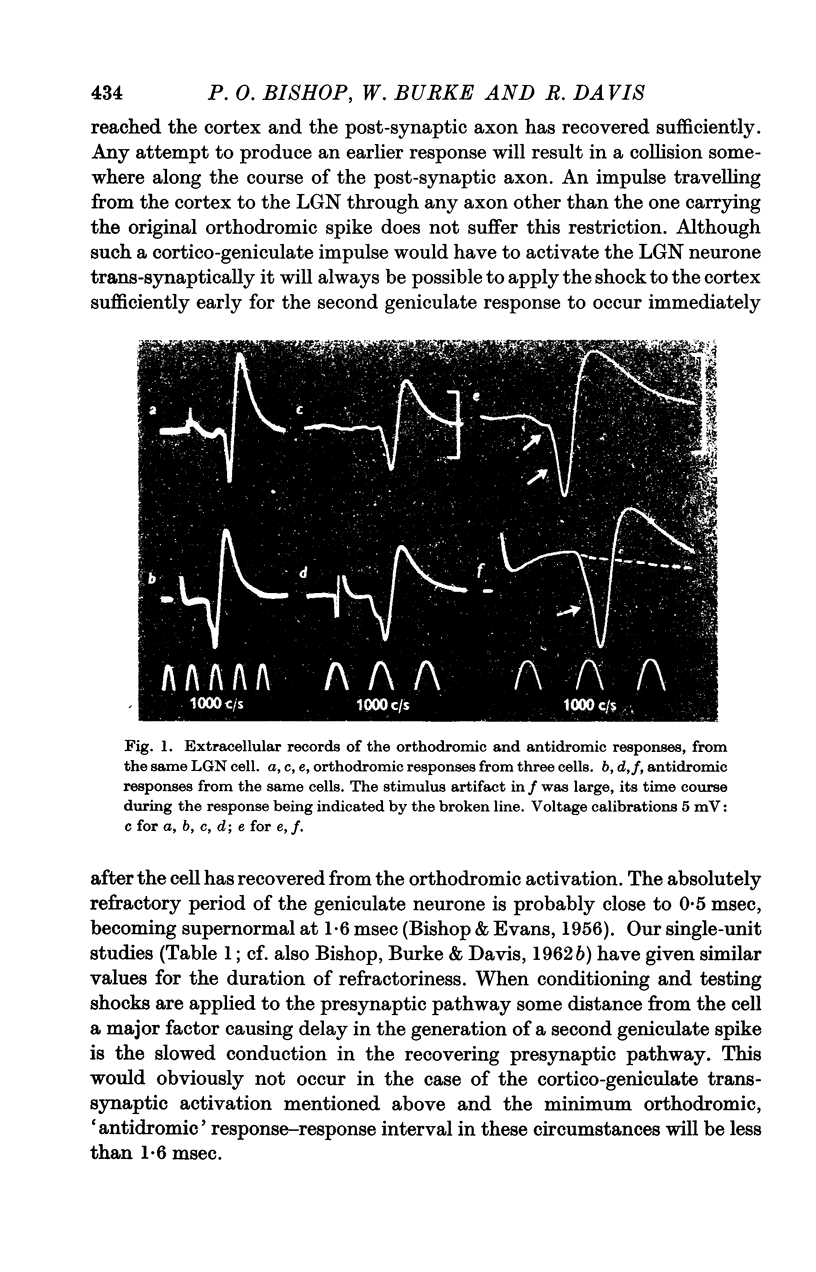
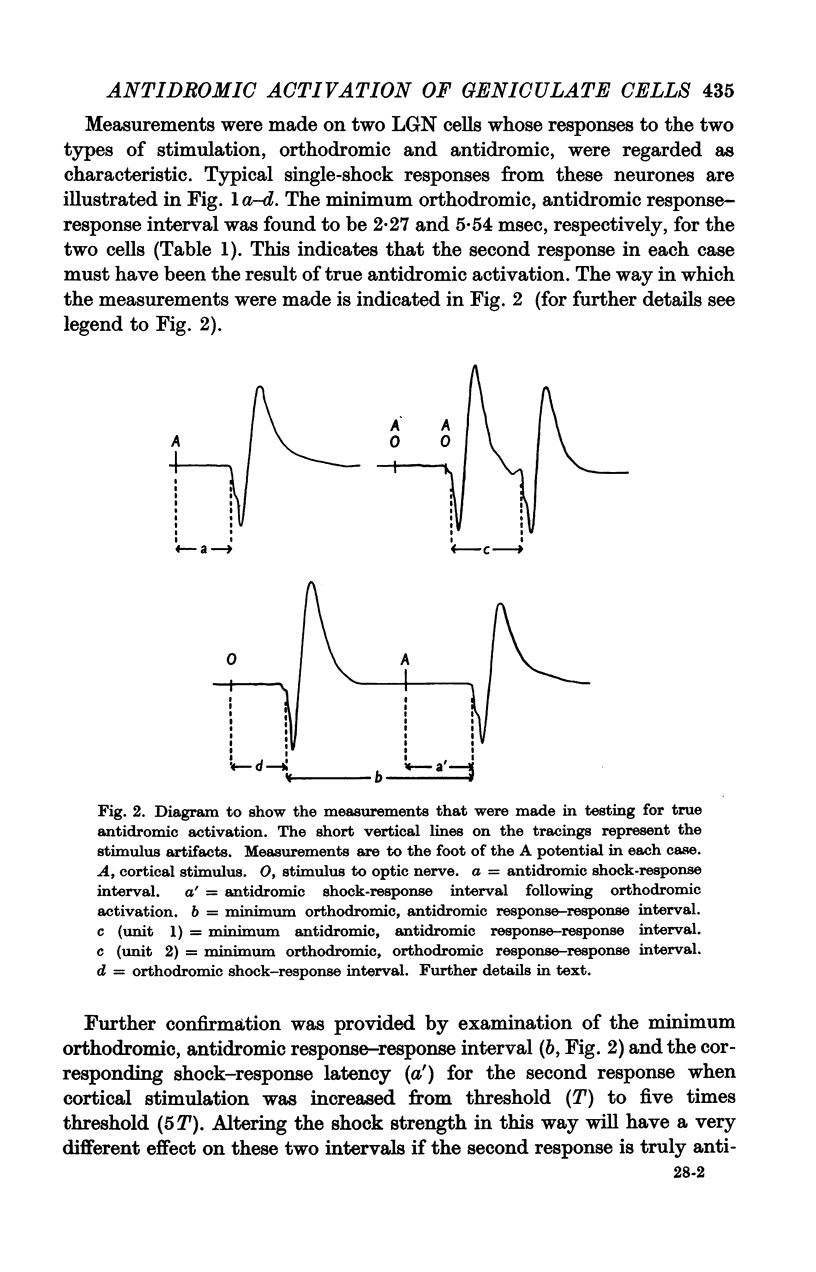
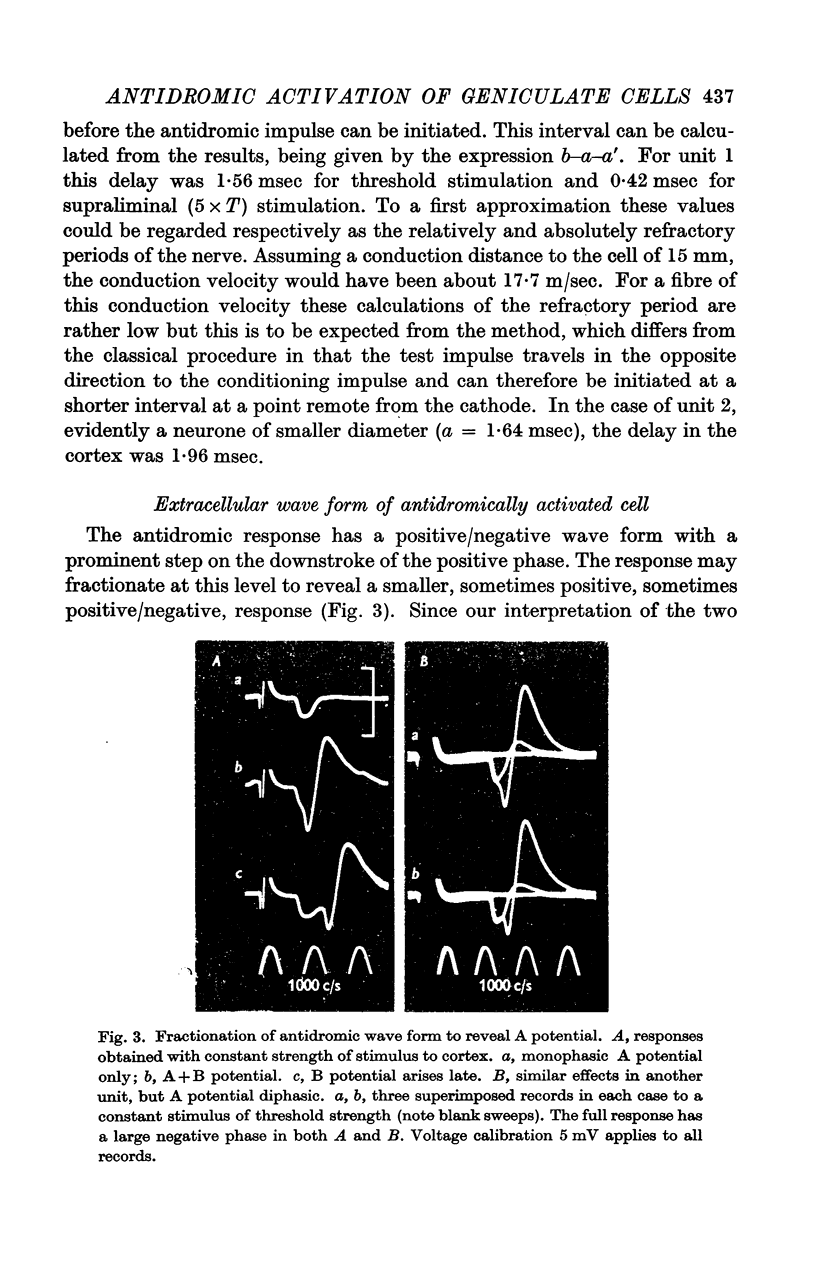
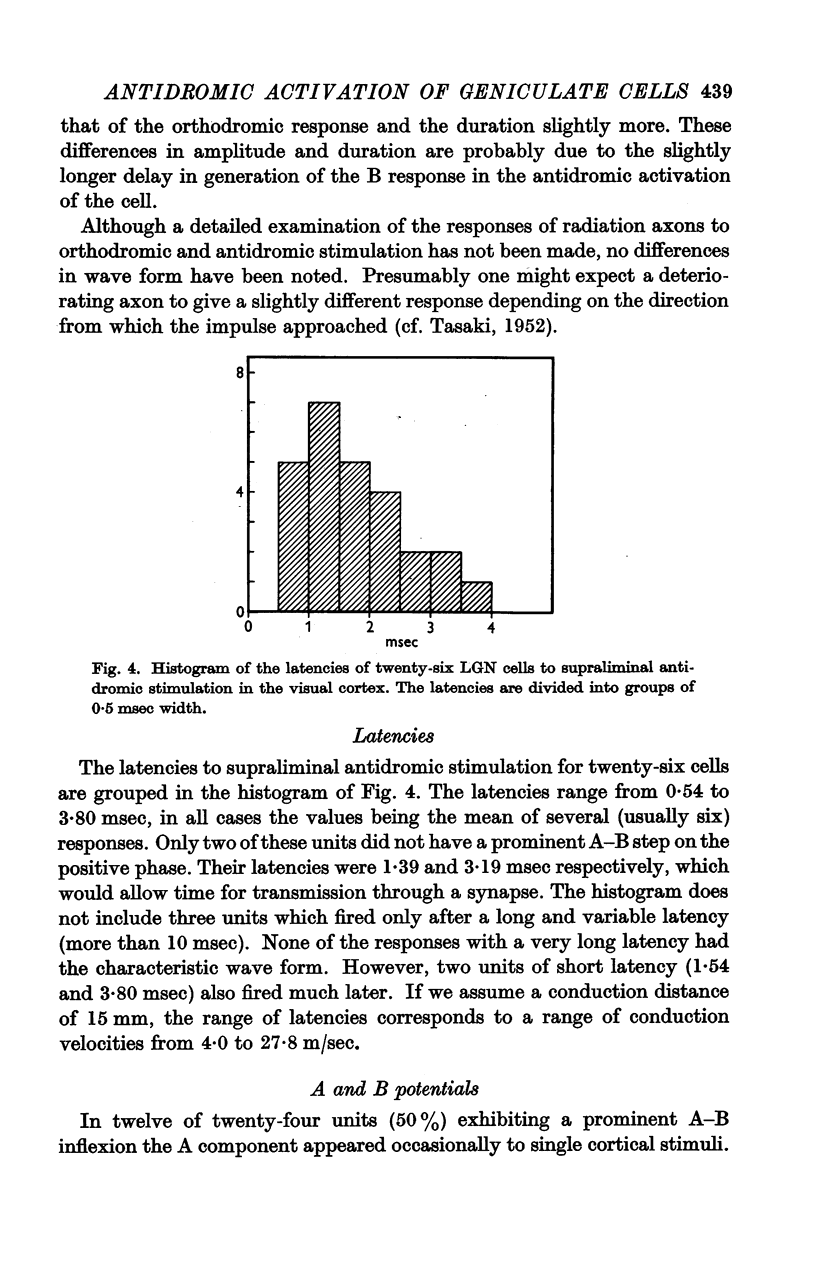
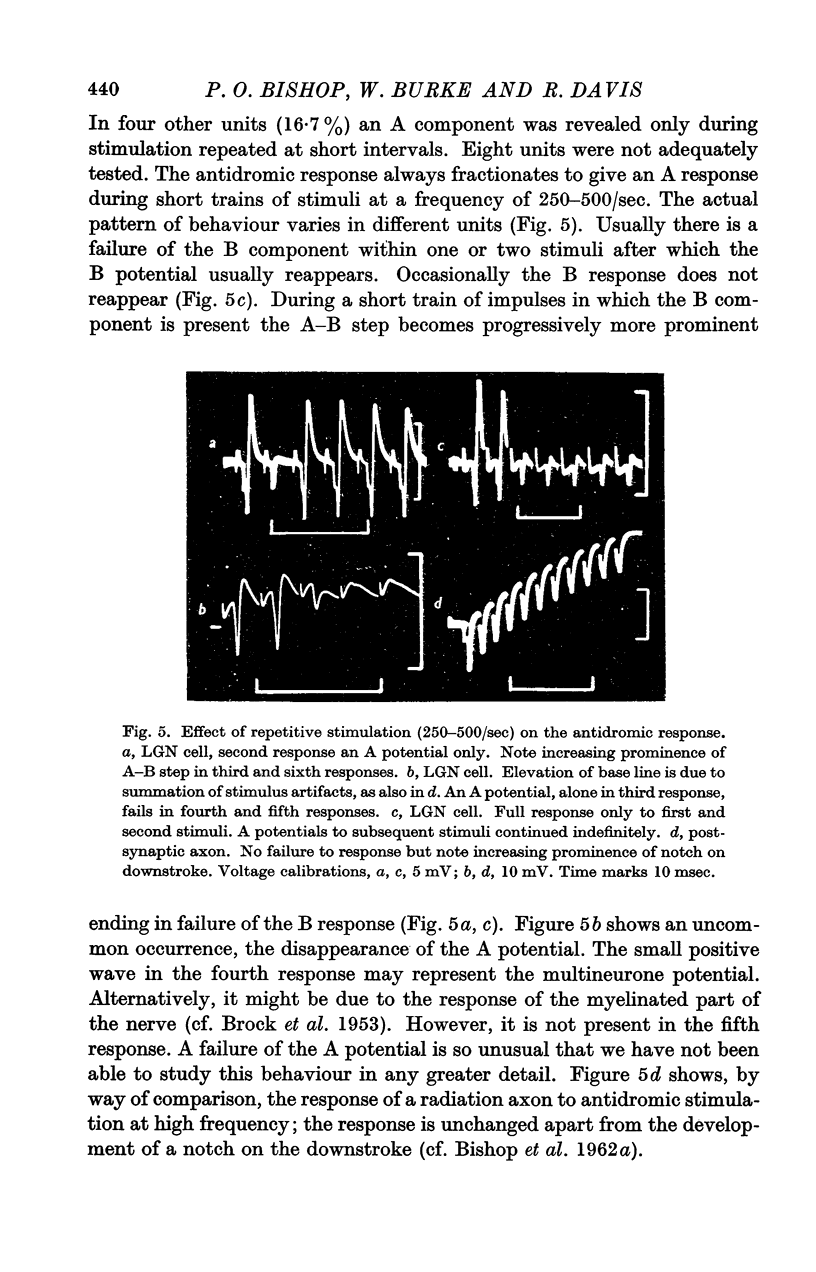
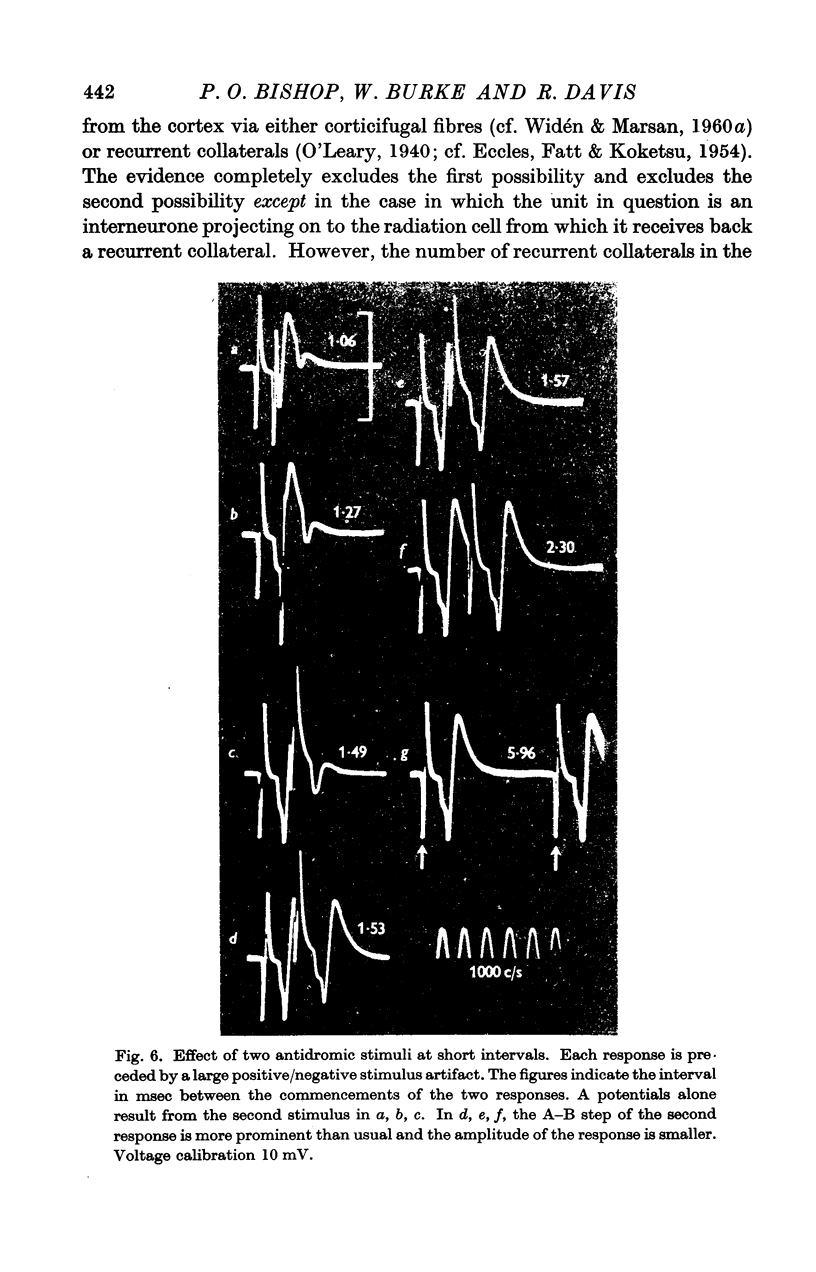
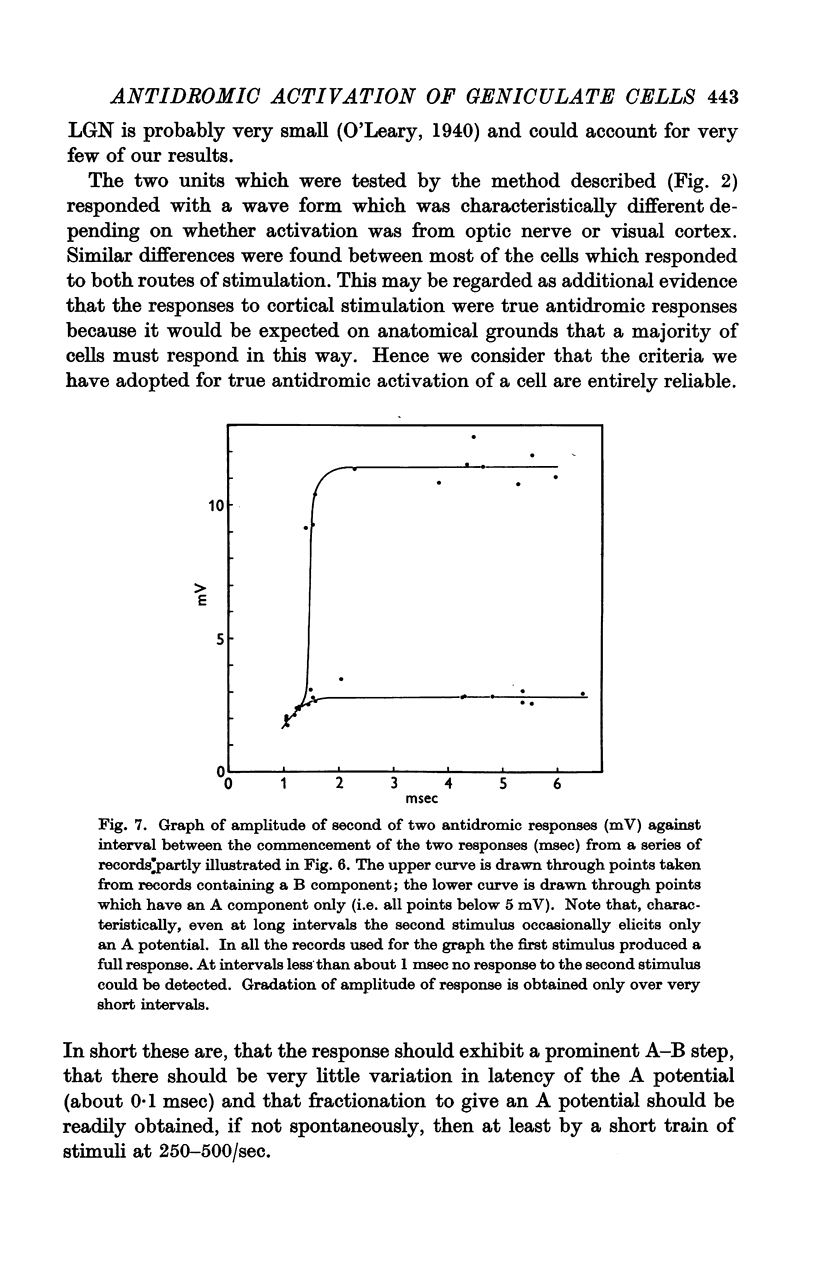
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARAKI T., OTANI T., FURUKAWA T. The electrical activities of single motoneurones in toad's spinal cord, recorded with intracellular electrodes. Jpn J Physiol. 1953 Dec 15;3(4):254–267. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.3.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARAKI T., OTANI T. Response of single motoneurons to direct stimulation in toad's spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 1955 Sep;18(5):472–485. doi: 10.1152/jn.1955.18.5.