Abstract
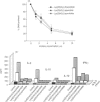
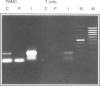
Various studies have shown that the membrane ectoenzyme dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DP IV; CD26), expressed on T, natural killer (NK) and B cells in the immune system, is involved in the regulation of DNA synthesis and cytokine production. We show that the specific DP IV inhibitors Lys[Z(NO2)]-thiazolidide, Lys[Z(NO2)]-piperidide, and Lys[Z(NO2)]-pyrrolidide inhibit DNA synthesis as well as production of interleukin-2 (IL-2), IL-10, IL-12, and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) of pokeweed mitogen (PWM)-stimulated purified T cells. Most importantly, these inhibitors induce a three- to fourfold increased secretion of latent transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) by PWM-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and T cells, as measured with a specific TGF-beta 1 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and in the Mv1Lu bioassay. As we could demonstrate previously, TGF-beta 1 exhibits the same inhibitory effects as DP IV inhibitors on DNA synthesis and cytokine production (Cytokine 1994, 6, 382-8; J Interferon Cytokine Res 1995, 15, 685-90). A neutralizing chicken anti-TGF-beta 1 antibody was capable of abolishing the DP IV inhibitor-induced suppression of DNA synthesis of PWM-stimulated PBMC and T cells. These data suggest that TGF-beta 1 might have key functions in the molecular action of DP IV/CD26 in regulation of DNA synthesis and cytokine production.
Full text
PDF


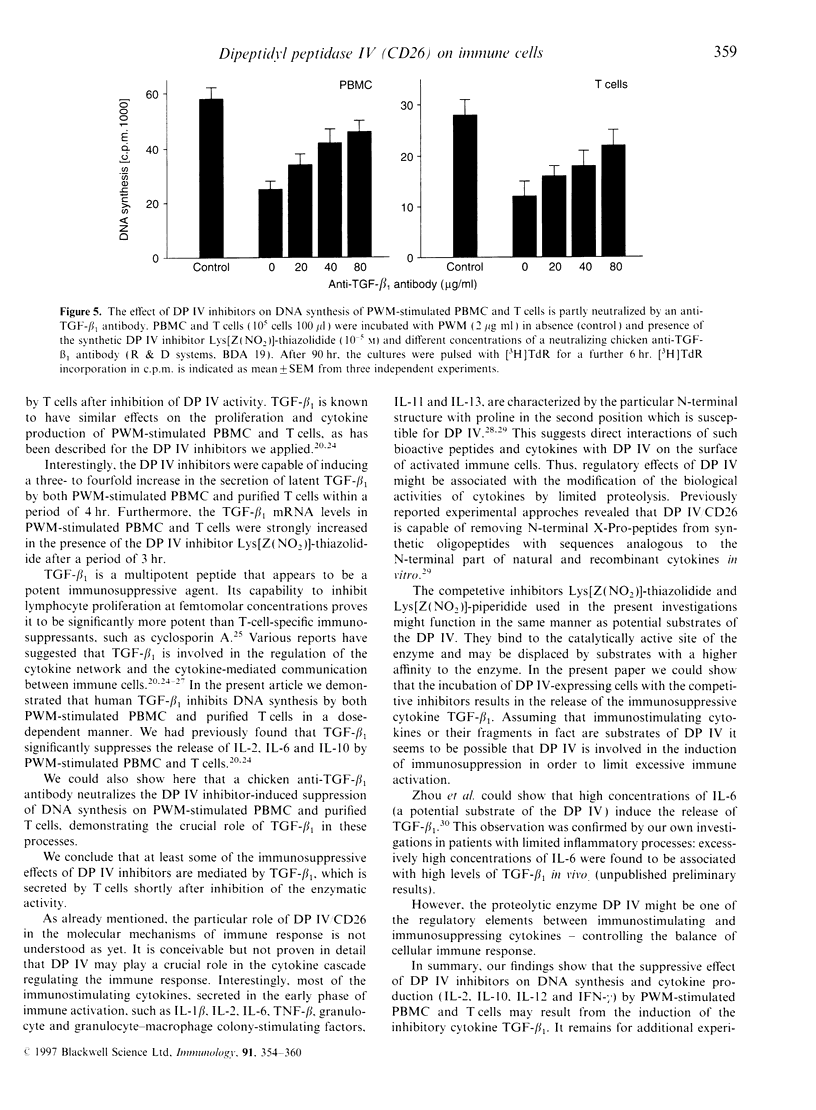

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ansorge S., Schön E., Kunz D. Membrane-bound peptidases of lymphocytes: functional implications. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1991;50(4-6):799–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bühling F., Junker U., Reinhold D., Neubert K., Jäger L., Ansorge S. Functional role of CD26 on human B lymphocytes. Immunol Lett. 1995 Feb;45(1-2):47–51. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(94)00230-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bühling F., Kunz D., Reinhold D., Ulmer A. J., Ernst M., Flad H. D., Ansorge S. Expression and functional role of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (CD26) on human natural killer cells. Nat Immun. 1994 Sep-Oct;13(5):270–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang N. H., Torimoto Y., Deusch K., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Comitogenic effect of solid-phase immobilized anti-1F7 on human CD4 T cell activation via CD3 and CD2 pathways. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 1;144(11):4092–4100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang N. H., Torimoto Y., Sugita K., Daley J. F., Schow P., Prado C., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Cell surface modulation of CD26 by anti-1F7 monoclonal antibody. Analysis of surface expression and human T cell activation. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):3963–3971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielpour D. Improved sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for transforming growth factor beta 1. J Immunol Methods. 1993 Jan 14;158(1):17–25. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(93)90254-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espevik T., Figari I. S., Ranges G. E., Palladino M. A., Jr Transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) and recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha reciprocally regulate the generation of lymphokine-activated killer cell activity. Comparison between natural porcine platelet-derived TGF-beta 1 and TGF-beta 2, and recombinant human TGF-beta 1. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2312–2316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espevik T., Waage A., Faxvaag A., Shalaby M. R. Regulation of interleukin-2 and interleukin-6 production from T-cells: involvement of interleukin-1 beta and transforming growth factor-beta. Cell Immunol. 1990 Mar;126(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90299-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B. CD26: a surface protease involved in T-cell activation. Immunol Today. 1994 Apr;15(4):180–184. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(94)90316-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann T., Faust J., Neubert K., Ansorge S. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV (CD 26) and aminopeptidase N (CD 13) catalyzed hydrolysis of cytokines and peptides with N-terminal cytokine sequences. FEBS Lett. 1993 Dec 20;336(1):61–64. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81609-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekow J., Wachsman W., McCutchan J. A., Gross W. L., Zachariah M., Carson D. A., Lotz M. Transforming growth factor-beta and suppression of humoral immune responses in HIV infection. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):1010–1016. doi: 10.1172/JCI115059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. Type beta transforming growth factor from feline sarcoma virus-transformed rat cells. Isolation and biological properties. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9756–9761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittrücker H. W., Steeg C., Malissen B., Fleischer B. The cytoplasmic tail of the T cell receptor zeta chain is required for signaling via CD26. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Jan;25(1):295–297. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Torimoto Y., Levinson G., Rudd C. E., Schrieber M., Dang N. H., Letvin N. L., Schlossman S. F. 1F7, a novel cell surface molecule, involved in helper function of CD4 cells. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 1;143(11):3430–3439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plana M., Viñas O., De la Calle-Martin O., Lozano F., Inglés-Esteve J., Romero M., Alberola-Ila J., Yagüe J., Vilella R., Vives J. Induction of interleukin 2 (IL 2) and interferon-gamma and enhancement of IL 2 receptor expression by a CD26 monoclonal antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Apr;21(4):1085–1088. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold D., Bank U., Bühling F., Kähne T., Kunt D., Faust J., Neubert K., Ansorge S. Inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DP IV, CD26) specifically suppress proliferation and modulate cytokine production of strongly CD26 expressing U937 cells. Immunobiology. 1994 Dec;192(1-2):121–136. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80412-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold D., Bank U., Bühling F., Lendeckel U., Ansorge S. Transforming growth factor beta 1 inhibits interleukin-10 mRNA expression and production in pokeweed mitogen-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells and T cells. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1995 Aug;15(8):685–690. doi: 10.1089/jir.1995.15.685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold D., Bank U., Bühling F., Lendeckel U., Ulmer A. J., Flad H. D., Ansorge S. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) inhibits DNA synthesis of PWM-stimulated PBMC via suppression of IL-2 and IL-6 production. Cytokine. 1994 Jul;6(4):382–388. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(94)90062-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold D., Bank U., Bühling F., Neubert K., Mattern T., Ulmer A. J., Flad H. D., Ansorge S. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV (CD26) on human lymphocytes. Synthetic inhibitors of and antibodies against dipeptidyl peptidase IV suppress the proliferation of pokeweed mitogen-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells, and IL-2 and IL-6 production. Immunobiology. 1993 Aug;188(4-5):403–414. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80223-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schön E., Born I., Demuth H. U., Faust J., Neubert K., Steinmetzer T., Barth A., Ansorge S. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV in the immune system. Effects of specific enzyme inhibitors on activity of dipeptidyl peptidase IV and proliferation of human lymphocytes. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1991 May;372(5):305–311. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1991.372.1.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schön E., Demuth H. U., Barth A., Ansorge S. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV of human lymphocytes. Evidence for specific hydrolysis of glycylproline p-nitroanilide in T-lymphocytes. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):255–258. doi: 10.1042/bj2230255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schön E., Demuth H. U., Eichmann E., Horst H. J., Körner I. J., Kopp J., Mattern T., Neubert K., Noll F., Ulmer A. J. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV in human T lymphocytes. Impaired induction of interleukin 2 and gamma interferon due to specific inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Feb;29(2):127–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schön E., Eichmann E., Grunow R., Jahn S., Kiessig S. T., Volk H. D., Ansorge S. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV in human T lymphocytes. An approach to the role of a membrane peptidase in the immune system. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1986;45(11-12):1523–1528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Kameoka J., Yaron A., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. The costimulatory activity of the CD26 antigen requires dipeptidyl peptidase IV enzymatic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4586–4590. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Hunt D. A., Wong H. L., Dougherty S., McCartney-Francis N., Wahl L. M., Ellingsworth L., Schmidt J. A., Hall G., Roberts A. B. Transforming growth factor-beta is a potent immunosuppressive agent that inhibits IL-1-dependent lymphocyte proliferation. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3026–3032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaron A., Naider F. Proline-dependent structural and biological properties of peptides and proteins. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1993;28(1):31–81. doi: 10.3109/10409239309082572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D., Munster A., Winchurch R. A. Pathologic concentrations of interleukin 6 inhibit T cell responses via induction of activation of TGF-beta. FASEB J. 1991 Aug;5(11):2582–2585. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.11.1868982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]