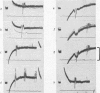
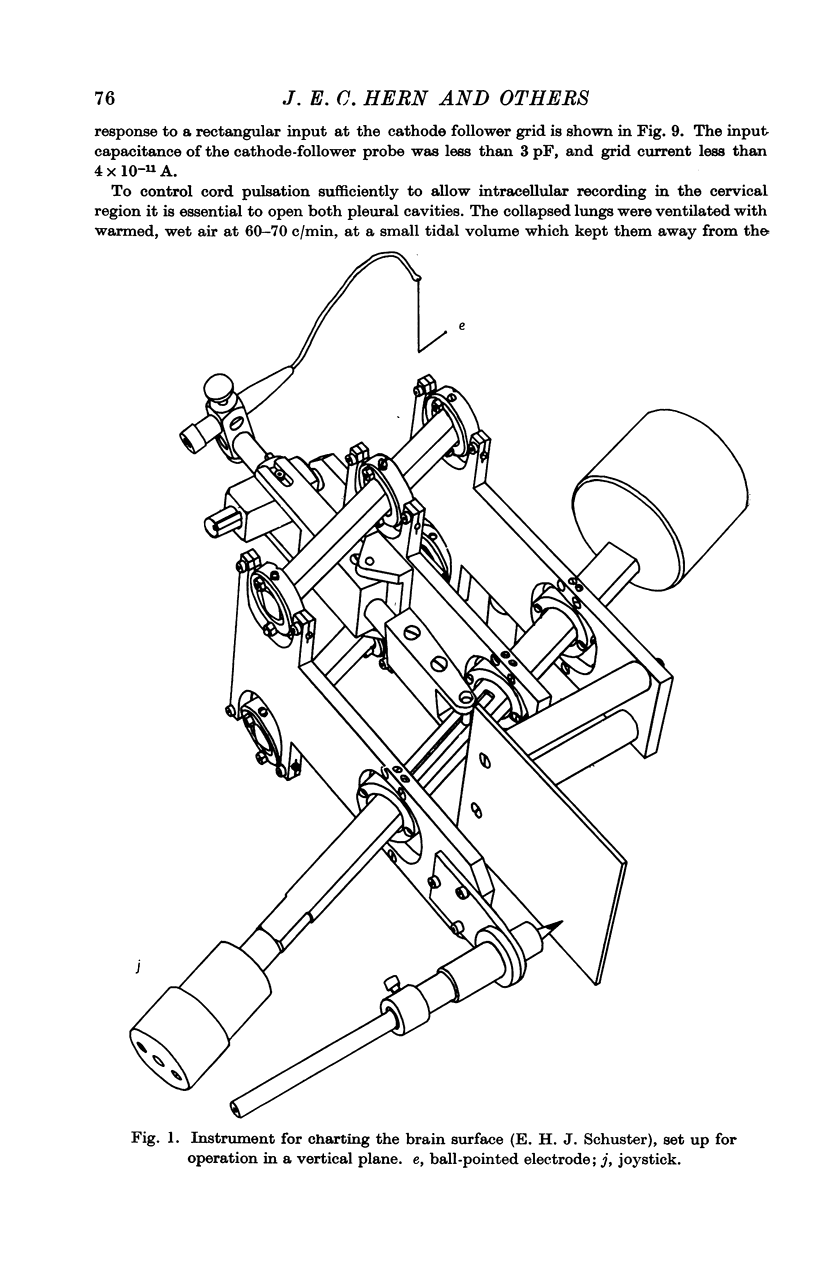
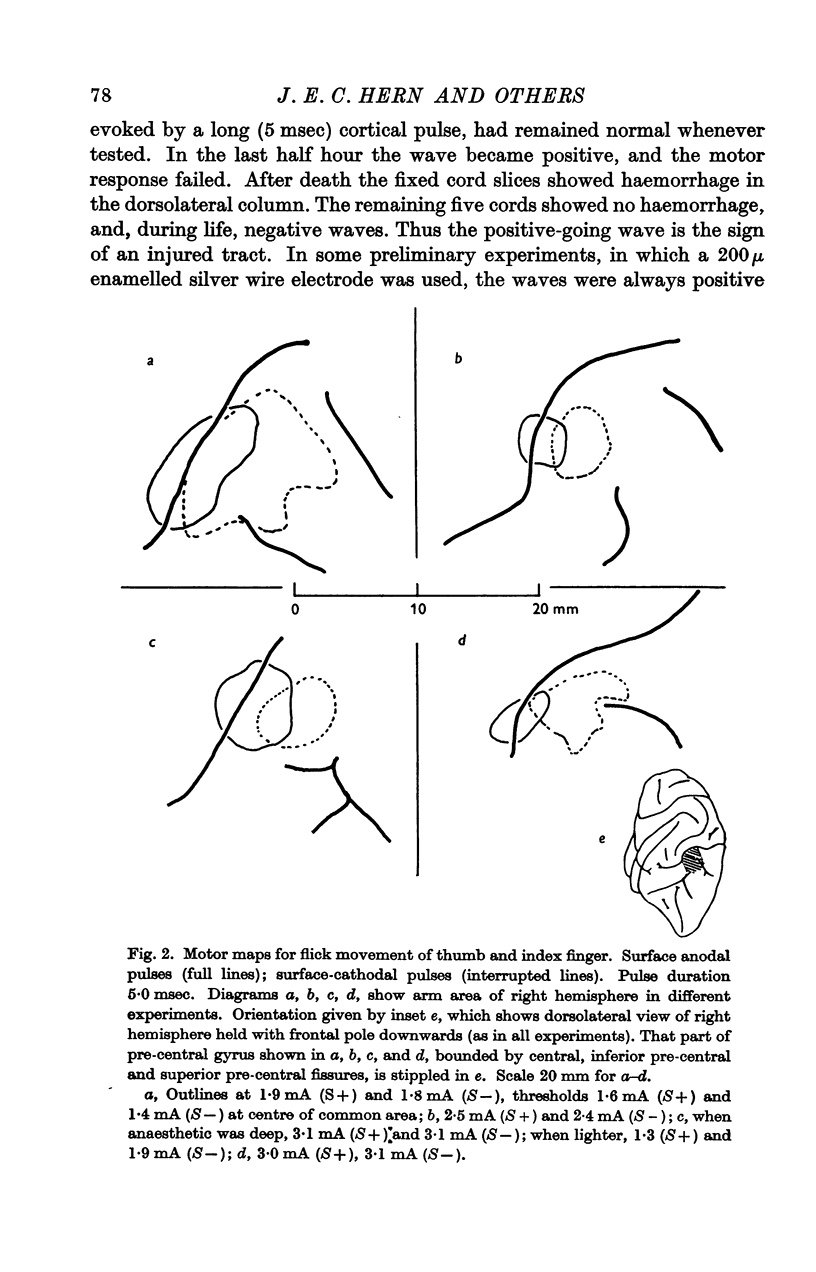
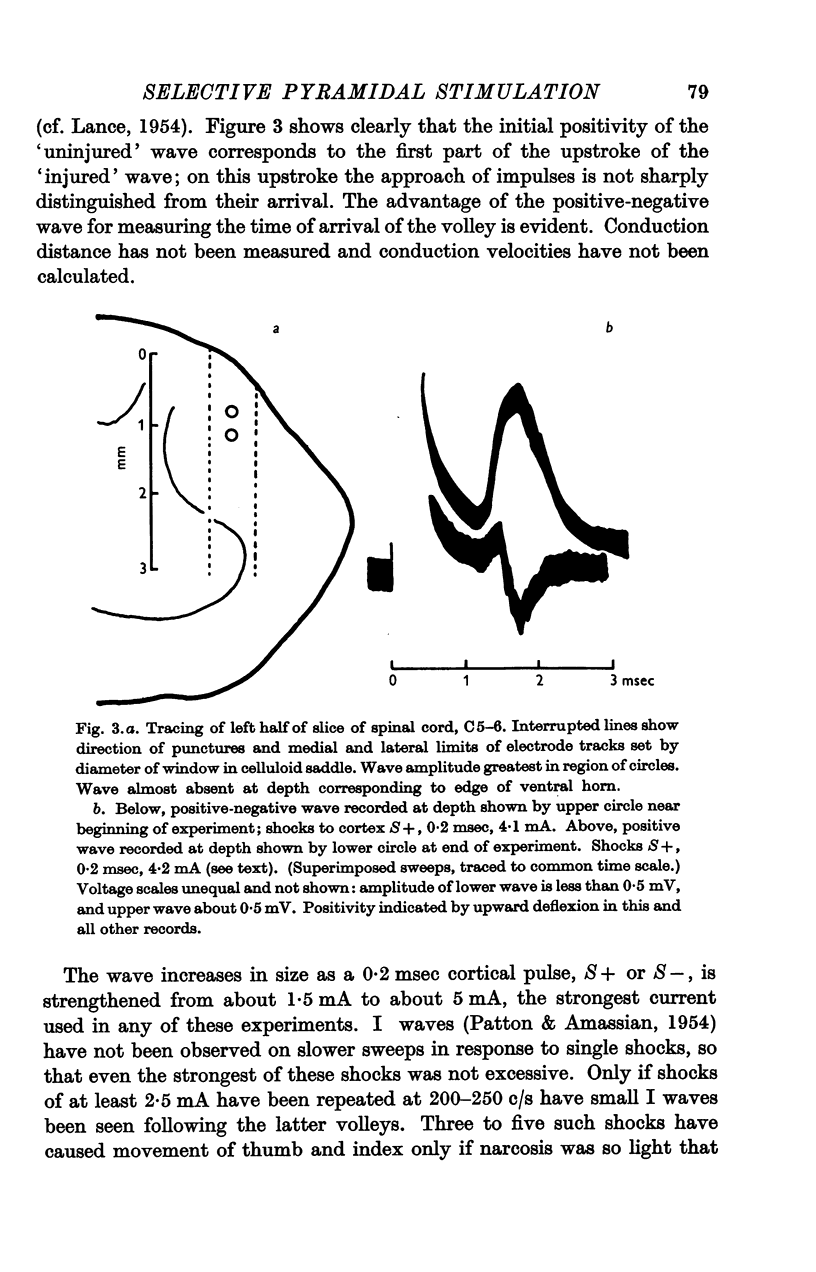
Full text
PDF



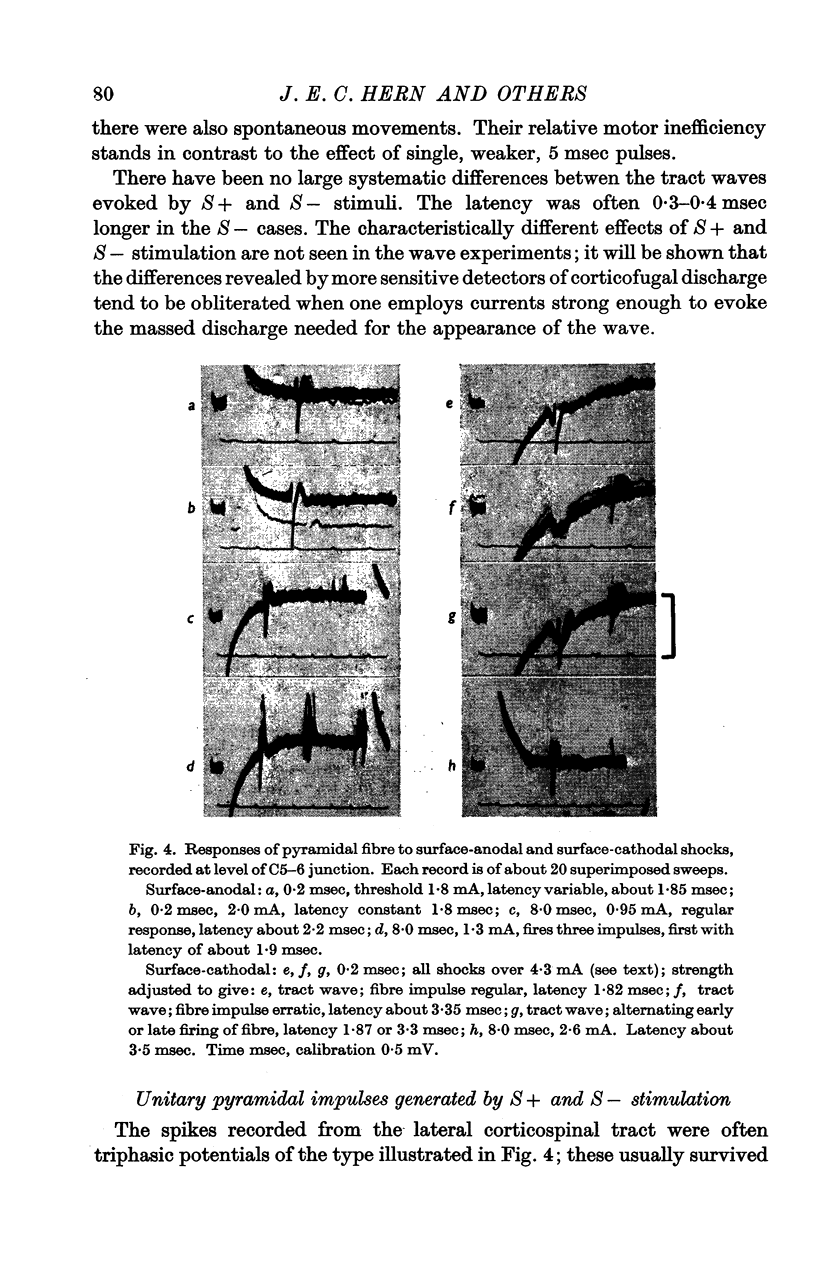

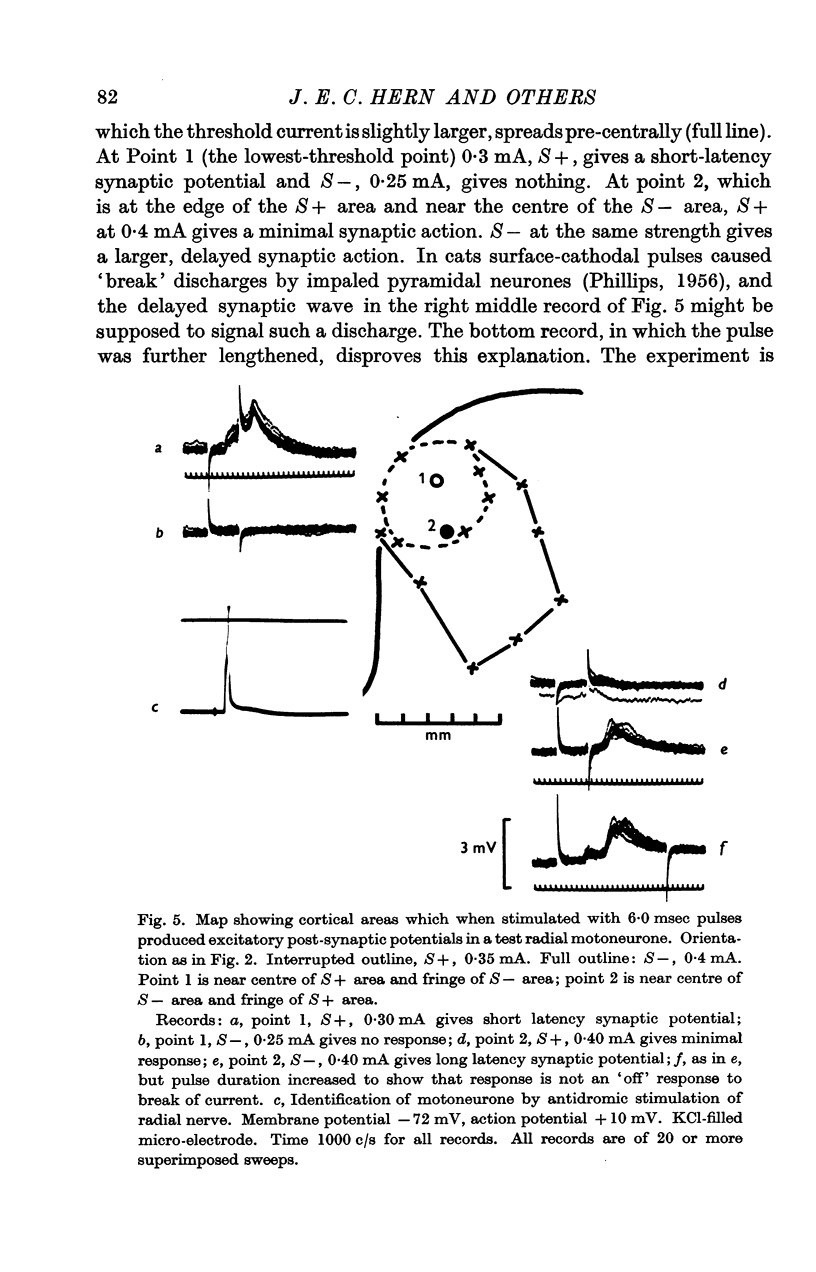
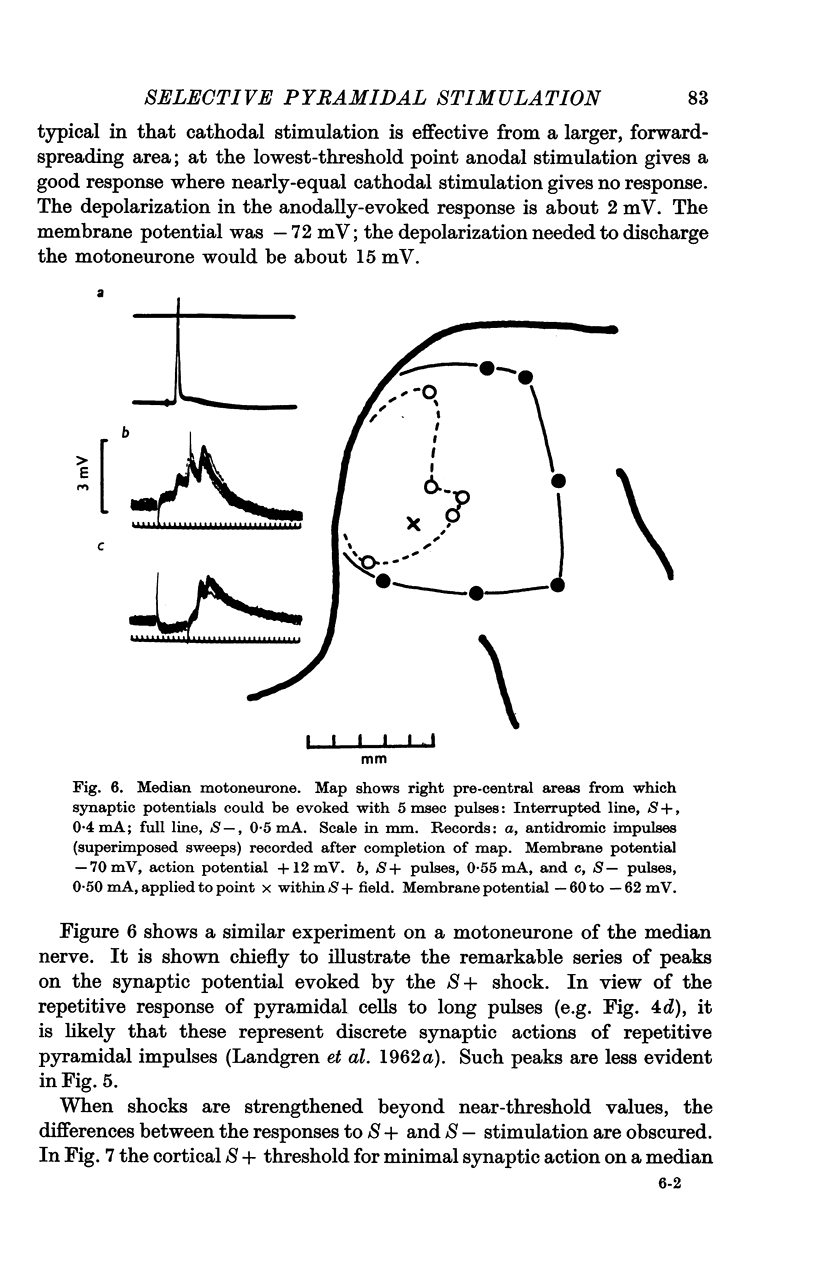
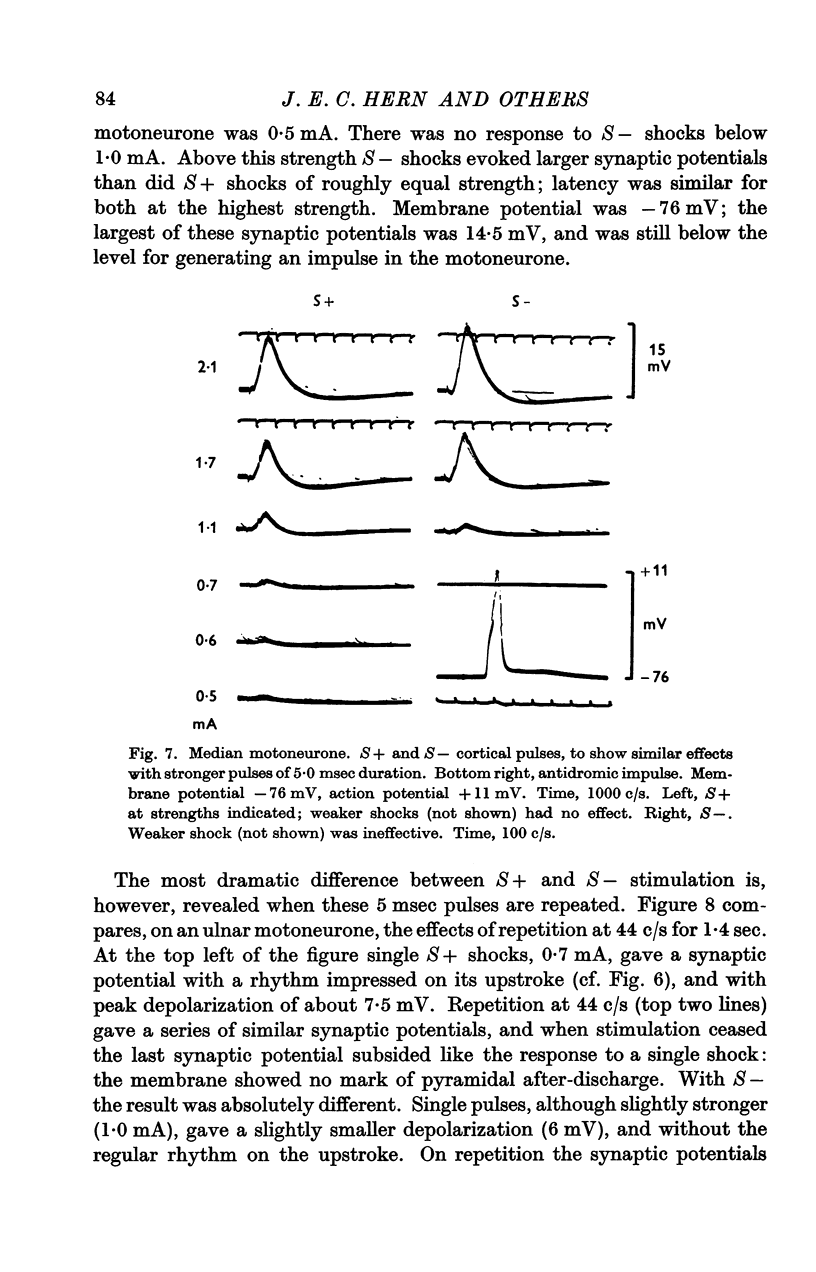
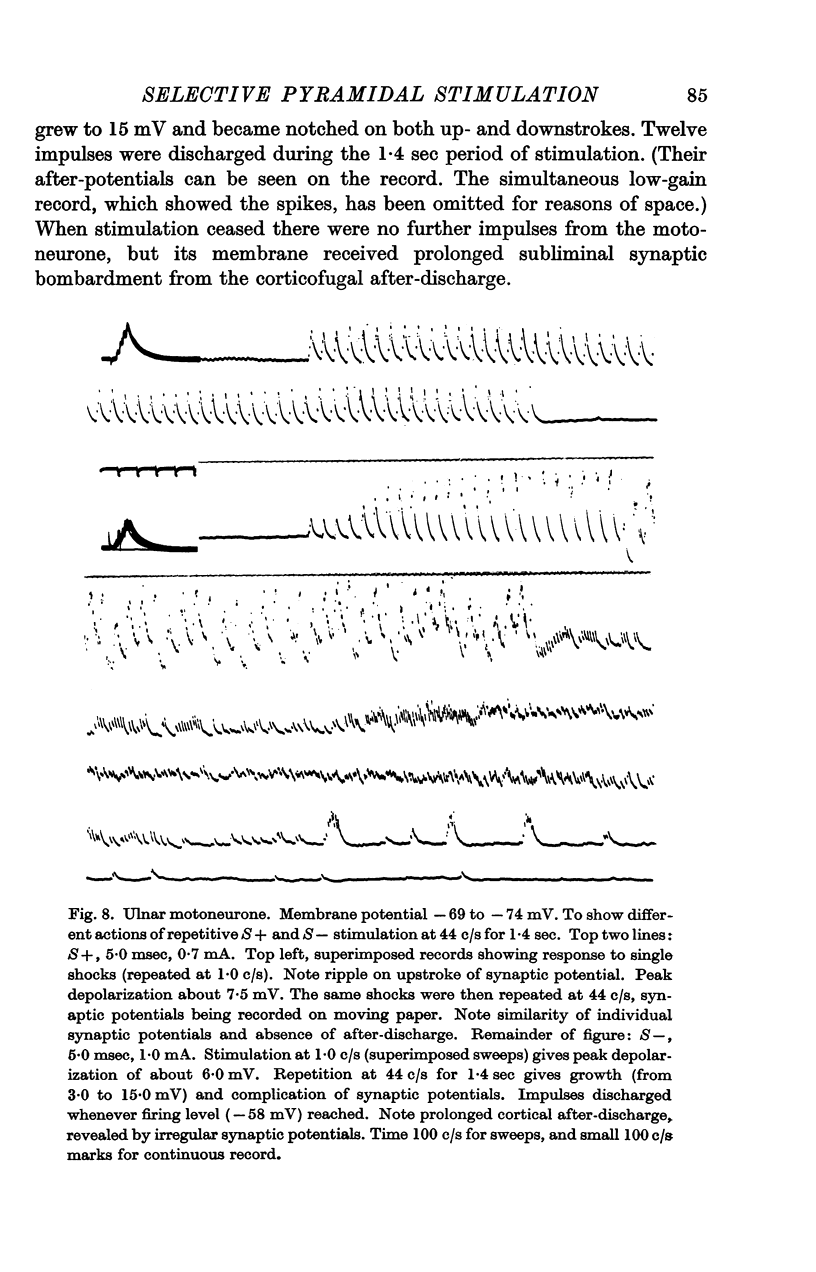





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROCK L. G., COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C. The recording of potentials from motoneurones with an intracellular electrode. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):431–460. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C., FATT P. The specific ionic conductances and the ionic movements across the motoneuronal membrane that produce the inhibitory post-synaptic potential. J Physiol. 1955 Nov 28;130(2):326–374. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., PHILLIPS C. G. Effects on Purkinje cells of surface stimulation of the cerebellum. J Physiol. 1957 Jan 23;135(1):73–92. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCE J. W. Pyramidal tract in spinal cord of cat. J Neurophysiol. 1954 May;17(3):253–270. doi: 10.1152/jn.1954.17.3.253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDGREN S., PHILLIPS C. G., PORTER R. Cortical fields of origin of the monosynaptic pyramidal pathways to some alpha motoneurones of the baboon's hand and forearm. J Physiol. 1962 Apr;161:112–125. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDGREN S., PHILLIPS C. G., PORTER R. Minimal synaptic actions of pyramidal impulses on some alpha motoneurones of the baboon's hand and forearm. J Physiol. 1962 Apr;161:91–111. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIDDELL E. G. T., PHILLIPS C. G. Overlapping areas in the motor cortex of the baboon. J Physiol. 1951 Feb;112(3-4):392–399. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIDDELL E. G. T., PHILLIPS C. G. The cortical representation of motor units. Brain. 1952 Dec;75(4):510–525. doi: 10.1093/brain/75.4.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIDDELL E. G. T., PHILLIPS C. G. Thresholds of cortical representation. Brain. 1950 Jun;73(2):125–140. doi: 10.1093/brain/73.2.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIDDELL E. G. The brain and muscle management. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1953;38(3):125–137. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1953.sp001018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARUHASHI J., MIZUGUCHI K., TASAKI I. Action currents in single afferent nerve fibres elicited by stimulation of the skin of the toad and the cat. J Physiol. 1952 Jun;117(2):129–151. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY R. W. The response of the lateralis organs of Xenopus laevis to electrical stimulation by direct current. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):408–420. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTON H. D., AMASSIAN V. E. Single and multiple-unit analysis of cortical stage of pyramidal tract activation. J Neurophysiol. 1954 Jul;17(4):345–363. doi: 10.1152/jn.1954.17.4.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]