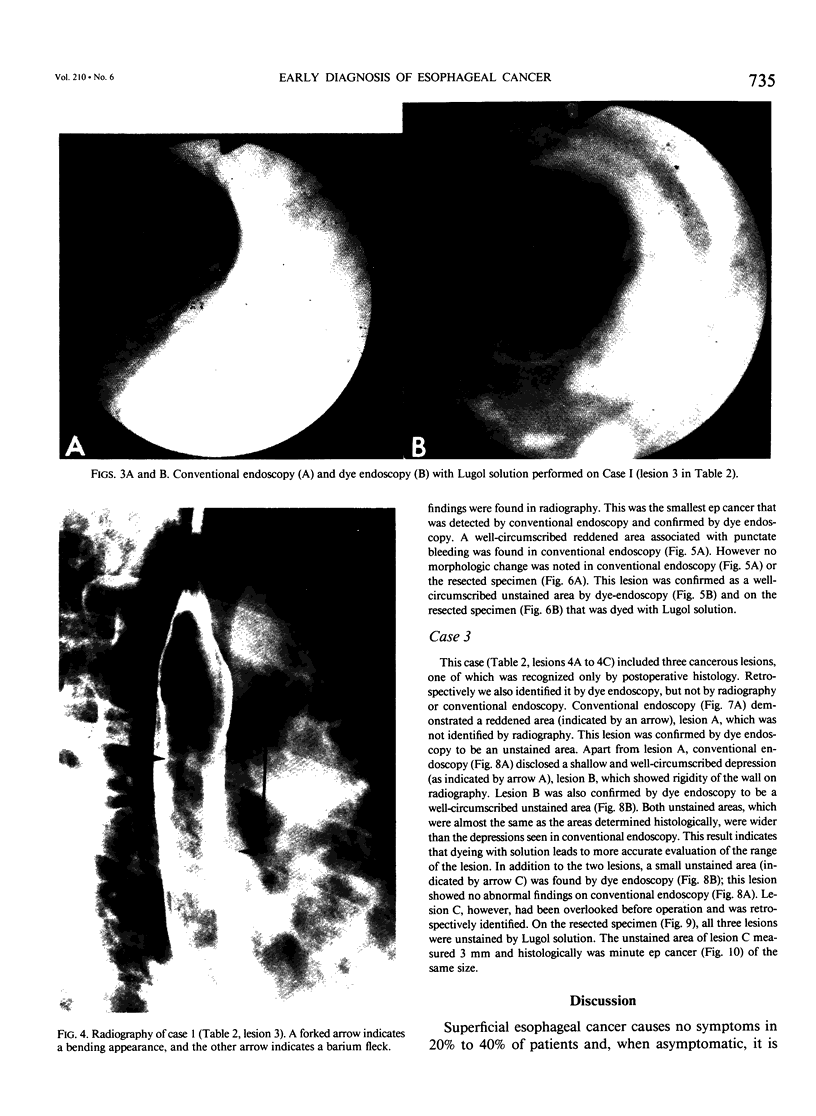
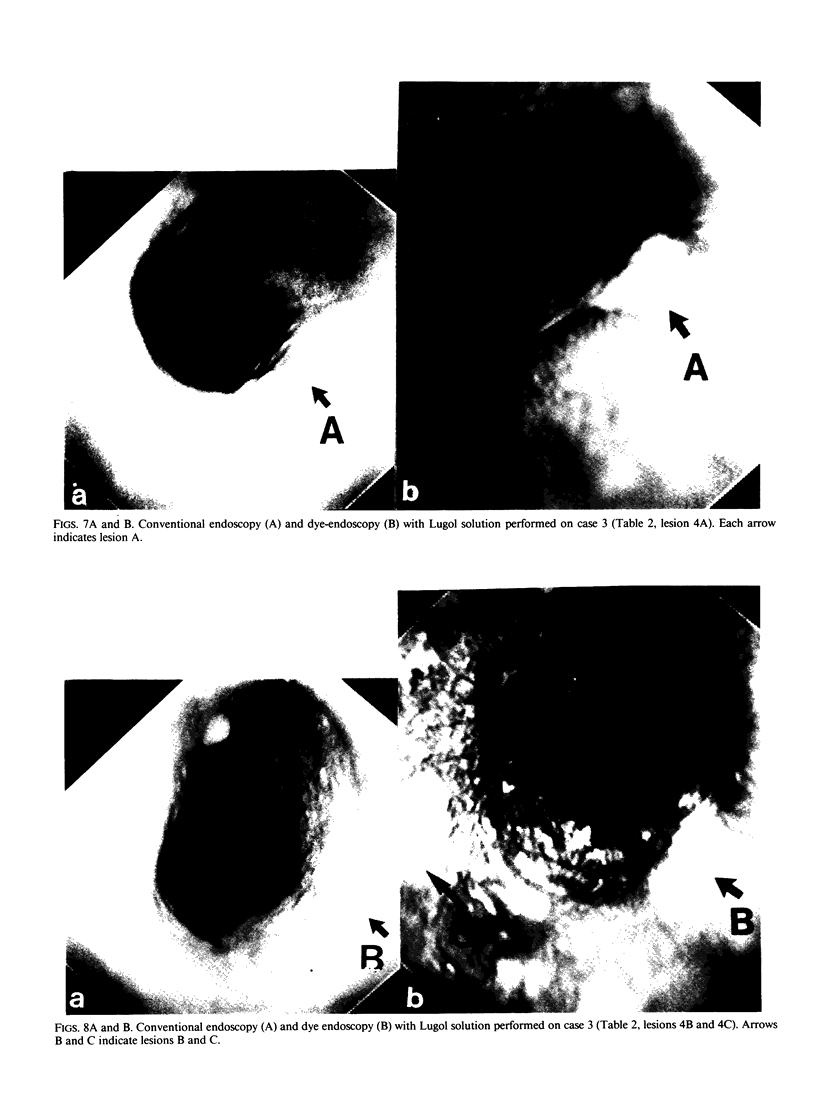
We reviewed 11 patients with esophageal mucosal carcinoma in various aspects to improve the early diagnosis of the disease. Eighteen lesions measuring 0.5 to 5.0 cm were confirmed histologically in the 11 cases. Histologically 10 of the 18 lesions were carcinomas in situ (ep cancer), and the other 8 lesions were carcinomas confined to the mucosa other than ep cancer (mm cancer); all 18 lesions were squamous cell carcinomas. Six (85.7%) of the seven mm cancers showed abnormal radiographic findings regardless of the size. Similarly these findings were noted on four of five (80%) ep carcinomas 2 cm or larger in size. All 15 lesions diagnosed before operation showed abnormal findings on conventional endoscopy