Abstract
Seventy-one burned patients requiring intensive care unit management underwent 570 central venous and 167 femoral arterial catheterizations. These patients were surveyed by repeated physical examinations and duplex scans for vascular-related complications. Catheter sites were rotated every 3 days. No arterial thrombi or occlusions were noted. Fourteen patients (19.6%) had 19 positive venous duplex scans. Five patients (7%) had symptomatic deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and nine (12.6%) had asymptomatic DVT. Mean number of venous cannulations before a positive scan was 4.3 (range 1 to 17). All five symptomatic patients had DVT that originated in the lower extremities. No patient had clinical evidence of a pulmonary embolus, or limb morbidity resulting from the DVT. Follow-up duplex scans in the five asymptomatic and three symptomatic patients showed complete resolution in each case. This study demonstrates the high incidence and natural history of central DVT in a group of critically ill burn patients.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed N. Thrombosis after central venous cannulation. Med J Aust. 1976 Feb 21;1(8):217–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borozan P. G., Zukowski A., Thorpe L., Auer A. I., Caracci B. F. Noninvasive imaging for deep venous thrombosis. Am J Surg. 1988 Dec;156(6):474–476. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(88)80532-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chastre J., Cornud F., Bouchama A., Viau F., Benacerraf R., Gibert C. Thrombosis as a complication of pulmonary-artery catheterization via the internal jugular vein: prospective evaluation by phlebography. N Engl J Med. 1982 Feb 4;306(5):278–281. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198202043060506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clagett G. P., Reisch J. S. Prevention of venous thromboembolism in general surgical patients. Results of meta-analysis. Ann Surg. 1988 Aug;208(2):227–240. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198808000-00016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comerota A. J., White J. V., Katz M. L. Diagnostic methods for deep vein thrombosis: venous Doppler examination, phleborheography, iodine-125 fibrinogen uptake, and phlebography. Am J Surg. 1985 Oct 8;150(4A):14–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crandon A. J., Peel K. R., Anderson J. A., Thompson V., McNicol G. P. Prophylaxis of postoperative deep vein thrombosis: selective use of low-dose heparin in high-risk patients. Br Med J. 1980 Aug 2;281(6236):345–347. doi: 10.1136/bmj.281.6236.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalen J. E., Paraskos J. A., Ockene I. S., Alpert J. S., Hirsh J. Venous thromboembolism. Scope of the problem. Chest. 1986 May;89(5 Suppl):370S–373S. doi: 10.1378/chest.89.5.370s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dauzat M. M., Laroche J. P., Charras C., Blin B., Domingo-Faye M. M., Sainte-Luce P., Domergue A., Lopez F. M., Janbon C. Real-time B-mode ultrasonography for better specificity in the noninvasive diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis. J Ultrasound Med. 1986 Nov;5(11):625–631. doi: 10.7863/jum.1986.5.11.625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiSerio F. J., Sasahara A. A. United States trial of dihydroergotamine and heparin prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis. Am J Surg. 1985 Oct 8;150(4A):25–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dye L. E., Segall P. H., Russell R. O., Jr, Mantle J. A., Rogers W. J., Rackley C. E. Deep venous thrombosis of the upper extremity associated with use of the Swan-Ganz catheter. Chest. 