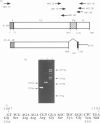
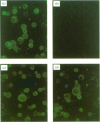
Abstract
We have previously shown, using human T-cell lymphocytotrophic virus-I (HTLV-I)-infected cell lines, that soluble interleukin-6 receptor (sIL-6R) is generated through an alternative splicing mechanism. In this study, we examined human sera for the presence of alternatively spliced soluble IL-6R (AS-sIL-6R). We produced a monoclonal antibody (mAb) recognizing the unique sequence of AS-sIL-6R peptide, generated by an altered reading frame. We also made recombinant AS-sIL-6R protein in Spodoptera frugiperda-9 (Sf-9) cells carrying baculovirus, which encoded altered sIL-6R or conventional IL-6R cDNA. mAbs specifically recognized AS-sIL-6R, but not conventional IL-6R, as demonstrated by Western blot analyses, fluorescence-activated cell sorter, immunofluorescence analyses and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). We adapted an ELISA system and used it for detection of altered sIL-6R in sera from 23 healthy persons, 12 patients with adult T-cell leukaemia (ATL) and 13 patients with HTLV-I-associated myelopathy (HAM). Serum levels of AS-sIL-6R were 6.4 or 6.1 times greater in ATL (28.7+/-20.4 ng/ml, P<0.0001) and in HAM patients (27.5+/-12.1 ng/ml, P<0.0001) than in healthy individuals (4.5+/-2.1 ng/ml). High levels of AS-sIL-6R were also observed in plasma from rheumatoid arthritis patients and in persons with elevated levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), antinuclear antibody (ANA), or alpha-fetoprotein (AFP). However, in human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1), hepatitis B virus (HBV) or hepatitis C virus (HCV)-infected individuals, AS-sIL-6R levels were not elevated. In this study, we confirmed that AS-sIL-6R is indeed present in human sera. These observations suggest that alternative splicing of IL-6R mRNA is of consequence in ATL, HAM and in some autoimmune diseases. The HTLV-I-infected T cells appeared to play an important role in AS-sIL-6R production.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- De Benedetti F., Massa M., Pignatti P., Albani S., Novick D., Martini A. Serum soluble interleukin 6 (IL-6) receptor and IL-6/soluble IL-6 receptor complex in systemic juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1994 May;93(5):2114–2119. doi: 10.1172/JCI117206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabay C., Silacci P., Genin B., Mentha G., Le Coultre C., Guerne P. A. Soluble interleukin-6 receptor strongly increases the production of acute-phase protein by hepatoma cells but exerts minimal changes on human primary hepatocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Aug;25(8):2378–2383. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. P., Bataille R., Brailly H., Zuber C., Yasukawa K., Attal M., Maruo N., Taga T., Kishimoto T., Klein B. Increased and highly stable levels of functional soluble interleukin-6 receptor in sera of patients with monoclonal gammopathy. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Apr;23(4):820–824. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauldie J., Richards C., Harnish D., Lansdorp P., Baumann H. Interferon beta 2/B-cell stimulatory factor type 2 shares identity with monocyte-derived hepatocyte-stimulating factor and regulates the major acute phase protein response in liver cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7251–7255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota H., Yoshida K., Kishimoto T., Taga T. Continuous activation of gp130, a signal-transducing receptor component for interleukin 6-related cytokines, causes myocardial hypertrophy in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 23;92(11):4862–4866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.11.4862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Moran T., Andersson M. A rapid and efficient immunization protocol for production of monoclonal antibodies reactive with autoantigens. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Nov 7;83(2):379–384. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90260-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda M., Yamamoto S., Cheng M., Yasukawa K., Suzuki H., Saito T., Osugi Y., Tokunaga T., Kishimoto T. Human soluble IL-6 receptor: its detection and enhanced release by HIV infection. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2175–2180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi S., Koyanagi Y., Tanaka Y., Waki M., Matsumoto A., Zhou Y. W., Yamamoto M., Yamamoto N. Altered interleukin-2 receptor alpha-chain is expressed in human T-cell leukaemia virus type-I-infected T-cell lines and human peripheral blood mononuclear cells of adult T-cell leukaemia patients through an alternative splicing mechanism. Immunology. 1997 May;91(1):28–34. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1997.00236.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi S., Koyanagi Y., Zhou Y., Miyamoto H., Tanaka Y., Waki M., Matsumoto A., Yamamoto M., Yamamoto N. Soluble interleukin-6 receptors released from T cell or granulocyte/macrophage cell lines and human peripheral blood mononuclear cells are generated through an alternative splicing mechanism. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Aug;24(8):1945–1948. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyland J. A., Freemont A. J., Sharpe P. T. Interleukin-6, IL-6 receptor, and IL-6 nuclear factor gene expression in Paget's disease. J Bone Miner Res. 1994 Jan;9(1):75–80. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650090111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikebuchi K., Wong G. G., Clark S. C., Ihle J. N., Hirai Y., Ogawa M. Interleukin 6 enhancement of interleukin 3-dependent proliferation of multipotential hemopoietic progenitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9035–9039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue J., Seiki M., Taniguchi T., Tsuru S., Yoshida M. Induction of interleukin 2 receptor gene expression by p40x encoded by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2883–2888. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04583.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lust J. A., Donovan K. A., Kline M. P., Greipp P. R., Kyle R. A., Maihle N. J. Isolation of an mRNA encoding a soluble form of the human interleukin-6 receptor. Cytokine. 1992 Mar;4(2):96–100. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(92)90043-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T. Mechanisms of alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):33–34. doi: 10.1126/science.1824726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama M., Shibuya H., Harada H., Hatakeyama M., Seiki M., Fujita T., Inoue J., Yoshida M., Taniguchi T. Evidence for aberrant activation of the interleukin-2 autocrine loop by HTLV-1-encoded p40x and T3/Ti complex triggering. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):343–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90437-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattox W., Ryner L., Baker B. S. Autoregulation and multifunctionality among trans-acting factors that regulate alternative pre-mRNA processing. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19023–19026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara M., Moriya Y., Kishimoto T., Ohsugi Y. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) induces the proliferation of synovial fibroblastic cells in the presence of soluble IL-6 receptor. Br J Rheumatol. 1995 Apr;34(4):321–325. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/34.4.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami-Mori K., Taga T., Kishimoto T., Nakamura S. The soluble form of the IL-6 receptor (sIL-6R alpha) is a potent growth factor for AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) cells; the soluble form of gp130 is antagonistic for sIL-6R alpha-induced AIDS-KS cell growth. Int Immunol. 1996 Apr;8(4):595–602. doi: 10.1093/intimm/8.4.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllberg J., Oberthür W., Lottspeich F., Mehl E., Dittrich E., Graeve L., Heinrich P. C., Rose-John S. The soluble human IL-6 receptor. Mutational characterization of the proteolytic cleavage site. J Immunol. 1994 May 15;152(10):4958–4968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtani K., Ninomiya H., Hasegawa Y., Kobayashi T., Kojima H., Nagasawa T., Abe T. Clinical significance of elevated soluble interleukin-6 receptor levels in the sera of patients with plasma cell dyscrasias. Br J Haematol. 1995 Sep;91(1):116–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1995.tb05255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paonessa G., Graziani R., De Serio A., Savino R., Ciapponi L., Lahm A., Salvati A. L., Toniatti C., Ciliberto G. Two distinct and independent sites on IL-6 trigger gp 130 dimer formation and signalling. EMBO J. 1995 May 1;14(9):1942–1951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose-John S., Heinrich P. C. Soluble receptors for cytokines and growth factors: generation and biological function. Biochem J. 1994 Jun 1;300(Pt 2):281–290. doi: 10.1042/bj3000281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taga T., Hibi M., Hirata Y., Yamasaki K., Yasukawa K., Matsuda T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Interleukin-6 triggers the association of its receptor with a possible signal transducer, gp130. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):573–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90438-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udagawa N., Takahashi N., Katagiri T., Tamura T., Wada S., Findlay D. M., Martin T. J., Hirota H., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Interleukin (IL)-6 induction of osteoclast differentiation depends on IL-6 receptors expressed on osteoblastic cells but not on osteoclast progenitors. J Exp Med. 1995 Nov 1;182(5):1461–1468. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.5.1461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki K., Taga T., Hirata Y., Yawata H., Kawanishi Y., Seed B., Taniguchi T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Cloning and expression of the human interleukin-6 (BSF-2/IFN beta 2) receptor. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):825–828. doi: 10.1126/science.3136546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]