regardless of the size and depth of transmural invasion. Morphologic change was observed in 9 lesions (53.3%), while 13 (86.7%) showed color change; most of the lesions (80%) were manifested as redness. Dyeing of the resected specimen with Lugol solution (Katayama Chemical Industries, Osaka, Japan) showed all 18 cancerous lesions as unstained areas. Among the 18 lesions, two lesions were unstained areas, which agreed with the areas determined histologically. An additional lesion was visible with dye endoscopy as an unstained area but it was not visible with radiography or conventional endoscopy. Dye endoscopy using Lugol solution is very important because it allows detection and evaluation of the extent of esophageal mucosal cancer.
Full text
PDF
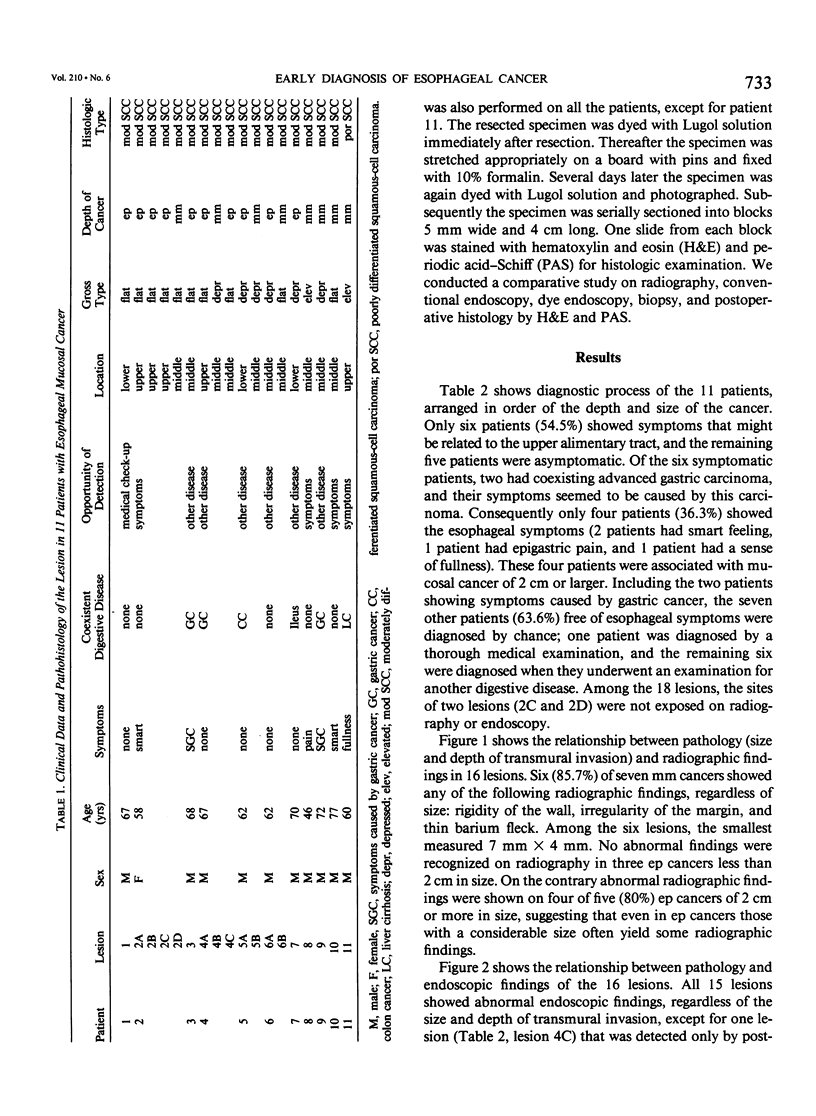