1978 May;73(5):673–675. doi: 10.1378/chest.73.5.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott C. G., Zimmerman G. A., Clemmer T. P. Complications of pulmonary artery catheterization in the care of critically ill patients. A prospective study. Chest. 1979 Dec;76(6):647–652. doi: 10.1378/chest.76.6.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman E. K., Pakter R. L., Gayler B. W., Wheeler P. S., Siegelman S. S. Jugular venous thrombosis: diagnosis by computed tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1984 Oct;8(5):963–968. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198410000-00030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley D. P., White R. A., Nelson R. J., Mehringer C. M. Pulmonary embolism secondary to venous thrombosis of the arm. Am J Surg. 1984 Feb;147(2):221–224. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(84)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill S. L., Martin D., McDannald E. R., Jr, Donato A. T. Early diagnosis of iliofemoral venous thrombosis by Doppler examination. Am J Surg. 1988 Jul;156(1):11–15. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(88)80160-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horattas M. C., Wright D. J., Fenton A. H., Evans D. M., Oddi M. A., Kamienski R. W., Shields E. F. Changing concepts of deep venous thrombosis of the upper extremity--report of a series and review of the literature. Surgery. 1988 Sep;104(3):561–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R. D., Raskob G. E., Hirsh J. Prophylaxis of venous thromboembolism. An overview. Chest. 1986 May;89(5 Suppl):374S–383S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langsfeld M., Hershey F. B., Thorpe L., Auer A. I., Binnington H. B., Hurley J. J., Woods J. J. Duplex B-mode imaging for the diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis. Arch Surg. 1987 May;122(5):587–591. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1987.01400170093013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lensing A. W., Prandoni P., Brandjes D., Huisman P. M., Vigo M., Tomasella G., Krekt J., Wouter Ten Cate J., Huisman M. V., Büller H. R. Detection of deep-vein thrombosis by real-time B-mode ultrasonography. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 9;320(6):342–345. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902093200602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn K. L., Maling T. M. A major pulmonary embolus as a complication of femoral vein catheterization. Br J Radiol. 1977 Sep;50(597):667–668. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-50-597-667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malatinský J., Faybík M., Sámel M., Májek M. Surgical, infectious and thromboembolic complications of central venous catheterization. Resuscitation. 1983 Aug;10(4):271–281. doi: 10.1016/0300-9572(83)90029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer A. H., Au F. C., Malmud L. S., Harwick R. R. Radionuclide venography in subclavian vein thrombosis complicating parenteral nutrition. Clin Nucl Med. 1984 Jul;9(7):397–399. doi: 10.1097/00003072-198407000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowall R. A. Pulmonary embolism and deep venous thrombosis in burned patients. Br J Plast Surg. 1973 Apr;26(2):176–177. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1226(73)80014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser K. M., LeMoine J. R., Nachtwey F. J., Spragg R. G. Deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Frequency in a respiratory intensive care unit. JAMA. 1981 Sep 25;246(13):1422–1424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruitt B. A., Jr, McManus W. F., Kim S. H., Treat R. C. Diagnosis and treatment of cannula-related intravenous sepsis in burn patients. Ann Surg. 1980 May;191(5):546–554. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198005000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruitt B. A., Jr, McManus W. F., Kim S. H., Treat R. C. Diagnosis and treatment of cannula-related intravenous sepsis in burn patients. Ann Surg. 1980 May;191(5):546–554. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198005000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purdue G. F., Hunt J. L. Pulmonary emboli in burned patients. J Trauma. 1988 Feb;28(2):218–220. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198802000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purdue G. F., Hunt J. L. Vascular access through the femoral vessels: indications and complications. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1986 Nov-Dec;7(6):498–500. doi: 10.1097/00004630-198611000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins D. L., Semrow C. M., Friedell M. L., Calligaro K. D., Buchbinder D. Progress in the diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis: the efficacy of real-time B-mode ultrasonic imaging. J Vasc Surg. 1988 May;7(5):638–641. doi: 10.1067/mva.1988.avs0070638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. A., Jr, Abel R. M., Abbott W. M., Hopkins C. C., Chesney T. M., Colley R., Phillips K., Fischer J. E. Catheter complications in total parenteral nutrition. A prospective study of 200 consecutive patients. N Engl J Med. 1974 Apr 4;290(14):757–761. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197404042901401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVITT S., GALLAGHER N. Venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. A clinico-pathological study in injured and burned patients. Br J Surg. 1961 Mar;48:475–489. doi: 10.1002/bjs.18004821103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan E. D., Peter D. J., Cranley J. J. Real-time B-mode venous ultrasound. J Vasc Surg. 1984 May;1(3):465–471. doi: 10.1067/mva.1984.avs0010465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szendro G., Nicolaides A. N., Zukowski A. J., Christopoulos D., Malouf G. M., Christodoulou C., Myers K. Duplex scanning in the assessment of deep venous incompetence. J Vasc Surg. 1986 Sep;4(3):237–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
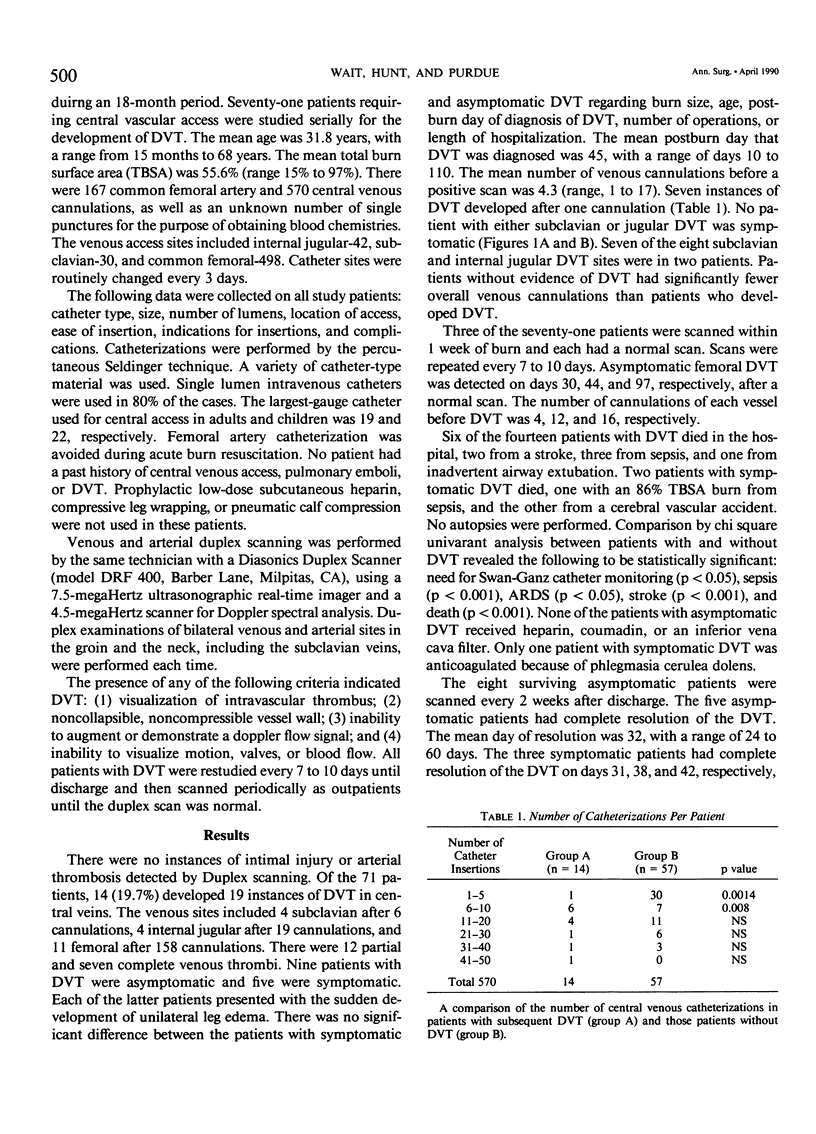
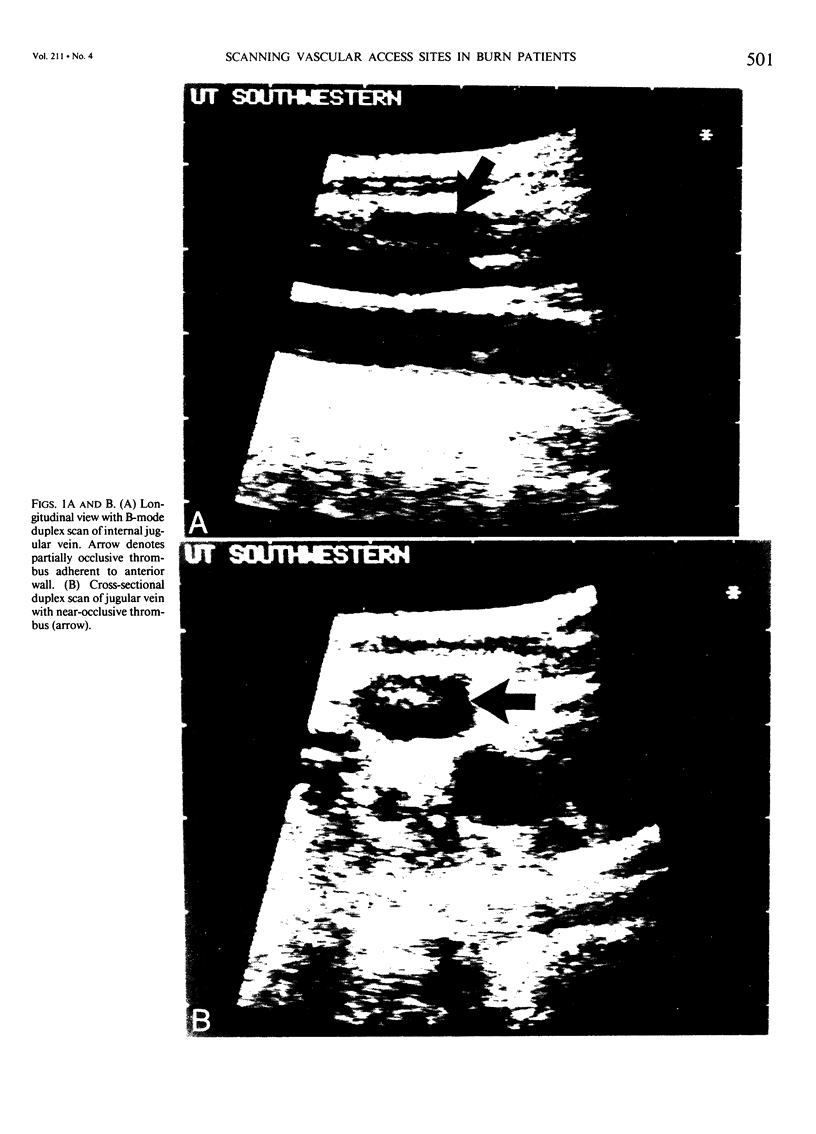
- Warden G. D., Wilmore D. W., Pruitt B. A., Jr Central venous thrombosis: a hazard of medical progress. J Trauma. 1973 Jul;13(7):620–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler H. B. Diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis. Review of clinical evaluation and impedance plethysmography. Am J Surg. 1985 Oct 8;150(4A):7–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]