Abstract
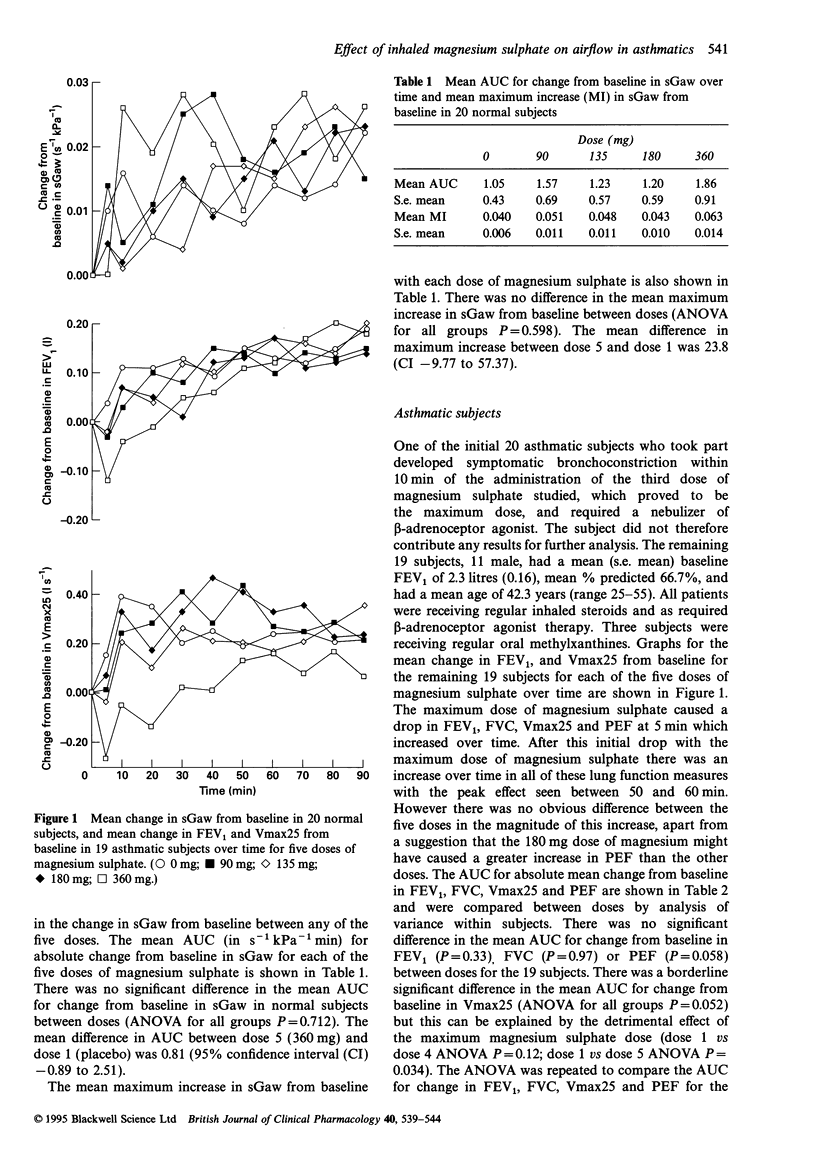
1. Magnesium is a dietary cation with a wide range of actions of potential relevance to asthma. 2. To determine the dose-response relationship and time-course of the effect of inhaled magnesium sulphate on the airway, we have studied the effect of 0, 90, 135, 180 and 360 mg of magnesium sulphate given by nebulizer on specific airways conductance (sGaw) in 20 normal subjects, and forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), forced vital capacity (FVC), flow at 25% forced vital capacity (Vmax25) and peak expiratory flow (PEF) in 19 asthmatic subjects. 3. On five occasions after baseline measurements of airway calibre, one of the five doses of magnesium sulphate in 3 ml normal saline was administered by nebulizer in a randomized, double-blind design. Measurements of sGaw or FEV1, FVC, Vmax25 and PEF were made at 5 and 10 min after nebulization and at 10 min intervals thereafter up to 90 min. 4. There was no significant difference in the mean area under the curve (AUC) for change from baseline in sGaw or maximum increase from baseline between doses in normal subjects. 5. In asthmatic subjects there was no significant difference in the mean AUC for change from baseline in FEV1, FVC or Vmax25 when compared between doses by analysis of variance. There was a difference in the mean AUC for change from baseline in PEF between doses (ANOVA P for all groups 0.052) but this can be explained by a detrimental effect of the maximum dose of magnesium sulphate. 6. It would appear that inhaled magnesium does not act as a bronchodilator in normal or asthmatic subjects.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
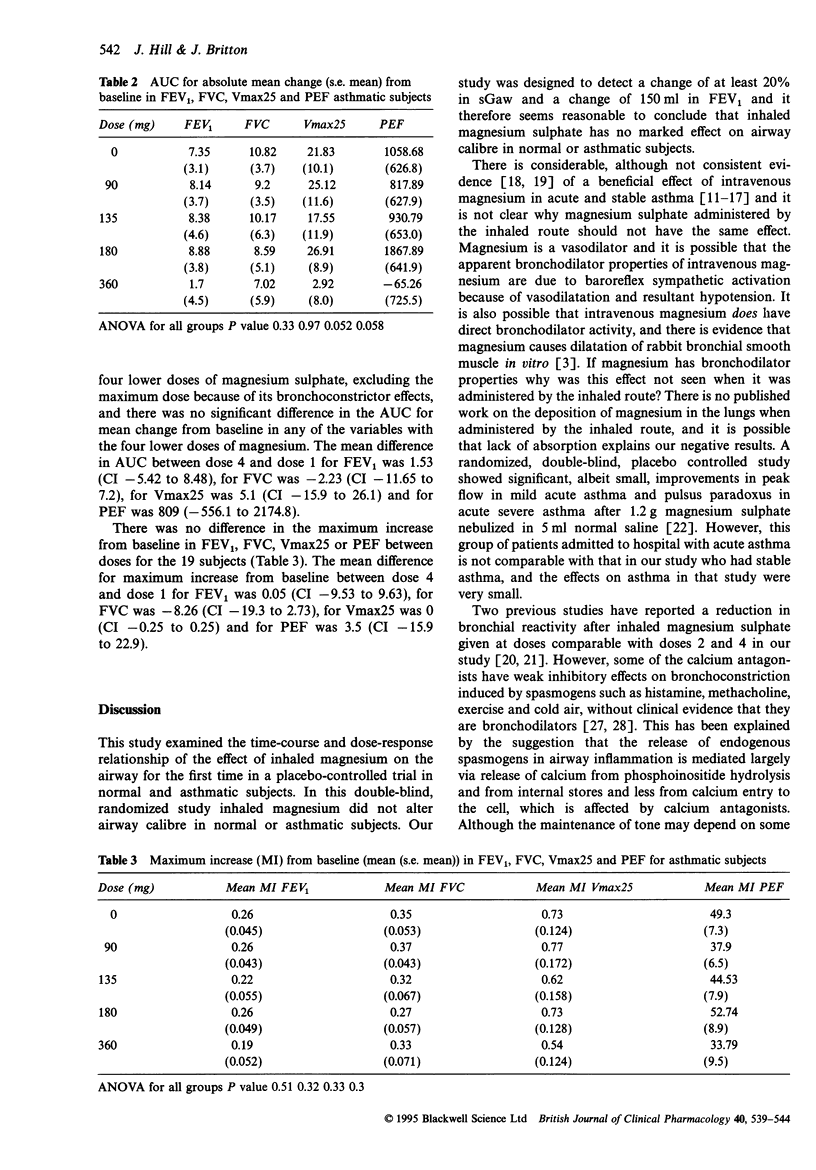
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altura B. M., Altura B. T., Carella A. Magnesium deficiency-induced spasms of umbilical vessels: relation to preeclampsia, hypertension, growth retardation. Science. 1983 Jul 22;221(4608):376–378. doi: 10.1126/science.6867714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altura B. M., Altura B. T. Magnesium and contraction of arterial smooth muscle. Microvasc Res. 1974 Mar;7(2):145–155. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(74)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altura B. M., Altura B. T. Magnesium ions and contraction of vascular smooth muscles: relationship to some vascular diseases. Fed Proc. 1981 Oct;40(12):2672–2679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOIS P. Effect of magnesium deficiency on mast cells and urinary histamine in rats. Br J Exp Pathol. 1963 Apr;44:151–155. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. J., Wilson N. M., Brown M. J. A calcium antagonist, nifedipine, modifies exercise-induced asthma. Thorax. 1981 Oct;36(10):726–730. doi: 10.1136/thx.36.10.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton J., Pavord I., Richards K., Wisniewski A., Knox A., Lewis S., Tattersfield A., Weiss S. Dietary magnesium, lung function, wheezing, and airway hyperreactivity in a random adult population sample. Lancet. 1994 Aug 6;344(8919):357–362. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91399-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner E. H., Delabroise A. M., Haddad Z. H. Effect of parenteral magnesium on pulmonary function, plasma cAMP, and histamine in bronchial asthma. J Asthma. 