Abstract
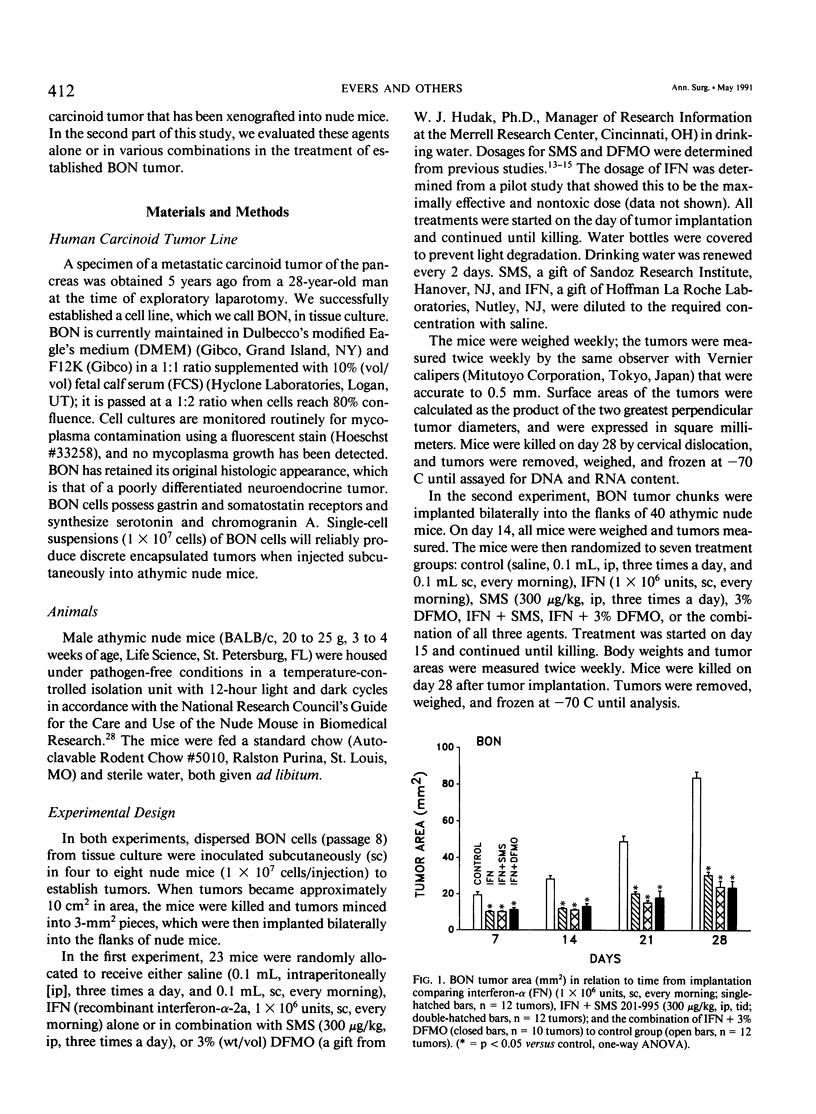
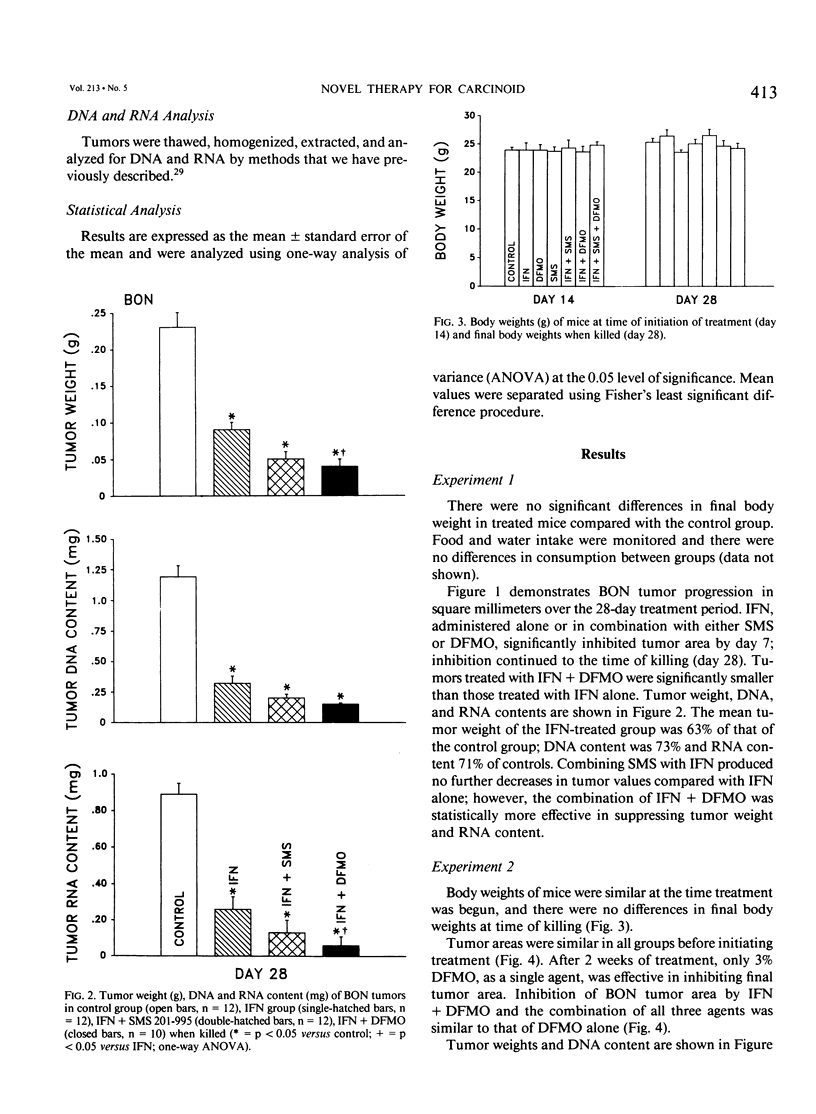
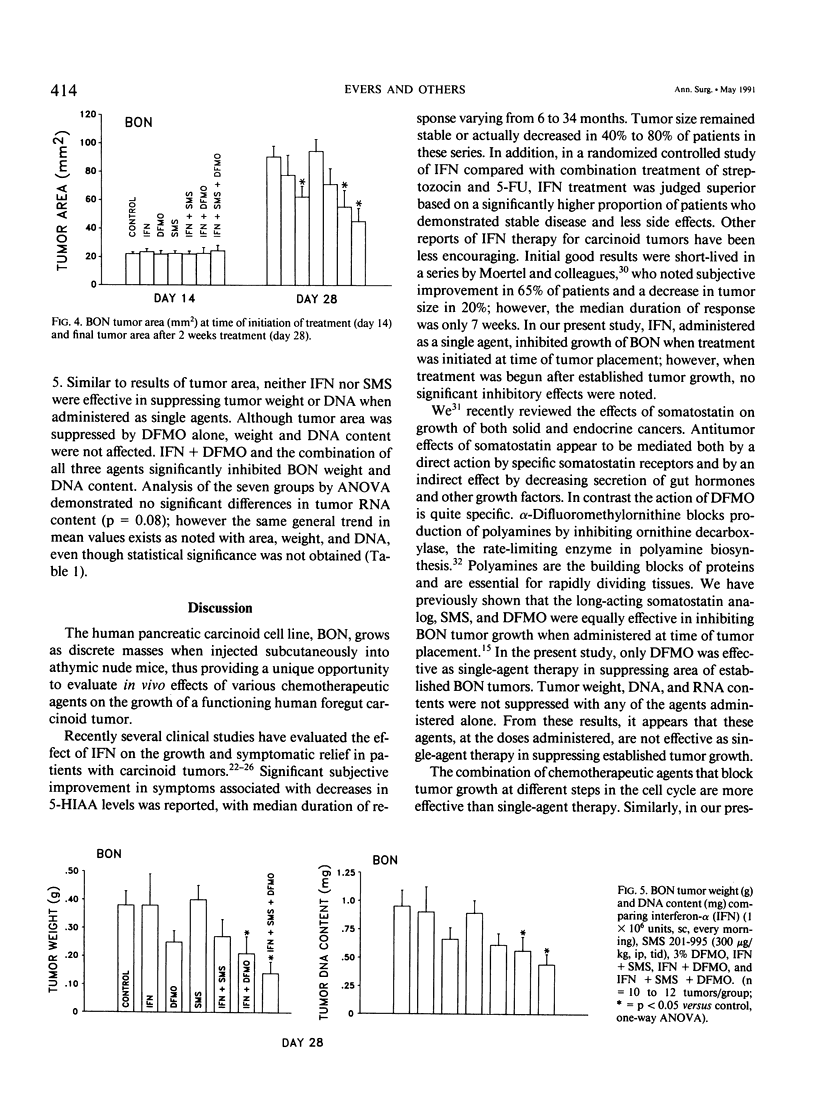
Development of effective treatment for patients with carcinoid tumors has been hampered by lack of an experimental model. The authors have established the only long-term cell line of a functioning human pancreatic carcinoid tumor (BON) that produces tumors in nude mice. In this study the authors examined the effect of three agents, alpha-interferon (IFN), a somatostatin analog, SMS 201-995 (SMS), and an inhibitor of polyamine biosynthesis, alpha-difluoromethylornithine (DFMO), on the growth of BON tumors. BON was implanted bilaterally as 3-mm2 pieces (subcutaneously [sc]) into male BALB/c nude mice. In the first study, 23 mice were randomized to four groups: control, IFN (1 x 10(6) units, sc, four times a day), IFN + SMS (300 micrograms/kg, intraperitoneally, three times a day), and IFN + 3% DFMO in drinking water. Treatments were initiated on day of tumor implantation. In the second study, mice were randomized to six groups: control, IFN, SMS, DFMO, IFN + SMS, IFN + DFMO, and IFN + SMS + DFMO. Treatments were started on day 15 after tumor implantation. Tumor area and body weights were measured weekly. In both studies mice were killed on day 28 after BON implantation and tumors removed, weighed, and analyzed for DNA and RNA content. In the first study, IFN either alone or in combination with SMS or DFMO suppressed BON tumor growth. When treatment was initiated after established tumor growth (study 2), however, the only effective treatments for suppression of growth of BON were IFN + DFMO and IFN + DFMO + SMS.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson T., Wilander E., Eriksson B., Lindgren P. G., Oberg K. Effects of interferon on tumor tissue content in liver metastases of human carcinoid tumors. Cancer Res. 1990 Jun 1;50(11):3413–3415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balkwill F. R., Goldstein L., Stebbing N. Differential action of six human interferons against two human carcinomas growing in nude mice. Int J Cancer. 1985 May 15;35(5):613–617. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910350508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balkwill F. R. Interferons. Lancet. 