Abstract
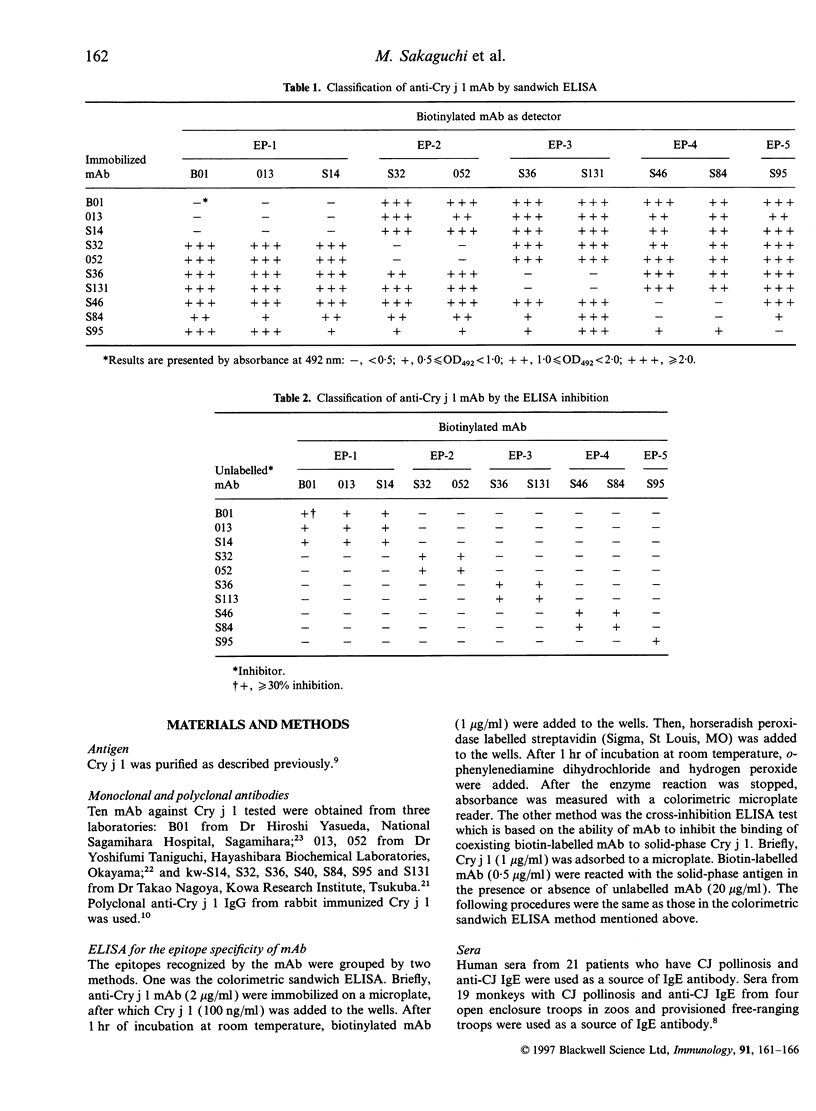
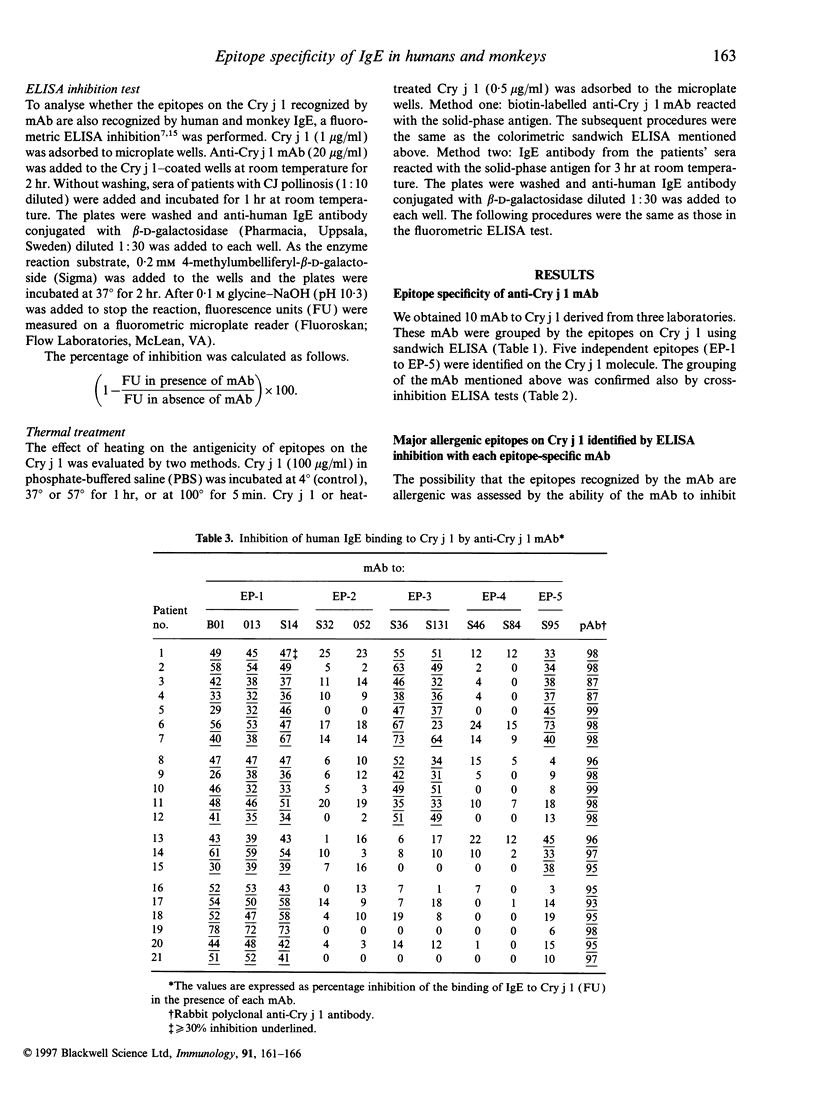
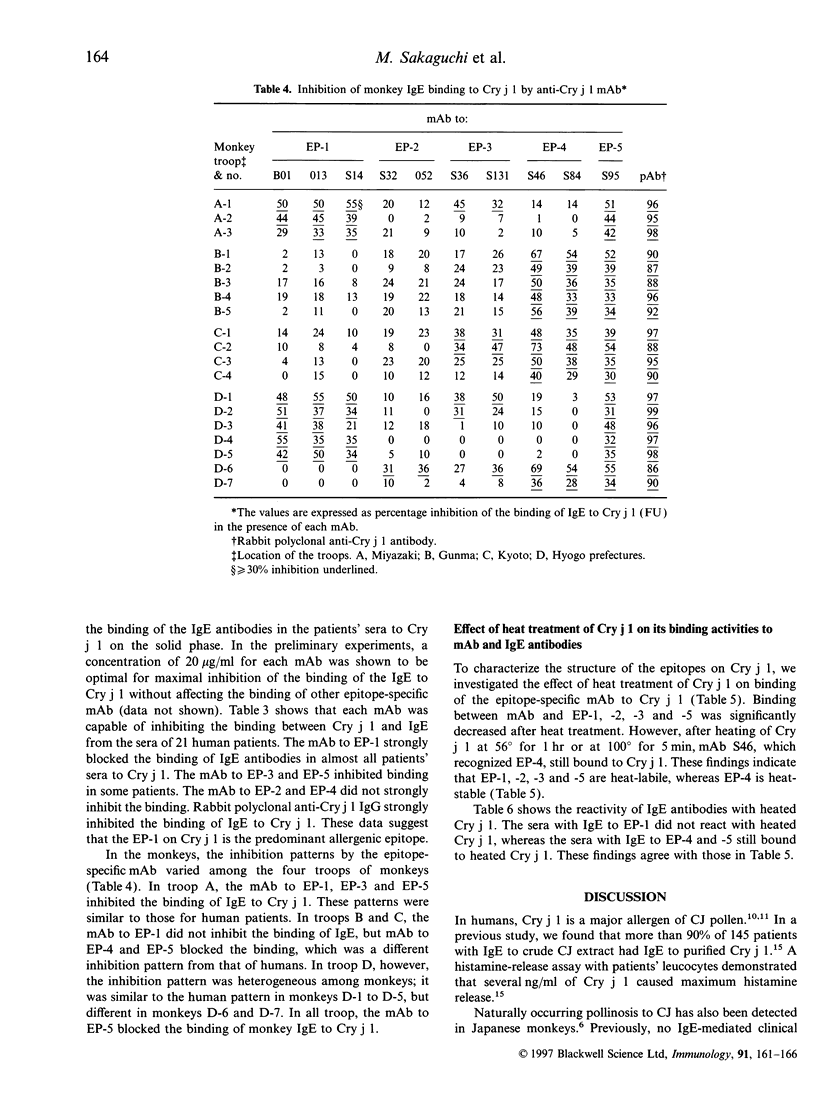
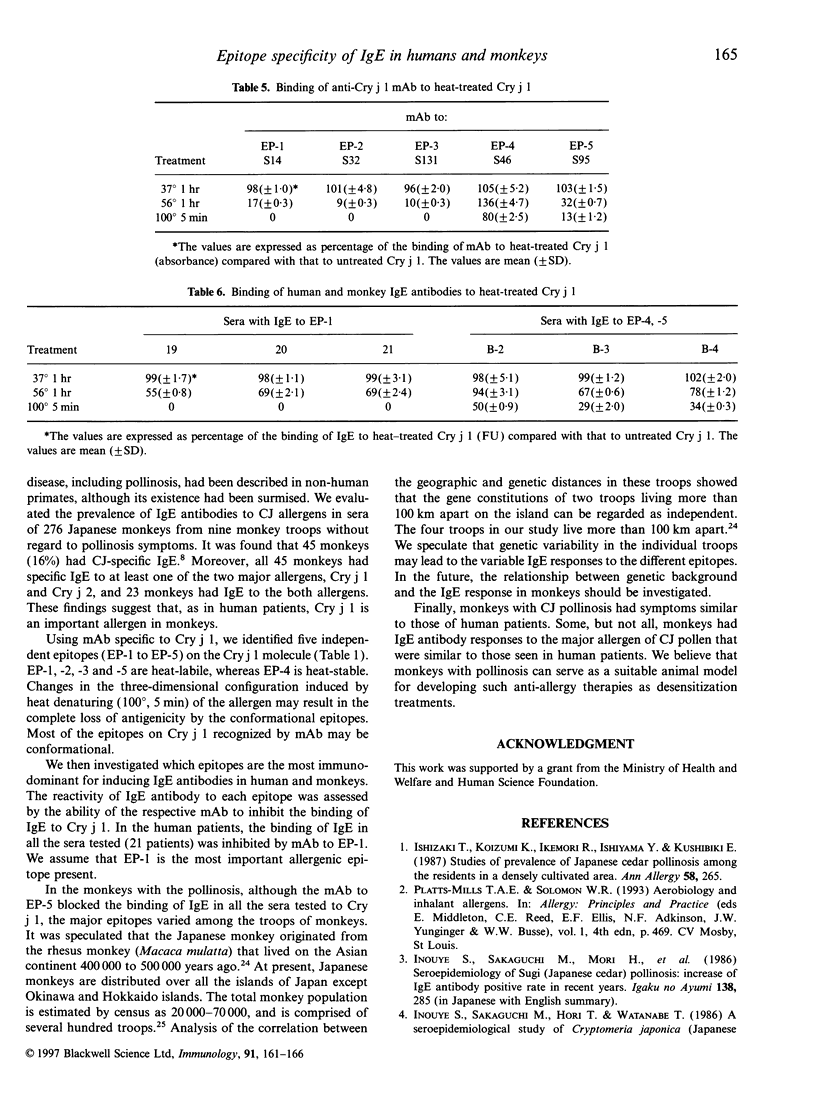
Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica) pollinosis has been reported to occur naturally in Japanese monkeys (Macaca fuscata) as well as humans. Using monoclonal antibodies (mAb) specific to Cry j 1, a major allergen in Japanese cedar pollen, we identified five independent epitopes (EP-1 to EP-5) on the molecule. The epitopes recognized by IgE antibodies in the sera of humans and monkeys with the pollinosis were analysed by an IgE enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay inhibition method with these mAb. In human patients, the mAb to EP-1 strongly blocked the binding of IgE antibodies in all patients' sera to Cry j 1. The reaction patterns of IgE antibodies in monkeys, however, varied among the troops of monkeys. In some troops, the mAb to EP-1 showed a blocking pattern similar to that for human patients. In other troops, mAb to EP-4 and EP-5 blocked binding of IgE. These results indicate that some, but not all, monkeys have antibody responses to the major allergen similar to those of humans.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bose R., Rector E. S., Fischer J., Taronno R., Delespesse G. Production and characterization of mouse monoclonal antibodies to allergenic epitopes on LolpI (Rye I). Immunology. 1986 Oct;59(2):309–315. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekramoddoullah A. K., Kisil F. T., Cook R. T., Sehon A. H. Recognition of a site of a Kentucky bluegrass pollen allergen by antibodies in the sera of allergic and non-atopic humans and a murine monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1739–1743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto M., Kobayashi T., Nigi H., Saito S., Nakayama I., Narita T., Iwata M., Yasueda H., Taniguchi Y., Kurimoto M. Responses of monkeys with pollinosis to two major allergens of Japanese cedar pollen. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1997 Jan;112(1):88–92. doi: 10.1159/000237436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto M., Nigi H., Sakaguchi M., Inouye S., Imaoka K., Miyazawa H., Taniguchi Y., Kurimoto M., Yasueda H., Ogawa T. Sensitivity to two major allergens (Cry j I and Cry j II) in patients with Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica) pollinosis. Clin Exp Allergy. 1995 Sep;25(9):848–852. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1995.tb00027.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto M., Sakaguchi M., Inouye S., Imaoka K., Nigi H., Fujimoto K., Honjo S., Taniguchi Y., Kurimoto M., Gotoh S. Prevalence of IgE antibody to crude and purified allergens of Japanese cedar pollen among different troops of Japanese monkeys (Macaca fuscata). J Med Primatol. 1994 Sep;23(7):393–396. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0684.1994.tb00126.