Abstract
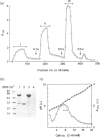
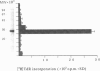
A superantigen (Streptococcus pyogenes mitogen-2; SPM-2) that stimulates human helper T cells bearing unique types of variable domains of T-cell receptor beta-chain (TCR V beta) was isolated from the culture supernatant of S. pyogenes strain T12. The active molecule isolated by diethylaminoethyl (DEAE)-cellulose chromatography and isoelectric focusing was a protein with a molecular weight (MW) of 29,000 and isoelectric point (pl) of 6.0. This new superantigen was found to activate preferentially V beta 4+, 7+, and 8+ T cells, whereas recombinant streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin A and C activated V beta 12+ and V beta 2+ T cells, respectively, as determined by flow cytometry and reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) methods. This proliferative response was significantly inhibited by anti-HLA-DR monoclonal antibody, and required paraformaldehyde-fixed antigen-presenting cells (APC), indicating that this action is dependent on major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules without processing. Analysis of the amino-terminal amino acid sequence of the molecule failed to find any identical or significantly homologous proteins. We have previously reported that cytoplasmic membrane-associated protein (CAP), a streptococcal superantigen isolated from the cell membranes of S. pyogenes T12 strain, stimulated mainly V beta 8+ T cells. Both SPM-2 and CAP preferentially stimulated helper T cells, and rabbit antiserum against SPM-2 completely neutralized the T-cell-stimulating activities of CAP, suggesting that SPM-2 and CAP belong to a family of streptococcal mitogenic proteins. The SPM-2 activity with stimulation of V beta 8+ T cells was detected extensively in the culture fluids of group A streptococci, but not in those of other streptococcal species, including groups B and D streptococci, and most of the activities detected were completely inhibited by anti-SPM-2 serum. These results indicate that SPM-2 may be a newly discovered superantigen molecule, which can be commonly synthesized by group A streptococci.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe J., Forrester J., Nakahara T., Lafferty J. A., Kotzin B. L., Leung D. Y. Selective stimulation of human T cells with streptococcal erythrogenic toxins A and B. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 1;146(11):3747–3750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abo T., Sugawara S., Amenomori A., Itoh H., Rikiishi H., Moro I., Kumagai K. Selective phagocytosis of gram-positive bacteria and interleukin 1-like factor production by a subpopulation of large granular lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 May 1;136(9):3189–3197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun M. A., Gerlach D., Hartwig U. F., Ozegowski J. H., Romagné F., Carrel S., Köhler W., Fleischer B. Stimulation of human T cells by streptococcal "superantigen" erythrogenic toxins (scarlet fever toxins). J Immunol. 1993 Mar 15;150(6):2457–2466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone L. A., Woodard D. R., Schlievert P. M., Tomory G. S. Clinical and bacteriologic observations of a toxic shock-like syndrome due to Streptococcus pyogenes. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 16;317(3):146–149. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707163170305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B., Gerardy-Schahn R., Metzroth B., Carrel S., Gerlach D., Köhler W. An evolutionary conserved mechanism of T cell activation by microbial toxins. Evidence for different affinities of T cell receptor-toxin interaction. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):11–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goshorn S. C., Schlievert P. M. Nucleotide sequence of streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin type C. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2518–2520. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2518-2520.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Satoh H., Isono N., Rikiishi H., Kumagai K. Mechanism of stimulation of T cells by Streptococcus pyogenes: isolation of a major mitogenic factor, cytoplasmic membrane-associated protein. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3128–3135. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3128-3135.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. P., Schlievert P. M. Group A streptococcal phage T12 carries the structural gene for pyrogenic exotoxin type A. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;194(1-2):52–56. doi: 10.1007/BF00383496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. P., Tomai M. A., Schlievert P. M. Bacteriophage involvement in group A streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin A production. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):623–627. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.623-627.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leggiadro R. J., Bugnitz M. C., Peck B. A., Luedtke G. S., Kim M. H., Kaplan E. L., Schlievert P. M. Group A streptococcal bacteremia in a mid-south children's hospital. South Med J. 1993 Jun;86(6):615–618. doi: 10.1097/00007611-199306000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollick J. A., Miller G. G., Musser J. M., Cook R. G., Grossman D., Rich R. R. A novel superantigen isolated from pathogenic strains of Streptococcus pyogenes with aminoterminal homology to staphylococcal enterotoxins B and C. J Clin Invest. 1993 Aug;92(2):710–719. doi: 10.1172/JCI116641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno J., Lipsky P. E. Differential ability of fixed antigen-presenting cells to stimulate nominal antigen-reactive and alloreactive T4 lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3579–3587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemoto E., Rikiishi H., Sugawara S., Okamoto S., Tamura K., Maruyama Y., Kumagai K. Isolation of a new superantigen with potent mitogenic activity to murine T cells from Streptococcus pyogenes. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1996 Sep;15(2-3):81–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.1996.tb00057.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby-Teglund A., Newton D., Kotb M., Holm S. E., Norgren M. Superantigenic properties of the group A streptococcal exotoxin SpeF (MF). Infect Immun. 1994 Dec;62(12):5227–5233. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.12.5227-5233.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Itoh T., Rikiishi H., Kumagai K. Cytoplasmic membrane-associated protein (CAP) isolated from Streptococcus pyogenes: as a new bacterial superantigen. Microbiol Immunol. 1994;38(2):139–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1994.tb01755.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt K. H., Gerlach D., Wollweber L., Reichardt W., Mann K., Ozegowski J. H., Fleischer B. Mitogenicity of M5 protein extracted from Streptococcus pyogenes cells is due to streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin C and mitogenic factor MF. Infect Immun. 1995 Dec;63(12):4569–4575. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.12.4569-4575.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senitzer D., Freimer E. H. Autoimmune mechanisms in the pathogenesis of rheumatic fever. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Nov-Dec;6(6):832–839. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.6.832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. L. Invasive group A streptococcus infections. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;14(1):2–11. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.1.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. L., Tanner M. H., Winship J., Swarts R., Ries K. M., Schlievert P. M., Kaplan E. Severe group A streptococcal infections associated with a toxic shock-like syndrome and scarlet fever toxin A. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jul 6;321(1):1–7. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198907063210101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomai M. A., Schlievert P. M., Kotb M. Distinct T-cell receptor V beta gene usage by human T lymphocytes stimulated with the streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxins and pep M5 protein. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):701–705. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.701-705.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe-Ohnishi R., Aelion J., LeGros L., Tomai M. A., Sokurenko E. V., Newton D., Takahara J., Irino S., Rashed S., Kotb M. Characterization of unique human TCR V beta specificities for a family of streptococcal superantigens represented by rheumatogenic serotypes of M protein. J Immunol. 1994 Feb 15;152(4):2066–2073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks C. R., Ferretti J. J. Nucleotide sequence of the type A streptococcal exotoxin (erythrogenic toxin) gene from Streptococcus pyogenes bacteriophage T12. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):144–150. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.144-150.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. E., Ferretti J. J. Frequency of the erythrogenic toxin B and C genes (speB and speC) among clinical isolates of group A streptococci. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):211–215. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.211-215.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. E., Ferretti J. J. Molecular epidemiologic analysis of the type A streptococcal exotoxin (erythrogenic toxin) gene (speA) in clinical Streptococcus pyogenes strains. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3715–3719. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3715-3719.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]