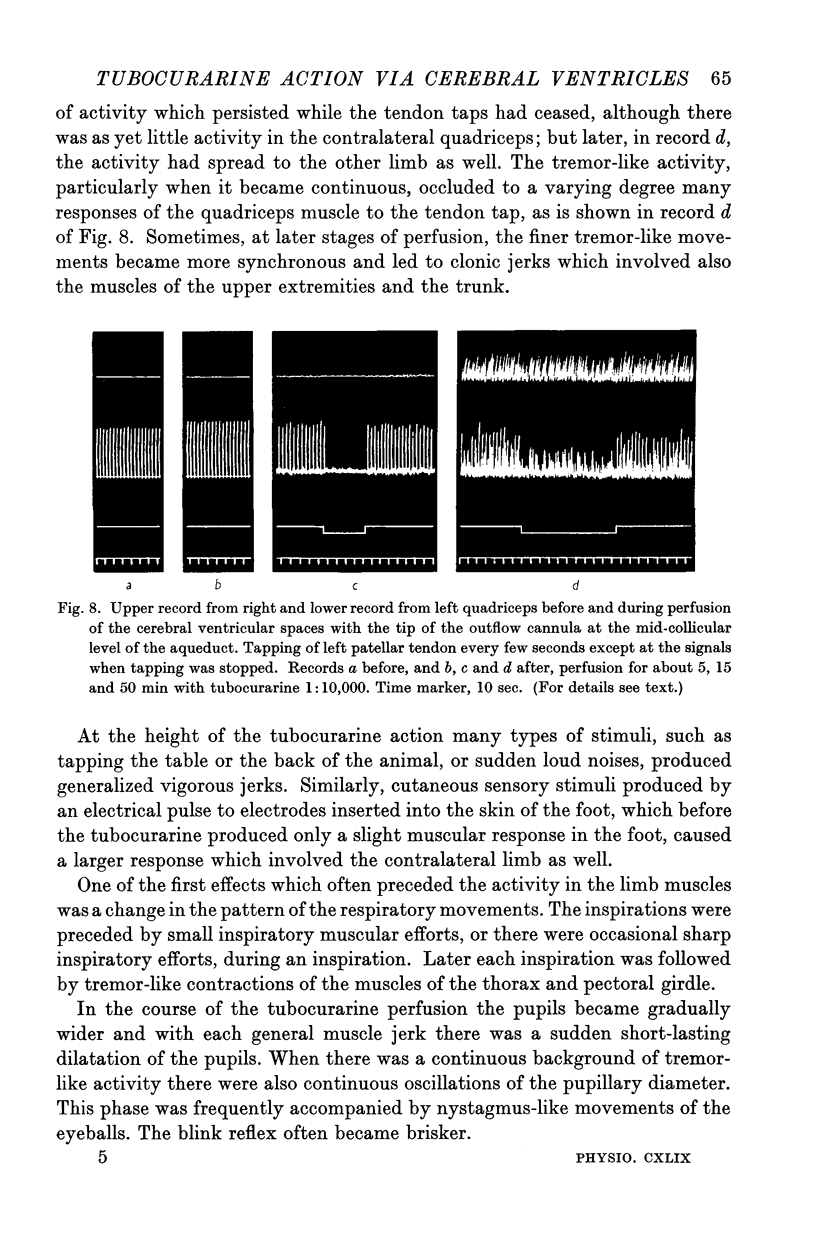
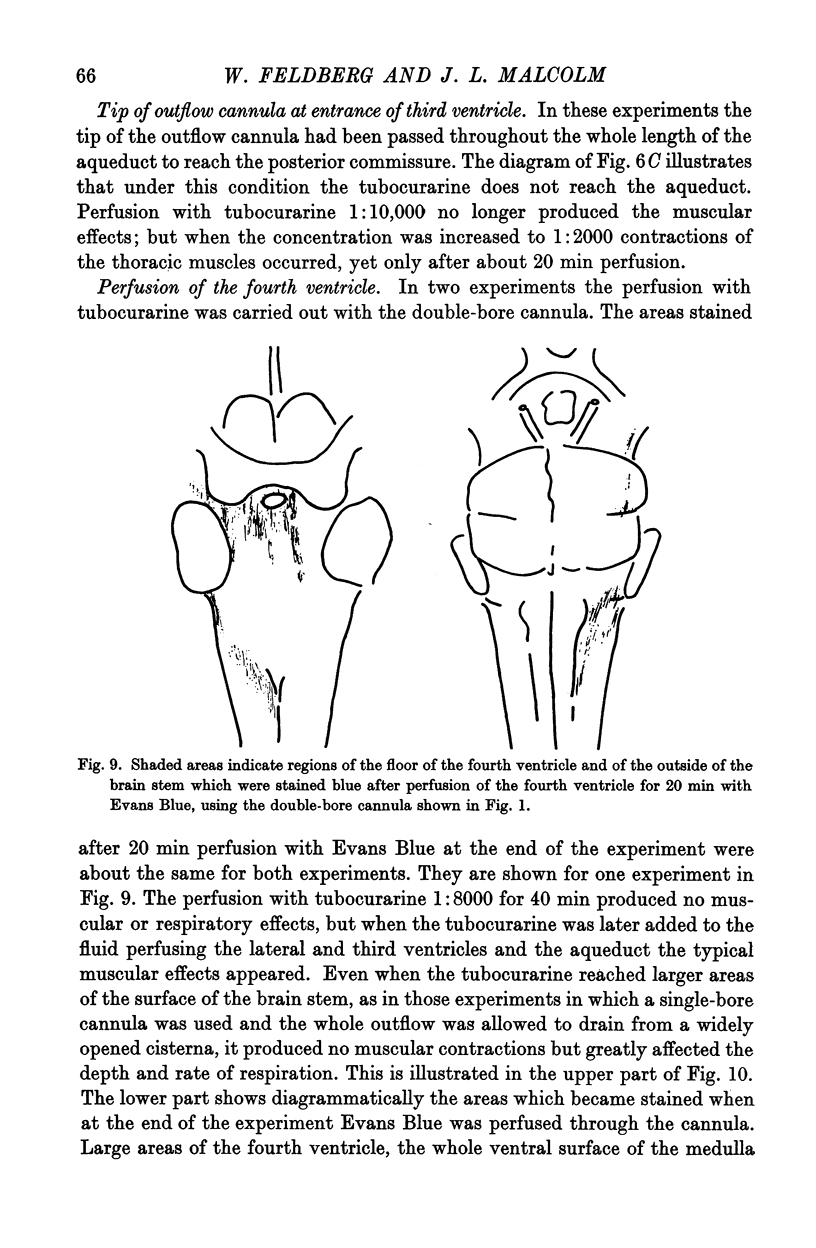
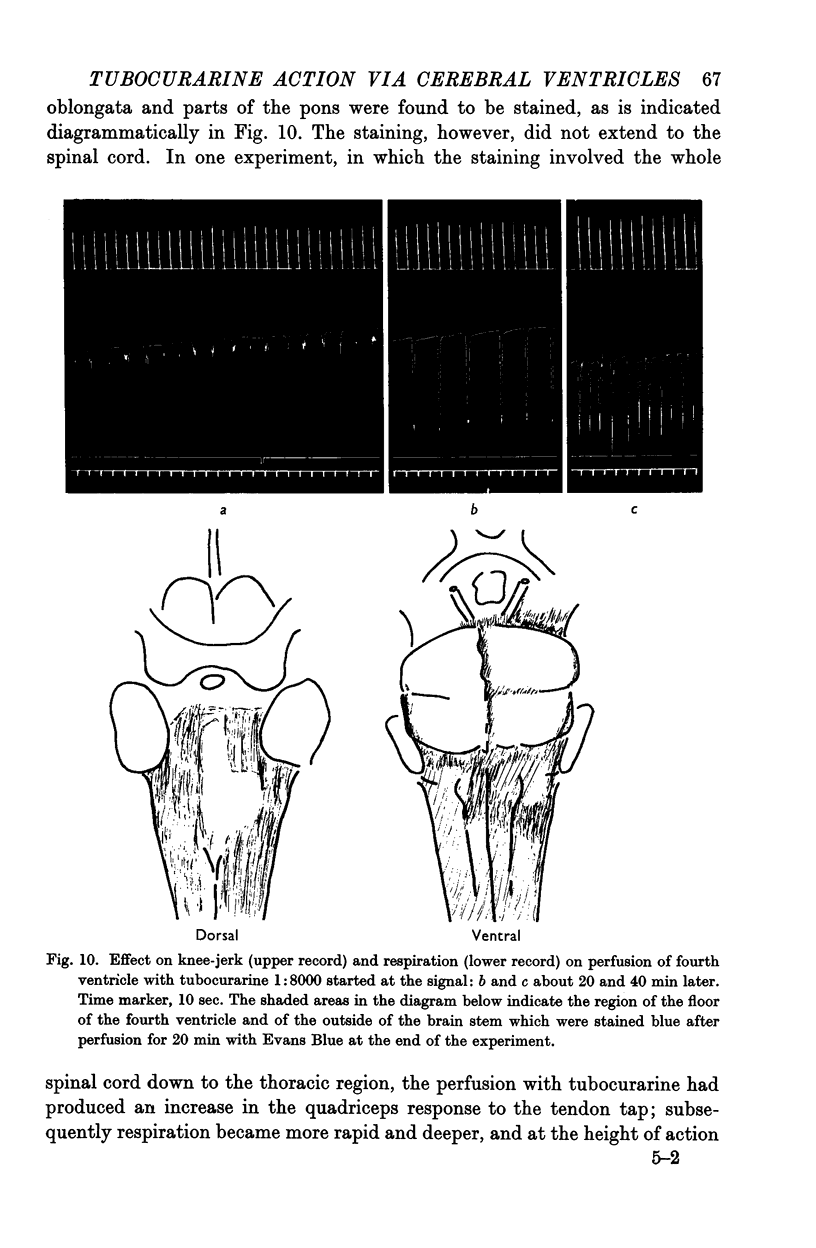
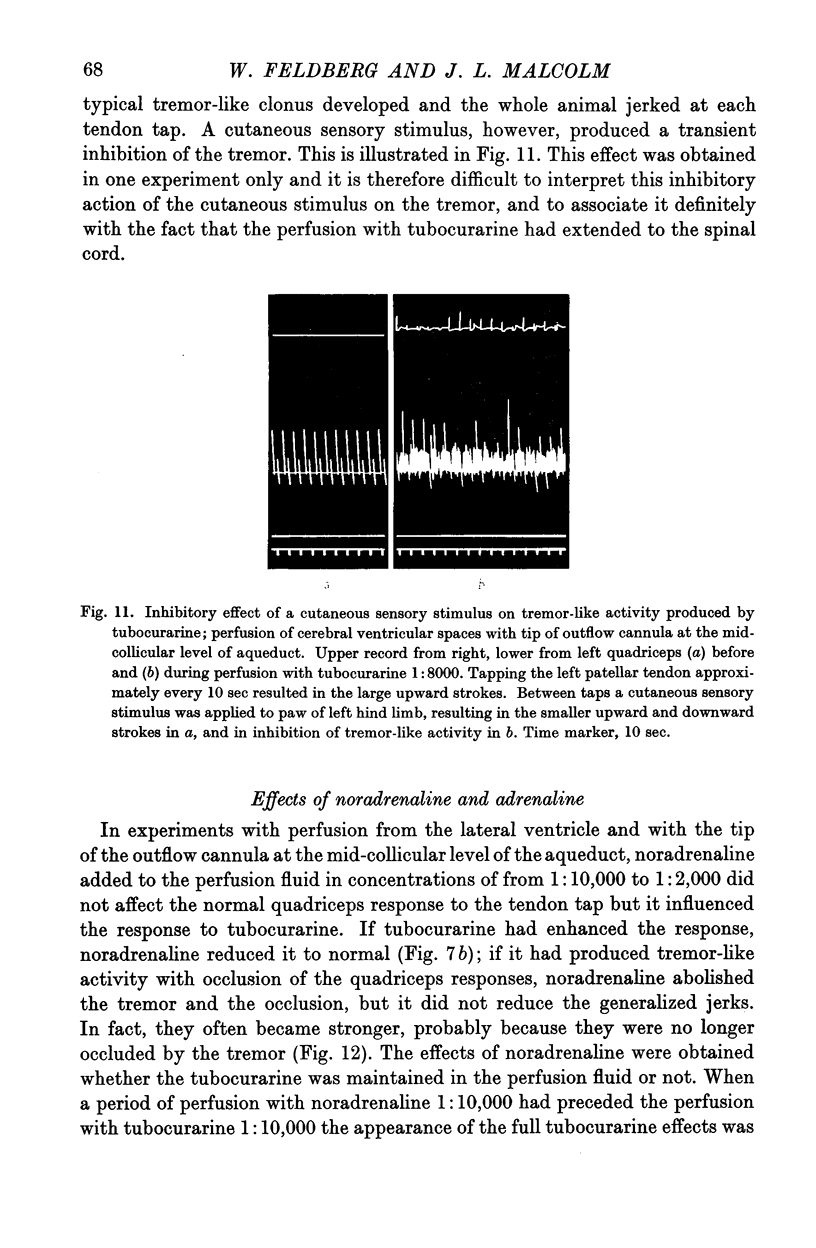
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARSA J. A., KLINE N. S. Treatment of two hundred disturbed psychotics with reserpine. J Am Med Assoc. 1955 May 14;158(2):110–113. doi: 10.1001/jama.1955.02960020016005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEIN H. J., GROSS F., TRIPOD J., MEIER R. Experimentelle Untersuchungen über Serpasol (Reserpin), ein neues, sehr wirksames Rauwolfiaalkaloid mit neuartiger zentraler Wirkung. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1953 Oct 17;83(42):1007–1012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BHATTACHARYA B. K., FELDBERG W. Perfusion of cerebral ventricles: effects of drugs on outflow from the cisterna and the aqueduct. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1958 Jun;13(2):156–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1958.tb00211.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHUSID J. G., KOPELOFF L. M., KOPELOFF N. Reserpine (serpasil) effects on epileptic monkeys. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Feb;88(2):276–277. doi: 10.3181/00379727-88-21562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDBERG W., MALCOLM J. L., SMITH I. D. Effect of tubocurarine on the electrical activity of the cat's brain under chloralose. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):178–201. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDBERG W., SHERWOOD S. L. Behaviour of cats after intraventricular injections of eserine and DFP. J Physiol. 1954 Sep 28;125(3):488–500. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDBERG W., SHERWOOD S. L. Injections of drugs into the lateral ventricle of the cat. J Physiol. 1954 Jan;123(1):148–167. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLACH F. F. Clinical effectiveness of reserpine. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1955 Apr 15;61(1):161–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1955.tb42462.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLISTER L. E., KRIEGER G. E., KRINGEL A., ROBERTS R. H. Treatment of chronic schizophrenic reactions with reserpine. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1955 Apr 15;61(1):92–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1955.tb42455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLZBAUER M., VOGT M. Depression by reserpine of the noradrenaline concentration in the hypothalamus of the cat. J Neurochem. 1956 May;1(1):8–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1956.tb12048.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKNER F. L., WARD A., Jr Bulbar reticular formation and tremor. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1953 Oct;70(4):489–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KINROSS-WRIGHT V. Chlorpromazine and reserpine in the treatment of psychoses. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1955 Apr 15;61(1):174–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1955.tb42464.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLINE N. S., STANLEY A. M. Use of reserpine in a neuropsychiatric hospital. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1955 Apr 15;61(1):85–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1955.tb42454.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEUSEN I. The influence of calcium, potassium and magnesium ions in cerebrospinal fluid on vasomotor system. J Physiol. 1949 Dec;110(3-4):319–329. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOESCHCKE H. H., KOEPCHEN H. P., GERTZ K. H. Uber den Einfluss von Wasserstoffionenkonzentration und CO2-Druck im Liquor cerebrospinalis auf die Atmung. Pflugers Arch. 1958;266(6):569–585. doi: 10.1007/BF00363036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOESCHCKE H. H., KOEPCHEN H. P. Uber das Verhalten der Atmung und des arteriellen Drucks bei Einbringen von Veratridin, Lobelin und Cyanid in den Liquor cerebrospinalis. Pflugers Arch. 1958;266(6):586–610. doi: 10.1007/BF00363037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOESCHCKE H. H., KOEPCHEN H. P. Versuche zur Lokalisation des Angriffsortes der Atmung- und Kreislaufwirkung von Novocain im Liquor cerebrospinalis. Pflugers Arch. 1958;266(6):628–641. doi: 10.1007/BF00363039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSCHOLL E., VOGT M. The action of reserpine on the peripheral sympathetic system. J Physiol. 1958 Apr 3;141(1):132–155. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERSON E. W., MAGOUN H. W. Production of postural tremor. J Neurophysiol. 1949 Nov;12(6):371–384. doi: 10.1152/jn.1949.12.6.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNEIDER J. A., EARL A. E. Effects of serpasil on behavior and autonomic regulating mechanisms. Neurology. 1954 Sep;4(9):657–667. doi: 10.1212/wnl.4.9.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPIEGEL E. A., SZEKELY E. G., WYCIS H. T. Tremor on stimulation of the midbrain tegmentum after degeneration of the brachium conjunctivum. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1957 Jan;16(1):79–84. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195701000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGT M. The concentration of sympathin in different parts of the central nervous system under normal conditions and after the administration of drugs. J Physiol. 1954 Mar 29;123(3):451–481. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBER E. Ein Rauwolfiaalkaloid in der Psychiatrie: seine Wirkungsähnlichkeit mit Chloropromazin. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1954 Aug 21;84(34):968–970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


