Abstract
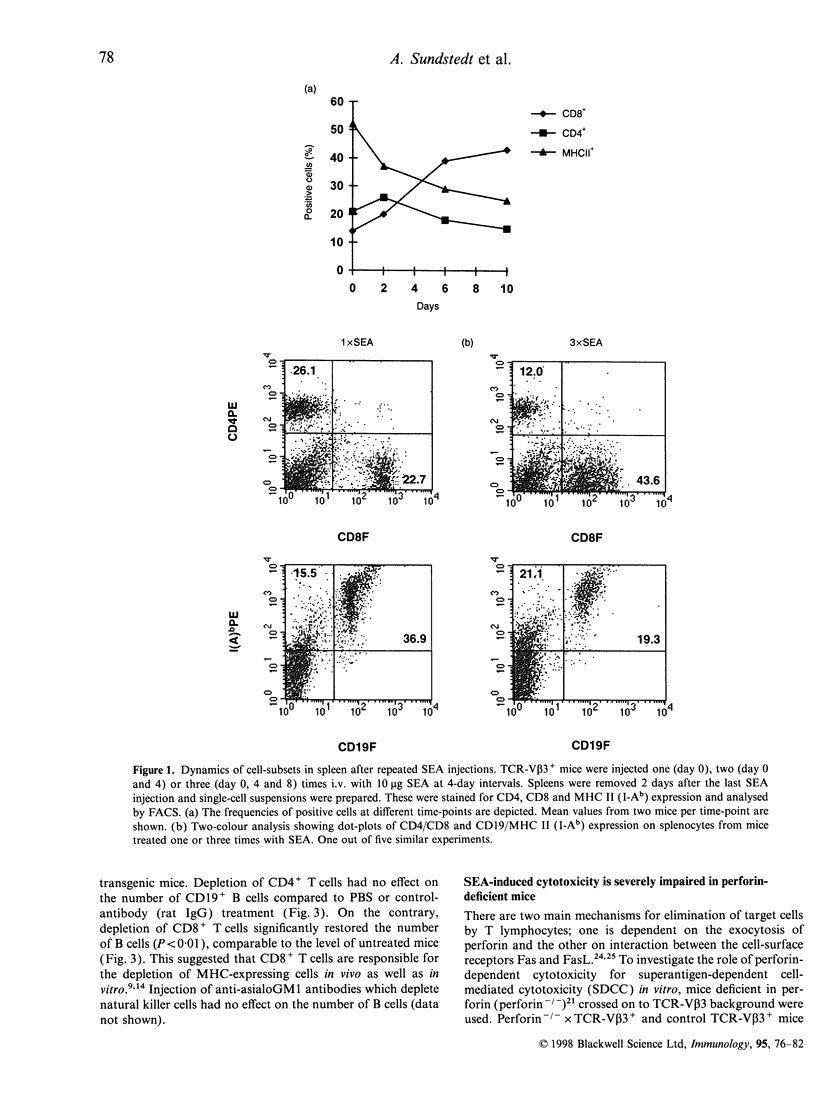
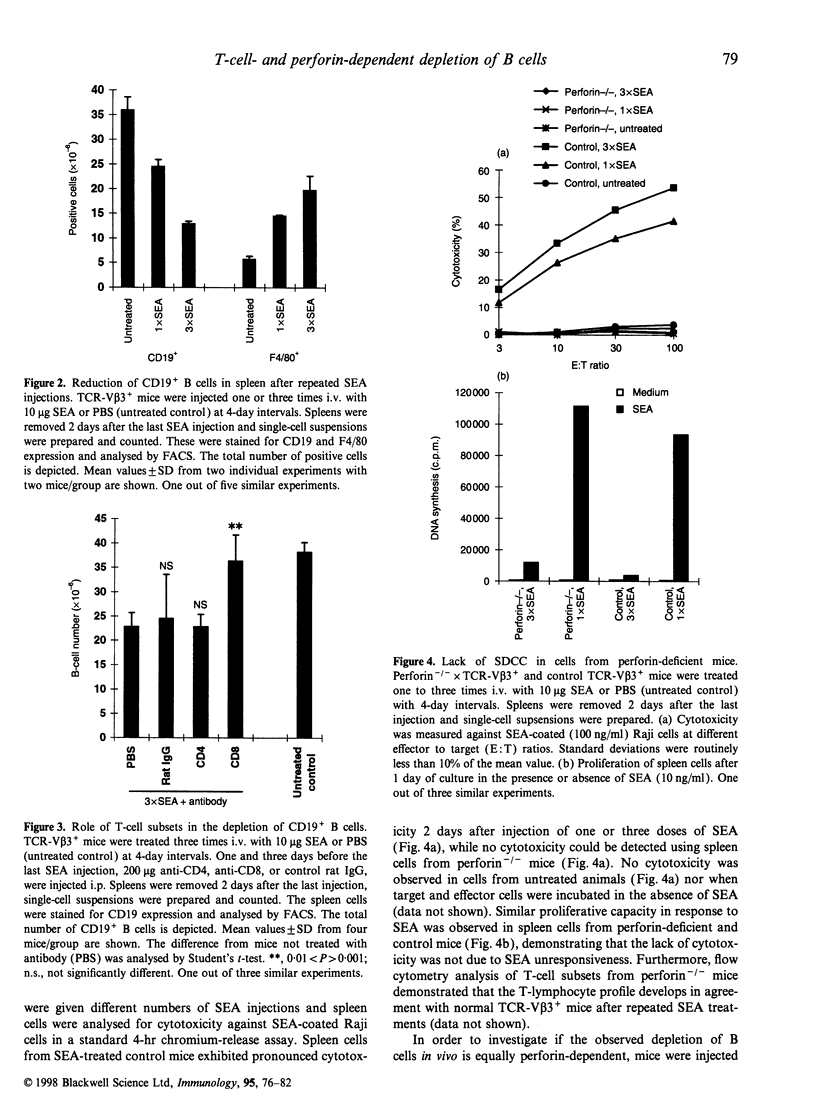
Bacterial superantigens bind to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II and subsequently activate both CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes expressing certain T-cell receptor (TCR)-Vbeta chains. In response to superantigen exposure these subsets proliferate, produce large amounts of proinflammatory cytokines and in addition CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) are induced. Previous studies in vitro have shown that these CTL effectively lyse MHC class II-expressing cells presenting the proper superantigen. However, it is unknown whether superantigens induce a similar response towards MHC class II+ antigen-presenting cells in vivo. In this study we demonstrate that administration of repeated injections of the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin A (SEA) to TCR-Vbeta3 transgenic mice results in a loss of MHC class II-expressing cells in the spleen. Analysis of different MHC class II+ subsets revealed a selective depletion of CD19+ B cells, while F4/80+ macrophages increased in number. Depletion of T cells with anti-CD4 or anti-CD8 monoclonal antibody indicated that CD8+ T cells were crucial for SEA-induced cytotoxicity in vivo. Repeated injections of SEA to perforin-deficient mice resulted in significantly less B-cell depletion compared with control mice. This suggests that superantigen-activated CD8+ T cells lyse MHC class II+ antigen-presenting cells in a perforin-dependent manner in vivo. It is suggested that this represents a novel bacterial immune escape mechanism, which may particularly impair local humoral immune responses.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bean A. G., Freiberg R. A., Andrade S., Menon S., Zlotnik A. Interleukin 10 protects mice against staphylococcal enterotoxin B-induced lethal shock. Infect Immun. 1993 Nov;61(11):4937–4939. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.11.4937-4939.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg L. J., Pullen A. M., Fazekas de St Groth B., Mathis D., Benoist C., Davis M. M. Antigen/MHC-specific T cells are preferentially exported from the thymus in the presence of their MHC ligand. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1035–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90502-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohach G. A., Fast D. J., Nelson R. D., Schlievert P. M. Staphylococcal and streptococcal pyrogenic toxins involved in toxic shock syndrome and related illnesses. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1990;17(4):251–272. doi: 10.3109/10408419009105728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlsten M., Björklund M., Sundstedt A., Hedlund G., Samson D., Kalland T. Immunopharmacology of the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin A in T-cell receptor V beta 3 transgenic mice. Immunology. 1993 Aug;79(4):520–527. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlsten M., Lando P. A., Hedlund G., Trowsdale J., Kalland T. Targeting of human cytotoxic T lymphocytes to MHC class II-expressing cells by staphylococcal enterotoxins. Immunology. 1990 Sep;71(1):96–100. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ettinger R., Panka D. J., Wang J. K., Stanger B. Z., Ju S. T., Marshak-Rothstein A. Fas ligand-mediated cytotoxicity is directly responsible for apoptosis of normal CD4+ T cells responding to a bacterial superantigen. J Immunol. 1995 May 1;154(9):4302–4308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B., Schrezenmeier H. T cell stimulation by staphylococcal enterotoxins. Clonally variable response and requirement for major histocompatibility complex class II molecules on accessory or target cells. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1697–1707. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J. D. High-affinity binding of staphylococcal enterotoxins A and B to HLA-DR. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):221–223. doi: 10.1038/339221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedlund G., Dohlsten M., Herrmann T., Buell G., Lando P. A., Segrén S., Schrimsher J., MacDonald H. R., Sjögren H. O., Kalland T. A recombinant C-terminal fragment of staphylococcal enterotoxin A binds to human MHC class II products but does not activate T cells. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 15;147(12):4082–4085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedlund G., Dohlsten M., Lando P. A., Kalland T. Staphylococcal enterotoxins direct and trigger CTL killing of autologous HLA-DR+ mononuclear leukocytes and freshly prepared leukemia cells. Cell Immunol. 1990 Sep;129(2):426–434. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90218-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedlund G., Dohlsten M., Petersson C., Kalland T. Superantigen-based tumor therapy: in vivo activation of cytotoxic T cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1993;36(2):89–93. doi: 10.1007/BF01754407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann T., Baschieri S., Lees R. K., MacDonald H. R. In vivo responses of CD4+ and CD8+ cells to bacterial superantigens. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jul;22(7):1935–1938. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofer M. F., Newell K., Duke R. C., Schlievert P. M., Freed J. H., Leung D. Y. Differential effects of staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 on B cell apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 May 28;93(11):5425–5430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.11.5425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J., Kotzin B., Herron L., Gelfand E. W., Bigler R. D., Boylston A., Carrel S., Posnett D. N., Choi Y., Marrack P. V beta-specific stimulation of human T cells by staphylococcal toxins. Science. 1989 May 19;244(4906):811–813. doi: 10.1126/science.2524876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotzin B. L., Leung D. Y., Kappler J., Marrack P. Superantigens and their potential role in human disease. Adv Immunol. 1993;54:99–166. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60534-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. Y., Harbeck R., Bina P., Reiser R. F., Yang E., Norris D. A., Hanifin J. M., Sampson H. A. Presence of IgE antibodies to staphylococcal exotoxins on the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis. Evidence for a new group of allergens. J Clin Invest. 1993 Sep;92(3):1374–1380. doi: 10.1172/JCI116711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. Y., Meissner H. C., Fulton D. R., Murray D. L., Kotzin B. L., Schlievert P. M. Toxic shock syndrome toxin-secreting Staphylococcus aureus in Kawasaki syndrome. Lancet. 1993 Dec 4;342(8884):1385–1388. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)92752-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowin B., Beermann F., Schmidt A., Tschopp J. A null mutation in the perforin gene impairs cytolytic T lymphocyte- and natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 22;91(24):11571–11575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.24.11571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowin B., Hahne M., Mattmann C., Tschopp J. Cytolytic T-cell cytotoxicity is mediated through perforin and Fas lytic pathways. Nature. 1994 Aug 25;370(6491):650–652. doi: 10.1038/370650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Baschieri S., Lees R. K. Clonal expansion precedes anergy and death of V beta 8+ peripheral T cells responding to staphylococcal enterotoxin B in vivo. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Aug;21(8):1963–1966. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrack P., Kappler J. The staphylococcal enterotoxins and their relatives. