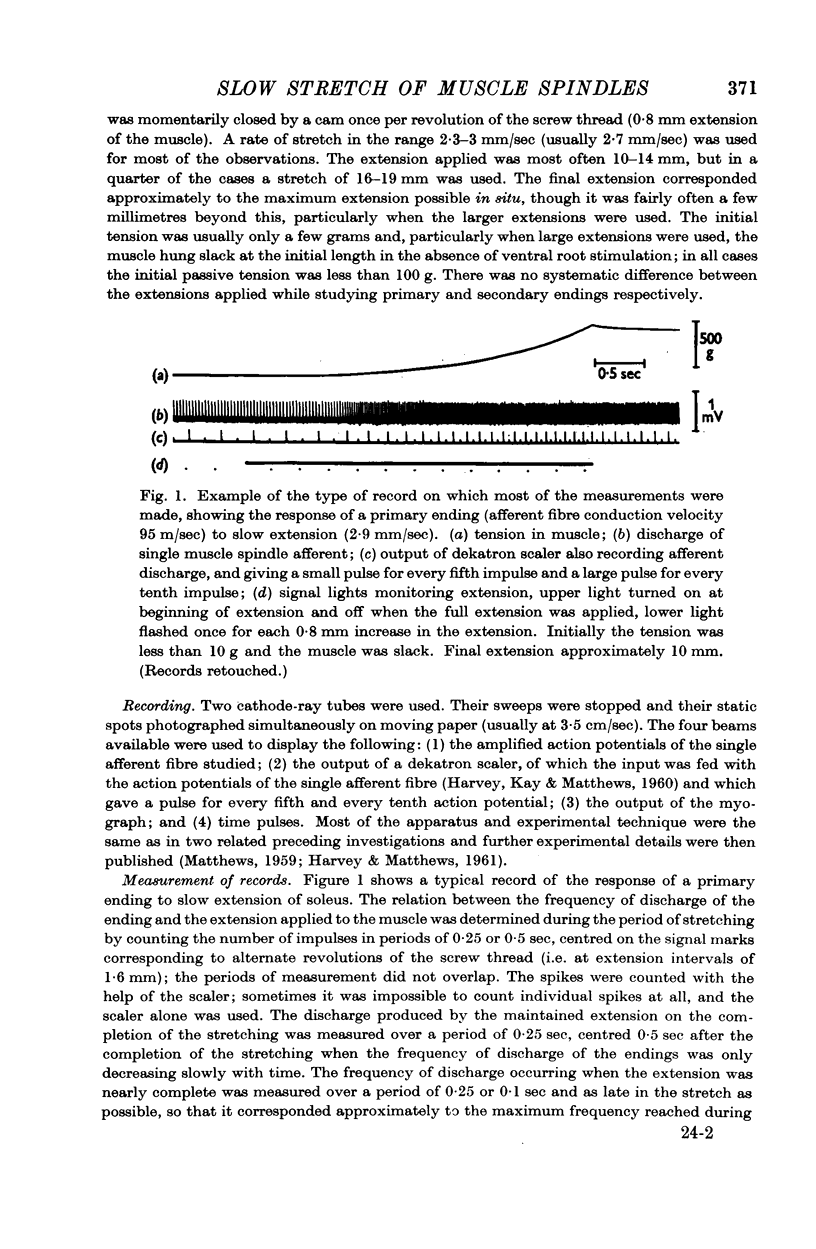
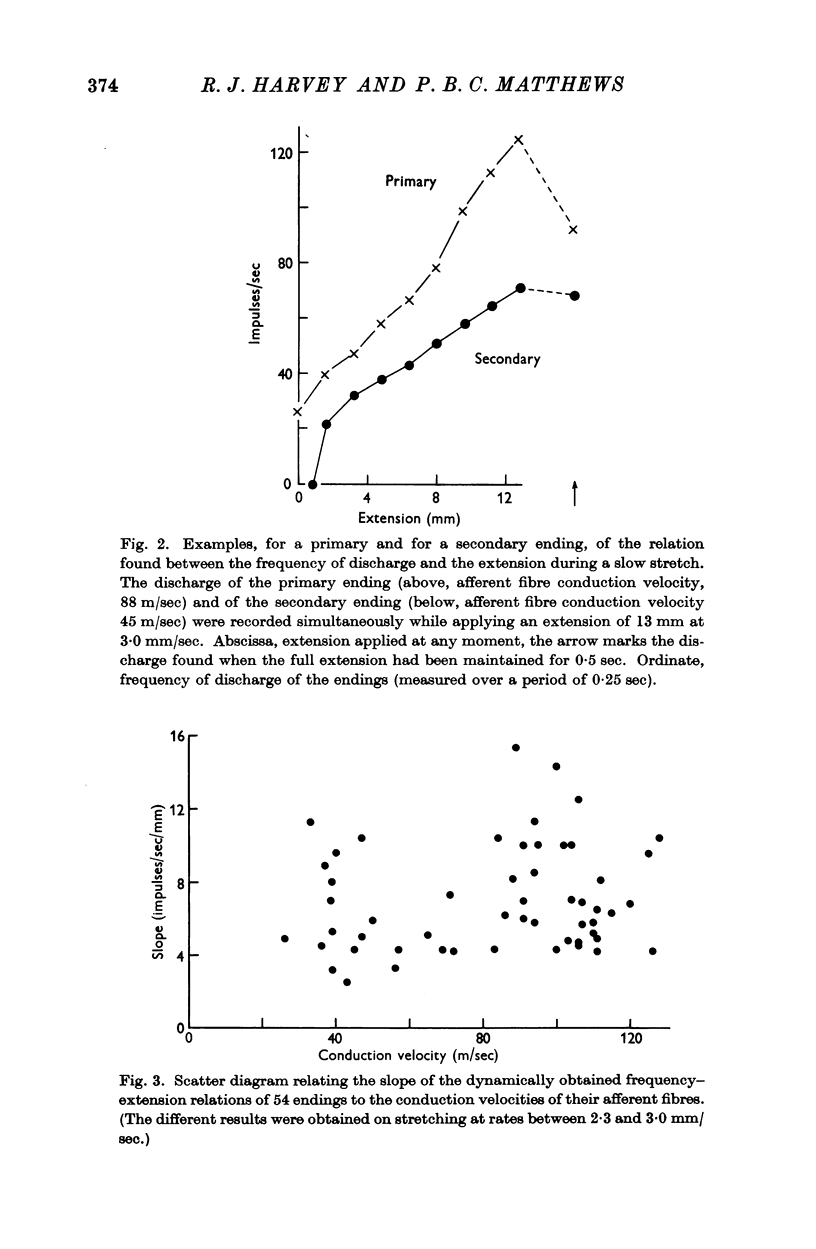
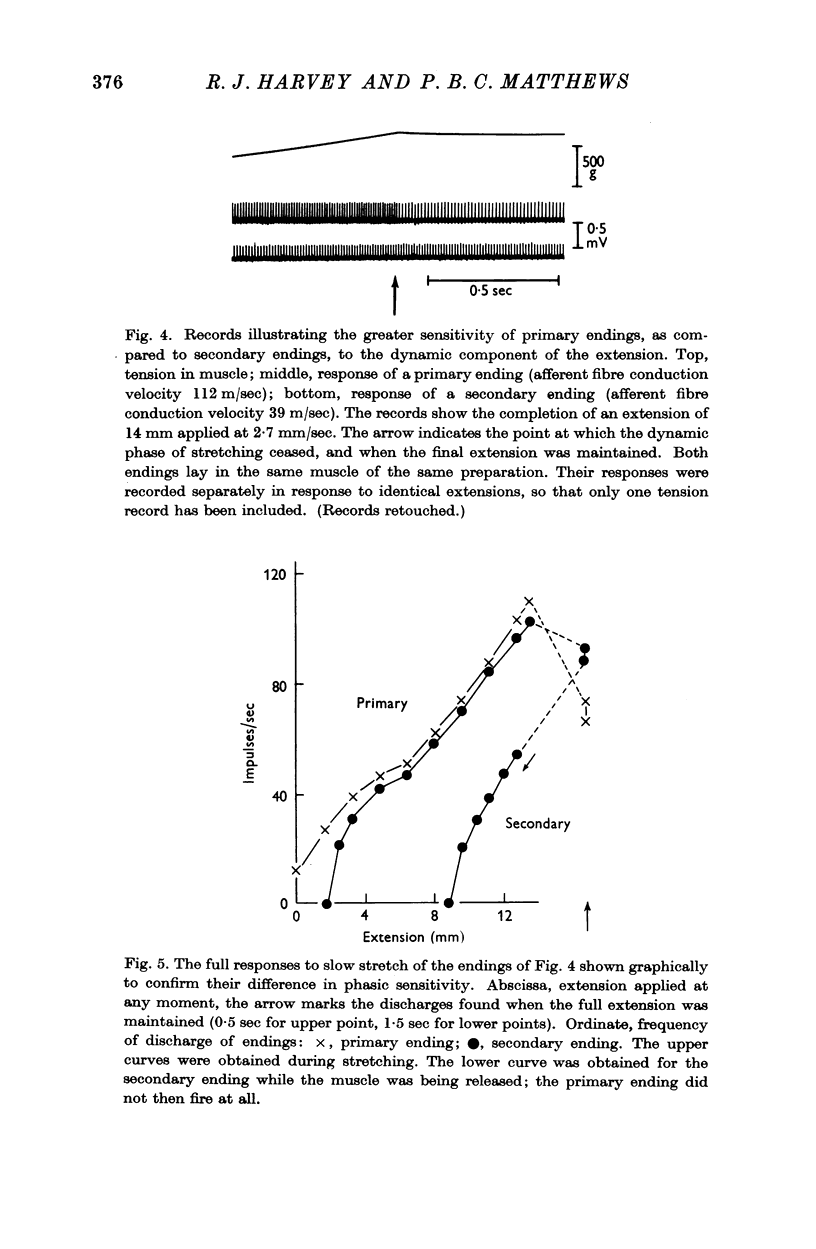
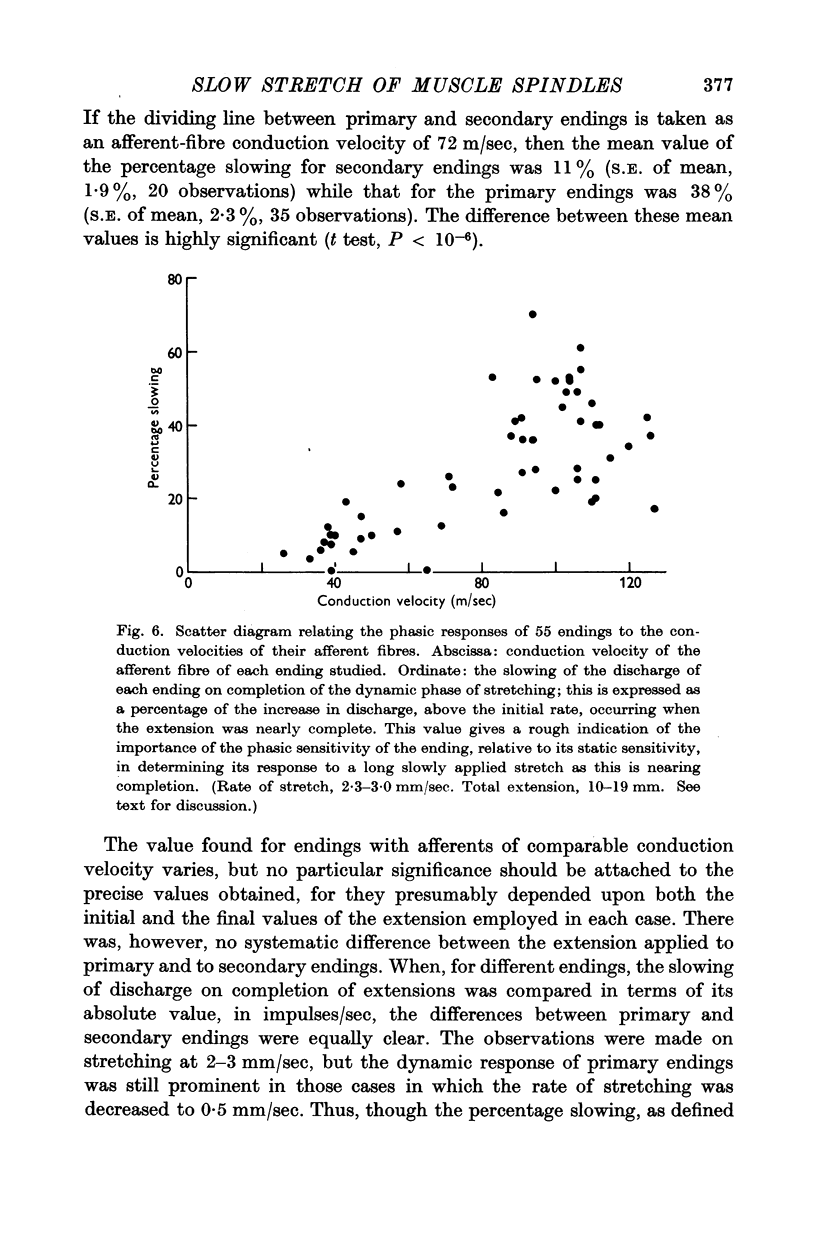
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BULLER A. J., ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M. Differentiation of fast and slow muscles in the cat hind limb. J Physiol. 1960 Feb;150:399–416. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S. The isometric responses of mammalian muscles. J Physiol. 1930 Jun 27;69(4):377–385. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1930.sp002657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELDRED E., GRANIT R., MERTON P. A. Supraspinal control of the muscle spindles and its significance. J Physiol. 1953 Dec 29;122(3):498–523. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp005017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELDRED E., LINDSLEY D. F., BUCHWALD J. S. The effect of cooling on mammalian muscle spindles. Exp Neurol. 1960 Apr;2:144–157. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(60)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EYZAGUIRRE C. The motor regulation of mammalian spindle discharges. J Physiol. 1960 Jan;150:186–200. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., HOMMA S. Phasic stretch and 'spindle constant' in slow and fast rabbit muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1959 Jun 24;46:174–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1959.tb01746.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., HOMMA S. The discharge to maintained stretch of spindles in slow and fast muscles of rabbit. Acta Physiol Scand. 1959 Jun 24;46:165–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1959.tb01745.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R. Neuromuscular interaction in postural tone of the cat's isometric soleus muscle. J Physiol. 1958 Oct 31;143(3):387–402. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARVEY R. J., MATTHEWS P. B. Some effects of stimulation of the muscle nerve on afferent endings of muscle spindles, and the classification of their responses into types A1 and A2. J Physiol. 1961 May;156:470–497. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBBARD S. J. A study of rapid mechanical events in a mechanoreceptor. J Physiol. 1958 Apr 30;141(2):198–218. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT C. C., KUFFLER S. W. Further study of efferent small-nerve fibers to mammalian muscle spindles; multiple spindle innervation and activity during contraction. J Physiol. 1951 Apr;113(2-3):283–297. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT C. C. Relation of function to diameter in afferent fibers of muscle nerves. J Gen Physiol. 1954 Sep 20;38(1):117–131. doi: 10.1085/jgp.38.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUFFLER S. W., HUNT C. C., QUILLIAM J. P. Function of medullated small-nerve fibers in mammalian ventral roots; efferent muscle spindle innervation. J Neurophysiol. 1951 Jan;14(1):29–54. doi: 10.1152/jn.1951.14.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIPPOLD O. C., NICHOLLS J. G., REDFEARN J. W. Electrical and mechanical factors in the adaptation of a mammalian muscle spindle. J Physiol. 1960 Sep;153:209–217. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIPPOLD O. C., REDFEARN J. W., VUCO J. The effect of sinusoidal stretching upon the activity of stretch receptors in voluntary muscle and their reflex responses. J Physiol. 1958 Dec 30;144(3):373–386. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOEWENSTEIN W. R. Excitation and changes in adaptation by stretch of mechanoreceptors. J Physiol. 1956 Sep 27;133(3):588–602. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERTON P. A. The silent period in a muscle of the human hand. J Physiol. 1951 Jun;114(1-2):183–198. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. H. Nerve endings in mammalian muscle. J Physiol. 1933 Apr 13;78(1):1–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1933.sp002984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews P. B. The dependence of tension upon extension in the stretch reflex of the soleus muscle of the decerebrate cat. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;147(3):521–546. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAINTAL A. S. Facilitation and depression of muscle stretch receptors by repetitive antidromic stimulation, adrenaline and asphyxia. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:252–266. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffini A. On the Minute Anatomy of the Neuromuscular Spindles of the Cat, and on their Physiological Significance. J Physiol. 1898 Jul 26;23(3):190–208.3. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1898.sp000723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWETT J. E., ELDRED E. Comparisons in structure of stretch receptors in medial gastrocnemius and soleus muscles of the cat. Anat Rec. 1960 Aug;137:461–473. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091370406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


