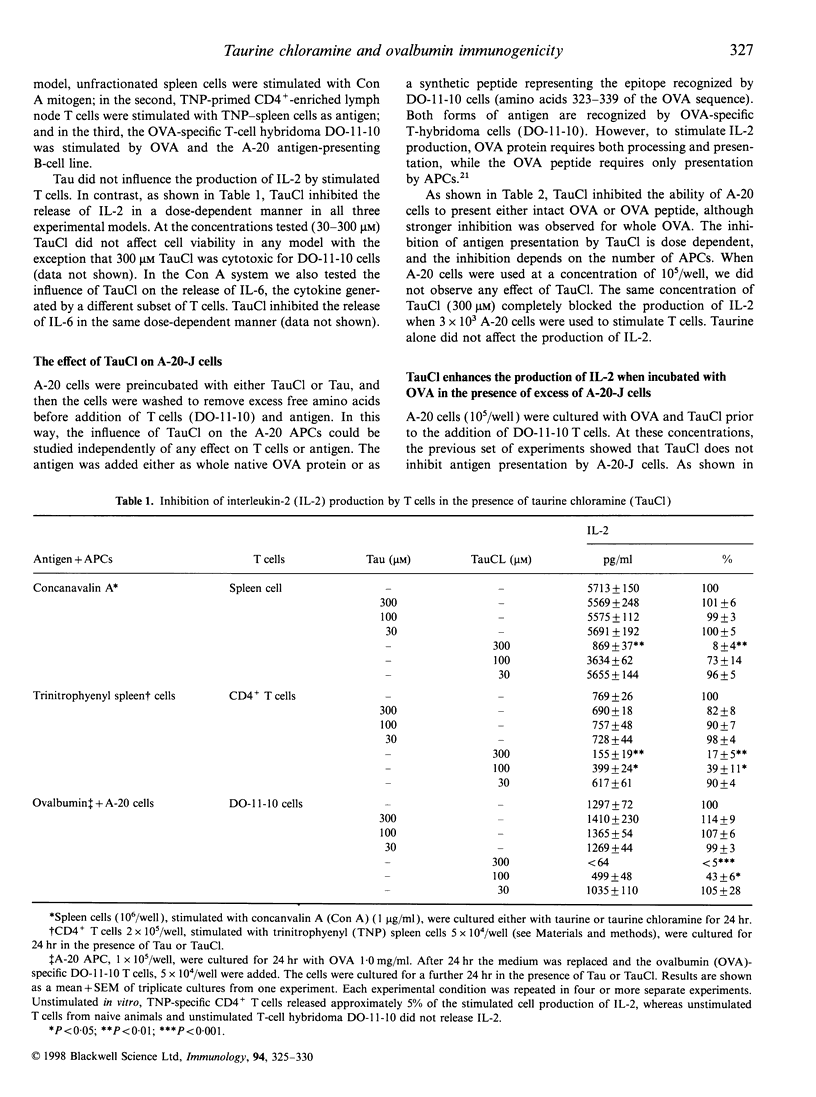
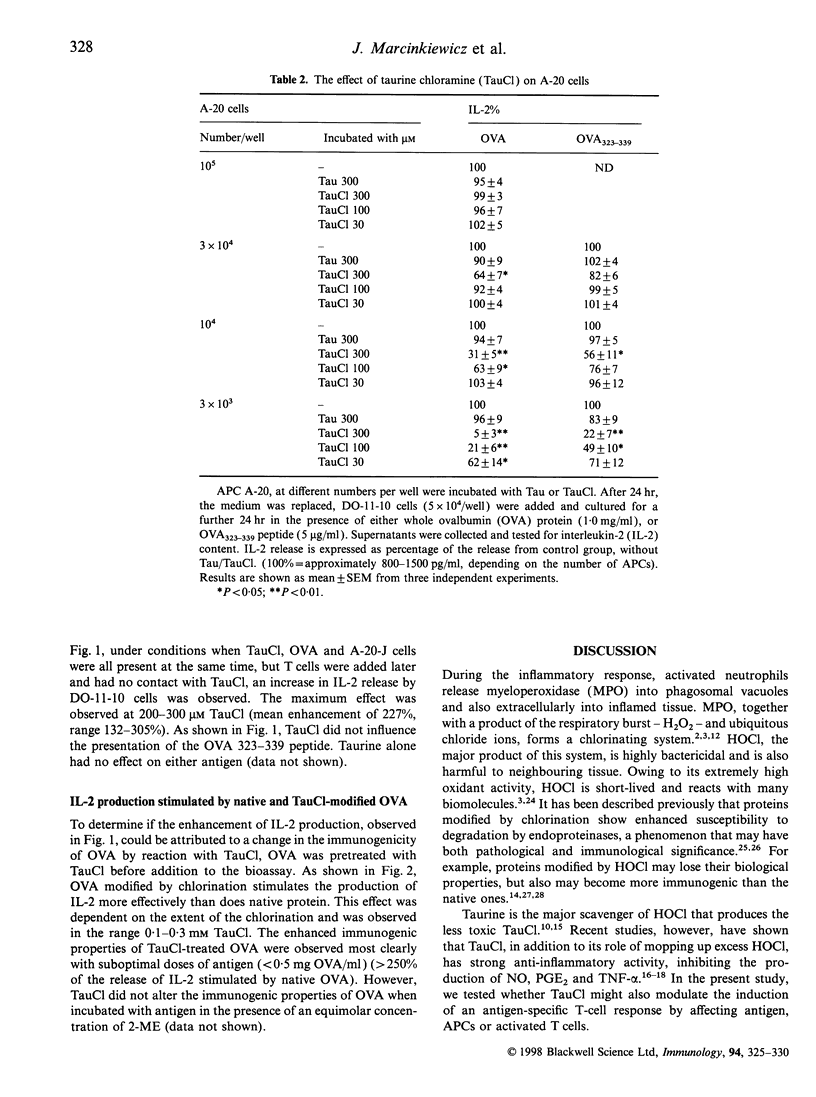
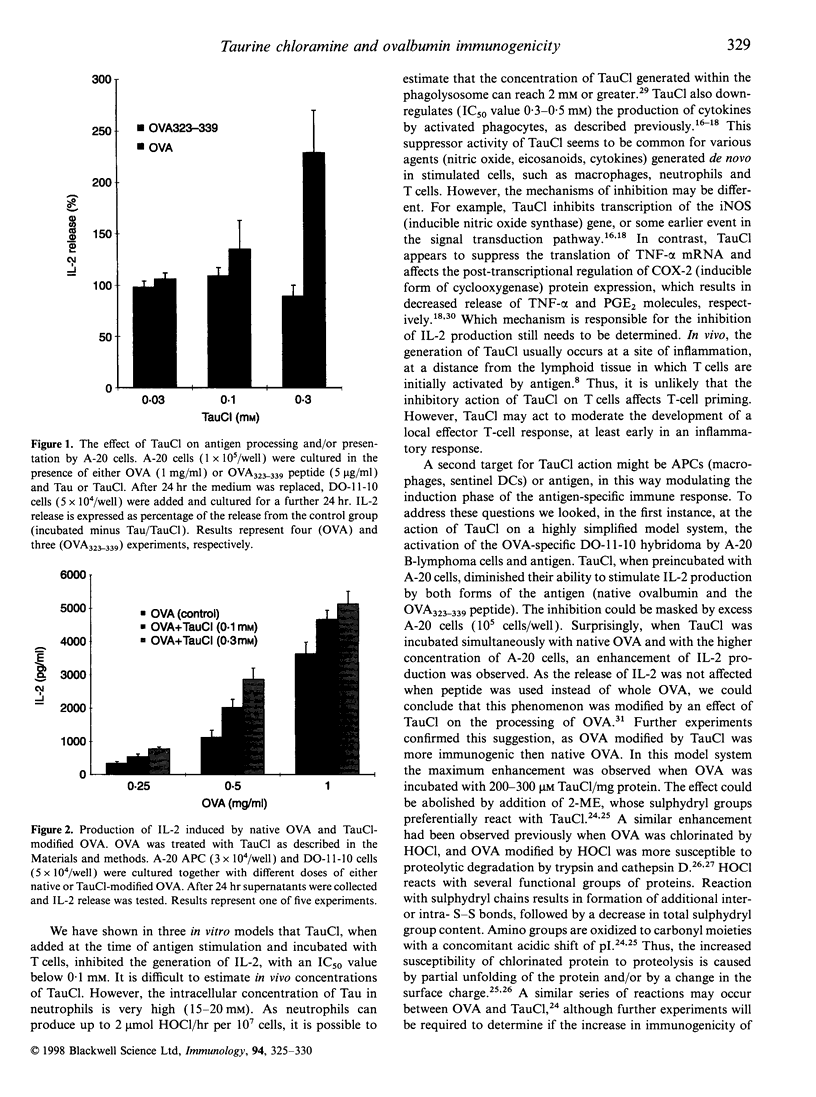
Abstract
Taurine chloramine (TauCl) is produced during inflammation by reaction of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) with taurine, the most abundant free amino acid in neutrophils. We previously reported that TauCl inhibits the generation of macrophage inflammatory mediators such as nitric oxide, prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). In this study, the activity of TauCl in modulating T-cell activation was investigated. Treatment of T cells with TauCl (0.1-0.3 mM), prior to activation, was found to inhibit interleukin-2 (IL-2) release in response to both mitogen and antigen stimulation. Similarly, pretreatment of A-20 antigen presenting cells (APCs), at low cell numbers, was found to inhibit their ability to process and present ovalbumin (OVA) to a specific T-cell hybridoma. In contrast, pretreatment of higher numbers of A-20 cells with TauCl in the presence of OVA enhanced subsequent presentation of OVA. Finally, OVA modified with TauCl was processed and presented more efficiently than native OVA. Thus, TauCl is able to modulate induction of a specific adaptive immune response at several independent points of the overall antigen-presenting pathway.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cantin A. M. Taurine modulation of hypochlorous acid-induced lung epithelial cell injury in vitro. Role of anion transport. J Clin Invest. 1994 Feb;93(2):606–614. doi: 10.1172/JCI117013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chain B. M., Kaye P. M., Shaw M. A. The biochemistry and cell biology of antigen processing. Immunol Rev. 1988 Dec;106:33–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00772.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claesson R., Karlsson M., Zhang Y., Carlsson J. Relative role of chloramines, hypochlorous acid, and proteases in the activation of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte collagenase. J Leukoc Biol. 1996 Nov;60(5):598–602. doi: 10.1002/jlb.60.5.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. J., Delsignore M. E., Lin S. W. Protein damage and degradation by oxygen radicals. II. Modification of amino acids. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9902–9907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim M. A., Chain B. M., Katz D. R. The injured cell: the role of the dendritic cell system as a sentinel receptor pathway. Immunol Today. 1995 Apr;16(4):181–186. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(95)80118-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Hamon C. B. Role of myeloperoxidase-mediated antimicrobial systems in intact leukocytes. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1972 Aug;12(2):170–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learn D. B., Fried V. A., Thomas E. L. Taurine and hypotaurine content of human leukocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 1990 Aug;48(2):174–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd A. R., Oppenheim J. J. Poly's lament: the neglected role of the polymorphonuclear neutrophil in the afferent limb of the immune response. Immunol Today. 1992 May;13(5):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90121-M. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcinkiewicz J., Chain B. M., Olszowska E., Olszowski S., Zgliczyński J. M. Enhancement of immunogenic properties of ovalbumin as a result of its chlorination. Int J Biochem. 1991;23(12):1393–1395. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(91)90280-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcinkiewicz J., Czajkowska B., Grabowska A., Kasprowicz A., Kociszewska B. Differential effects of chlorination of bacteria on their capacity to generate NO, TNF-alpha and IL-6 in macrophages. Immunology. 1994 Dec;83(4):611–616. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcinkiewicz J., Grabowska A., Bereta J., Stelmaszynska T. Taurine chloramine, a product of activated neutrophils, inhibits in vitro the generation of nitric oxide and other macrophage inflammatory mediators. J Leukoc Biol. 1995 Dec;58(6):667–674. doi: 10.1002/jlb.58.6.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcinkiewicz J., Grabowska A., Chain B. M. Is there a role for nitric oxide in regulation of T cell secretion of IL-2? J Immunol. 1996 Jun 15;156(12):4617–4621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcinkiewicz J. Neutrophil chloramines: missing links between innate and acquired immunity. Immunol Today. 