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):705–711. doi: 10.1126/science.2185544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson D., Tschopp J. Isolation of a lytic, pore-forming protein (perforin) from cytolytic T-lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9069–9072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miethke T., Wahl C., Heeg K., Echtenacher B., Krammer P. H., Wagner H. T cell-mediated lethal shock triggered in mice by the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B: critical role of tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):91–98. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migita K., Ochi A. The fate of anergic T cells in vivo. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 1;150(3):763–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley A. B., Huston D. P. Mechanism of Staphylococcus aureus exotoxin A inhibition of Ig production by human B cells. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 1;146(3):826–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller C., Tschopp J. Resistance of CTL to perforin-mediated lysis. Evidence for a lymphocyte membrane protein interacting with perforin. J Immunol. 1994 Sep 15;153(6):2470–2478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata S., Suda T. Fas and Fas ligand: lpr and gld mutations. Immunol Today. 1995 Jan;16(1):39–43. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(95)80069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi J. I., Kanekura S., Takei S., Kitajima I., Nakajima T., Wahid M. R., Masuda K., Yoshinaga M., Maruyama I., Miyata K. B cell epitope mapping of the bacterial superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B: the dominant epitope region recognized by intravenous IgG. J Immunol. 1997 Jan 1;158(1):247–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rellahan B. L., Jones L. A., Kruisbeek A. M., Fry A. M., Matis L. A. In vivo induction of anergy in peripheral V beta 8+ T cells by staphylococcal enterotoxin B. J Exp Med. 1990 Oct 1;172(4):1091–1100. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.4.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinkai Y., Ishikawa H., Hattori M., Okumura K. Resistance of mouse cytolytic cells to pore-forming protein-mediated cytolysis. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jan;18(1):29–33. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohl W., Elliott J. E. Differential human T cell-dependent B cell differentiation induced by staphylococcal superantigens (SAg). Regulatory role for SAg-dependent B cell cytolysis. J Immunol. 1995 Aug 15;155(4):1838–1850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohl W., Elliott J. E., Linsley P. S. Human T cell-dependent B cell differentiation induced by staphylococcal superantigens. J Immunol. 1994 Jul 1;153(1):117–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundstedt A., Dohlsten M., Hedlund G., Höidén I., Björklund M., Kalland T. Superantigens anergize cytokine production but not cytotoxicity in vivo. Immunology. 1994 May;82(1):117–125. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundstedt A., Höiden I., Rosendahl A., Kalland T., van Rooijen N., Dohlsten M. Immunoregulatory role of IL-10 during superantigen-induced hyporesponsiveness in vivo. J Immunol. 1997 Jan 1;158(1):180–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundstedt A., Höidén I., Hansson J., Hedlund G., Kalland T., Dohlsten M. Superantigen-induced anergy in cytotoxic CD8+ T cells. J Immunol. 1995 Jun 15;154(12):6306–6313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Herman A., Pullen A. M., Kubo R., Kappler J. W., Marrack P. The V beta-specific superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B: stimulation of mature T cells and clonal deletion in neonatal mice. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90980-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


