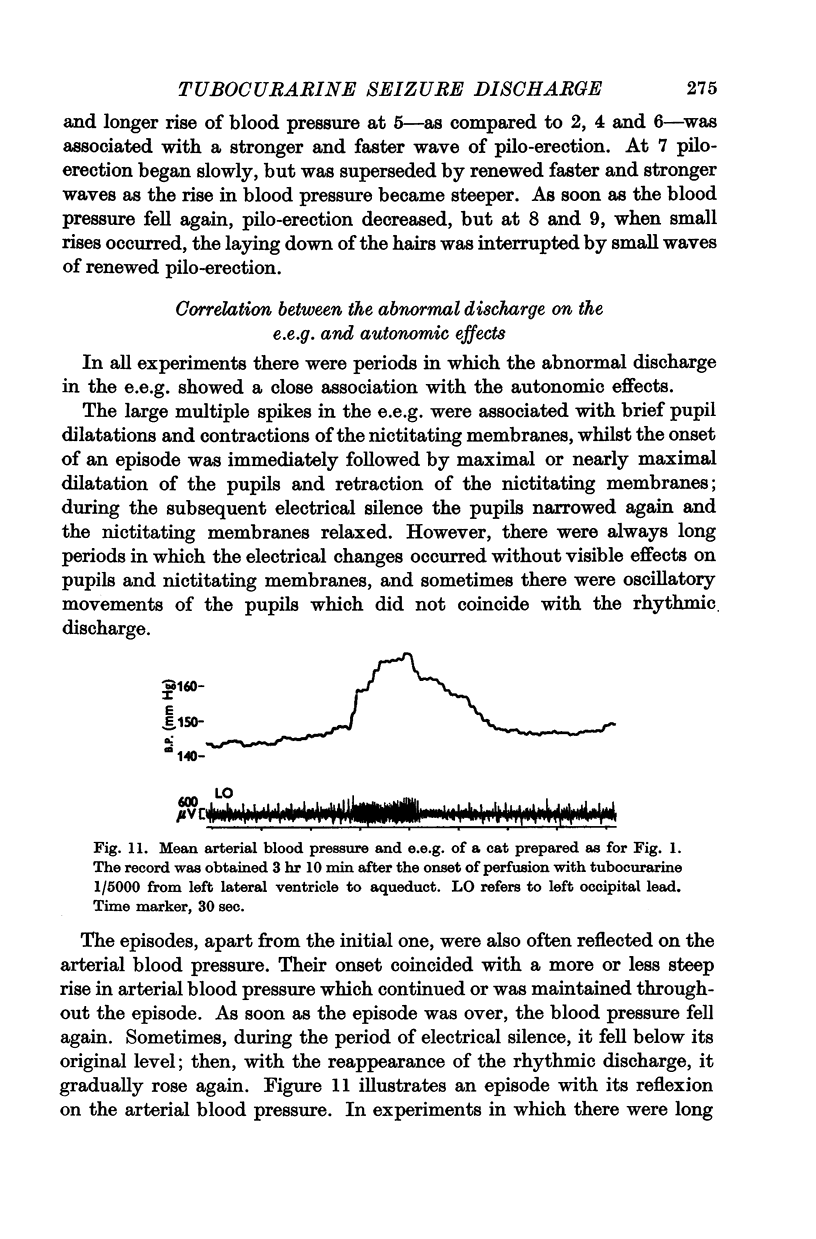
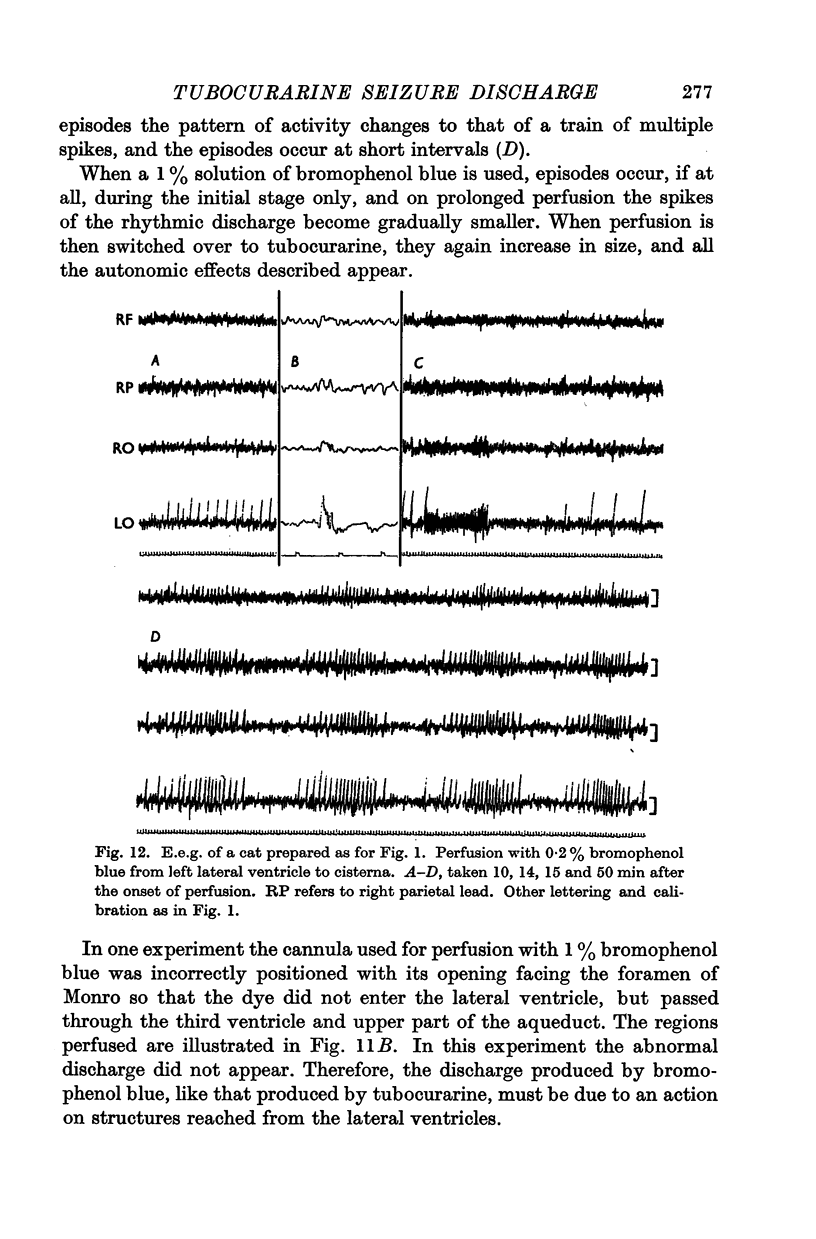
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BHATTACHARYA B. K., FELDBERG W. Perfusion of the ventricular system of the brain in the anaesthetized cat. J Physiol. 1957 Jan 23;135(1):4–5P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREUTZFELDT O. Die Krampfausbreitung im Temporallappen der Katze; die Krampfentladungen des Ammonshorns und ihre Beziehungen zum übrigen Rhinencephálon und Isocortex. Schweiz Arch Neurol Psychiatr. 1956;77(1-2):163–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEINDEL W., GLOOR P. Comparison of electrographic effects of stimulation of the amygdala and brain stem reticular formation in cats. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1954 Aug;6(3):389–402. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(54)90053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDBERG W., FLEISCHHAUER K. Penetration of bromophenol blue from the perfused cerebral ventricles into the brain tissue. J Physiol. 1960 Feb;150:451–462. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
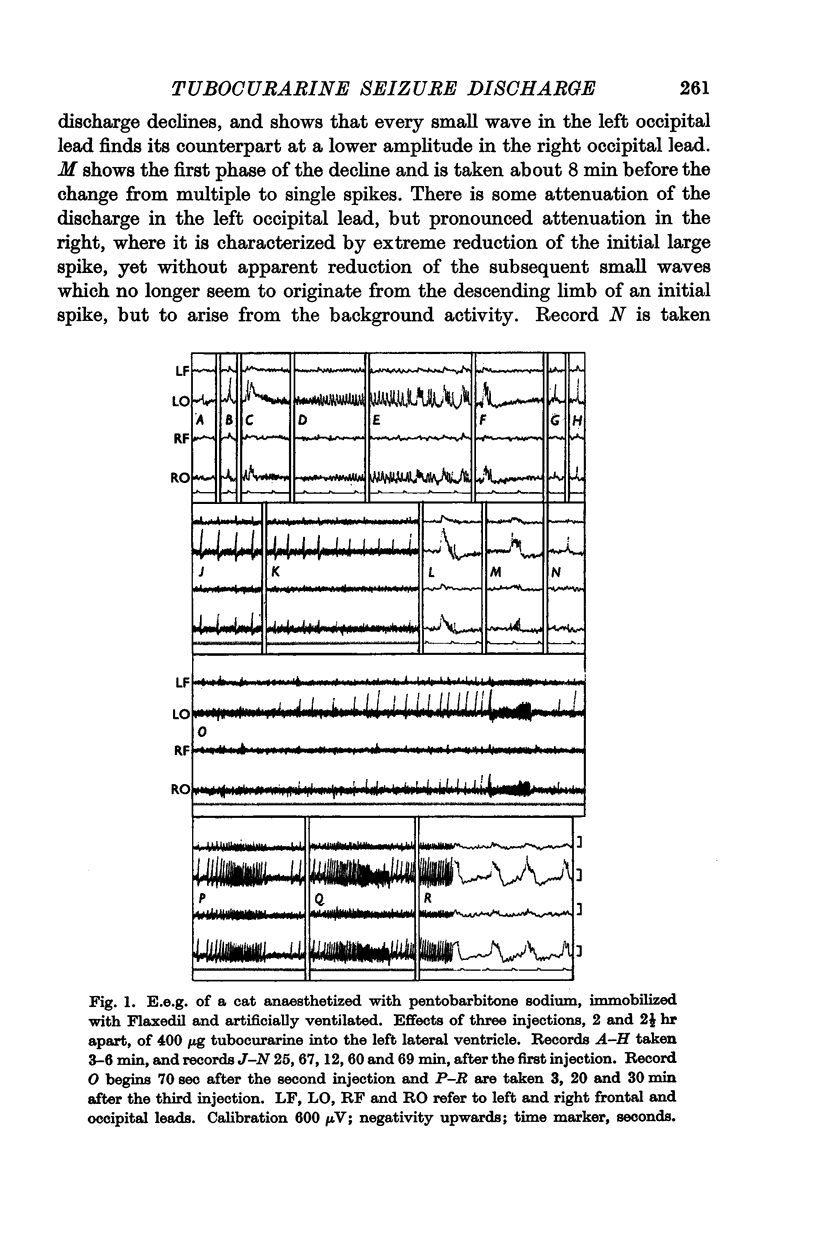
- FELDBERG W., MALCOLM J. L., SHERWOOD S. L. Some effects of tubocurarine on the electrical activity of the cat's brain. J Physiol. 1956 Apr 27;132(1):130–145. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDBERG W., MALCOLM J. L., SMITH I. D. Effect of tubocurarine on the electrical activity of the cat's brain under chloralose. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):178–201. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
