Abstract
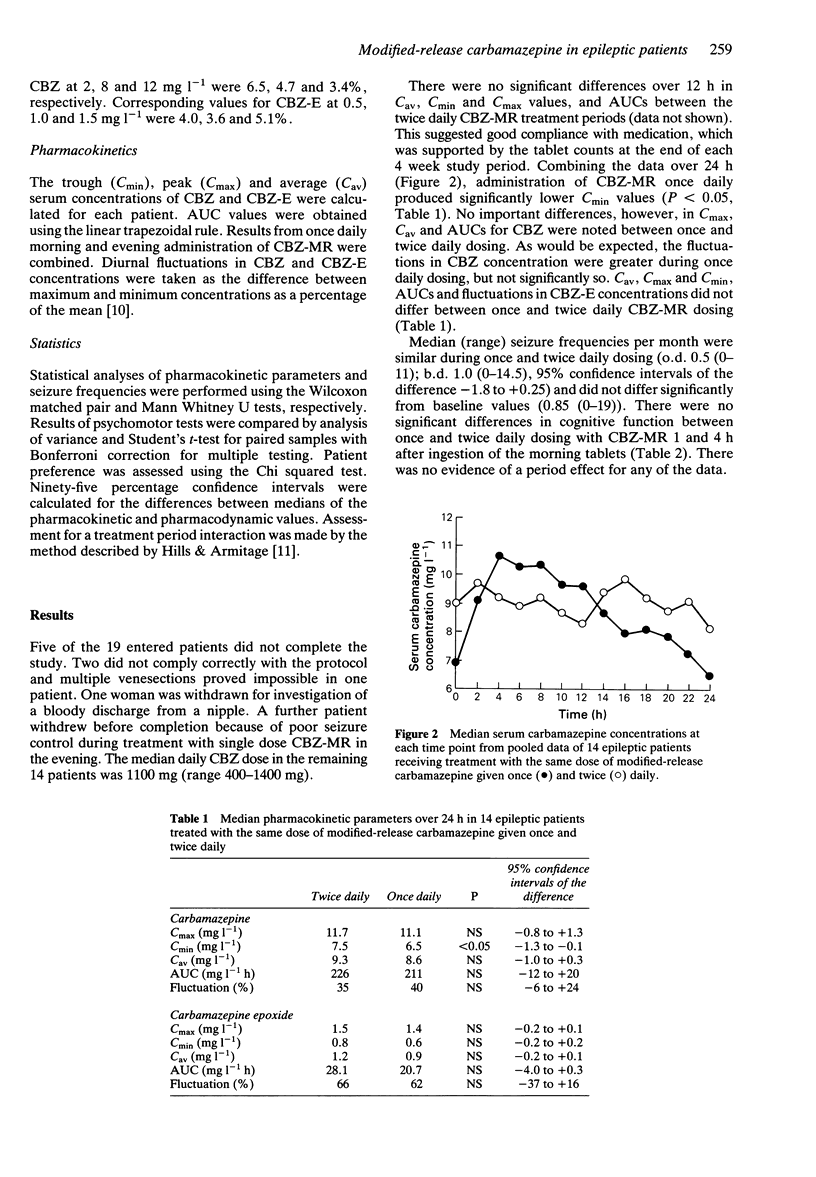
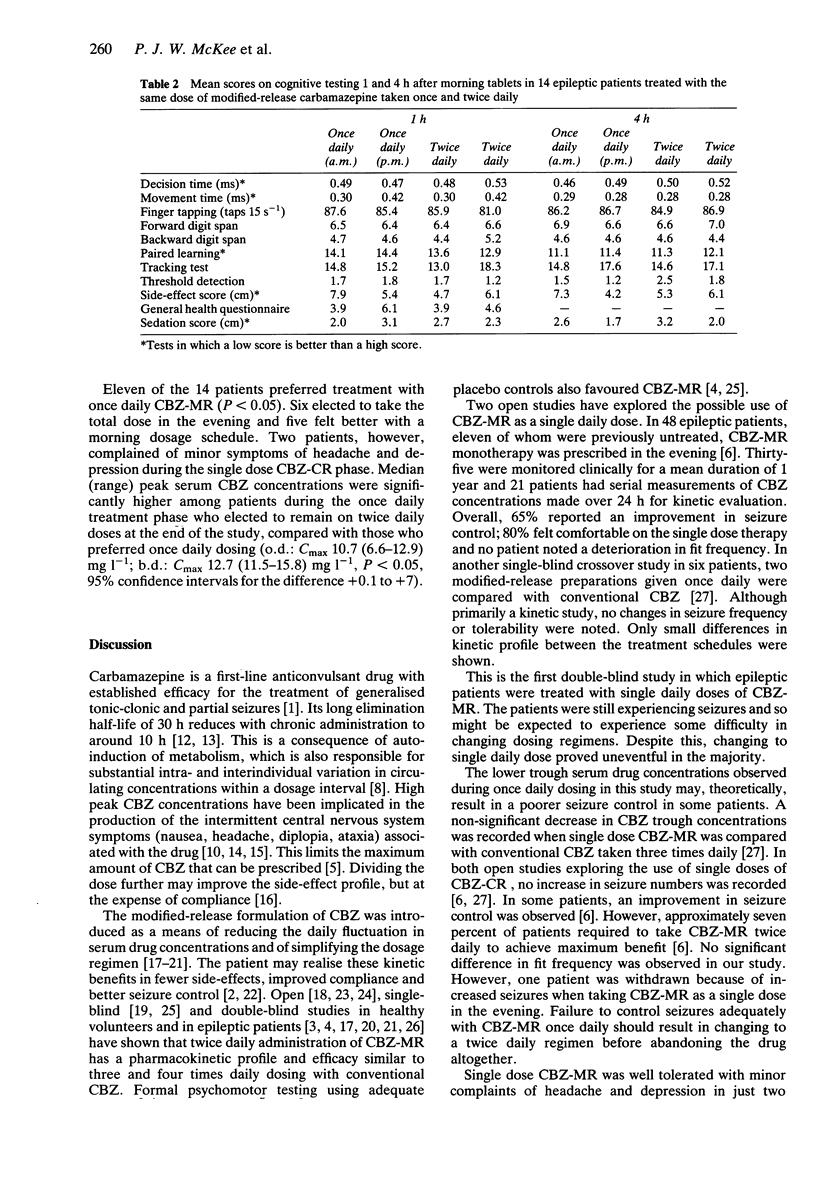
1. Fourteen patients with refractory epilepsy on a twice daily regimen of modified-release carbamazepine (CBZ-MR. Tegretol Retard. Ciba Pharmaceuticals) completed a balanced, double-blind, double dummy, random order, crossover comparison of 8 weeks treatment with once (o.d.) and twice daily (b.d.) dosing. In order to obtain a profile of serum CBZ concentrations over 24 h on once daily dosing, patients were randomised to taking it in the morning (o.d. a.m.) or evening (o.d. p.m.) for 4 weeks. Each treatment was taken with a placebo of the other and total tablet numbers were matched. Blood sampling was undertaken 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12 and 24 h after the morning tablets at the end of each 4 week treatment period. 2. Overall, trough serum drug concentrations (Cmin) were lower with once daily dosing (Cmin: b.d. 7.5 mg l-1, o.d. 6.5 mg l-1, P < 0.05, 95% CI of the difference -1.3 to -0.1), but no significant differences were found in average (Cav) or peak (Cmax) concentrations, AUC values or fluctuations in CBZ concentrations. 3. Pharmacokinetic parameters for CBZ 10.11 epoxide, the active metabolite of CBZ did not differ significantly between the dosage schedules. 4. Seizure control was similar during once and twice daily dosing with CBZ-MR (median seizures/month (range): b.d. 1 (0-14.5), o.d. 0.5 (0-11), NS, 95% CI of the difference -1.8 to + 0.25). 5. There were no differences in psychomotor performance between the treatment periods. 6. More patients (n = 11) preferred treatment (P < 0.05) with once daily than twice daily dosing (n = 3) with CBZ-MR. 7. Once daily dosing with CBZ-MR should be possible in the majority of patients receiving the drug as monotherapy.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldenkamp A. P., Alpherts W. C., Moerland M. C., Ottevanger N., Van Parys J. A. Controlled release carbamazepine: cognitive side effects in patients with epilepsy. Epilepsia. 1987 Sep-Oct;28(5):507–514. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1987.tb03679.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodie M. J. Established anticonvulsants and treatment of refractory epilepsy. Lancet. 1990 Aug 11;336(8711):350–354. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91886-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canger R., Altamura A. C., Belvedere O., Monaco F., Monza G. C., Muscas G. C., Mutani R., Panetta B., Pisani F., Zaccara G. Conventional vs controlled-release carbamazepine: a multicentre, double-blind, cross-over study. Acta Neurol Scand. 1990 Jul;82(1):9–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1990.tb01579.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eeg-Olofsson O., Nilsson H. L., Tonnby B., Arvidsson J., Grahn P. A., Gylje H., Larsson C., Norén L. Diurnal variation of carbamazepine and carbamazepine-10,11-epoxide in plasma and saliva in children with epilepsy: a comparison between conventional and slow-release formulations. J Child Neurol. 1990 Apr;5(2):159–165. doi: 10.1177/088307389000500219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichelbaum M., Ekbom K., Bertilsson L., Ringberger V. A., Rane A. Plasma kinetics of carbamazepine and its epoxide metabolite in man after single and multiple doses. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1975 Jun 13;8(5):337–341. doi: 10.1007/BF00562659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichelbaum M., Köthe K. W., Hoffmann F., von Unruh G. E. Use of stable labelled carbamazepine to study its kinetics during chronic carbamazepine treatment. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1982;23(3):241–244. doi: 10.1007/BF00547561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillham R. A., Williams N., Wiedmann K., Butler E., Larkin J. G., Brodie M. J. Concentration-effect relationships with carbamazepine and its epoxide on psychomotor and cognitive function in epileptic patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988 Jul;51(7):929–933. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.51.7.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hills M., Armitage P. The two-period cross-over clinical trial. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;8(1):7–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1979.tb05903.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höppener R. J., Kuyer A., Meijer J. W., Hulsman J. Correlation between daily fluctuations of carbamazepine serum levels and intermittent side effects. Epilepsia. 1980 Aug;21(4):341–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1980.tb04081.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen P. K., Møller A., Gram L., Jensen N. O., Dam M. Pharmacokinetic comparison of two carbamazepine slow-release formulations. Acta Neurol Scand. 1990 Aug;82(2):135–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1990.tb01603.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkin J. G., McLellan A., Munday A., Sutherland M., Butler E., Brodie M. J. A double-blind comparison of conventional and controlled-release carbamazepine in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989 Mar;27(3):313–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1989.tb05371.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macphee G. J., Butler E., Brodie M. J. Intradose and circadian variation in circulating carbamazepine and its epoxide in epileptic patients: a consequence of autoinduction of metabolism. Epilepsia. 1987 May-Jun;28(3):286–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1987.tb04220.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macphee G. J., Thompson G. G., Scobie G., Agnew E., Park B. K., Murray T., McColl K. E., Brodie M. J. Effects of cimetidine on carbamazepine auto- and hetero-induction in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;18(3):411–419. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1984.tb02483.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee P. J., Blacklaw J., Butler E., Gillham R. A., Brodie M. J. Monotherapy with conventional and controlled-release carbamazepine: a double-blind, double-dummy comparison in epileptic patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1991 Jul;32(1):99–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1991.tb05619.