1985;22(1):3–11. doi: 10.3109/02770908509079880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Angelo E. K., Singer H. A., Rembold C. M. Magnesium relaxes arterial smooth muscle by decreasing intracellular Ca2+ without changing intracellular Mg2+. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jun;89(6):1988–1994. doi: 10.1172/JCI115807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., ENGBAEK L. The nature of the neuromuscular block produced by magnesium. J Physiol. 1954 May 28;124(2):370–384. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnett J., Nayler W. G. Calcium efflux from cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum: effects of calcium and magnesium. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1978 May;10(5):487–498. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(78)90369-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. M., Rothrock S. G. Intravenous magnesium for acute asthma: failure to decrease emergency treatment duration or need for hospitalization. Ann Emerg Med. 1992 Mar;21(3):260–265. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0644(05)80885-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D., Gallagher C., Cavanaugh M., Yip R., Mayers I. The lack of effect of routine magnesium administration on respiratory function in mechanically ventilated patients. Chest. 1993 Aug;104(2):536–541. doi: 10.1378/chest.104.2.536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp P. A., Gardiner S. M., Bennett T., Rubin P. C. Magnesium sulphate reverses the carotid vasoconstriction caused by endothelin-I, angiotensin II and neuropeptide-Y, but not that caused by NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester, in conscious rats. Clin Sci (Lond) 1993 Aug;85(2):175–181. doi: 10.1042/cs0850175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp P. A., Gardiner S. M., March J. E., Bennett T., Rubin P. C. Effects of NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester on regional haemodynamic responses to MgSO4 in conscious rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jan;111(1):325–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14063.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura T., Yasue H., Sakaino N., Rokutanda M., Jougasaki M., Araki H. Effects of magnesium on the tone of isolated human coronary arteries. Comparison with diltiazem and nitroglycerin. Circulation. 1989 May;79(5):1118–1124. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.79.5.1118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuitert L. M., Kletchko S. L. Intravenous magnesium sulfate in acute, life-threatening asthma. Ann Emerg Med. 1991 Nov;20(11):1243–1245. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0644(05)81481-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurant P., Moussard C., Alber D., Henry J. C., Berthelot A. In vivo and in vitro magnesium effects on aortic prostacyclin generation in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 1992 Nov;47(3):183–186. doi: 10.1016/0952-3278(92)90236-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara R. M., Spivey W. H., Skobeloff E., Jacubowitz S. Intravenous magnesium sulfate in the management of acute respiratory failure complicating asthma. Ann Emerg Med. 1989 Feb;18(2):197–199. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0644(89)80114-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton E., Jr Calcium antagonists and asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1985 Aug;76(2 Pt 2):341–346. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(85)90651-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler J. L., Goodson S., Rude R. K. Evidence that prostacyclin mediates the vascular action of magnesium in humans. Hypertension. 1987 Apr;9(4):379–383. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.9.4.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noppen M., Vanmaele L., Impens N., Schandevyl W. Bronchodilating effect of intravenous magnesium sulfate in acute severe bronchial asthma. Chest. 1990 Feb;97(2):373–376. doi: 10.1378/chest.97.2.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Aikawa T., Okayama M., Sasaki H., Mue S., Takishima T. Bronchodilating effect of intravenous magnesium sulfate in bronchial asthma. JAMA. 1987 Feb 27;257(8):1076–1078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolla G., Bucca C., Arossa W., Bugiani M. Magnesium attenuates methacholine-induced bronchoconstriction in asthmatics. Magnesium. 1987;6(4):201–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolla G., Bucca C., Bugiani M., Arossa W., Spinaci S. Reduction of histamine-induced bronchoconstriction by magnesium in asthmatic subjects. Allergy. 1987 Apr;42(3):186–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1987.tb02198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolla G., Bucca C., Caria E., Arossa W., Bugiani M., Cesano L., Caropreso A. Acute effect of intravenous magnesium sulfate on airway obstruction of asthmatic patients. Ann Allergy. 1988 Nov;61(5):388–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skobeloff E. M., Spivey W. H., McNamara R. M., Greenspon L. Intravenous magnesium sulfate for the treatment of acute asthma in the emergency department. JAMA. 1989 Sep 1;262(9):1210–1213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivey W. H., Skobeloff E. M., Levin R. M. Effect of magnesium chloride on rabbit bronchial smooth muscle. Ann Emerg Med. 1990 Oct;19(10):1107–1112. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0644(05)81513-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson E. W., Podolsky R. J. Regulation by magnesium of intracellular calcium movement in skinned muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Jan;69(1):1–16. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersfield A. E., Keeping I. M. Assessing change in airway calibre--measurement of airway resistance. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Oct;8(4):307–319. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1979.tb04711.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweeddale P. M., Alexander F., McHardy G. J. Short term variability in FEV1 and bronchodilator responsiveness in patients with obstructive ventilatory defects. Thorax. 1987 Jul;42(7):487–490. doi: 10.1136/thx.42.7.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweeddale P. M., Merchant S., Leslie M., Alexander F., McHardy G. J. Short term variability in FEV1: relation to pretest activity, level of FEV1, and smoking habits. Thorax. 1984 Dec;39(12):928–932. doi: 10.1136/thx.39.12.928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


