Abstract
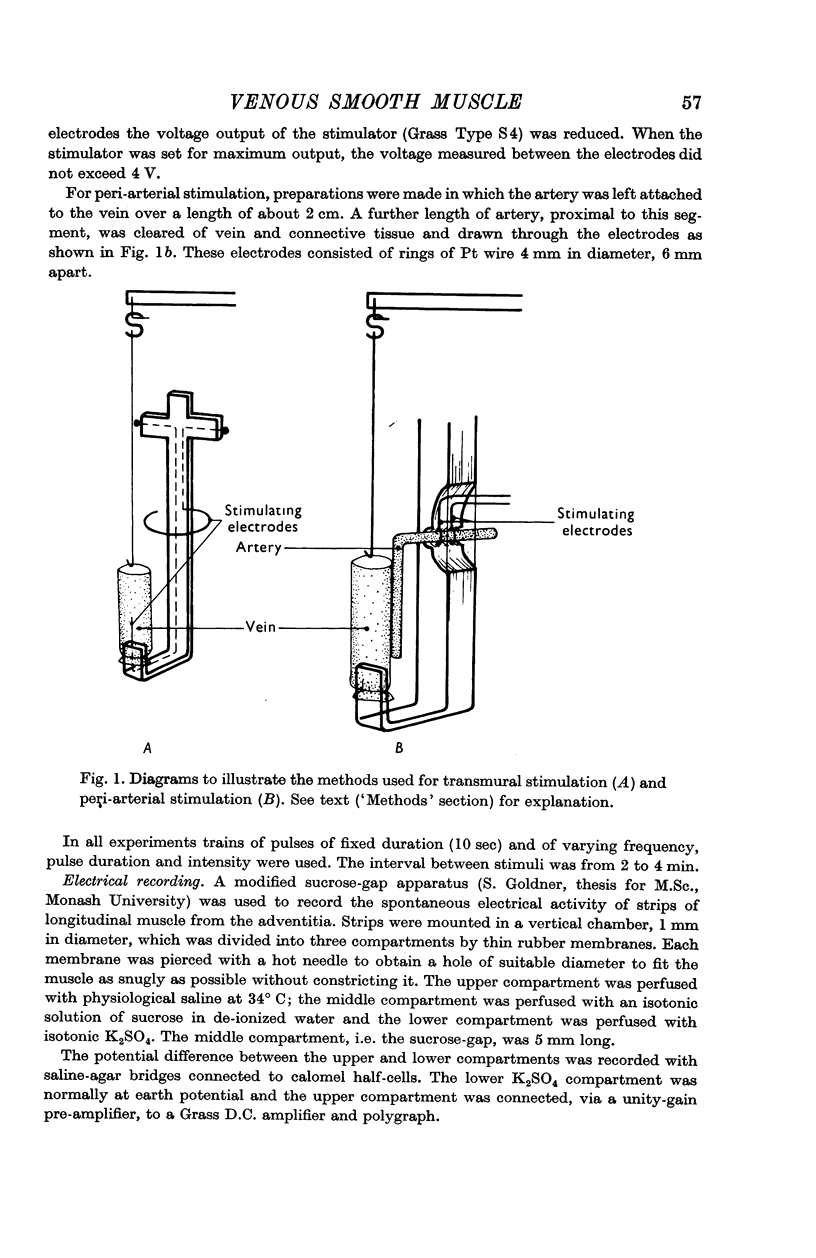
1. An isolated preparation of sheep mesenteric vein is described from which contractions of the longitudinal smooth muscle of the adventitia have been recorded in response to stimulation of intramural and periarterial nerves.