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENNETT M. V., CRAIN S. M., GRUNDFEST H. Electrophysiology of supramedullary neurons in Spheroides maculatus. I. Orthodromic and antidromic responses. J Gen Physiol. 1959 Sep;43:159–188. doi: 10.1085/jgp.43.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BISHOP P. O., BURKE W., DAVIS R. The identification of single units in central visual pathways. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;162:409–431. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BISHOP P. O., BURKE W., DAVIS R. The interpretation of the extracellular response of single lateral geniculate cells. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;162:451–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BISHOP P. O., EVANS W. A. The refractory period of the sensory synapses of the lateral geniculate nucleus. J Physiol. 1956 Dec 28;134(3):538–557. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCK L. G., COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C. Intracellular recording from antidromically activated motoneurones. J Physiol. 1953 Dec 29;122(3):429–461. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp005013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., CURTIS D. R., ECCLES J. C. The generation of impulses in motoneurones. J Physiol. 1957 Dec 3;139(2):232–249. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., CURTIS D. R., ECCLES J. C. The interpretation of spike potentials of motoneurones. J Physiol. 1957 Dec 3;139(2):198–231. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOTY R. W. Potentials evoked in cat cerebral cortex by diffuse and by punctiform photic stimuli. J Neurophysiol. 1958 Sep;21(5):437–464. doi: 10.1152/jn.1958.21.5.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., IGGO A., LUNDBERG A. Electrophysiological studies on gamma motoneurones. Acta Physiol Scand. 