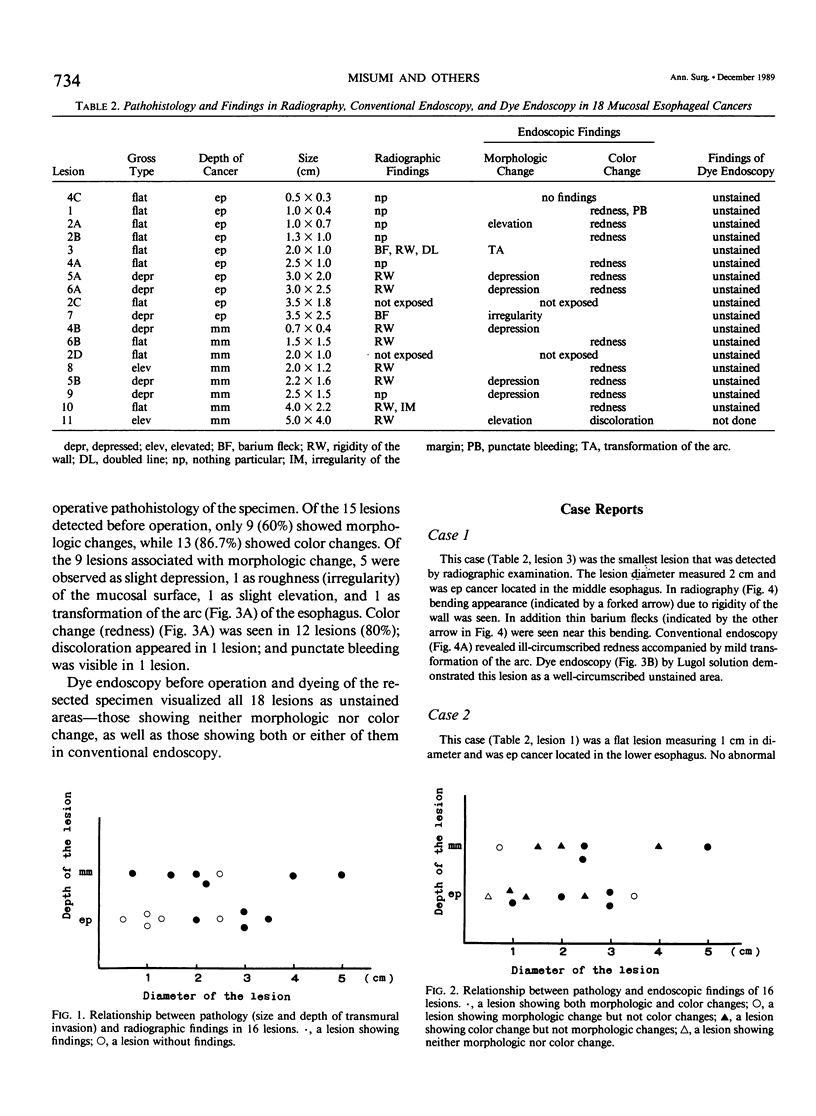



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Misumi A., Kondou H., Murakami A., Arima K., Honmyou U., Baba K., Akagi M. Endoscopic diagnosis of reflux esophagitis by the dye-spraying method. Endoscopy. 1989 Jan;21(1):1–6. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1012883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nothmann B. J., Wright J. R., Schuster M. M. In vivo vital staining as an aid to identification of esophagogastric mucosal junction in man. Am J Dig Dis. 1972 Oct;17(10):919–924. doi: 10.1007/BF02239531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rywlin A. M., Ortega R. Glycogenic acanthosis of the esophagus. Arch Pathol. 1970 Nov;90(5):439–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]