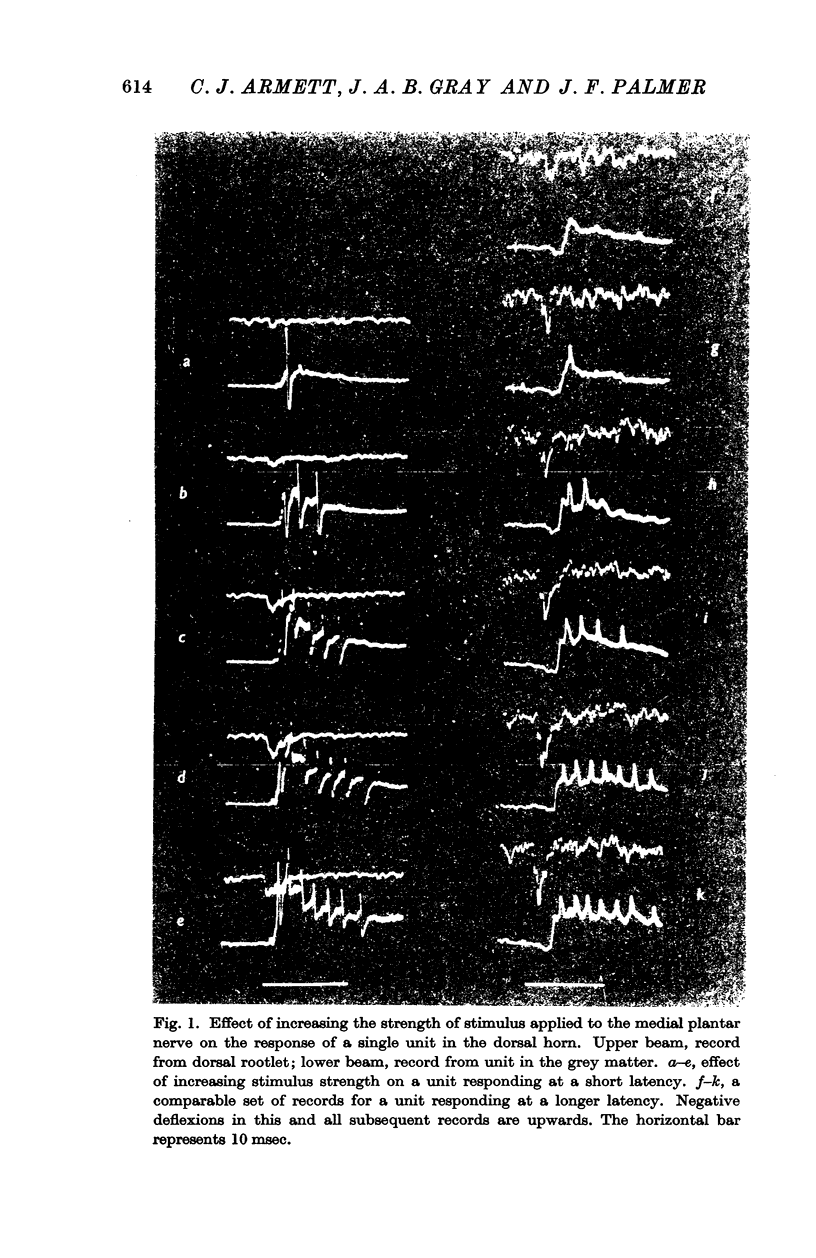
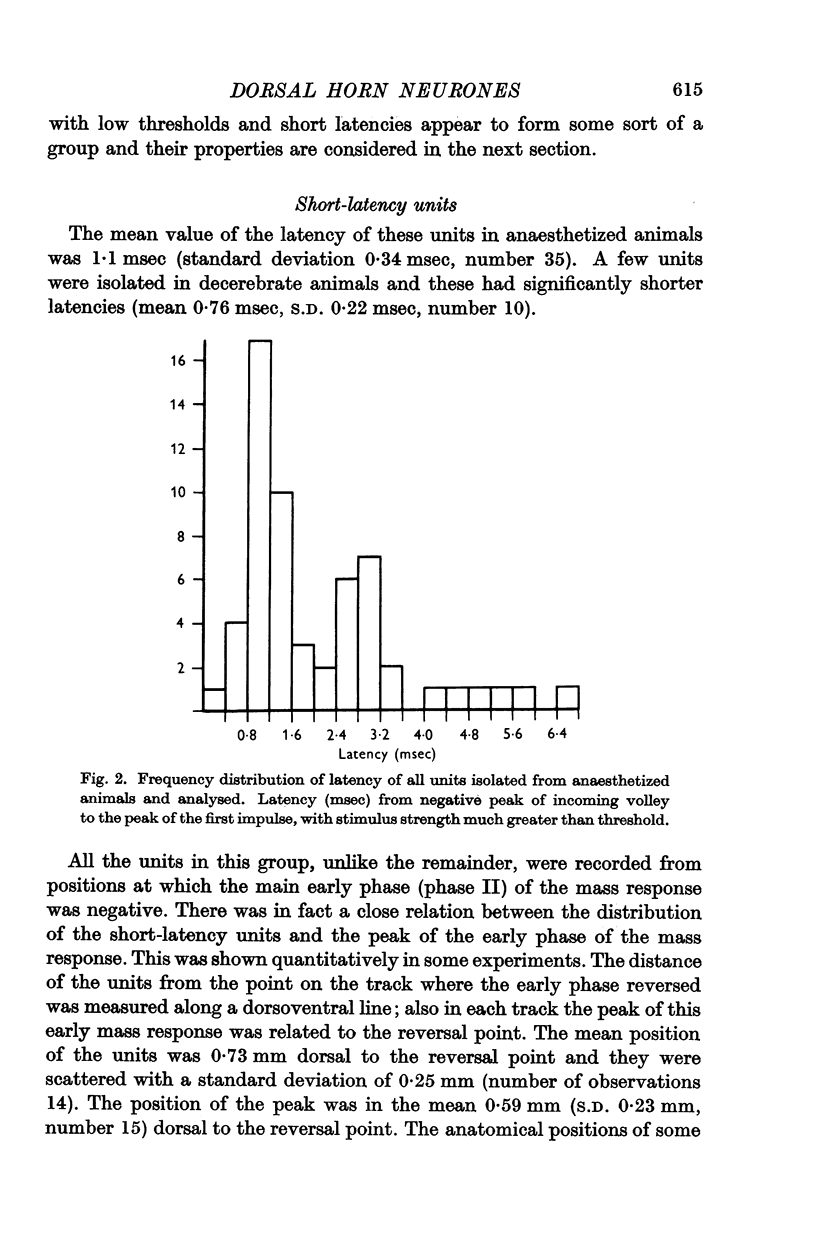
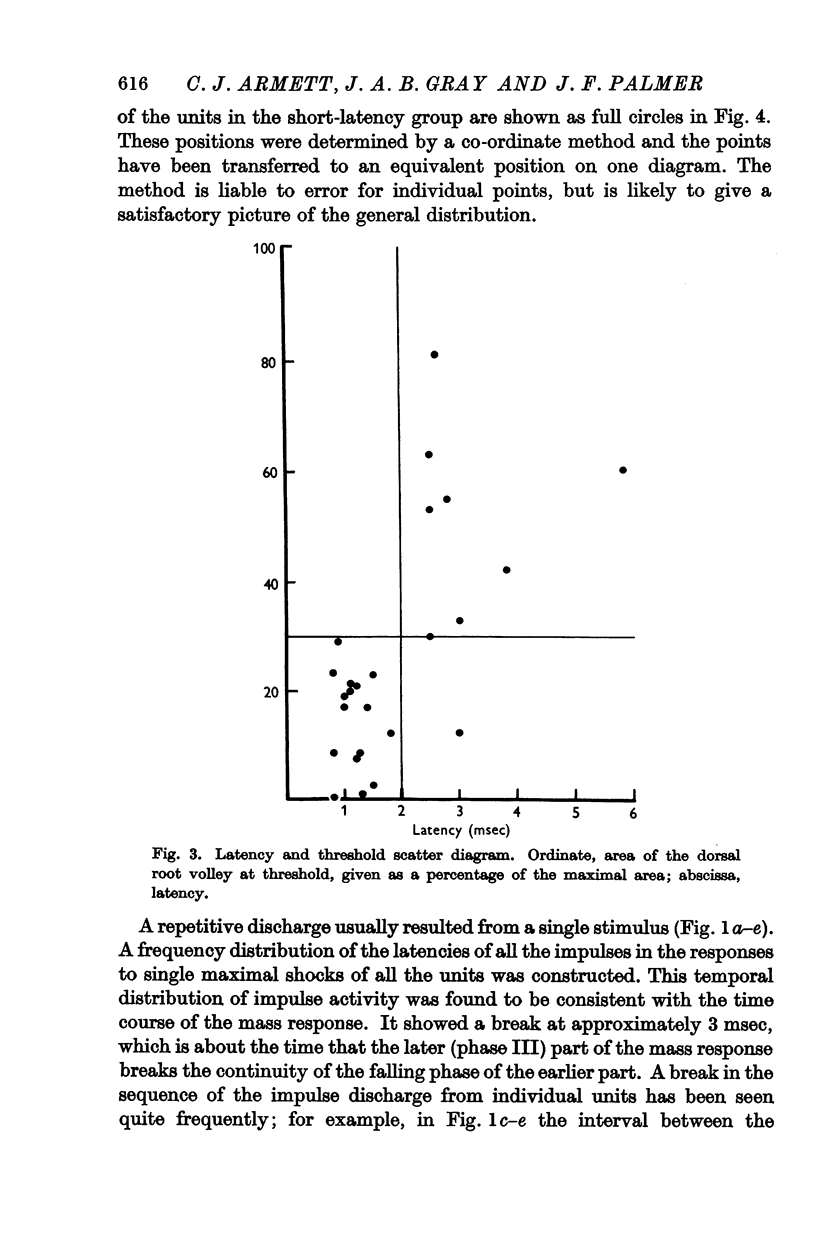
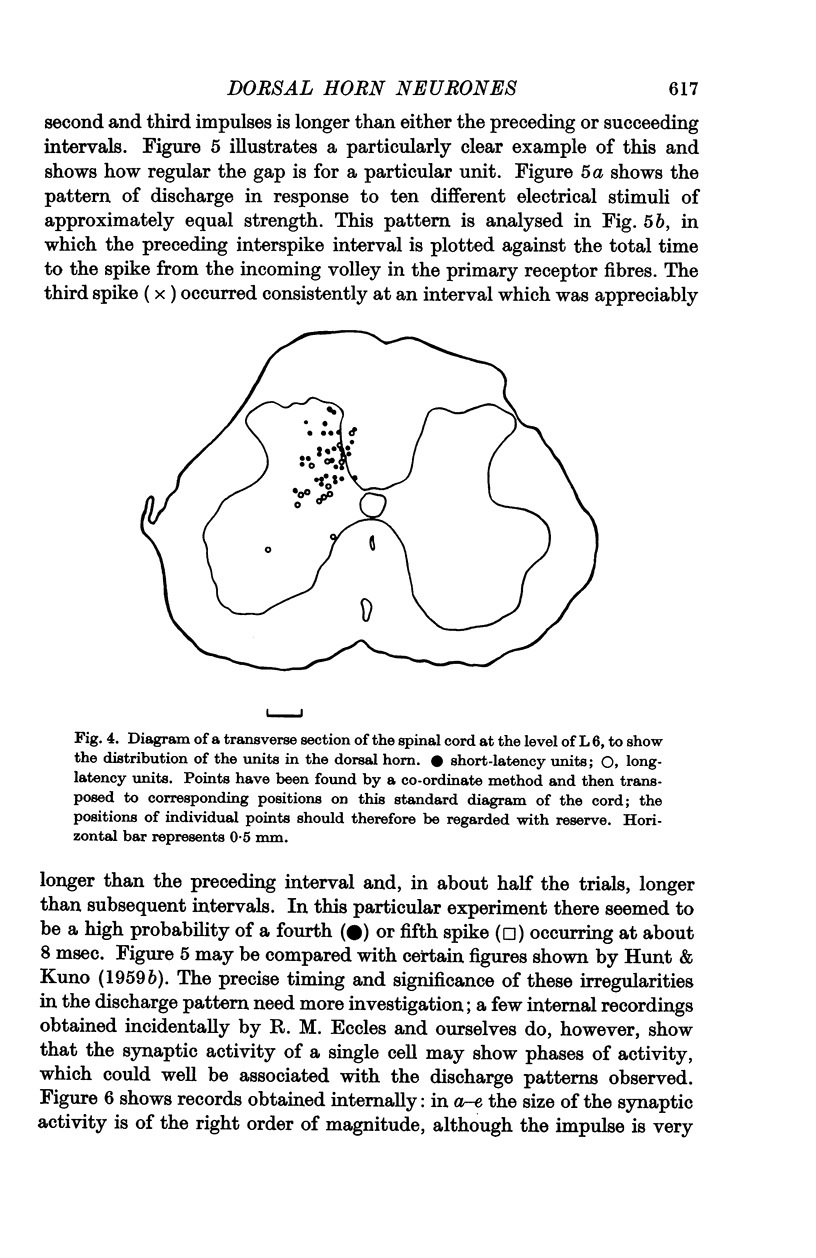
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COOMBS J. S., CURTIS D. R., LANDGREN S. Spinal cord potentials generated by impulses in muscle and cutaneous afferent fibres. J Neurophysiol. 1956 Sep;19(5):452–467. doi: 10.1152/jn.1956.19.5.452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., FATT P., LANDGREN S., WINSBURY G. J. Spinal cord potentials generated by volleys in the large muscle afferents. J Physiol. 1954 Sep 28;125(3):590–606. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERNANDEZ DE MOLINA A., GRAY J. A. Activity in the dorsal spinal grey matter after stimulation of cutaneous nerves. J Physiol. 1957 Jun 18;137(1):126–140. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANK K., FUORTES M. G. Potentials recorded from the spinal cord with microelectrodes. J Physiol. 1955 Dec 29;130(3):625–654. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANK K., FUORTES M. G. Unitary activity of spinal interneurones of cats. J Physiol. 1956 Feb 28;131(2):424–435. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAAPANEN L., KOLMODIN G. M., SKOGLUND C. R. Membrane and action potentials of spinal interneurons in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1958 Oct 8;43(3-4):315–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1958.tb01598.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT C. C., KUNO M. Background discharge and evoked responses of spinal interneurones. J Physiol. 1959 Sep 2;147:364–384. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT C. C., KUNO M. Properties of spinal interneurones. J Physiol. 1959 Sep 2;147:346–363. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALL P. D. Cord cells responding to touch, damage, and temperature of skin. J Neurophysiol. 1960 Mar;23:197–210. doi: 10.1152/jn.1960.23.2.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODBURY J. W., PATTON H. D. Electrical activity of single spinal cord elements. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1952;17:185–188. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1952.017.01.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


