Abstract
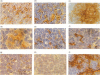
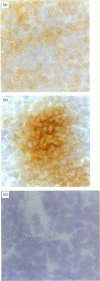
The network of thymic epithelium contributes significantly to the thymic stromal cell environment, which plays a vital role in the generation and maturation of thymocytes. Monoclonal antibodies (mAb) have revealed considerable heterogeneity within this epithelial component of the mouse thymic microenvironment, but many of these antibodies recognize epitopes that are located inside the cell and so cannot be used in functional studies. As an alternative approach to isolate antibodies specific to thymic epithelium, we used a phage display library expressing single chain Fv antibodies. For selection, a thymic cell suspension was incubated with the phage display library, and major histocompatibility complex class II positive cells, the majority of which are epithelial, were then specifically selected. Phage bound to these cells were eluted and the selection procedure was repeated for a further five rounds. Immunohistochemical analysis revealed that these phage antibodies show differential staining of thymic epithelial subsets. Flow cytometric analysis of a thymic epithelial cell line using a panel of these antibodies demonstrated that they recognize epitopes on the cell surface. Furthermore, some of these antibodies also labelled human thymic epithelium, suggesting that the epitopes recognized by these antibodies are conserved between human and rodent thymus. Our approach therefore provides a rapid method to select antibodies specific for thymic epithelial cell surface determinants in their native configuration.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson G., Moore N. C., Owen J. J., Jenkinson E. J. Cellular interactions in thymocyte development. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:73–99. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.14.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson G., Owen J. J., Moore N. C., Jenkinson E. J. Thymic epithelial cells provide unique signals for positive selection of CD4+CD8+ thymocytes in vitro. J Exp Med. 1994 Jun 1;179(6):2027–2031. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.6.2027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya A., Dorf M. E., Springer T. A. A shared alloantigenic determinant on Ia antigens encoded by the I-A and I-E subregions: evidence for I region gene duplication. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2488–2495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd R. L., Tucek C. L., Godfrey D. I., Izon D. J., Wilson T. J., Davidson N. J., Bean A. G., Ladyman H. M., Ritter M. A., Hugo P. The thymic microenvironment. Immunol Today. 1993 Sep;14(9):445–459. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90248-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condra J. H., Sardana V. V., Tomassini J. E., Schlabach A. J., Davies M. E., Lineberger D. W., Graham D. J., Gotlib L., Colonno R. J. Bacterial expression of antibody fragments that block human rhinovirus infection of cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2292–2295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr A. G., Anderson S. K., Marrack P., Kappler J. Expression of antigen-specific, major histocompatibility complex-restricted receptors by cortical and medullary thymocytes in situ. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):543–550. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90183-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink P. J., Bevan M. J. Positive selection of thymocytes. Adv Immunol. 1995;59:99–133. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60630-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. G., Larsson L., Goff L. K., Restall D. E., Happerfield L., Merkenschlager M. Human thymocyte development in mouse organ cultures. Int Immunol. 1990;2(6):571–578. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.6.571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George A. J., Titus J. A., Jost C. R., Kurucz I., Perez P., Andrew S. M., Nicholls P. J., Huston J. S., Segal D. M. Redirection of T cell-mediated cytotoxicity by a recombinant single-chain Fv molecule. J Immunol. 1994 Feb 15;152(4):1802–1811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey D. I., Izon D. J., Tucek C. L., Wilson T. J., Boyd R. L. The phenotypic heterogeneity of mouse thymic stromal cells. Immunology. 1990 May;70(1):66–74. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imami N., Ladyman H. M., Spanopoulou E., Ritter M. A. A novel adhesion molecule in the murine thymic microenvironment: functional and biochemical analysis. Dev Immunol. 1992;2(2):161–173. doi: 10.1155/1992/18016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kampinga J., Berges S., Boyd R. L., Brekelmans P., Colić M., van Ewijk W., Kendall M. D., Ladyman H., Nieuwenhuis P., Ritter M. A. Thymic epithelial antibodies: immunohistological analysis and introduction of nomenclature. Thymus. 1989;13(3-4):165–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanariou M., Huby R., Ladyman H., Colic M., Sivolapenko G., Lampert I., Ritter M. Immunosuppression with cyclosporin A alters the thymic microenvironment. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Nov;78(2):263–270. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A., Kang A. S., Bain J. D., Burton D. R., Barbas C. F., 3rd Antibodies without immunization. Science. 1992 Nov 20;258(5086):1313–1314. doi: 10.1126/science.1455226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks J. D., Hoogenboom H. R., Bonnert T. P., McCafferty J., Griffiths A. D., Winter G. By-passing immunization. Human antibodies from V-gene libraries displayed on phage. J Mol Biol. 1991 Dec 5;222(3):581–597. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90498-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks J. D., Ouwehand W. H., Bye J. M., Finnern R., Gorick B. D., Voak D., Thorpe S. J., Hughes-Jones N. C., Winter G. Human antibody fragments specific for human blood group antigens from a phage display library. Biotechnology (N Y) 1993 Oct;11(10):1145–1149. doi: 10.1038/nbt1093-1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabarra B., Papiernik M. Phenotype of thymic stromal cells. An immunoelectron microscopic study with anti-IA, anti-MAC-1, and anti-MAC-2 antibodies. Lab Invest. 1988 May;58(5):524–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissim A., Hoogenboom H. R., Tomlinson I. M., Flynn G., Midgley C., Lane D., Winter G. Antibody fragments from a 'single pot' phage display library as immunochemical reagents. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 1;13(3):692–698. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06308.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer D. B., Viney J. L., Ritter M. A., Hayday A. C., Owen M. J. Expression of the alpha beta T-cell receptor is necessary for the generation of the thymic medulla. Dev Immunol. 1993;3(3):175–179. doi: 10.1155/1993/56290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plum J., De Smedt M., Defresne M. P., Leclercq G., Vandekerckhove B. Human CD34+ fetal liver stem cells differentiate to T cells in a mouse thymic microenvironment. Blood. 1994 Sep 1;84(5):1587–1593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritter M. A., Boyd R. L. Development in the thymus: it takes two to tango. Immunol Today. 1993 Sep;14(9):462–469. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90250-O. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spanopoulou E., Early A., Elliott J., Crispe N., Ladyman H., Ritter M., Watt S., Grosveld F., Kioussis D. Complex lymphoid and epithelial thymic tumours in Thy1-myc transgenic mice. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):185–189. doi: 10.1038/342185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ewijk W., Rouse R. V., Weissman I. L. Distribution of H-2 microenvironments in the mouse thymus. Immunoelectron microscopic identification of I-A and H-2K bearing cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Oct;28(10):1089–1099. doi: 10.1177/28.10.6999083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Vliet E., Melis M., Van Ewijk W. Monoclonal antibodies to stromal cell types of the mouse thymus. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Jun;14(6):524–529. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson R. W., Anderson G., Owen J. J., Jenkinson E. J. Positive selection of thymocytes involves sustained interactions with the thymic microenvironment. J Immunol. 1995 Dec 1;155(11):5234–5240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter G., Griffiths A. D., Hawkins R. E., Hoogenboom H. R. Making antibodies by phage display technology. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:433–455. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.002245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kruif J., Terstappen L., Boel E., Logtenberg T. Rapid selection of cell subpopulation-specific human monoclonal antibodies from a synthetic phage antibody library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 25;92(9):3938–3942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.9.3938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]