Abstract
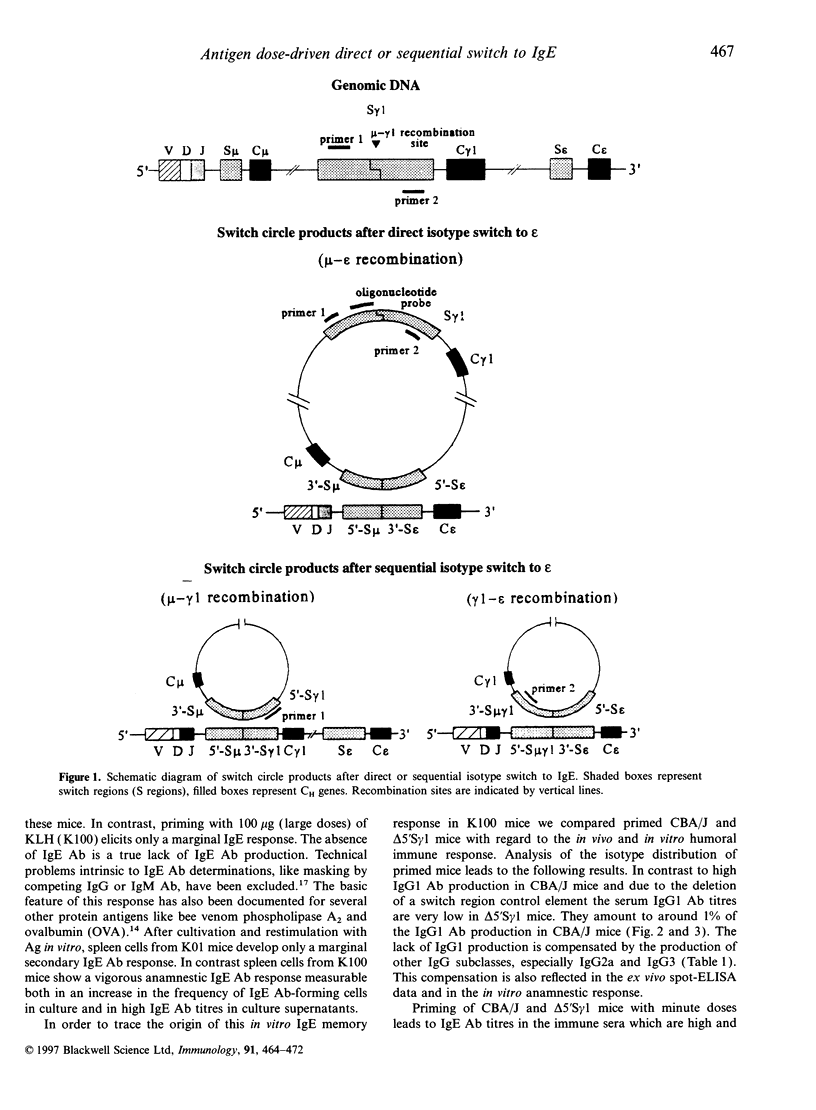
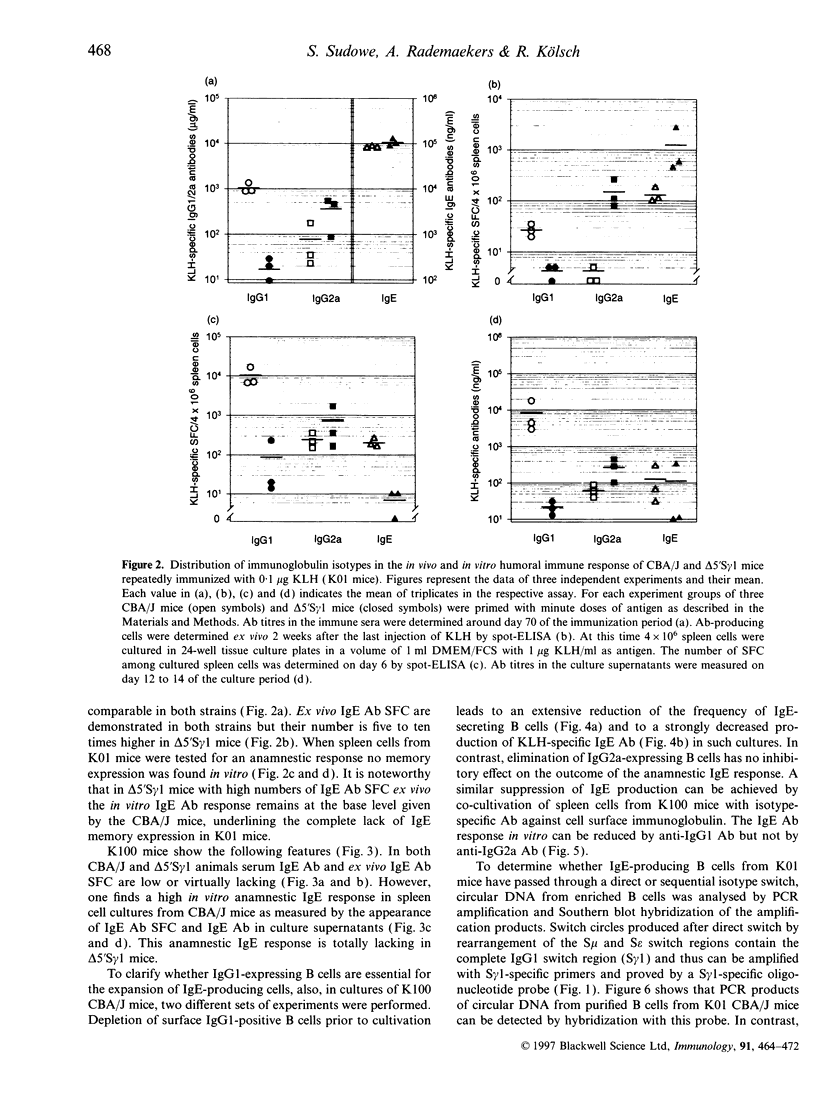
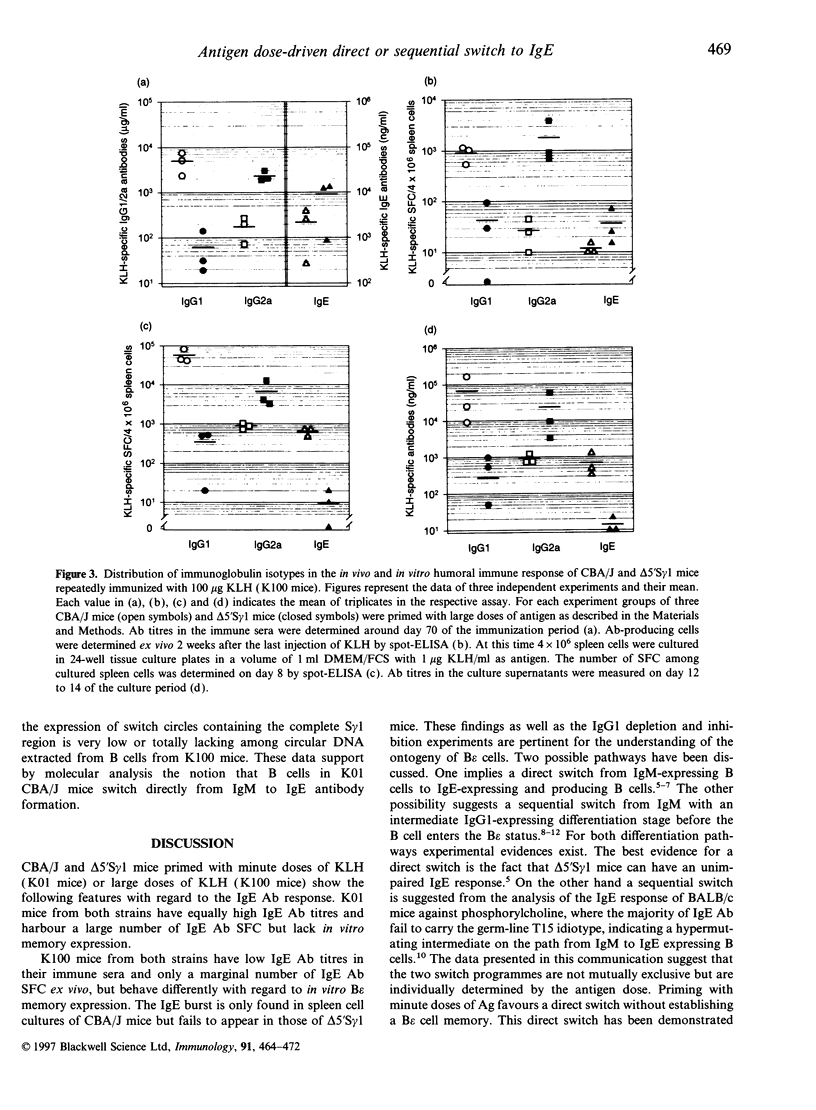
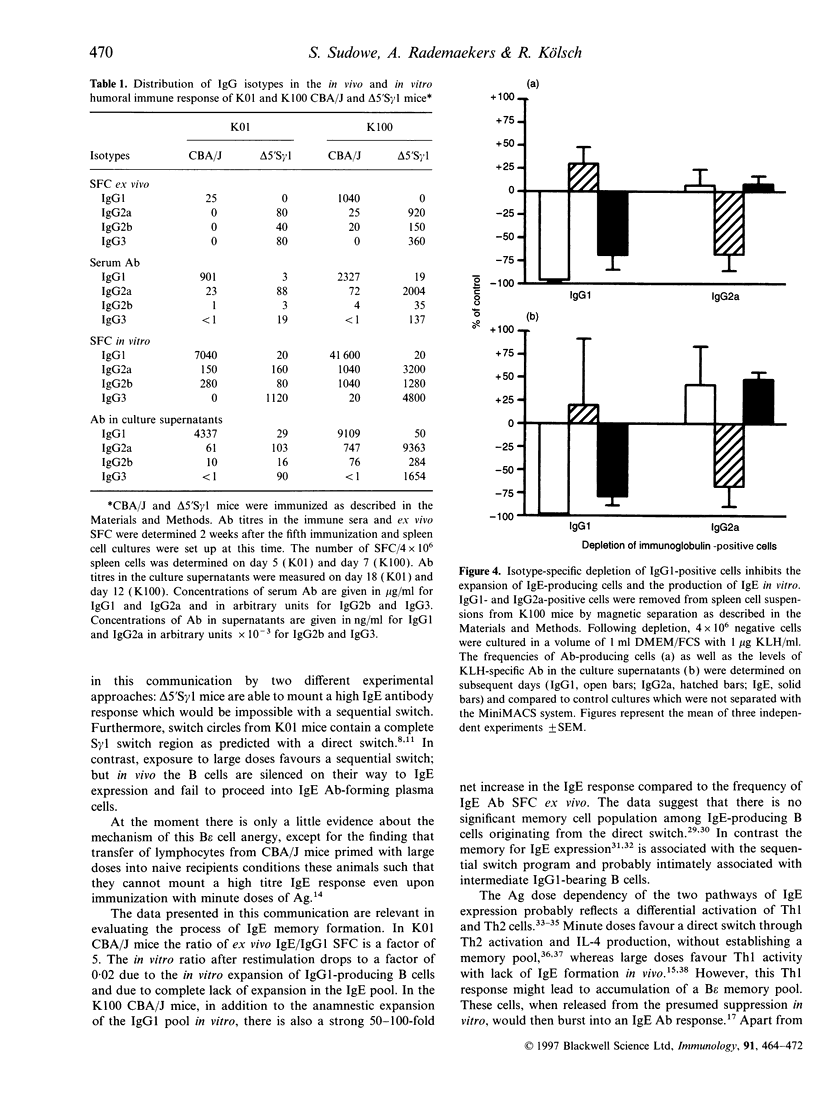
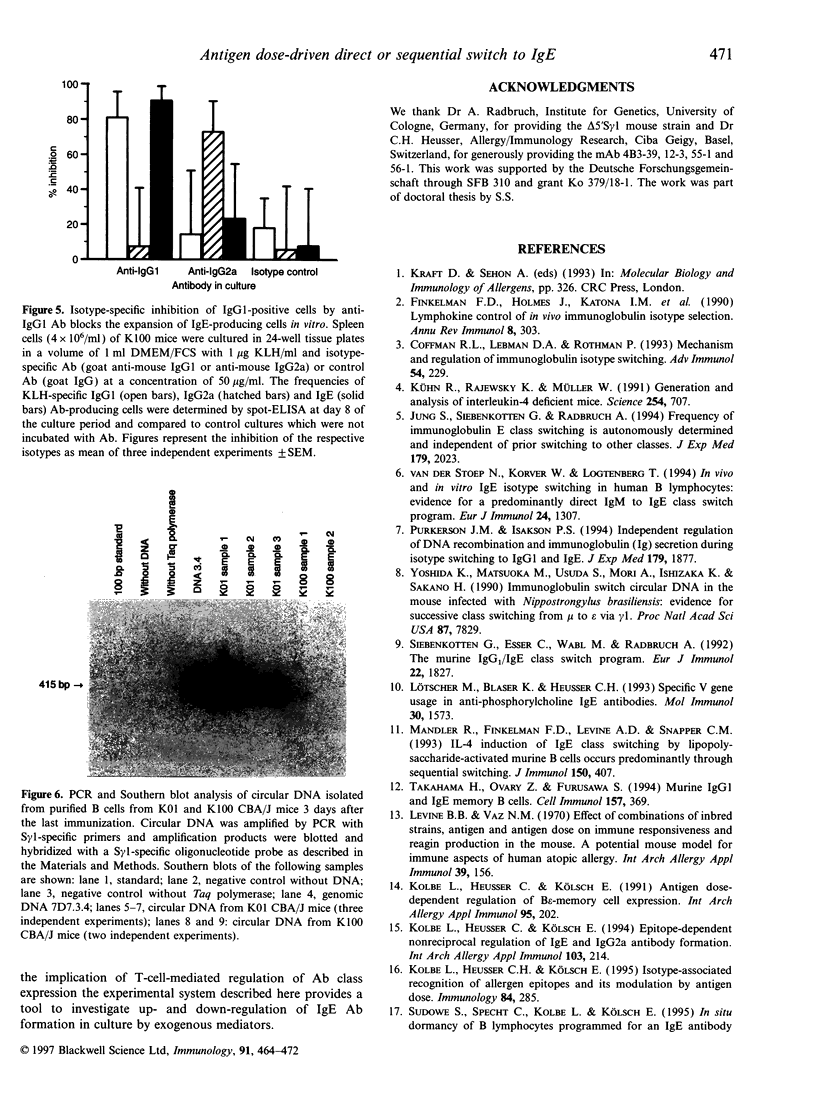
Priming of CBA/J mice with minute doses of protein antigens (Ag) leads to high IgE antibody (Ab) titres in the immune sera of these animals. In contrast priming with large doses elicits only a marginal production of IgE Ab. In vitro restimulation of spleen cells from animals primed with large doses and lacking in vivo IgE Ab leads to a burst of IgE Ab-forming cells. This in vitro anamnestic response is lacking in mice primed with minute doses of Ag. In order to trace the cellular basis of the in vitro IgE memory response we have extended the analysis of the distribution of Ab isotypes to Ag-primed IgG1-deficient delta 5'S gamma 1 mice. The data presented here must be interpreted as followed. Priming of mice with minute doses of Ag leads to a direct switch from IgM to IgE Ab expression in both strains. These animals have high IgE Ab titres without establishing an IgE memory. The direct switch was verified by polymerase chain reaction and Southern blot analysis of switch circle DNA isolated from Ag-specific B cells of CBA/J mice primed with minute doses of Ag. In contrast to immunization with minute doses, priming with large doses of Ag fails to induce in vivo IgE Ab production in CBA/J and delta 5'S gamma 1 mice but establishes a B epsilon memory in CBA/J mice which involves IgG1-bearing intermediate B cells. In vivo these B epsilon memory cells do not enter the status of IgE Ab-producing cells. In vitro they can be released from this anergy and presumed suppression and develop in an anamnestic response into a large population of IgE Ab-forming B cells. This increase in the number of IgE Ab-producing cells after restimulation in vitro is lacking in delta 5'S gamma 1 mice, apparently because of their inability to generate IgG1-expressing precursor cells. The notion of a