1960 Sep 30;50:32–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1960.tb02070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., FATT P., KOKETSU K. Cholinergic and inhibitory synapses in a pathway from motor-axon collaterals to motoneurones. J Physiol. 1954 Dec 10;126(3):524–562. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARDS C., OTTOSON D. The site of impulse initiation in a nerve cell of a crustacean stretch receptor. J Physiol. 1958 Aug 29;143(1):138–148. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P. Electric potentials occurring around a neurone during its antidromic activation. J Neurophysiol. 1957 Jan;20(1):27–60. doi: 10.1152/jn.1957.20.1.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANK K., FUORTES M. G. Potentials recorded from the spinal cord with microelectrodes. J Physiol. 1955 Dec 29;130(3):625–654. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREYGANG W. H., Jr, FRANK K. Extracellular potentials from single spinal motoneurons. J Gen Physiol. 1959 Mar 20;42(4):749–760. doi: 10.1085/jgp.42.4.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUORTES M. G., FRANK K., BECKER M. C. Steps in the production of motoneuron spikes. J Gen Physiol. 1957 May 20;40(5):735–752. doi: 10.1085/jgp.40.5.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., PHILLIPS C. G. Excitatory and inhibitory processes acting upon individual Purkinje cells of the cerebellum in cats. J Physiol. 1956 Sep 27;133(3):520–547. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANDEL E. R., SPENCER W. A., BRINLEY F. J., Jr Electrophysiology of hippocampal neurons. I. Sequential invasion and synaptic organization. J Neurophysiol. 1961 May;24:225–242. doi: 10.1152/jn.1961.24.3.