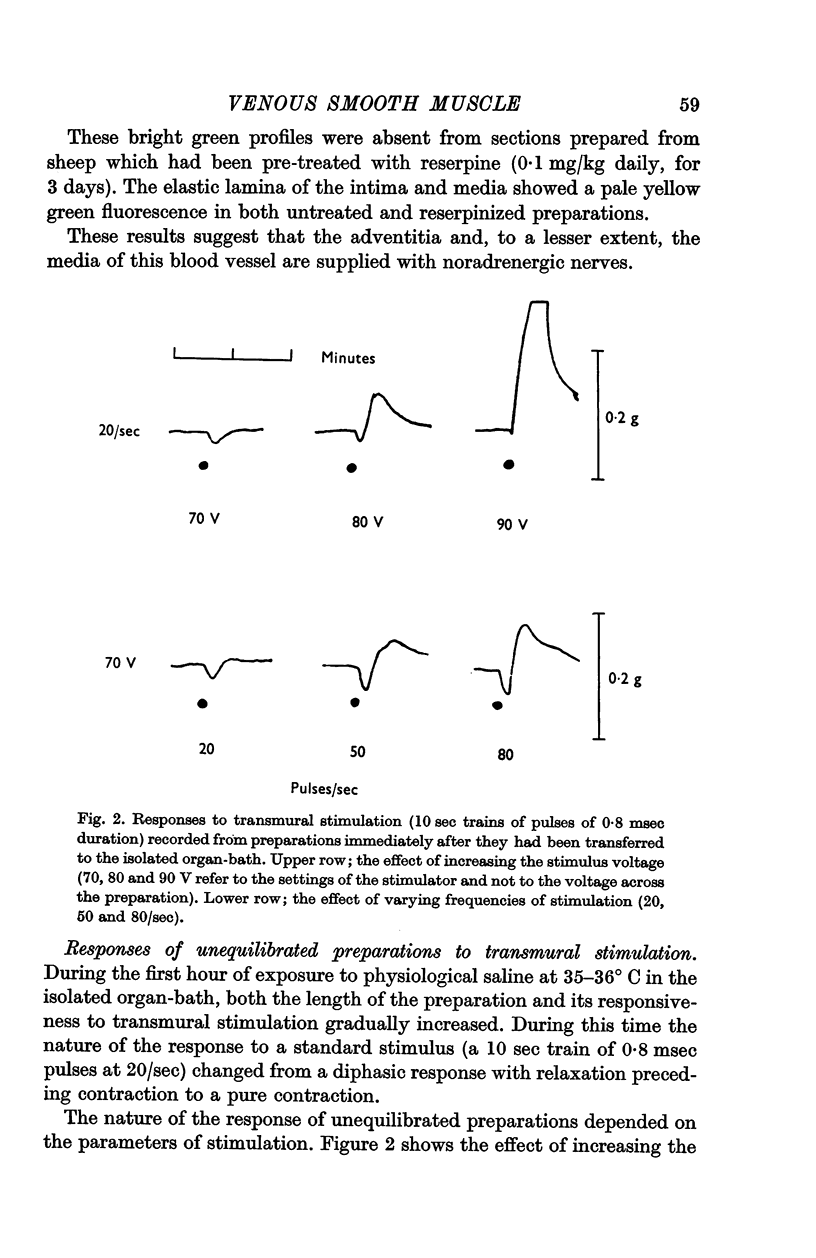
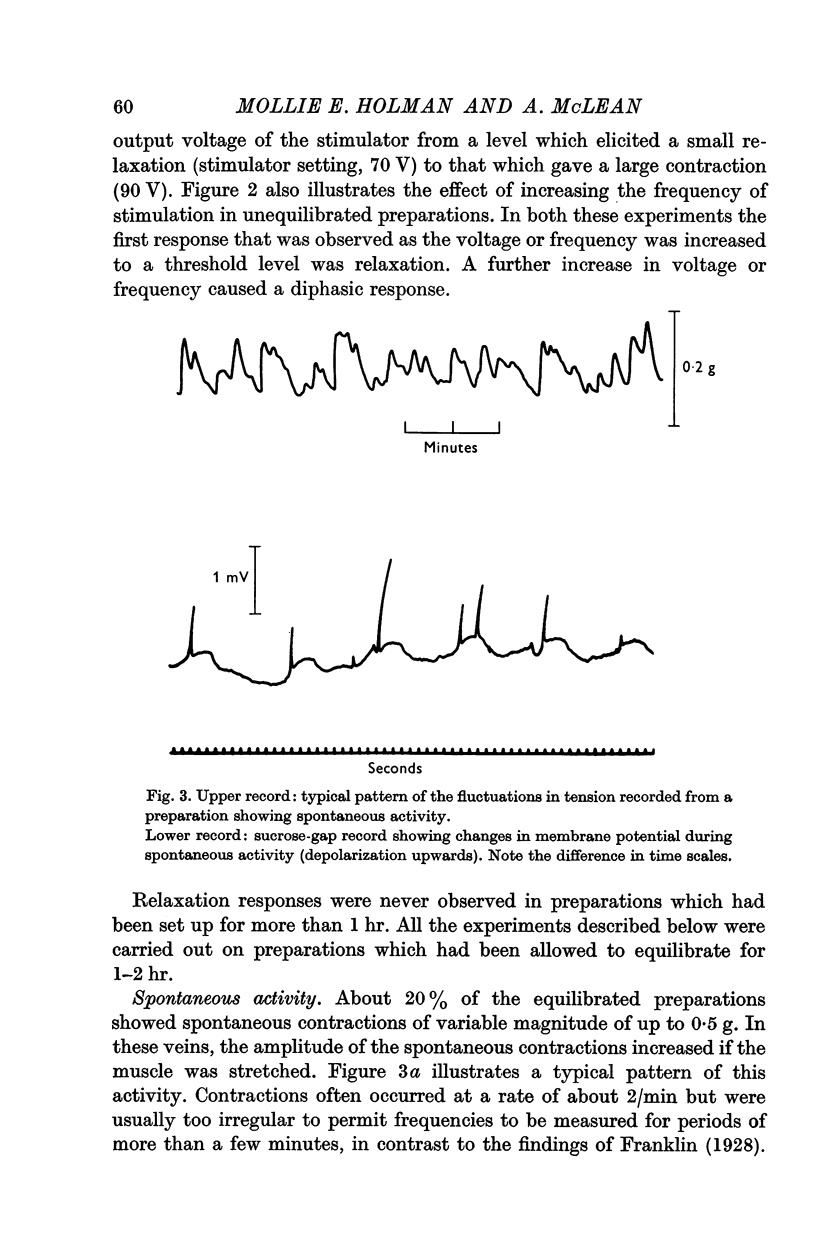
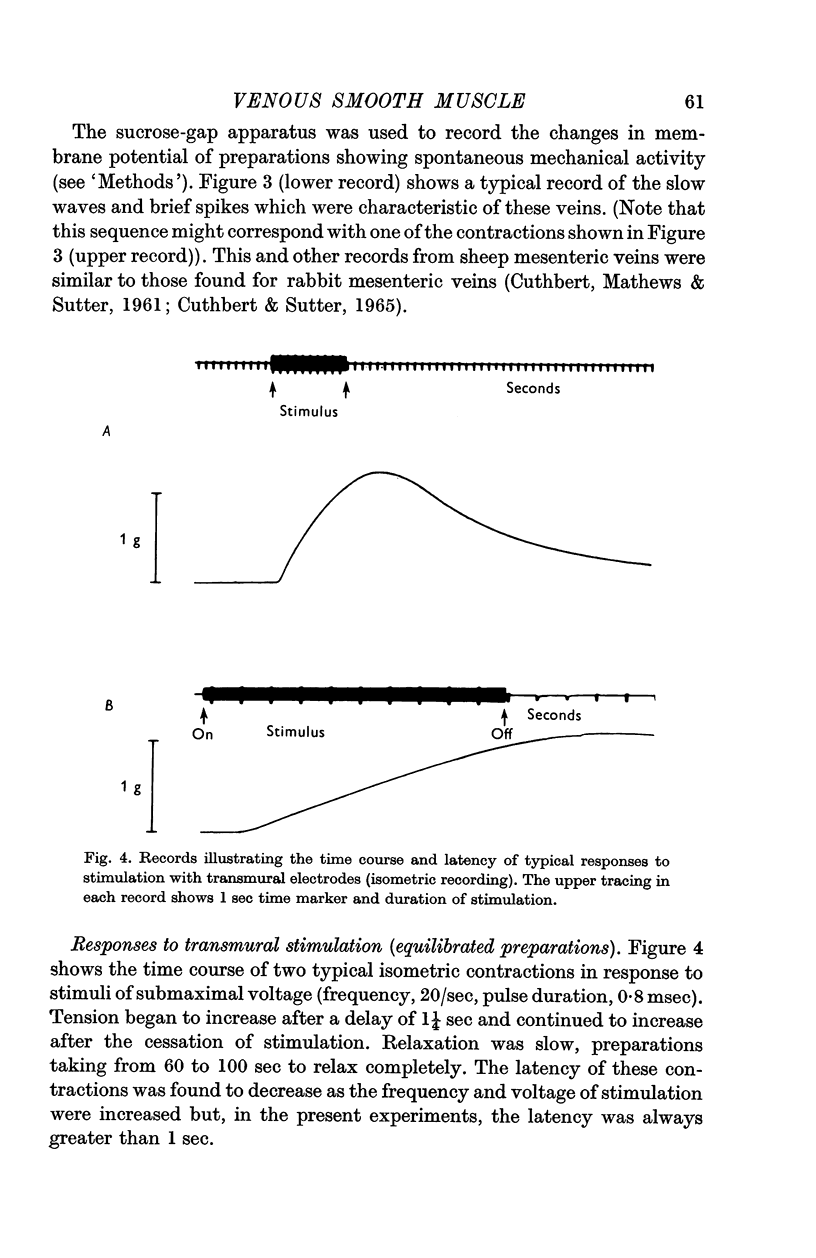
