Abstract
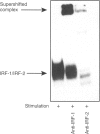
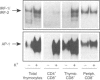
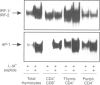
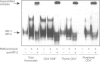
Selection events in the thymus occur at the double-positive CD4+ CD8+ (DP) developmental stage leading either to further differentiation of the CD4+ and CD8+ lineages or to deletion. The interferon-regulatory factor IRF-1 has been implicated in signalling for T-cell death and also in CD8+ thymic differentiation. IRF-1 is an activator and IRF-2 a repressor of gene transcription regulated by type 1 interferons (IFN). To evaluate the role of IRF-1 and IRF-2 in the differentiation of CD4 and CD8 thymocytes, we analysed their DNA-binding activity before and after antigenic stimulation at different stages of thymic development and in peripheral T cells. Unseparated, double-positive and single-positive thymocytes as well as peripheral T lymphocytes from mice transgenic (tg) for a T-cell receptor (TCR), restricted either by major histocompatibility complex class I or class II, were stimulated by their nominal antigen. Our results demonstrate that the DNA-binding activity of IRF-2 and, weakly, that of IRF-1 are inducible in total thymocytes in response to antigen. There is no induction of IRF-1/IRF-2 binding activity at the double-positive stage of thymic development in the MHC class II-restricted model whereas in the MHC class I-restricted model IRF-1/IRF-2 activity is induced weakly. At the single-positive stage, antigen induces the IRF-1/IRF-2 DNA binding in both CD4+ and CD8+ thymocytes, but not in mature lymphocytes from the periphery. This pattern of expression suggests that IRF-1/IRF-2 binding activities resulting from antigen stimulation are developmentally regulated. No evidence for a selective role of IRF-1 in the development of the CD8+ lineage was found, however.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Driggers P. H., Ennist D. L., Gleason S. L., Mak W. H., Marks M. S., Levi B. Z., Flanagan J. R., Appella E., Ozato K. An interferon gamma-regulated protein that binds the interferon-inducible enhancer element of major histocompatibility complex class I genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3743–3747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Sakakibara J., Sudo Y., Miyamoto M., Kimura Y., Taniguchi T. Evidence for a nuclear factor(s), IRF-1, mediating induction and silencing properties to human IFN-beta gene regulatory elements. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3397–3405. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03213.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada H., Fujita T., Miyamoto M., Kimura Y., Maruyama M., Furia A., Miyata T., Taniguchi T. Structurally similar but functionally distinct factors, IRF-1 and IRF-2, bind to the same regulatory elements of IFN and IFN-inducible genes. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada H., Kitagawa M., Tanaka N., Yamamoto H., Harada K., Ishihara M., Taniguchi T. Anti-oncogenic and oncogenic potentials of interferon regulatory factors-1 and -2. Science. 1993 Feb 12;259(5097):971–974. doi: 10.1126/science.8438157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada H., Willison K., Sakakibara J., Miyamoto M., Fujita T., Taniguchi T. Absence of the type I IFN system in EC cells: transcriptional activator (IRF-1) and repressor (IRF-2) genes are developmentally regulated. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90163-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho W. Y., Cooke M. P., Goodnow C. C., Davis M. M. Resting and anergic B cells are defective in CD28-dependent costimulation of naive CD4+ T cells. J Exp Med. 1994 May 1;179(5):1539–1549. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.5.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuida K., Lippke J. A., Ku G., Harding M. W., Livingston D. J., Su M. S., Flavell R. A. Altered cytokine export and apoptosis in mice deficient in interleukin-1 beta converting enzyme. Science. 1995 Mar 31;267(5206):2000–2003. doi: 10.1126/science.7535475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Grossman A., Mittrücker H. W., Siderovski D. P., Kiefer F., Kawakami T., Richardson C. D., Taniguchi T., Yoshinaga S. K., Mak T. W. Molecular cloning of LSIRF, a lymphoid-specific member of the interferon regulatory factor family that binds the interferon-stimulated response element (ISRE). Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Jun 25;23(12):2127–2136. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.12.2127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Kimura T., Kitagawa M., Pfeffer K., Kawakami T., Watanabe N., Kündig T. M., Amakawa R., Kishihara K., Wakeham A. Targeted disruption of IRF-1 or IRF-2 results in abnormal type I IFN gene induction and aberrant lymphocyte development. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):83–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N., Kanno Y., Hong C., Contursi C., Fujita T., Fowlkes B. J., O'Connell E., Hu-Li J., Paul W. E., Jankovic D. Expression of IFN regulatory factor family proteins in lymphocytes. Induction of Stat-1 and IFN consensus sequence binding protein expression by T cell activation. J Immunol. 1996 May 15;156(10):3711–3720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palombella V. J., Maniatis T. Inducible processing of interferon regulatory factor-2. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3325–3336. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrington J., Rogers N. C., Gewert D. R., Pine R., Veals S. A., Levy D. E., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. The interferon-stimulable response elements of two human genes detect overlapping sets of transcription factors. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Jun 15;214(3):617–626. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17961.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis L. F., Ruffner H., Stark G., Aguet M., Weissmann C. Mice devoid of interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF-1) show normal expression of type I interferon genes. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 17;13(20):4798–4806. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06805.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönrich G., Kalinke U., Momburg F., Malissen M., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M., Malissen B., Hämmerling G. J., Arnold B. Down-regulation of T cell receptors on self-reactive T cells as a novel mechanism for extrathymic tolerance induction. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):293–304. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90163-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman C. L., Marshall J. D., Von Boehmer H. Transgenic T cell receptor interactions in the lymphoproliferative and autoimmune syndromes of lpr and gld mutant mice. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Feb;22(2):499–504. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon A. K., Auphan N., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M. Developmental control of antigen-induced thymic transcription factors. Int Immunol. 1996 Sep;8(9):1421–1428. doi: 10.1093/intimm/8.9.1421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surh C. D., Sprent J. T-cell apoptosis detected in situ during positive and negative selection in the thymus. Nature. 1994 Nov 3;372(6501):100–103. doi: 10.1038/372100a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Tanaka M., Inazawa J., Abe T., Suda T., Nagata S. Human Fas ligand: gene structure, chromosomal location and species specificity. Int Immunol. 1994 Oct;6(10):1567–1574. doi: 10.1093/intimm/6.10.1567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura T., Ishihara M., Lamphier M. S., Tanaka N., Oishi I., Aizawa S., Matsuyama T., Mak T. W., Taki S., Taniguchi T. An IRF-1-dependent pathway of DNA damage-induced apoptosis in mitogen-activated T lymphocytes. Nature. 1995 Aug 17;376(6541):596–599. doi: 10.1038/376596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka N., Ishihara M., Kitagawa M., Harada H., Kimura T., Matsuyama T., Lamphier M. S., Aizawa S., Mak T. W., Taniguchi T. Cellular commitment to oncogene-induced transformation or apoptosis is dependent on the transcription factor IRF-1. Cell. 1994 Jun 17;77(6):829–839. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka N., Kawakami T., Taniguchi T. Recognition DNA sequences of interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF-1) and IRF-2, regulators of cell growth and the interferon system. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4531–4538. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe N., Sakakibara J., Hovanessian A. G., Taniguchi T., Fujita T. Activation of IFN-beta element by IRF-1 requires a posttranslational event in addition to IRF-1 synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4421–4428. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White L. C., Wright K. L., Felix N. J., Ruffner H., Reis L. F., Pine R., Ting J. P. Regulation of LMP2 and TAP1 genes by IRF-1 explains the paucity of CD8+ T cells in IRF-1-/- mice. Immunity. 1996 Oct;5(4):365–376. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80262-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteside S. T., Visvanathan K. V., Goodbourn S. Identification of novel factors that bind to the PRD I region of the human beta-interferon promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1531–1538. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan J., Shaham S., Ledoux S., Ellis H. M., Horvitz H. R. The C. elegans cell death gene ced-3 encodes a protein similar to mammalian interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):641–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90485-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Boehmer H. Thymic selection: a matter of life and death. Immunol Today. 1992 Nov;13(11):454–458. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90075-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]