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LI C. L., ORTIZ-GALVIN A., CHOU S. N., HOWARD S. Y. Cortical intracellular potentials in response to stimulation to lateral geniculate body. J Neurophysiol. 1960 Nov;23:592–601. doi: 10.1152/jn.1960.23.6.592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACHNE X., FADIGA E., BROOKHART J. M. Antidromic and synaptic activation of frog motor neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1959 Sep;22:483–503. doi: 10.1152/jn.1959.22.5.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN A. R., BRANCH C. L. Spontaneous activity of Betz cells in cats with midbrain lesions. J Neurophysiol. 1958 Jul;21(4):368–370. doi: 10.1152/jn.1958.21.4.368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISHI S., KOKETSU K. Electrical properties and activities of single sympathetic neurons in frogs. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1960 Feb;55:15–30. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030550104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TASAKI I. Properties of myelinated fibers in frog sciatic nerve and in spinal cord as examined with micro-electrodes. Jpn J Physiol. 1952 Nov;3(1):73–94. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.3.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VASTOLA E. F. Antidromic action potentials in lateral geniculate body. J Neurophysiol. 1957 Mar;20(2):167–185. doi: 10.1152/jn.1957.20.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIDEN L., AJMONE MARSAN C. Effects of corticipetal and corticifugal impulses upon single elements of the dorsolateral geniculate nucleus. Exp Neurol. 1960 Oct;2:468–502. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(60)90028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