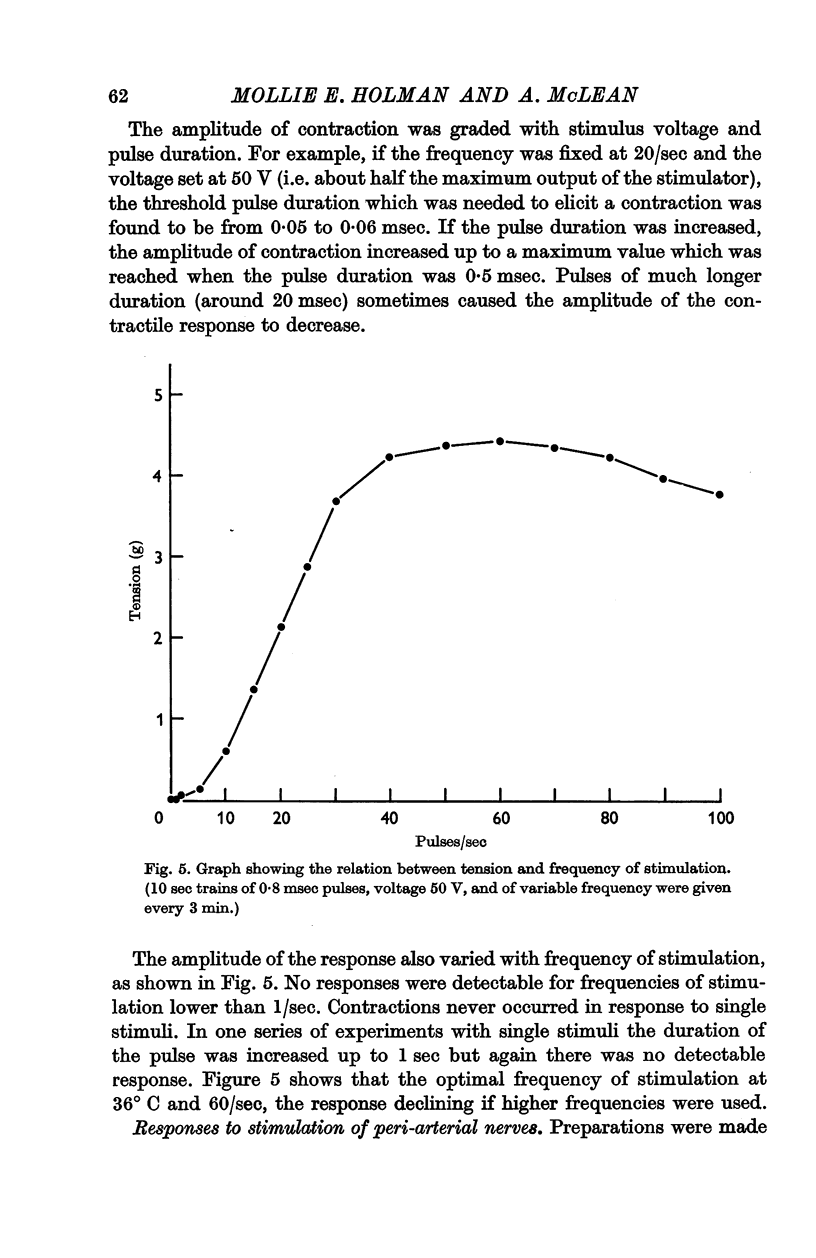
2. The preparation did not respond to single stimuli but the relation between amplitude of response and frequency of stimulation was characteristic of that described for other smooth muscles innervated by sympathetic nerves.
