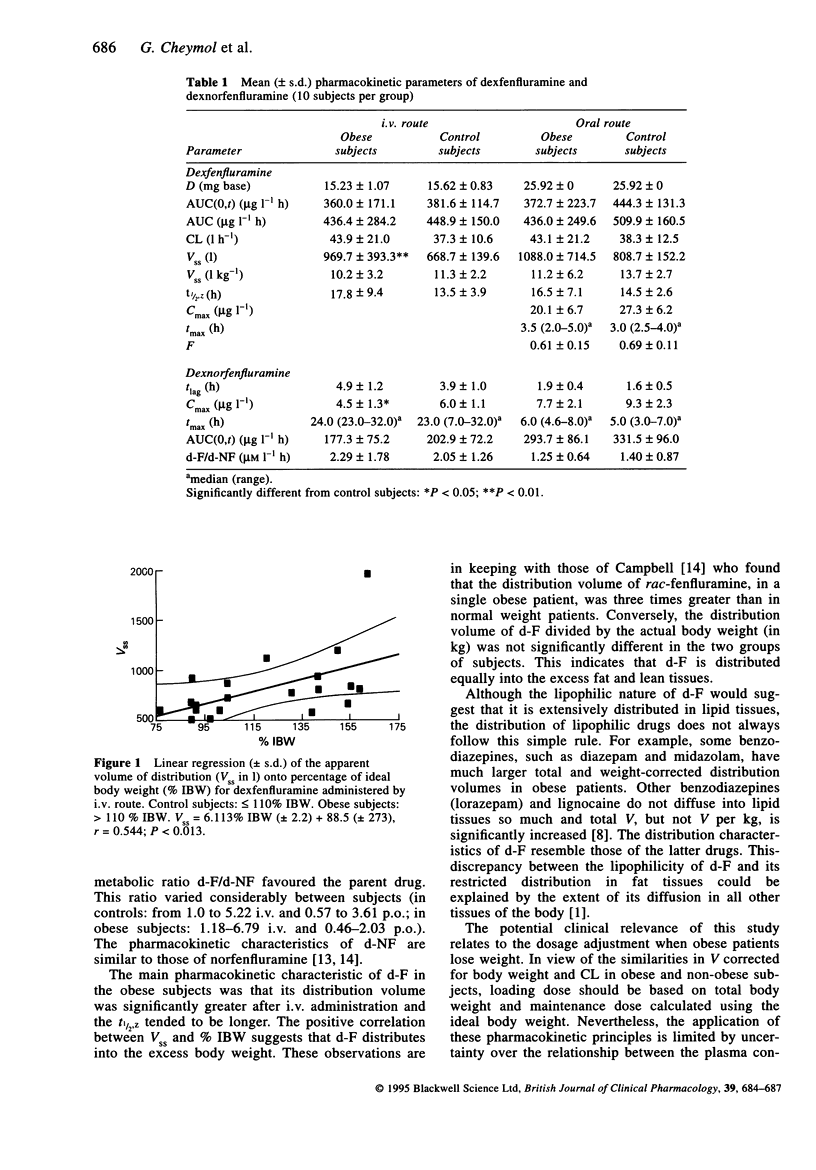
Abstract
The pharmacokinetics of dexfenfluramine (d-F) and its metabolite dexnorfenfluramine (d-NF) were compared in 10 obese (145 +/- 13 s.d. % of ideal body weight (IBW)) and 10 non-obese healthy volunteers (93 +/- 8% IBW). Each group included five men and five women, aged 28 +/- 8 years. Subjects were given single doses of d-F i.v. (15.5 mg base infused over 3 h) and orally (25.9 mg base in capsules) on separate occasions. After i.v. infusion in obese subjects, the volume of distribution (Vss) of d-F was significantly higher (969.7 +/- 393.3 l; 95% CI 688.6-1250 l) than in controls (668.7 +/- 139.6 l; 95% CI 568.9-768.5 l; P < 0.01). Clearance was not significantly different (43.9 +/- 21.0 l h-1 vs 37.3 +/- 10.6 l h-1) and the terminal half-life tended to be longer (17.8 +/- 9.4 vs 13.5 +/- 3.9 h NS). Combined data from the two groups indicated a positive correlation between Vss and % IBW (r = 0.544; P < 0.02). The oral bioavailability of d-F was 0.61 +/- 0.15 in obese subjects and 0.69 +/- 0.11 in controls. There was no significant difference between obese subjects and controls in Cmax, tmax and t1/2,z (Cmax: 20.1 +/- 6.7 and 27.3 +/- 6.2 micrograms l-1; tmax: 3.5 vs 3.0; t1/2,z: 16.5 +/- 7.1 vs 14.5 +/- 2.6 h respectively). The AUC ratio expressed in molar units for d-F/d-NF was 2.29 +/- 1.78 (i.v.) vs 1.25 +/- 0.64 (oral) in obese subjects and 2.05 +/- 1.26 (i.v.) vs 1.40 +/- 0.87 (oral) in controls.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abernethy D. R., Greenblatt D. J. Drug disposition in obese humans. An update. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1986 May-Jun;11(3):199–213. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198611030-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckett A. H., Salmon J. A. Pharmacokinetics of absorption, distribution and elimination of fenfluramine and its main metabolite in man. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1972 Feb;24(2):108–114. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1972.tb08942.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caccia S., Ballabio M., Guiso G., Rocchetti M., Garattini S. Species differences in the kinetics and metabolism of fenfluramine isomers. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1982 Jul;258(1):15–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caccia S., Conforti I., Duchier J., Garattini S. Pharmacokinetics of fenfluramine and norfenfluramine in volunteers given D- and DL-fenfluramine for 15 days. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1985;29(2):221–224. doi: 10.1007/BF00547426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. B. Gas chromatographic measurement of levels of fenfluramine and norfenfluramine in human plasma, red cells and urine following therapeutic doses. J Chromatogr. 1970 Jun 24;49(3):442–447. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)93657-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. B., Gordon B. H., Ings R. M., Richards R., Taylor D. W. Factors that may effect the reduction of hunger and body weight following d-fenfluramine administration. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1988;11 (Suppl 1):S160–S172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheymol G. Clinical pharmacokinetics of drugs in obesity. An update. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1993 Aug;25(2):103–114. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199325020-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomeni R. PHARM--an interactive graphic program for individual and population pharmacokinetic parameter estimation. Comput Biol Med. 1984;14(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0010-4825(84)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McTavish D., Heel R. C. Dexfenfluramine. A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic potential in obesity. Drugs. 1992 May;43(5):713–733. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199243050-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietrusko R., Stunkard A., Brownell K., Campbell D. B. Plasma fenfluramine levels, weight loss and side effects: a failure to find a relationship. Int J Obes. 1982;6(6):567–571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. P., Gordon B. H., Ings R. M., Campbell D. B., King L. J. The measurement of d-fenfluramine and its metabolite, d-norfenfluramine in plasma and urine with an application of the method to pharmacokinetic studies. Xenobiotica. 1989 May;19(5):547–553. doi: 10.3109/00498258909042294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