1997 Dec;18(12):577–580. doi: 10.1016/s0167-5699(97)01161-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcinkiewicz J., Olszowska E., Olszowski S., Zgliczynski J. M. Enhancement of trinitrophenyl-specific humoral response to TNP proteins as the result of carrier chlorination. Immunology. 1992 Jul;76(3):385–388. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olszowska E., Olszowski S., Zgliczyński J. M., Stelmaszyńska T. Enhancement of proteinase-mediated degradation of proteins modified by chlorination. Int J Biochem. 1989;21(7):799–805. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(89)90213-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olszowski S., Olszowska E., Stelmaszyńska T., Krawczyk A., Marcinkiewicz J., Baczek N. Oxidative modification of ovalbumin. Acta Biochim Pol. 1996;43(4):661–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park E., Quinn M. R., Wright C. E., Schuller-Levis G. Taurine chloramine inhibits the synthesis of nitric oxide and the release of tumor necrosis factor in activated RAW 264.7 cells. J Leukoc Biol. 1993 Aug;54(2):119–124. doi: 10.1002/jlb.54.2.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park E., Schuller-Levis G., Quinn M. R. Taurine chloramine inhibits production of nitric oxide and TNF-alpha in activated RAW 264.7 cells by mechanisms that involve transcriptional and translational events. J Immunol. 1995 May 1;154(9):4778–4784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn M. R., Park E., Schuller-Levis G. Taurine chloramine inhibits prostaglandin E2 production in activated RAW 264.7 cells by post-transcriptional effects on inducible cyclooxygenase expression. Immunol Lett. 1996 May;50(3):185–188. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(96)02542-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimonkevitz R., Kappler J., Marrack P., Grey H. Antigen recognition by H-2-restricted T cells. I. Cell-free antigen processing. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):303–316. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. A. Neutrophils, host defense, and inflammation: a double-edged sword. J Leukoc Biol. 1994 Dec;56(6):672–686. doi: 10.1002/jlb.56.6.