Abstract
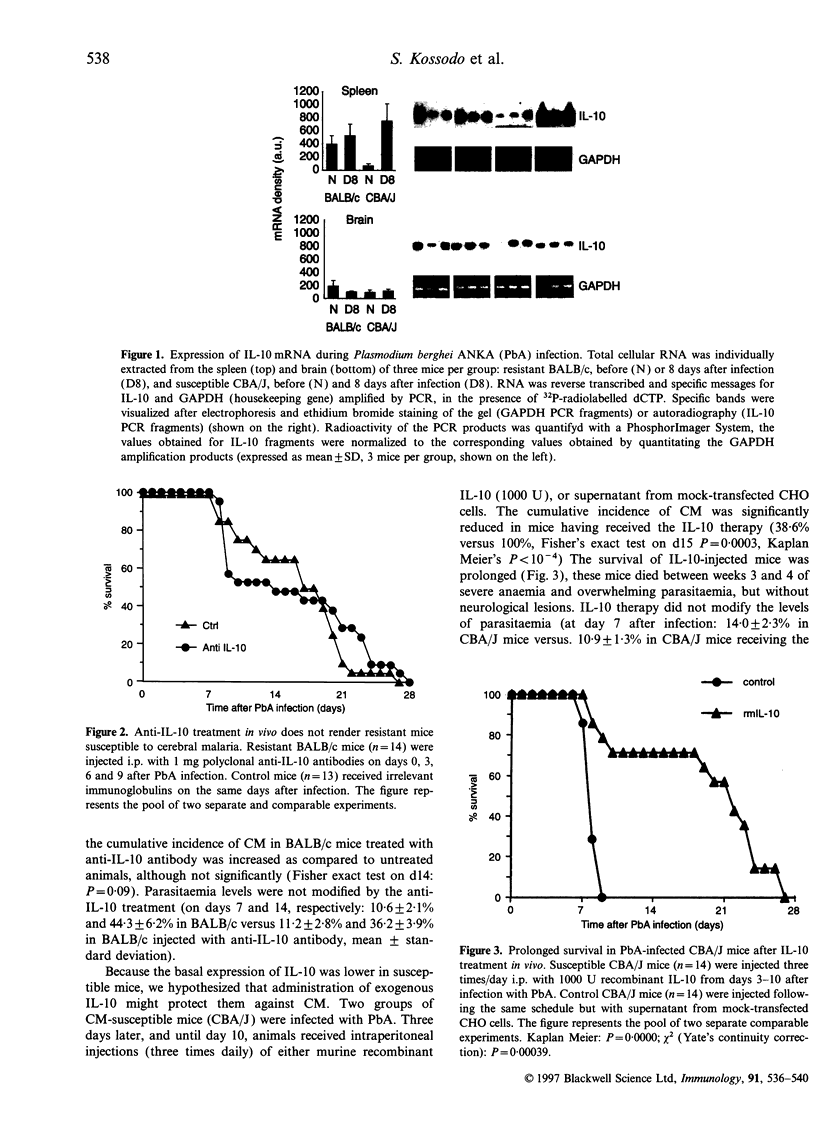
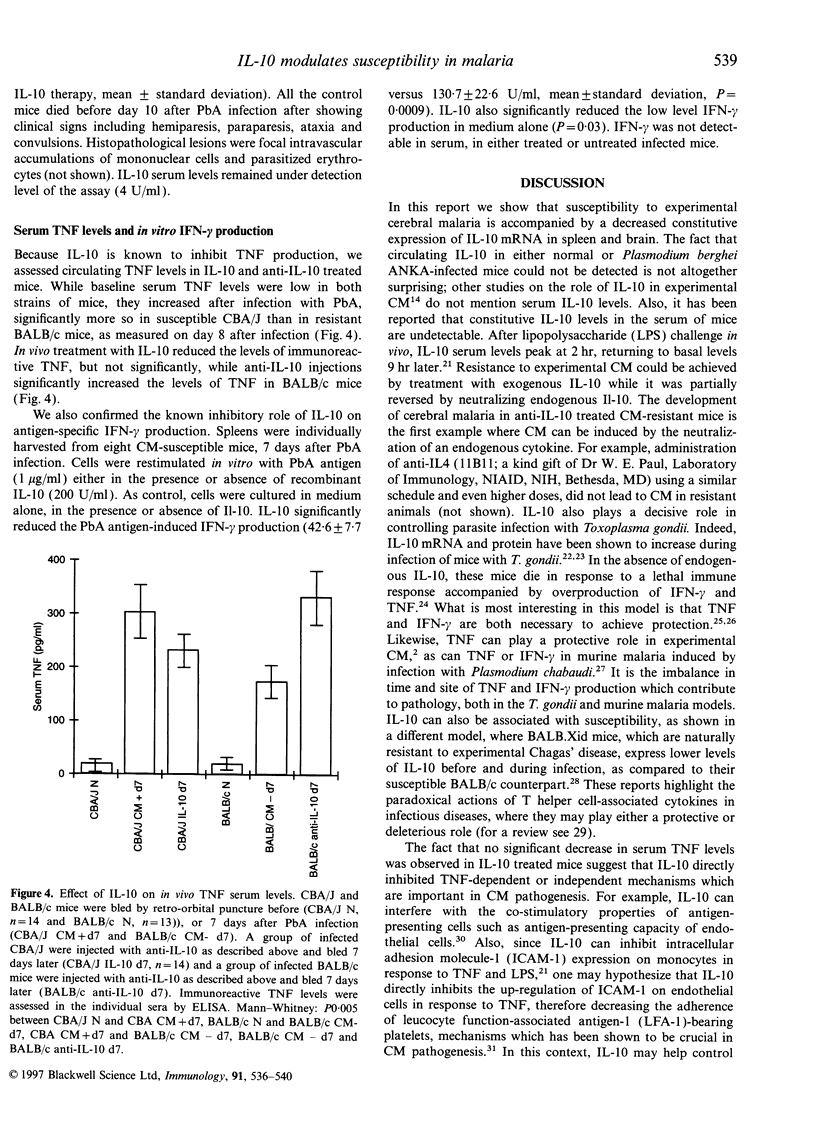
In this study, we examined the effects of interleukin-10 (IL-10) on the outcome of experimental cerebral malaria (CM), a lethal neurological syndrome that occurs in susceptible strains of mice after infection with Plasmodium berghei ANKA (PbA). Constitutive IL-10 mRNA levels were significantly higher in the spleen and brain of resistant animals. In vivo neutralization of endogenous IL-10 in CM-resistant mice induced the neurological syndrome in 35.7% of these mice, as opposed to 7.7% in controls. IL-10 inhibited PbA antigen-specific interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) production in vitro but not tumour necrosis factor (TNF) serum levels in vivo. Susceptible mice, on the other hand, were significantly protected against CM when injected with recombinant IL-10. Overall, our findings suggest that IL-10 plays a protective role against experimental cerebral malaria.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I. A., Hunt N. H., Butcher G. A., Cowden W. B. Inhibition of murine malaria (Plasmodium chabaudi) in vivo by recombinant interferon-gamma or tumor necrosis factor, and its enhancement by butylated hydroxyanisole. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3493–3496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durez P., Abramowicz D., Gérard C., Van Mechelen M., Amraoui Z., Dubois C., Leo O., Velu T., Goldman M. In vivo induction of interleukin 10 by anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody or bacterial lipopolysaccharide: differential modulation by cyclosporin A. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):551–555. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckwalanga M., Marussig M., Tavares M. D., Bouanga J. C., Hulier E., Pavlovitch J. H., Minoprio P., Portnoï D., Rénia L., Mazier D. Murine AIDS protects mice against experimental cerebral malaria: down-regulation by interleukin 10 of a T-helper type 1 CD4+ cell-mediated pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 16;91(17):8097–8101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.17.8097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiorentino D. F., Bond M. W., Mosmann T. R. Two types of mouse T helper cell. IV. Th2 clones secrete a factor that inhibits cytokine production by Th1 clones. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2081–2095. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiorentino D. F., Zlotnik A., Mosmann T. R., Howard M., O'Garra A. IL-10 inhibits cytokine production by activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 1;147(11):3815–3822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiorentino D. F., Zlotnik A., Vieira P., Mosmann T. R., Howard M., Moore K. W., O'Garra A. IL-10 acts on the antigen-presenting cell to inhibit cytokine production by Th1 cells. J Immunol. 1991 May 15;146(10):3444–3451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia I., Miyazaki Y., Araki K., Araki M., Lucas R., Grau G. E., Milon G., Belkaid Y., Montixi C., Lesslauer W. Transgenic mice expressing high levels of soluble TNF-R1 fusion protein are protected from lethal septic shock and cerebral malaria, and are highly sensitive to Listeria monocytogenes and Leishmania major infections. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Aug;25(8):2401–2407. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzinelli R. T., Eltoum I., Wynn T. A., Sher A. Acute cerebral toxoplasmosis is induced by in vivo neutralization of TNF-alpha and correlates with the down-regulated expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and other markers of macrophage activation. J Immunol. 1993 Oct 1;151(7):3672–3681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzinelli R. T., Wysocka M., Hieny S., Scharton-Kersten T., Cheever A., Kühn R., Müller W., Trinchieri G., Sher A. In the absence of endogenous IL-10, mice acutely infected with Toxoplasma gondii succumb to a lethal immune response dependent on CD4+ T cells and accompanied by overproduction of IL-12, IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha. J Immunol. 1996 Jul 15;157(2):798–805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Fajardo L. F., Piguet P. F., Allet B., Lambert P. H., Vassalli P. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) as an essential mediator in murine cerebral malaria. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1210–1212. doi: 10.1126/science.3306918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Heremans H., Piguet P. F., Pointaire P., Lambert P. H., Billiau A., Vassalli P. Monoclonal antibody against interferon gamma can prevent experimental cerebral malaria and its associated overproduction of tumor necrosis factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5572–5574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Modlin R. L. Immune mechanisms in bacterial and parasitic diseases: protective immunity versus pathology. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Aug;3(4):480–485. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(91)90007-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Piguet P. F., Engers H. D., Louis J. A., Vassalli P., Lambert P. H. L3T4+ T lymphocytes play a major role in the pathogenesis of murine cerebral malaria. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2348–2354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Piguet P. F., Vassalli P., Lambert P. H. Tumor-necrosis factor and other cytokines in cerebral malaria: experimental and clinical data. Immunol Rev. 1989 Dec;112:49–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00552.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Tacchini-Cottier F., Vesin C., Milon G., Lou J. N., Piguet P. F., Juillard P. TNF-induced microvascular pathology: active role for platelets and importance of the LFA-1/ICAM-1 interaction. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1993 Nov-Dec;4(6):415–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Taylor T. E., Molyneux M. E., Wirima J. J., Vassalli P., Hommel M., Lambert P. H. Tumor necrosis factor and disease severity in children with falciparum malaria. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jun 15;320(24):1586–1591. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198906153202404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gérard C., Bruyns C., Marchant A., Abramowicz D., Vandenabeele P., Delvaux A., Fiers W., Goldman M., Velu T. Interleukin 10 reduces the release of tumor necrosis factor and prevents lethality in experimental endotoxemia. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):547–550. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter C. A., Litton M. J., Remington J. S., Abrams J. S. Immunocytochemical detection of cytokines in the lymph nodes and brains of mice resistant or susceptible to toxoplasmic encephalitis. J Infect Dis. 1994 Oct;170(4):939–945. doi: 10.1093/infdis/170.4.