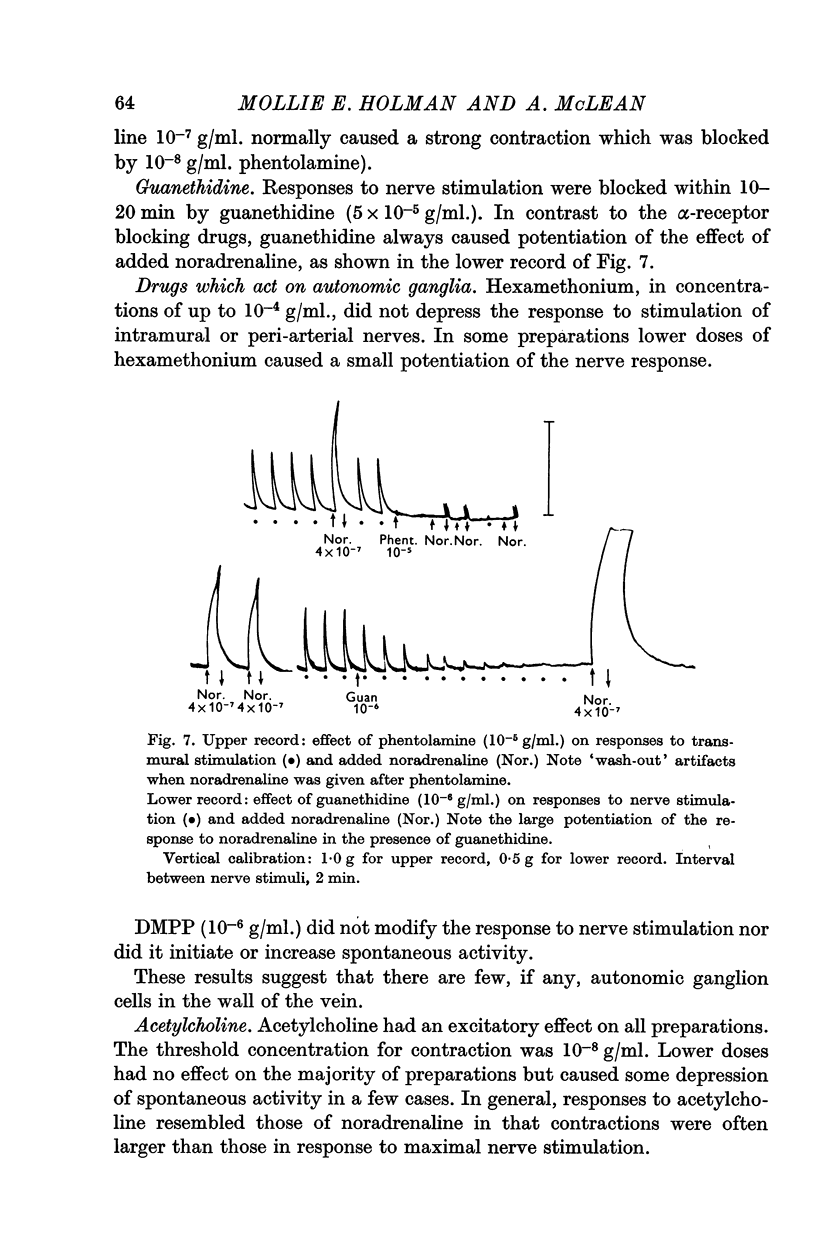
3. Responses were blocked by tetrodotoxin, guanethidine, and by a number of α-receptor blocking drugs. Responses to peri-arterial stimulation were unaffected by hexamethonium. It was concluded that the longitudinal smooth muscle is supplied with post-ganglionic noradrenergic motor nerves and the presence of such fibres in the adventitia was confirmed by fluorescence microscopy.