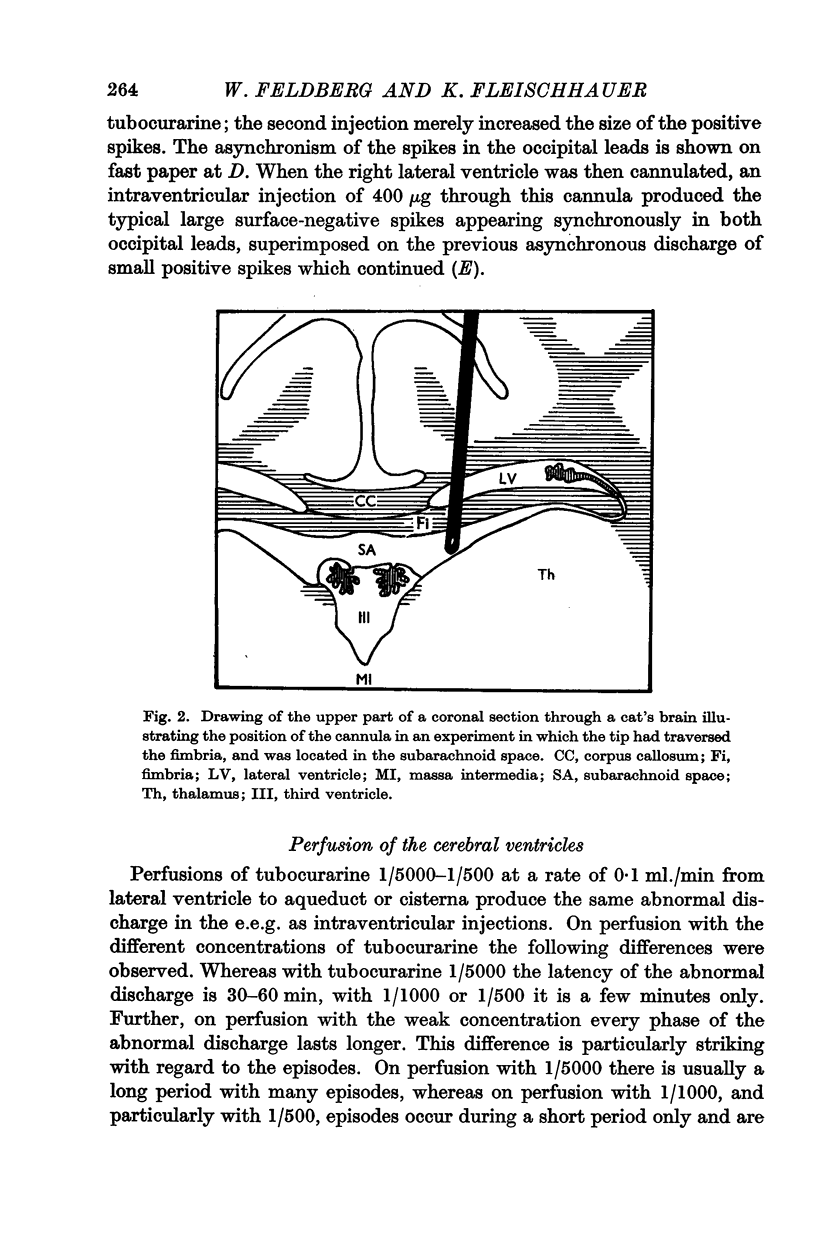
- FELDBERG W., MALCOLM J. Experiments on the site of action of tubocurarine when applied via the cerebral ventricles. J Physiol. 1959 Dec;149:58–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDBERG W., SHERWOOD S. L. A permanent cannula for intraventricular injections in cats. J Physiol. 1953 Apr 28;120(1-2):3P–5P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GASTAUT H. Corrélations entre le système nerveux végétatif et le système de la vie de relation dans le rhinencéphale. J Physiol (Paris) 1952;44(2):431–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLOOR P. The pattern of conduction of amygdaloid seizure discharge; an experimental study in the cat. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1957 Mar;77(3):247–258. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1957.02330330033004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEAN P. D. Chemical and electrical stimulation of hippocampus in unrestrained animals. I. Methods and electroencephalographic findings. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1957 Aug;78(2):113–127. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1957.02330380003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAWYER C. H., GERNANDT B. E. Effects of intracarotid and intraventricular injections of hypertonic solutions on electrical activity of the rabbit brain. Am J Physiol. 1956 Apr;185(1):209–216. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.185.1.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]