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. L. A protective role for endogenous tumor necrosis factor in Toxoplasma gondii infection. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):1979–1983. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.1979-1983.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern P., Hemmer C. J., Van Damme J., Gruss H. J., Dietrich M. Elevated tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6 serum levels as markers for complicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Am J Med. 1989 Aug;87(2):139–143. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(89)80688-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D., Hill A. V., Sambou I., Twumasi P., Castracane J., Manogue K. R., Cerami A., Brewster D. R., Greenwood B. M. TNF concentration in fatal cerebral, non-fatal cerebral, and uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Lancet. 1990 Nov 17;336(8725):1201–1204. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92827-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minoprio P., el Cheikh M. C., Murphy E., Hontebeyrie-Joskowicz M., Coffman R., Coutinho A., O'Garra A. Xid-associated resistance to experimental Chagas' disease is IFN-gamma dependent. J Immunol. 1993 Oct 15;151(8):4200–4208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. W., Vieira P., Fiorentino D. F., Trounstine M. L., Khan T. A., Mosmann T. R. Homology of cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor (IL-10) to the Epstein-Barr virus gene BCRFI. Science. 1990 Jun 8;248(4960):1230–1234. doi: 10.1126/science.2161559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peyron F., Burdin N., Ringwald P., Vuillez J. P., Rousset F., Banchereau J. High levels of circulating IL-10 in human malaria. Clin Exp Immunol. 1994 Feb;95(2):300–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1994.tb06527.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slade S. J., Langhorne J. Production of interferon-gamma during infection of mice with Plasmodium chabaudi chabaudi. Immunobiology. 1989 Oct;179(4-5):353–365. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(89)80041-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Orellana M. A., Schreiber R. D., Remington J. S. Interferon-gamma: the major mediator of resistance against Toxoplasma gondii. Science. 1988 Apr 22;240(4851):516–518. doi: 10.1126/science.3128869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vora M., Yssel H., de Vries J. E., Karasek M. A. Antigen presentation by human dermal microvascular endothelial cells. Immunoregulatory effect of IFN-gamma and IL-10. J Immunol. 1994 Jun 15;152(12):5734–5741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenisch C., Parschalk B., Narzt E., Looareesuwan S., Graninger W. Elevated serum levels of IL-10 and IFN-gamma in patients with acute Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1995 Jan;74(1):115–117. doi: 10.1006/clin.1995.1017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems F., Marchant A., Delville J. P., Gérard C., Delvaux A., Velu T., de Boer M., Goldman M. Interleukin-10 inhibits B7 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression on human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Apr;24(4):1007–1009. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kossodo S., Grau G. E. Profiles of cytokine production in relation with susceptibility to cerebral malaria. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 1;151(9):4811–4820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