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson L. I., Ben-Menachem E., Bengtsson E., Heinonen E. Differences in side effects between a conventional carbamazepine preparation and a slow-release preparation of carbamazepine. Epilepsy Res. 1990 Jul;6(2):134–140. doi: 10.1016/0920-1211(90)90088-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieters M. S., Jennekens-Schinkel A., Stijnen T., Edelbroek P. M., Brouwer O. F., Liauw L., Heyer A., Lanser J. B., Peters A. C. Carbamazepine (CBZ) controlled release compared with conventional CBZ: a controlled study of attention and vigilance in children with epilepsy. Epilepsia. 1992 Nov-Dec;33(6):1137–1144. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1992.tb01771.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapeport W. G., McInnes G. T., Thompson G. G., Forrest G., Park B. K., Brodie M. J. Hepatic enzyme induction and leucocyte delta-aminolaevulinic acid synthase activity: studies with carbamazepine. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983 Aug;16(2):133–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb04976.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reunanen M., Heinonen E., Anttila M., Järvensivu P., Lehto H., Hokkanen E. Multiple-dose pharmacokinetic study with a slow-release carbamazepine preparation. Epilepsy Res. 1990 Jul;6(2):126–133. doi: 10.1016/0920-1211(90)90087-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riva R., Albani F., Ambrosetto G., Contin M., Cortelli P., Perucca E., Baruzzi A. Diurnal fluctuations in free and total steady-state plasma levels of carbamazepine and correlation with intermittent side effects. Epilepsia. 1984 Aug;25(4):476–481. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1984.tb03446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan S. W., Forsythe I., Hartley R., Haworth M., Bowmer C. J. Slow release carbamazepine in treatment of poorly controlled seizures. Arch Dis Child. 1990 Sep;65(9):930–935. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.9.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivenius J., Heinonen E., Lehto H., Järvensivu P., Anttila M., Ylinen A., Riekkinen P. Reduction of dosing frequency of carbamazepine with a slow-release preparation. Epilepsy Res. 1988 Jan-Feb;2(1):32–36. doi: 10.1016/0920-1211(88)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefan H., Schäfer H., Kuhnen C., Schneider S. Clinical monitoring during carbamazepine slow-release, once-daily monotherapy. Epilepsia. 1988 Sep-Oct;29(5):571–577. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1988.tb03763.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomson T. Interdosage fluctuations in plasma carbamazepine concentration determine intermittent side effects. Arch Neurol. 1984 Aug;41(8):830–834. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1984.04050190036011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meyden C. H., Bartel P. R., Sommers D. K., Blom M., Becker P., Erasmus S., Griesel D. Effect of acute doses of controlled-release carbamazepine on clinical, psychomotor, electrophysiological, and cognitive parameters of brain function. Epilepsia. 1992 Mar-Apr;33(2):335–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1992.tb02324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


