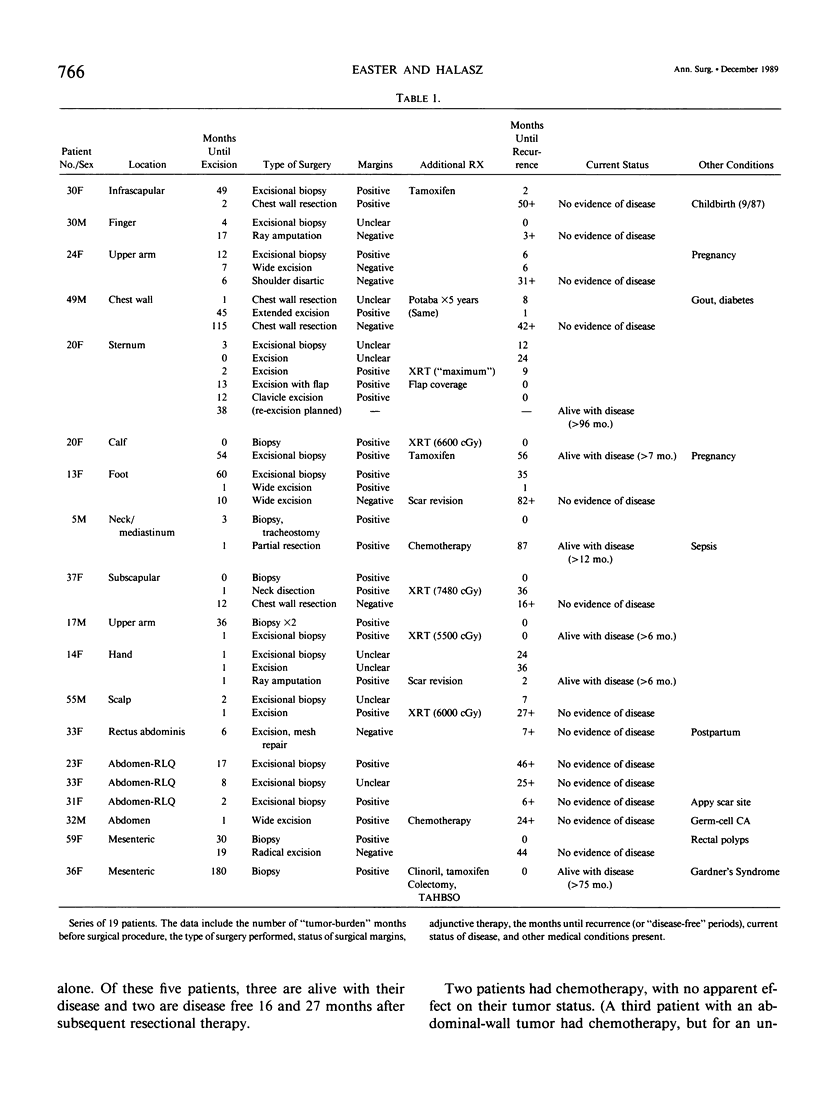
Abstract
Recent advances in the understanding of desmoid tumor biology affect therapeutic choices. This series of 19 patients and review of the literature outlines historic perspectives and discusses the options in the management of these locally aggressive tumors. Desmoid tumors tend to grow steadily, regardless of tumor location. However differences in the aggressive nature of these tumors are seen when age and sex distributions are scrutinized. Although recurrence rates are high, excisional therapy is the best first approach. An exception is the case in which tumor excision is either particularly dangerous or likely to result in significant physical handicap. Radiation or drug therapy are most often used with recurrent disease or as an alternative to mutilating surgery. Although many pharmacologic approaches have been advocated, (including antiestrogen therapy, cyclic-AMP, and prostaglandin inhibition), results are anecdotal at best.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belliveau P., Graham A. M. Mesenteric desmoid tumor in Gardner's syndrome treated by sulindac. Dis Colon Rectum. 1984 Jan;27(1):53–54. doi: 10.1007/BF02554079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crisi G., Calo' M., Mauri C. Case report 358: desmoid tumor of the greater wing of the right sphenoid bone. Skeletal Radiol. 1986;15(3):247–250. doi: 10.1007/BF00354070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHN I., JONSSON N., LUNDH G. DESMOID TUMOURS. A SERIES OF 33 CASES. Acta Chir Scand. 1963 Oct;126:305–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Darder J., Alacreu J. B., Garcia-Vázquez F. Desmoid tumor arising around the distal tubing of a cerebrospinal fluid shunt. Surg Neurol. 1986 Oct;26(4):365–367. doi: 10.1016/0090-3019(86)90137-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hial V., Horakova Z., Shaff F. E., Beaven M. A. Alteration of tumor growth by aspirin and indomethacin: studies with two transplantable tumors in mouse. Eur J Pharmacol. 1976 Jun;37(2):367–376. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(76)90044-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones I. T., Jagelman D. G., Fazio V. W., Lavery I. C., Weakley F. L., McGannon E. Desmoid tumors in familial polyposis coli. Ann Surg. 1986 Jul;204(1):94–97. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198607000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keus R., Bartelink H. The role of radiotherapy in the treatment of desmoid tumours. Radiother Oncol. 1986 Sep;7(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/s0167-8140(86)80118-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khorsand J., Karakousis C. P. Desmoid tumors and their management. Am J Surg. 1985 Feb;149(2):215–218. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(85)80067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiel K. D., Suit H. D. Radiation therapy in the treatment of aggressive fibromatoses (desmoid tumors). Cancer. 1984 Nov 15;54(10):2051–2055. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19841115)54:10<2051::aid-cncr2820541002>3.0.co;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim C. L., Walker M. J., Mehta R. R., Das Gupta T. K. Estrogen and antiestrogen binding sites in desmoid tumors. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1986 May;22(5):583–587. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(86)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markhede G., Lundgren L., Bjurstam N., Berlin O., Stener B. Extra-abdominal desmoid tumors. Acta Orthop Scand. 1986 Feb;57(1):1–7. doi: 10.3109/17453678608993204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAdam W. A., Goligher J. C. The occurrence of desmoids in patients with familial polyposis coli. Br J Surg. 1970 Aug;57(8):618–631. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800570816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Procter H., Singh L., Baum M., Brinkley D. Response of multicentric desmoid tumours to tamoxifen. Br J Surg. 1987 May;74(5):401–401. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800740527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitamo J. J., Scheinin T. M., Häyry P. The desmoid syndrome. New aspects in the cause, pathogenesis and treatment of the desmoid tumor. Am J Surg. 1986 Feb;151(2):230–237. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(86)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock M. G., Pritchard D. J., Reiman H. M., Soule E. H., Brewster R. C. Extra-abdominal desmoid tumors. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984 Dec;66(9):1369–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell W. R., Gerner R. E. Indomethacin and ascorbate inhibit desmoid tumors. J Surg Oncol. 1980;15(1):85–90. doi: 10.1002/jso.2930150113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell W. R. Treatment of intra-abdominal and abdominal wall desmoid tumors with drugs that affect the metabolism of cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate. Ann Surg. 1975 Mar;181(3):299–302. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197503000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