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stapleton P. P., Redmond H. P., Bouchier-Hayes D. J. Taurine and inflammation--a new approach to an old problem? J Leukoc Biol. 1997 Feb;61(2):231–232. doi: 10.1002/jlb.61.2.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M. The dendritic cell system and its role in immunogenicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:271–296. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.001415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada H., Shiho O., Kuroshima K., Koyama M., Tsukamoto K. An improved colorimetric assay for interleukin 2. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Nov 6;93(2):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90183-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L., Grisham M. B., Jefferson M. M. Preparation and characterization of chloramines. Methods Enzymol. 1986;132:569–585. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(86)32042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L. Myeloperoxidase-hydrogen peroxide-chloride antimicrobial system: effect of exogenous amines on antibacterial action against Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):110–116. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.110-116.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Klein R., Slivka A., Wei M. Chlorination of taurine by human neutrophils. Evidence for hypochlorous acid generation. J Clin Invest. 1982 Sep;70(3):598–607. doi: 10.1172/JCI110652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J. Tissue destruction by neutrophils. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 9;320(6):365–376. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902093200606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. E., Tallan H. H., Lin Y. Y., Gaull G. E. Taurine: biological update. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:427–453. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zgliczyński J. M., Stelmaszyńska T., Domański J., Ostrowski W. Chloramines as intermediates of oxidation reaction of amino acids by myeloperoxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 16;235(3):419–424. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90281-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