1989 May 13;1(8646):1060–1063. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92455-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balkwill F. R., Moodie E. M., Freedman V., Fantes K. H. Human interferon inhibits the growth of established human breast tumours in the nude mouse. Int J Cancer. 1982 Aug 15;30(2):231–235. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910300217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deghenghi R. Somatostatin analogues in the treatment of the carcinoid syndrome. Biomed Pharmacother. 1988;42(9):585–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engstrom P. F., Lavin P. T., Moertel C. G., Folsch E., Douglass H. O., Jr Streptozocin plus fluorouracil versus doxorubicin therapy for metastatic carcinoid tumor. J Clin Oncol. 1984 Nov;2(11):1255–1259. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1984.2.11.1255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evers B. M., Gomez G., Townsend C. M., Jr, Rajaraman S., Thompson J. C. Endogenous cholecystokinin regulates growth of human cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Surg. 1989 Sep;210(3):317–323. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198909000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Tovey M. G. Antitumor effects of interferon. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 27;516(2):231–247. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(78)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsen J., Lendorf A., Raskov H., Boesby S. Ketanserin versus placebo in carcinoid syndrome. A clinical controlled trial. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1986 Sep;21(7):816–818. doi: 10.3109/00365528609011123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutterman J. U., Blumenschein G. R., Alexanian R., Yap H. Y., Buzdar A. U., Cabanillas F., Hortobagyi G. N., Hersh E. M., Rasmussen S. L., Harmon M. Leukocyte interferon-induced tumor regression in human metastatic breast cancer, multiple myeloma, and malignant lymphoma. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Sep;93(3):399–406. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-3-399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanssen L. E., Schrumpf E., Kolbenstvedt A. N., Tausjø J., Dolva L. O. Treatment of malignant metastatic midgut carcinoid tumours with recombinant human alpha2b interferon with or without prior hepatic artery embolization. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1989 Sep;24(7):787–795. doi: 10.3109/00365528909089215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff G., Bjørneklett A., Moen I. E., Jenssen E. Epidemiology of polyps in the rectum and sigmoid colon. Evaluation of breath methane and predisposition for colorectal neoplasia. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1986 Mar;21(2):193–198. doi: 10.3109/00365528609034646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvols L. K., Buck M. Chemotherapy of metastatic carcinoid and islet cell tumors. A review. Am J Med. 1987 May 29;82(5B):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90430-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moertel C. G., Hanley J. A. Combination chemotherapy trials in metastatic carcinoid tumor and the malignant carcinoid syndrome. Cancer Clin Trials. 1979 Winter;2(4):327–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moertel C. G., Rubin J., Kvols L. K. Therapy of metastatic carcinoid tumor and the malignant carcinoid syndrome with recombinant leukocyte A interferon. J Clin Oncol. 1989 Jul;7(7):865–868. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1989.7.7.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moertel C. G. Treatment of the carcinoid tumor and the malignant carcinoid syndrome. J Clin Oncol. 1983 Nov;1(11):727–740. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1983.1.11.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberg K., Eriksson B. Medical treatment of neuroendocrine gut and pancreatic tumors. Acta Oncol. 1989;28(3):425–431. doi: 10.3109/02841868909111217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberg K., Funa K., Alm G. Effects of leukocyte interferon on clinical symptoms and hormone levels in patients with mid-gut carcinoid tumors and carcinoid syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jul 21;309(3):129–133. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198307213090301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberg K., Norheim I., Alm G. Treatment of malignant carcinoid tumors: a randomized controlled study of streptozocin plus 5-FU and human leukocyte interferon. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1989 Oct;25(10):1475–1479. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(89)90107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberg K., Norheim I., Lind E., Alm G., Lundqvist G., Wide L., Jonsdottir B., Magnusson A., Wilander E. Treatment of malignant carcinoid tumors with human leukocyte interferon: long-term results. Cancer Treat Rep. 1986 Nov;70(11):1297–1304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saydjari R., Townsend C. M., Jr, Barranco S. C., James E., Thompson J. C. Effects of cyclosporin A and alpha-difluoromethylornithine on the growth of hamster pancreatic cancer in vitro. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Nov;77(5):1087–1092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunkara P. S., Prakash N. J., Mayer G. D., Sjoerdsma A. Tumor suppression with a combination of alpha-difluoromethyl ornithine and interferon. Science. 1983 Feb 18;219(4586):851–853. doi: 10.1126/science.6186025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upp J. R., Jr, Olson D., Poston G. J., Alexander R. W., Townsend C. M., Jr, Thompson J. C. Inhibition of growth of two human pancreatic adenocarcinomas in vivo by somatostatin analog SMS 201-995. Am J Surg. 1988 Jan;155(1):29–35. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(88)80254-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaoka T., Takada H., Yanagi Y., Kataoka T., Sakurai Y. The antitumor effects of human lymphoblastoid interferon on human renal cell carcinoma in athymic nude mice. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1985;14(3):184–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00258113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Houten A. A., Nortier J. W., Vendrik C. P. Successful symptomatic treatment of malignant carcinoid syndrome with the somatostatin analogue SMS 201-995. Neth J Med. 1988 Apr;32(3-4):194–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


