Full text
PDF
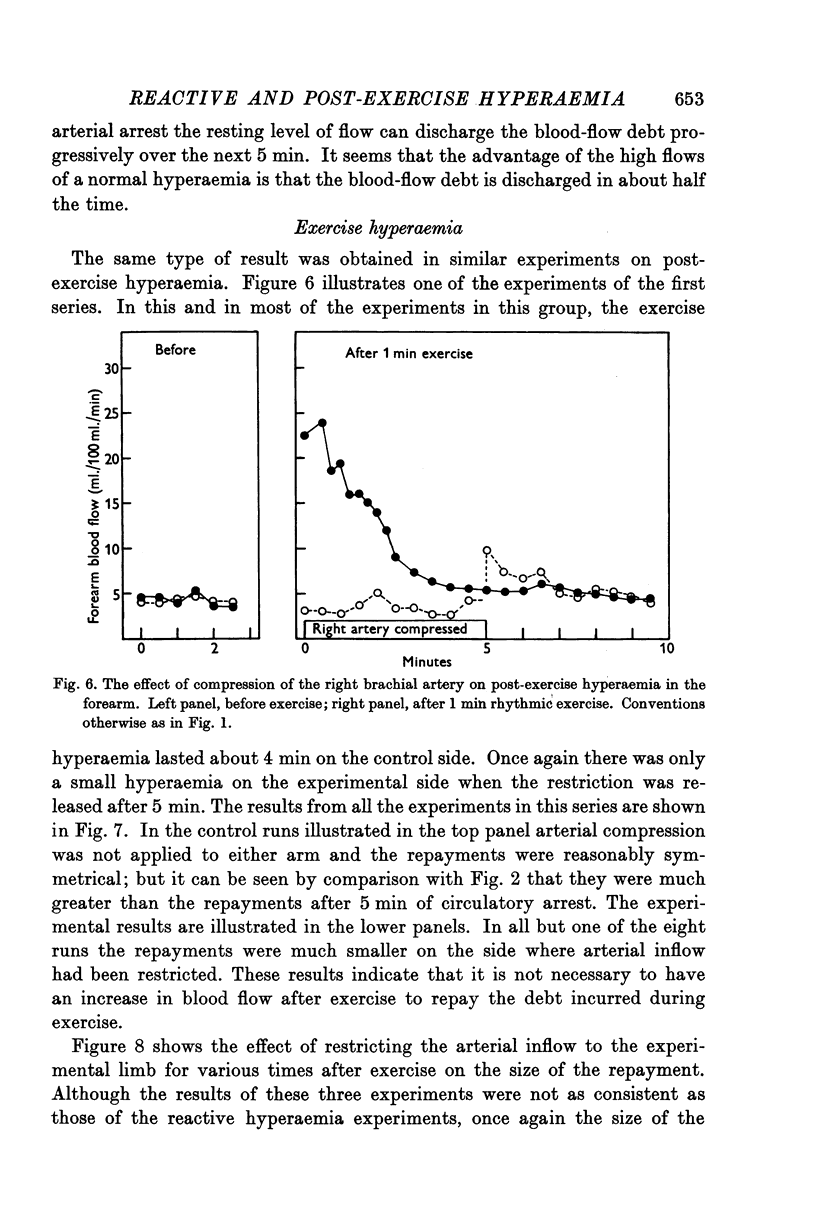
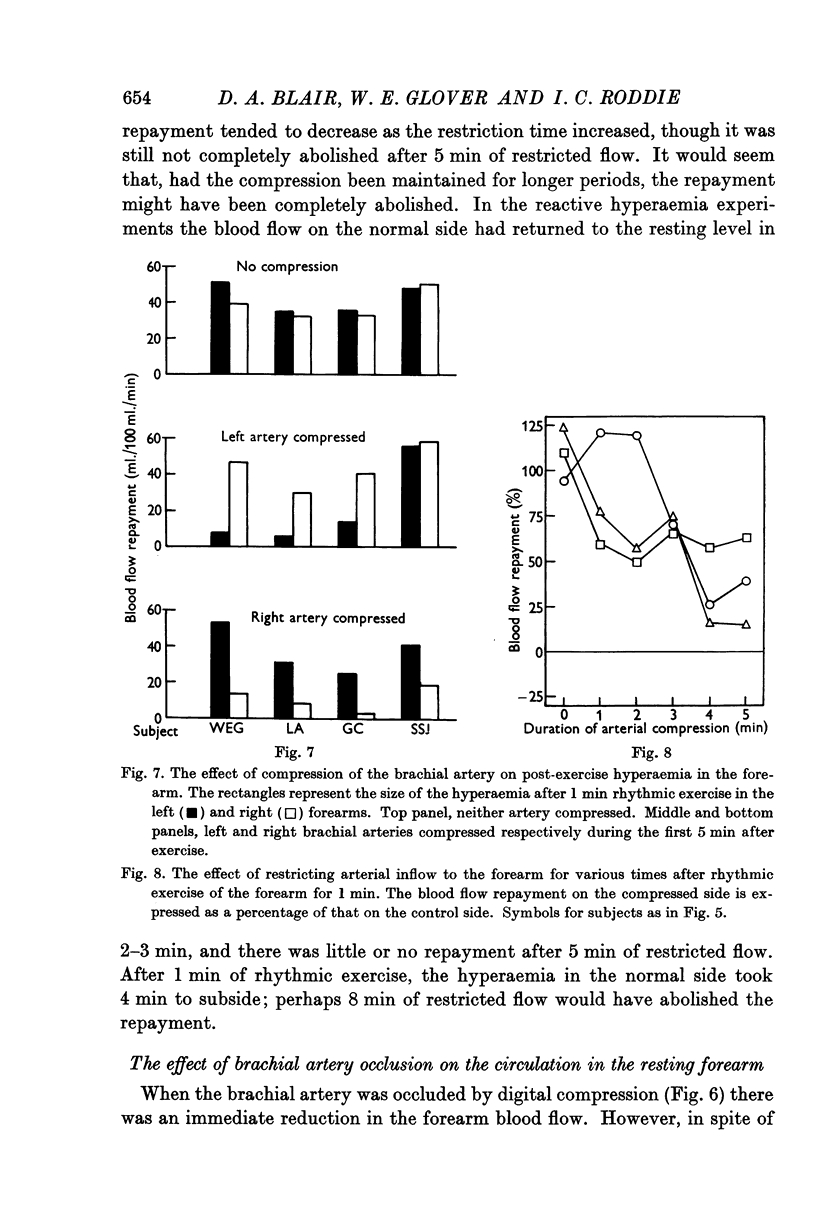
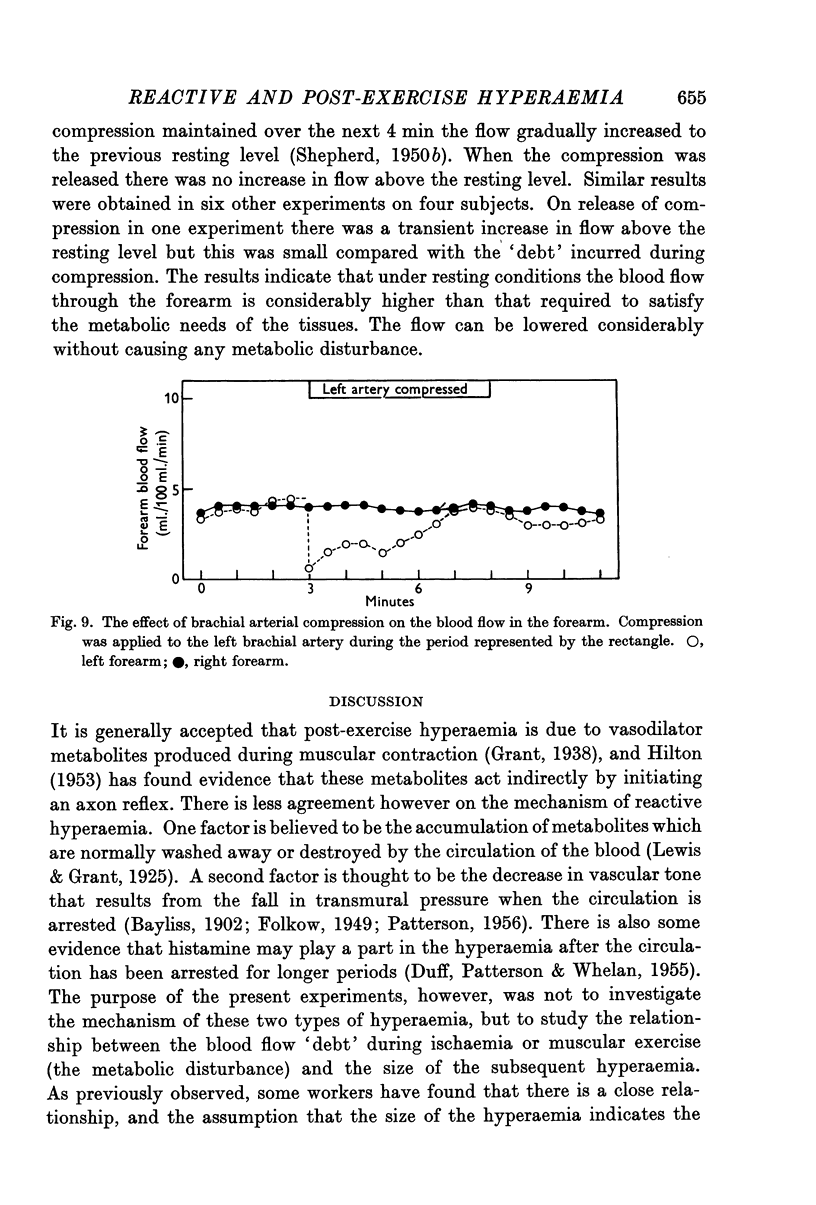



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayliss W. M. On the local reactions of the arterial wall to changes of internal pressure. J Physiol. 1902 May 28;28(3):220–231. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1902.sp000911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE R. S., HELLON R. F. Hyperaemia following sustained and rhythmic exercise in the human forearm at various temperatures. J Physiol. 1959 Mar 12;145(3):447–458. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLES D. R., COOPER K. E. Hyperaemia following arterial occlusion or exercise in the warm and cold human forearm. J Physiol. 1959 Mar 3;145(2):241–250. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DORNHORST A. C., WHELAN R. F. The blood flow in muscle following exercise and circulatory arrest; the influence of reduction in effective local blood pressure, of arterial hypoxia and of adrenaline. Clin Sci. 1953 Feb;12(1):33–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUFF F., PATTERSON G. C., WHELAN R. F. The effect of intra-arterial antihistamines on the hyperaemia following temporary arrest of the circulation in the human forearm. Clin Sci. 1955 May;14(2):267–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDHOLM O. G., HOWARTH S., SHARPEY-SCHAFER E. P. Resting blood flow and blood pressure in limbs with arterial obstruction. Clin Sci. 1951 Aug;10(3):361–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENFIELD A. D. A simple water filled plethysmograph for the hand or forearm with temperature control. J Physiol. 1954 Mar 29;123(3):62P–64P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILTON S. M. Experiments on the post contraction hyperaemia of skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1953 Apr 28;120(1-2):230–245. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLING H. E., VEREL D. Circulation in the elevated forearm. Clin Sci. 1957 May;16(2):197–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCARDLE B., VEREL D. Responses to ischaemic work in the human forearm. Clin Sci. 1956 May;15(2):305–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTERSON G. C. The role of intravascular pressure in the causation of reactive hyperaemia in the human forearm. Clin Sci. 1956 Feb;15(1):17–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTERSON G. C., WHELAN R. F. Reactive hyperaemia in the human forearm. Clin Sci. 1955 May;14(2):197–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD J. E., LITTER J., WILKINS R. W. The mechanism of limb segment reactive hyperemia in man. Circ Res. 1955 Nov;3(6):581–587. doi: 10.1161/01.res.3.6.581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