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaki T., Koizumi K., Ikemori R., Ishiyama Y., Kushibiki E. Studies of prevalence of Japanese cedar pollinosis among the residents in a densely cultivated area. Ann Allergy. 1987 Apr;58(4):265–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Marsh D. G. Monoclonal antibodies to the major Lolium perenne (rye grass) pollen allergen Lol p I (Rye I). Mol Immunol. 1986 Dec;23(12):1281–1288. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima T., Taniai M., Taniguchi Y., Usui M., Ando S., Kurimoto M., Matuhasi T. Antigenic analyses of Sugi basic protein by monoclonal antibodies: I. Distribution and characterization of B-cell-tropic epitopes of Cry j I molecules. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1992;98(2):110–117. doi: 10.1159/000236173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mourad W., Mécheri S., Peltre G., David B., Hébert J. Study of the epitope structure of purified Dac G I and Lol p I, the major allergens of Dactylis glomerata and Lolium perenne pollens, using monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3486–3491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S. [Investigation into the frequency of cases with Japanese cedar pollinosis among the students and staff members in our university]. Arerugi. 1990 May;39(5):476–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. R., Klapper D. G. Two major human allergenic sites on ragweed pollen allergen antigen E identified by using monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 15;136(6):2109–2115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi M., Inouye S., Imaoka K., Miyazawa H., Hashimoto M., Nigi H., Nakamura S., Gotoh S., Minezawa M., Fujimoto K. Measurement of serum IgE antibodies against Japanese cedar pollen (Cryptomeria japonica) in Japanese monkeys (Macaca fuscata) with pollinosis. J Med Primatol. 1992 Aug;21(6):323–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi M., Inouye S., Taniai M., Ando S., Usui M., Matuhasi T. Identification of the second major allergen of Japanese cedar pollen. Allergy. 1990 May;45(4):309–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1990.tb00501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sone T., Komiyama N., Shimizu K., Kusakabe T., Morikubo K., Kino K. Cloning and sequencing of cDNA coding for Cry j I, a major allergen of Japanese cedar pollen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Mar 15;199(2):619–625. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniai M., Ando S., Usui M., Kurimoto M., Sakaguchi M., Inouye S., Matuhasi T. N-terminal amino acid sequence of a major allergen of Japanese cedar pollen (Cry j I). FEBS Lett. 1988 Nov 7;239(2):329–332. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80945-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Tamura M., Nagoya T., Takahashi Y., Katagiri S. [A new counting method of airborne Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica) pollen allergens by immunoblotting using anti-Cry j I monoclonal antibody]. Arerugi. 1992 Jun;41(6):637–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


