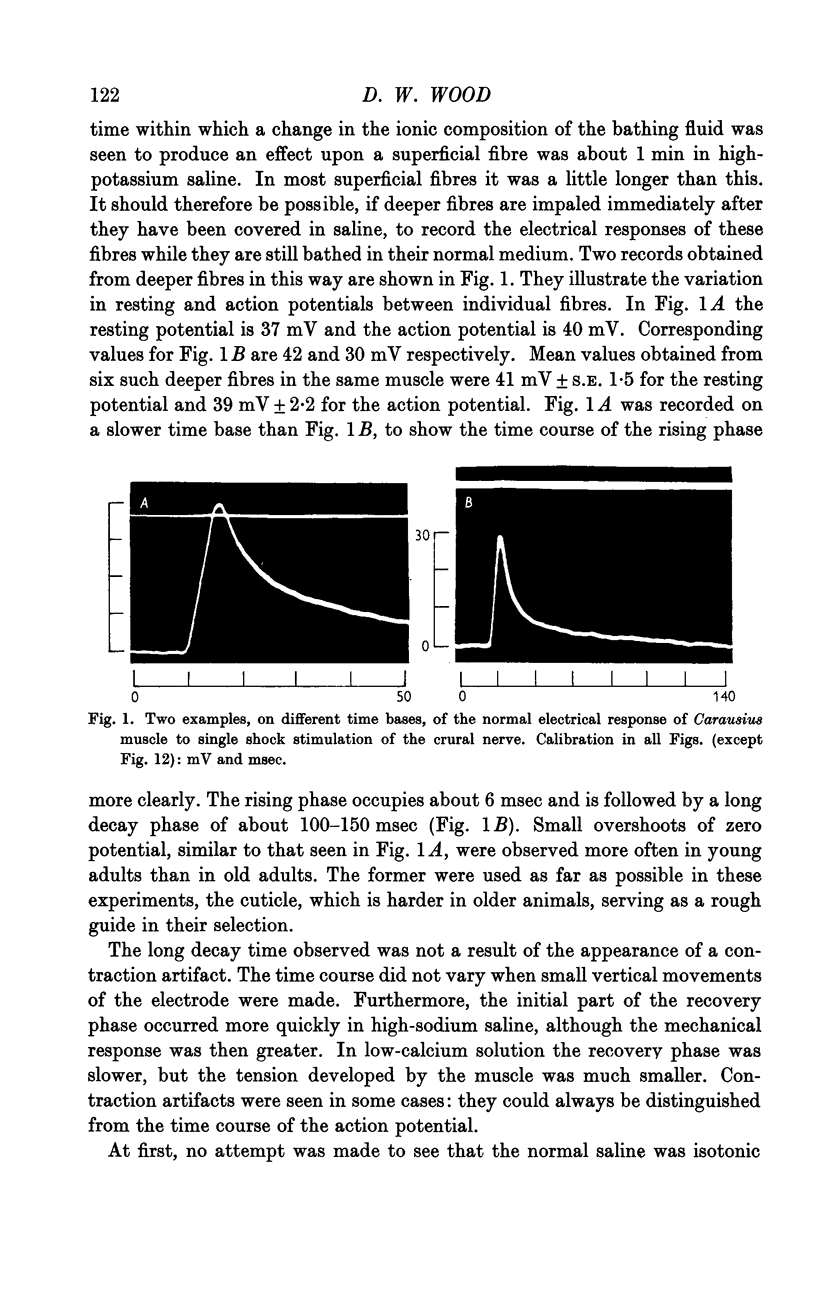
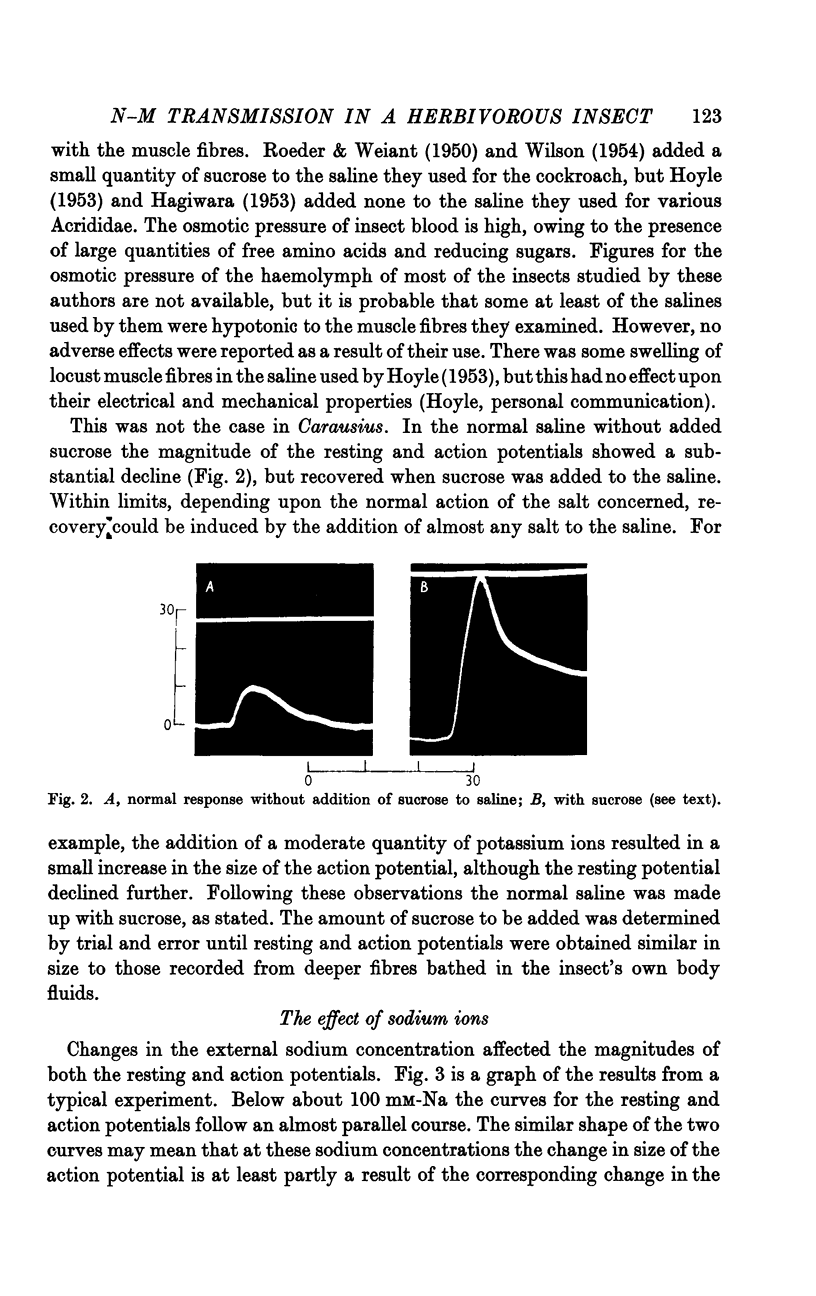
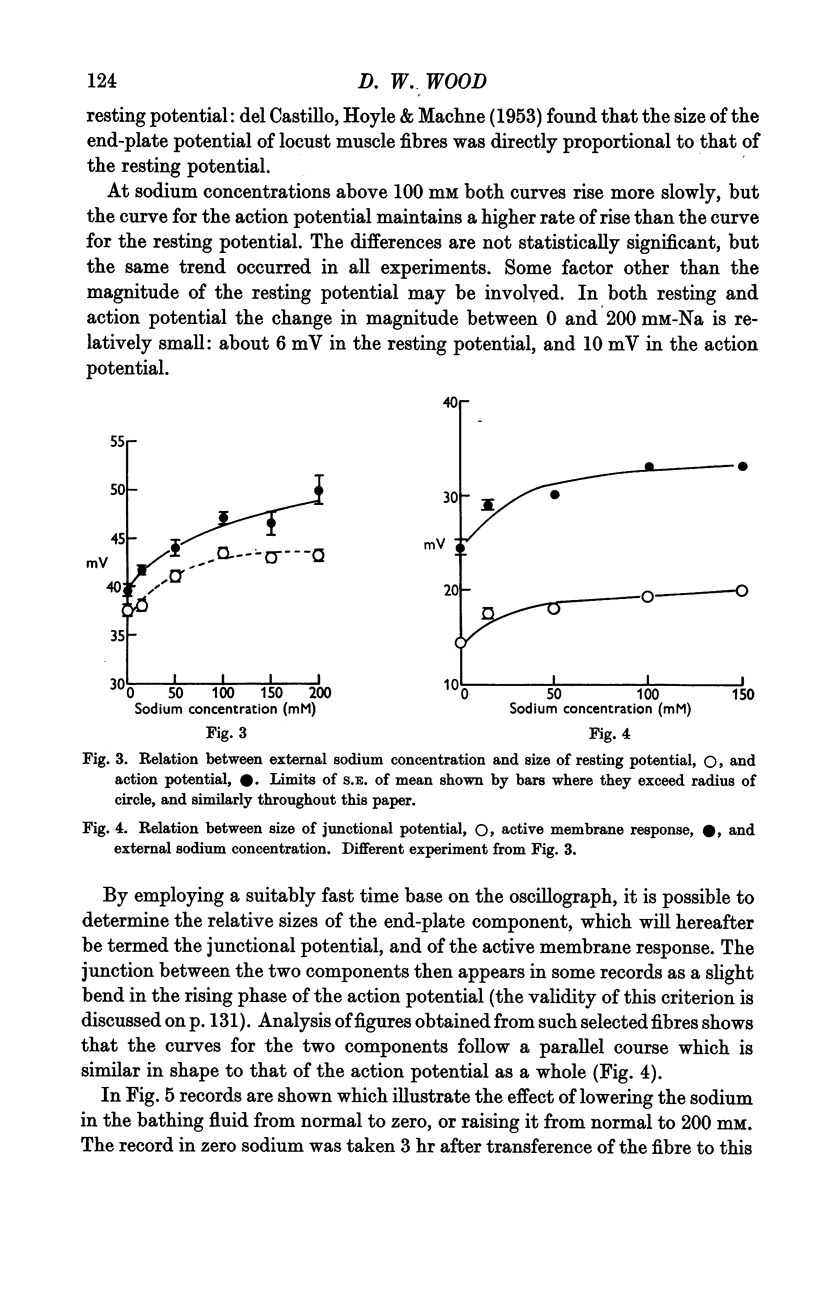
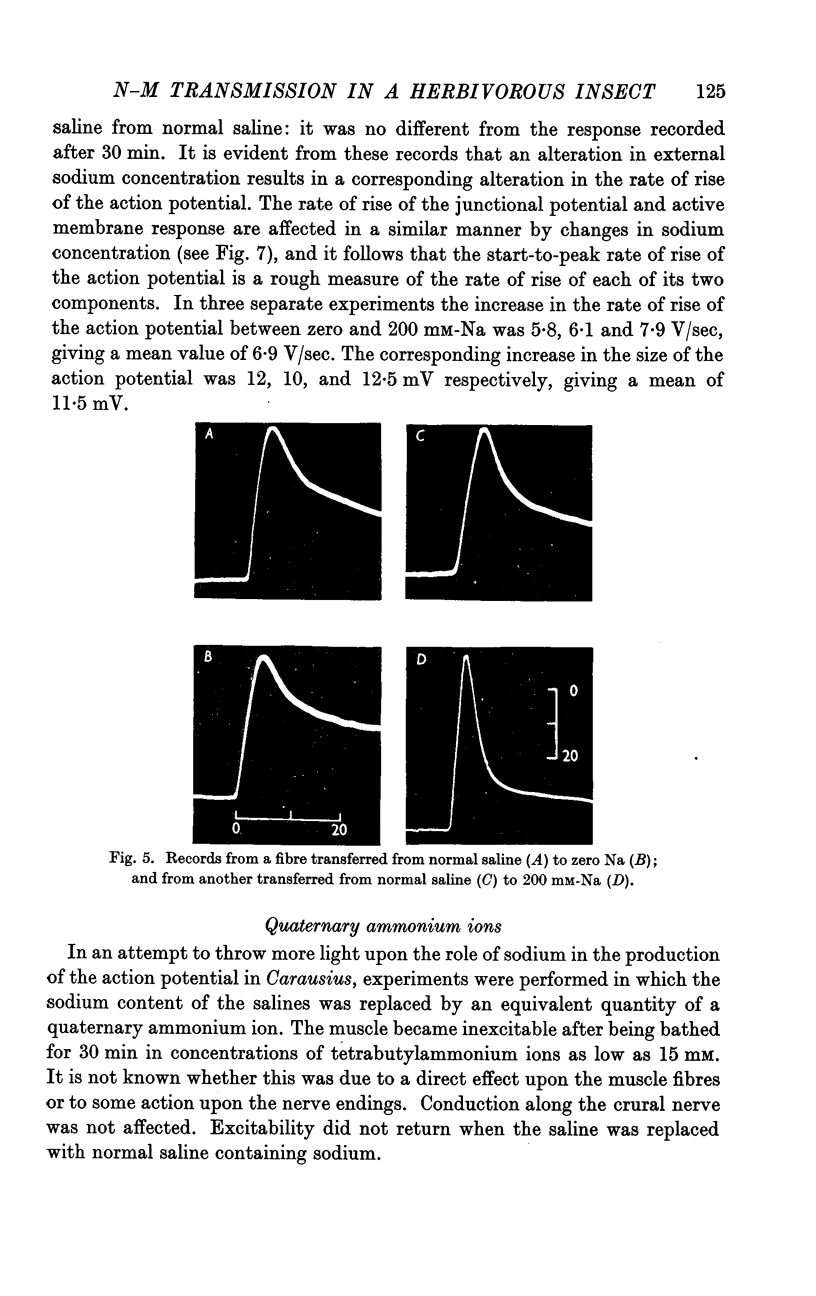
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBERT A. Quantitative studies of the avidity of naturally occurring substances for trace metals; amino-acids having only two ionizing groups. Biochem J. 1950 Nov-Dec;47(5):531–538. doi: 10.1042/bj0470531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., ENGBAEK L. The nature of the neuromuscular block produced by magnesium. J Physiol. 1954 May 28;124(2):370–384. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., HOYLE G., MACHNE X. Neuromuscular transmission in a locust. J Physiol. 1953 Sep;121(3):539–547. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., STARK L. The effect of calcium ions on the motor end-plate potentials. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):507–515. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUCHATEAU G., FLORKIN M., LECLERCQ J. Concentrations des bases fixes et types de composition de la base totale de l'hémolymphe des insectes. Arch Int Physiol. 1953 Nov;61(4):518–549. doi: 10.3109/13813455309146555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on neuromuscular transmission. J Physiol. 1952 Sep;118(1):73–87. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. The electrical properties of crustacean muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1953 Apr 28;120(1-2):171–204. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The effect of calcium on the sodium permeability of a giant nerve fibre. J Physiol. 1955 May 27;128(2):40–1P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGIWARA S. Neuro-muscular transmission in insects. Jpn J Physiol. 1953 Dec 15;3(4):284–296. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.3.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGIWARA S., WATANABE A. Action potential of insect muscle examined with intra-cellular electrode. Jpn J Physiol. 1954 Mar 5;4(1):65–78. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.4.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOYLE G. The anatomy and innervation of locust skeletal muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1955 Jan 27;143(911):281–292. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1955.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOYLE G. The effects of some common cations on neuromuscular transmission in insects. J Physiol. 1955 Jan 28;127(1):90–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES G. M. Giant fibres in dragonfly nymphs. Nature. 1953 Jan 10;171(4341):87–88. doi: 10.1038/171087b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LING G., GERARD R. W. The normal membrane potential of frog sartorius fibers. J Cell Physiol. 1949 Dec;34(3):383–396. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030340304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PROCEEDINGS of the Physiological Society. J Physiol. 1952 Jul;117(3):15–P. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