sequential switch and an IgG1 intermediate B epsilon memory status is also supported by depletion and inhibition experiments. Elimination of IgG1-expressing B cells in CBA/J mice primed with high doses of Ag prevents the IgE Ab burst after in vitro challenge with Ag. The data further suggest that the two switch pathways are not mutually exclusive and that the Ag dose can decide which pathway is preferentially used.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaser K., Heusser C. H. The IgE antibody response to the phosphorylcholine hapten. Int Rev Immunol. 1987 Jan;2(1):93–115. doi: 10.3109/08830188709044749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann V., Heusser C. H. T cell-dependent differentiation of human B cells into IgM, IgG, IgA, or IgE plasma cells: high rate of antibody production by IgE plasma cells, but limited clonal expansion of IgE precursors. Cell Immunol. 1993 Dec;152(2):323–332. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1993.1294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Lebman D. A., Rothman P. Mechanism and regulation of immunoglobulin isotype switching. Adv Immunol. 1993;54:229–270. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60536-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeKruyff R. H., Fang Y., Umetsu D. T. IL-4 synthesis by in vivo primed keyhole limpet hemocyanin-specific CD4+ T cells. I. Influence of antigen concentration and antigen-presenting cell type. J Immunol. 1992 Dec 1;149(11):3468–3476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelman F. D., Holmes J., Katona I. M., Urban J. F., Jr, Beckmann M. P., Park L. S., Schooley K. A., Coffman R. L., Mosmann T. R., Paul W. E. Lymphokine control of in vivo immunoglobulin isotype selection. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:303–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.001511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin B. E., Björck E., Bjursell G., Lindahl T. Sequence complexity of circular Epstein-Bar virus DNA in transformed cells. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):11–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.11-19.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltke H. J., Sagner G., Kessler C., Schmitz G. Sensitive chemiluminescent detection of digoxigenin-labeled nucleic acids: a fast and simple protocol and its applications. Biotechniques. 1992 Jan;12(1):104–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung S., Rajewsky K., Radbruch A. Shutdown of class switch recombination by deletion of a switch region control element. Science. 1993 Feb 12;259(5097):984–987. doi: 10.1126/science.8438159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung S., Siebenkotten G., Radbruch A. Frequency of immunoglobulin E class switching is autonomously determined and independent of prior switching to other classes. J Exp Med. 1994 Jun 1;179(6):2023–2026. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.6.2023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Kawakami T., Takahashi N., Honjo T. Rearrangement of immunoglobulin gamma 1-chain gene and mechanism for heavy-chain class switch. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):919–923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katona I. M., Urban J. F., Jr, Kang S. S., Paul W. E., Finkelman F. D. IL-4 requirements for the generation of secondary in vivo IgE responses. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 15;146(12):4215–4221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolbe L., Heusser C. H., Kölsch E. Isotype-associated recognition of allergen epitopes and its modulation by antigen dose. Immunology. 1995 Feb;84(2):285–289. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolbe L., Heusser C., Kölsch E. Antigen dose-dependent regulation of B epsilon-memory cell expression. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1991;95(2-3):202–206. doi: 10.1159/000235430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolbe L., Heusser C., Kölsch E. Epitope-dependent nonreciprocal regulation of IgE and IgG2a antibody formation. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1994;103(2):214–216. doi: 10.1159/000236630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn R., Rajewsky K., Müller W. Generation and analysis of interleukin-4 deficient mice. Science. 1991 Nov 1;254(5032):707–710. doi: 10.1126/science.1948049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Gros G., Schultze N., Walti S., Einsle K., Finkelman F., Kosco-Vilbois M. H., Heusser C. The development of IgE+ memory B cells following primary IgE immune responses. Eur J Immunol. 1996 Dec;26(12):3042–3047. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830261233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledermann F., Schlienger C., Wagner K., Heusser C. A sensitive and efficient induction system for murine IgE. Single cell analysis at the clonal level. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Aug 9;141(2):263–275. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B. B., Vaz N. M. Effect of combinations of inbred strain, antigen, and antigen dose on immune responsiveness and reagin production in the mouse. A potential mouse model for immune aspects of human atopic allergy. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;39(2-3):156–171. doi: 10.1159/000230343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lötscher M., Amstutz H., Heusser C. H., Blaser K. Fine specificity and heavy chain V gene usage of antibodies to the phosphorylcholine hapten. Mol Immunol. 1990 Apr;27(4):369–378. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(90)90050-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lötscher M., Blaser K., Heusser C. H. Specific V gene usage in anti-phosphorylcholine IgE antibodies. Mol Immunol. 1993 Dec;30(17):1573–1582. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(93)90448-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandler R., Finkelman F. D., Levine A. D., Snapper C. M. IL-4 induction of IgE class switching by lipopolysaccharide-activated murine B cells occurs predominantly through sequential switching. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 15;150(2):407–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcelletti J. F., Katz D. H. Antigen concentration determines helper T cell subset participation in IgE antibody responses. Cell Immunol. 1992 Sep;143(2):405–419. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(92)90036-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Coffman R. L. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer C., Stein J., Southwood S., Ketelaar H., Sette A., Bottomly K. Altered peptide ligands can control CD4 T lymphocyte differentiation in vivo. J Exp Med. 1995 Apr 1;181(4):1569–1574. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.4.1569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purkerson J. M., Isakson P. C. Independent regulation of DNA recombination and immunoglobulin (Ig) secretion during isotype switching to IgG1 and IgE. J Exp Med. 1994 Jun 1;179(6):1877–1883. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.6.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz G. G., Walter T., Seibl R., Kessler C. Nonradioactive labeling of oligonucleotides in vitro with the hapten digoxigenin by tailing with terminal transferase. Anal Biochem. 1991 Jan;192(1):222–231. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90212-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Secrist H., DeKruyff R. H., Umetsu D. T. Interleukin 4 production by CD4+ T cells from allergic individuals is modulated by antigen concentration and antigen-presenting cell type. J Exp Med. 1995 Mar 1;181(3):1081–1089. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.3.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick J. D., Czerkinsky C. Detection of cell-surface molecules, secreted products of single cells and cellular proliferation by enzyme immunoassay. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Jun 24;150(1-2):159–175. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(92)90075-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenkotten G., Esser C., Wabl M., Radbruch A. The murine IgG1/IgE class switch program. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jul;22(7):1827–1834. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stäb F., Austrup F., Kölsch E. Regulation of the anti-alpha(1----3) dextran IgG antibody response of BALB/c mice by idiotype-specific T suppressor lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):53–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahama H., Ovary Z., Furusawa S. Murine IgG1 and IgE memory B cells. Cell Immunol. 1994 Sep;157(2):369–380. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1994.1234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu P., Ward R. E. Ig repertoire expression of BALB/c primary and secondary B cell precursors specific for phosphorylcholine. J Immunol. 1993 May 1;150(9):3862–3872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada M., Nakazawa M., Kamata I., Arizono N. Low-level infection with the nematode Nippostrongylus brasiliensis induces significant and sustained specific and non-specific IgE antibody responses in rats. Immunology. 1992 Jan;75(1):36–40. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
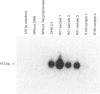
- Yoshida K., Matsuoka M., Usuda S., Mori A., Ishizaka K., Sakano H. Immunoglobulin switch circular DNA in the mouse infected with Nippostrongylus brasiliensis: evidence for successive class switching from mu to epsilon via gamma 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7829–7833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Stoep N., Korver W., Logtenberg T. In vivo and in vitro IgE isotype switching in human B lymphocytes: evidence for a predominantly direct IgM to IgE class switch program. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Jun;24(6):1307–1311. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]