Abstract
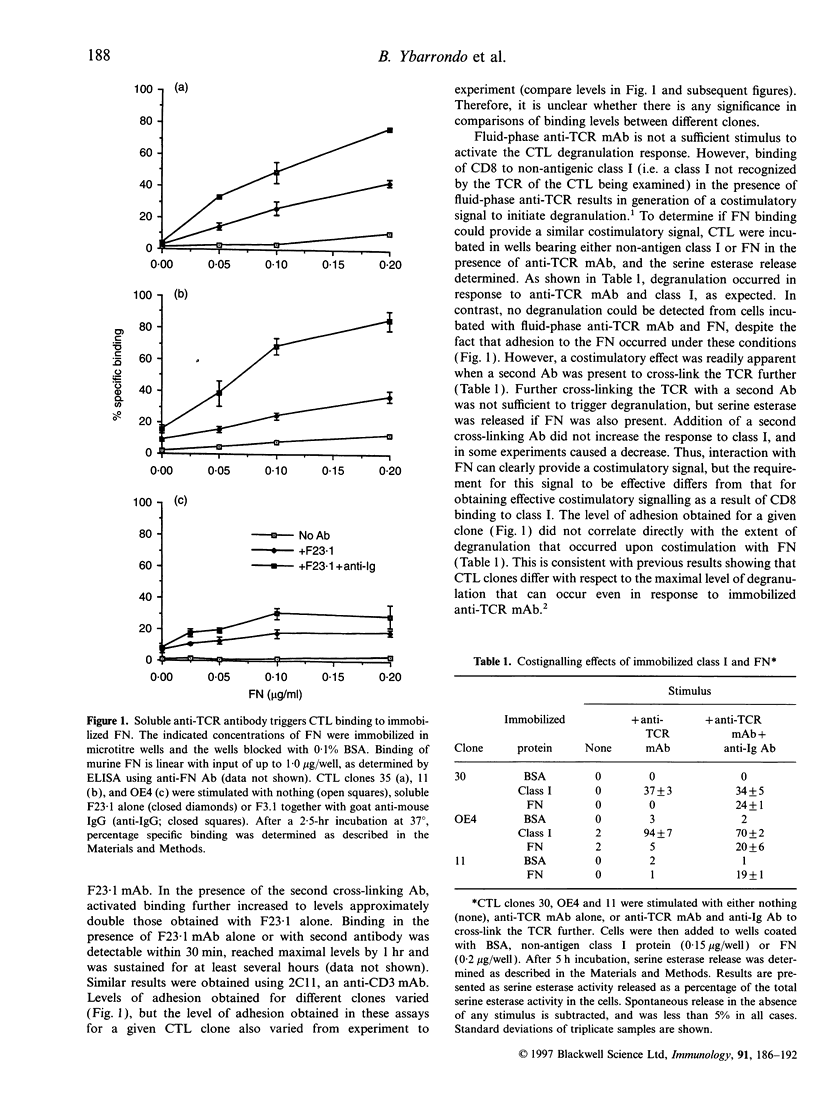
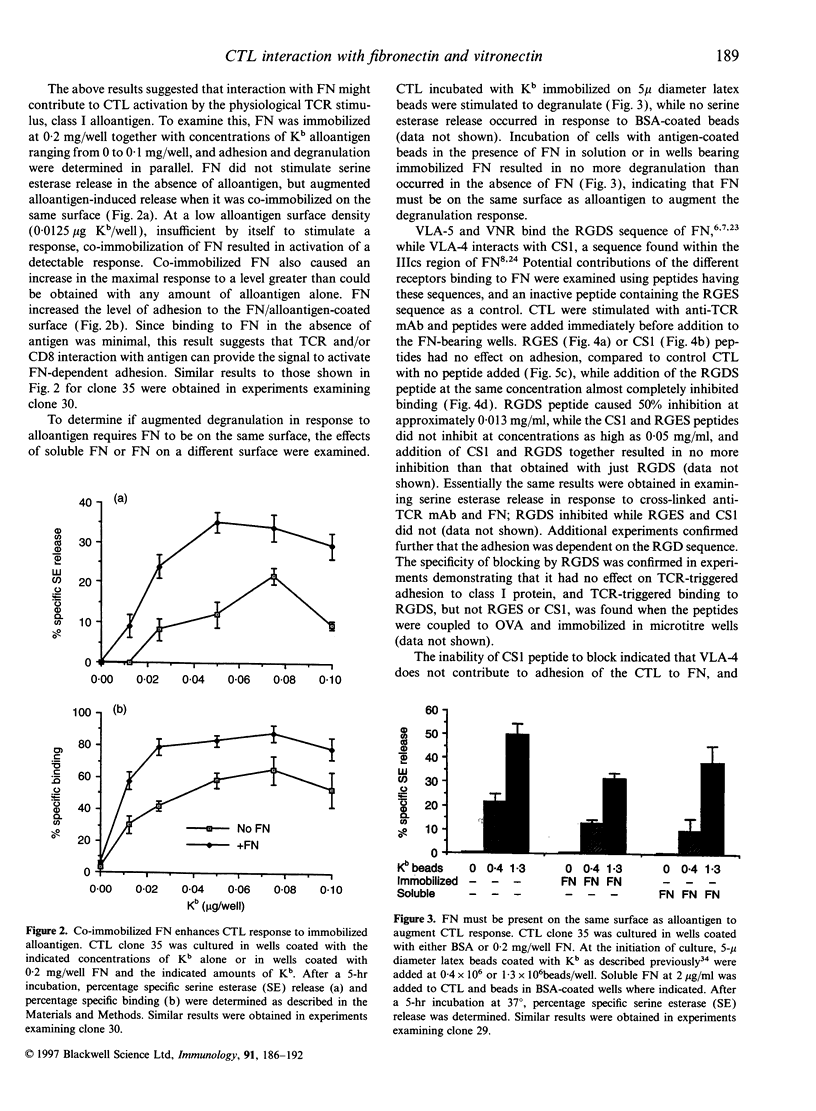
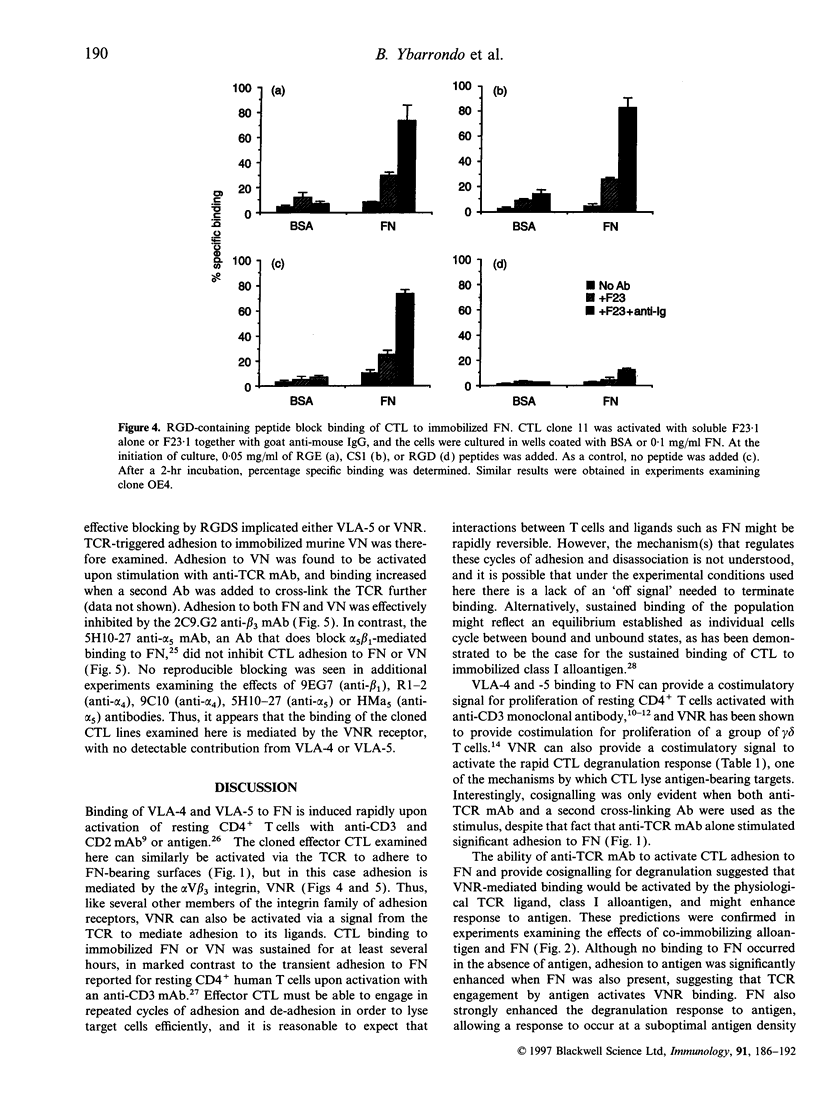
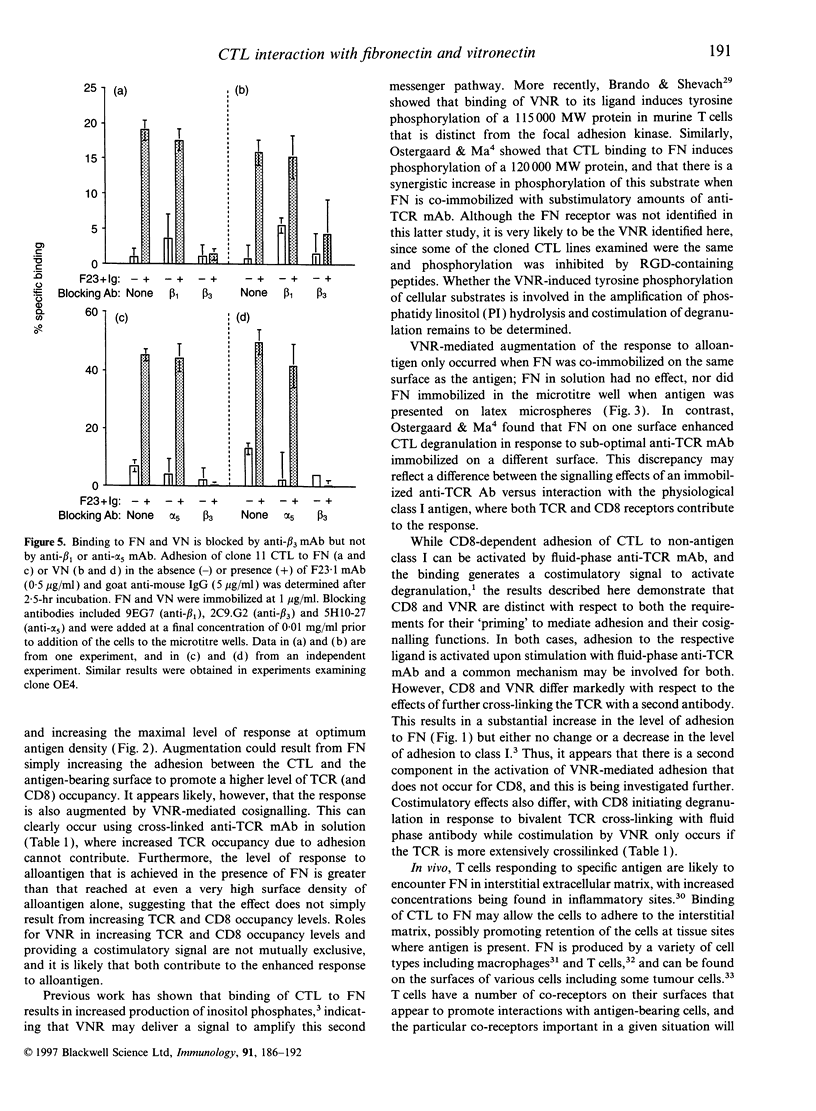
Stimulation of cloned cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) with anti-T-cell receptor (TCR) monoclonal antibody (mAb) in solution resulted in rapid and sustained activation of adhesion to immobilized fibronectin (FN) but did not initiate degranulation. Addition of a second antibody (Ab) to further cross-link the TCR substantially increased the level of adhesion and also activated degranulation, as measured by release of serine esterase, in the presence of immobilized FN but not in its absence. Thus, binding to FN can provide a costimulatory signal to activate degranulation. TCR cross-linking also activated CD8-dependent adhesion to class I, and CD8 provided a costimulatory signal upon binding to class I. However, the requirements for activating adhesion and generating the costimulatory signal differed significantly for FN versus class I ligand, suggesting that these two receptor-ligand systems do not share a common mechanism of action. Co-immobilizing FN and alloantigen resulted in increased serine esterase release in comparison with that stimulated by antigen alone, and required the FN and class I be on the same surface. Peptide and antibody blocking demonstrated that CTL binding to FN, and to vitronectin (VN), was mediated by the alpha V beta 3 vitronectin receptor (VNR). Thus, VNR is activated by a signal from the TCR to mediate adhesion to FN or VN, and delivers a costimulatory signal for degranulation via a different mechanism than costimulation by CD8 binding to class I.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alitalo K., Hovi T., Vaheri A. Fibronectin is produced by human macrophages. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):602–613. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brando C., Shevach E. M. Engagement of the vitronectin receptor (alpha V beta 3) on murine T cells stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of a 115-kDa protein. J Immunol. 1995 Mar 1;154(5):2005–2011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan B. M., Wong J. G., Rao A., Hemler M. E. T cell receptor-dependent, antigen-specific stimulation of a murine T cell clone induces a transient, VLA protein-mediated binding to extracellular matrix. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 15;147(2):398–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. S., Oppenheimer-Marks N., Bednarczyk J. L., McIntyre B. W., Lipsky P. E. Fibronectin promotes proliferation of naive and memory T cells by signaling through both the VLA-4 and VLA-5 integrin molecules. J Immunol. 1990 Aug 1;145(3):785–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey H. P., Canfield L. S., Kindler H. L., Angadi C. V., Tomasek J. J., Goodman J. W. Production of a fibronectin-associated lymphokine by cloned mouse T cells. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1508–1515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann S. H., Mescher M. F. Purification of the H-2Kk molecule of the murine major histocompatibility complex. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):8713–8716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries M. J., Komoriya A., Akiyama S. K., Olden K., Yamada K. M. Identification of two distinct regions of the type III connecting segment of human plasma fibronectin that promote cell type-specific adhesion. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6886–6892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane K. P., Champoux P., Mescher M. F. Solid-phase binding of class I and II MHC proteins: immunoassay and T cell recognition. Mol Immunol. 1989 Aug;26(8):759–768. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(89)90036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane K. P., Sherman L. A., Mescher M. F. Molecular interactions required for triggering alloantigen-specific cytolytic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4153–4160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinashi T., Springer T. A. Steel factor and c-kit regulate cell-matrix adhesion. Blood. 1994 Feb 15;83(4):1033–1038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingemann H. G., Ebert J., Deeg H. J. Fibronectin is present on B-cells but not on OKT 3-positive T-lymphocytes or Leu 11-positive natural killer cells. J Leukoc Biol. 1986 Oct;40(4):491–495. doi: 10.1002/jlb.40.4.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leo O., Foo M., Sachs D. H., Samelson L. E., Bluestone J. A. Identification of a monoclonal antibody specific for a murine T3 polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1374–1378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Yamada A., Kay J., Yamada K. M., Akiyama S. K., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Activation of CD4 cells by fibronectin and anti-CD3 antibody. A synergistic effect mediated by the VLA-5 fibronectin receptor complex. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1133–1148. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy J. B., Skubitz A. P., Qi Z., Yi X. Y., Mickelson D. J., Klein D. J., Furcht L. T. RGD-independent cell adhesion to the carboxy-terminal heparin-binding fragment of fibronectin involves heparin-dependent and -independent activities. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):777–787. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mescher M. F. Surface contact requirements for activation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Oct 1;149(7):2402–2405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder K., Roberts K., Shevach E. M., Coligan J. E. The mouse vitronectin receptor is a T cell activation antigen. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):343–347. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rourke A. M., Mescher M. F. Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte activation involves a cascade of signalling and adhesion events. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):253–255. doi: 10.1038/358253a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rourke A. M., Rogers J., Mescher M. F. Activated CD8 binding to class I protein mediated by the T-cell receptor results in signalling. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):187–189. doi: 10.1038/346187a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard H. L., Ma E. A. Fibronectin induces phosphorylation of a 120-kDa protein and synergizes with the T cell receptor to activate cytotoxic T cell clones. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Jan;25(1):252–256. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack M. S., Eisen H. N. A novel serine esterase expressed by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. 1985 Apr 25-May 1Nature. 314(6013):743–745. doi: 10.1038/314743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pytela R., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Identification and isolation of a 140 kd cell surface glycoprotein with properties expected of a fibronectin receptor. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):191–198. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90322-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts K., Yokoyama W. M., Kehn P. J., Shevach E. M. The vitronectin receptor serves as an accessory molecule for the activation of a subset of gamma/delta T cells. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):231–240. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):491–497. doi: 10.1126/science.2821619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y., Van Seventer G. A., Horgan K. J., Shaw S. Regulated expression and binding of three VLA (beta 1) integrin receptors on T cells. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):250–253. doi: 10.1038/345250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y., van Seventer G. A., Horgan K. J., Shaw S. Costimulation of proliferative responses of resting CD4+ T cells by the interaction of VLA-4 and VLA-5 with fibronectin or VLA-6 with laminin. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):59–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staerz U. D., Kanagawa O., Bevan M. J. Hybrid antibodies can target sites for attack by T cells. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):628–631. doi: 10.1038/314628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staerz U. D., Rammensee H. G., Benedetto J. D., Bevan M. J. Characterization of a murine monoclonal antibody specific for an allotypic determinant on T cell antigen receptor. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3994–4000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stallcup K. C., Springer T. A., Mescher M. F. Characterization of an anti-H-2 monoclonal antibody and its use in large-scale antigen purification. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):923–930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stecher V. J., Kaplan J. E., Connolly K., Mielens Z., Saelens J. K. Fibronectin in acute and chronic inflammation. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Mar;29(3):394–399. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayner E. A., Garcia-Pardo A., Humphries M. J., McDonald J. A., Carter W. G. Identification and characterization of the T lymphocyte adhesion receptor for an alternative cell attachment domain (CS-1) in plasma fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1321–1330. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M. Adhesive recognition sequences. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):12809–12812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M. Fibronectins: structure, functions and receptors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;1(5):956–963. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(89)90065-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