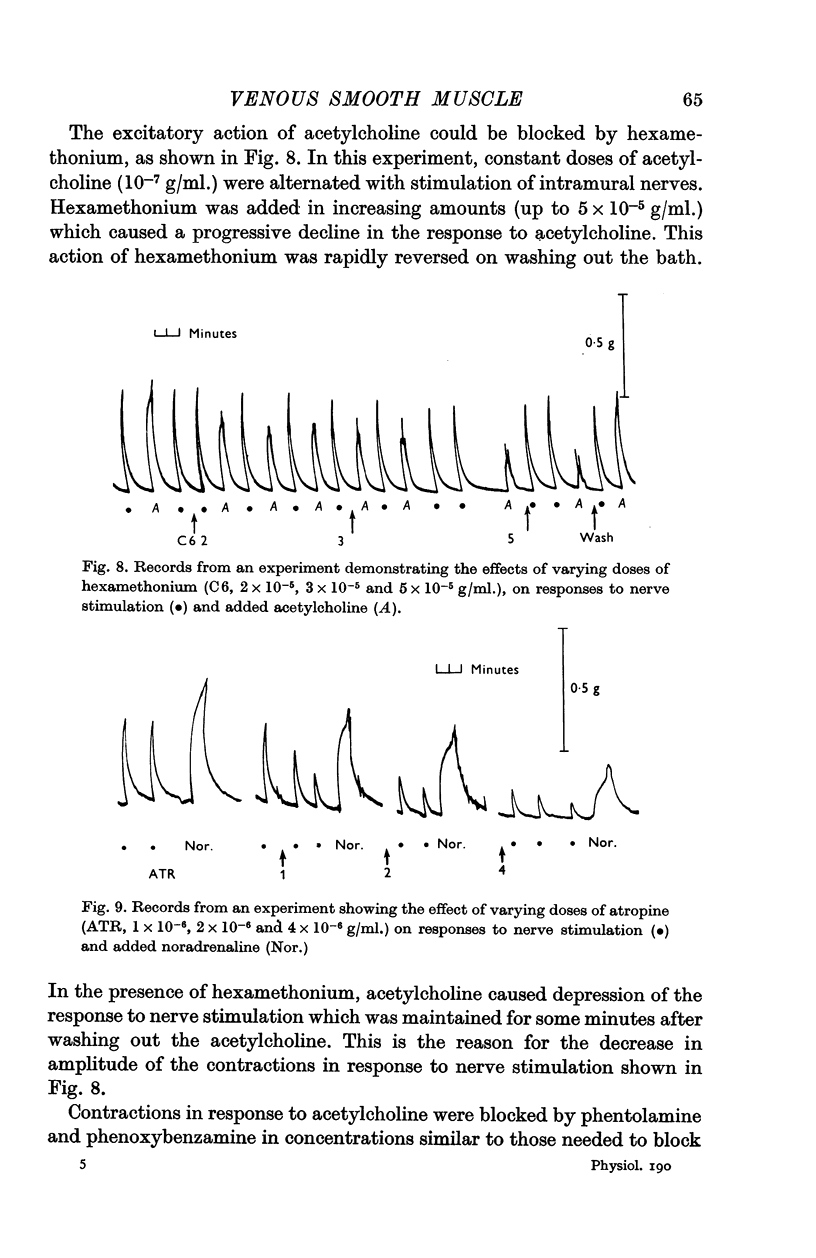
4. Acetylcholine also caused contractions. Although a direct excitatory action on the smooth muscle could not be excluded, results suggest that acetylcholine may release noradrenaline from the axons of the sympathetic ground plexus.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEVAN J. A. Some characteristics of the isolated sympathetic nerve-pulmonary artery preparation of the rabbit. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1962 Aug;137:213–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., Sutter M. C. The effects of drugs on the relation between the action potential discharge and tension in a mammalian vein. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1965 Dec;25(3):592–601. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1965.tb01783.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De la Lande I. S., Rand M. J. A simple isolated nerve-blood vessel preparation. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1965 Oct;43(5):639–656. doi: 10.1038/icb.1965.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERRY C. B. The synpathomimetic effect of acetylcholine on the spleen of the cat. J Physiol. 1963 Jul;167:487–504. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLKOW B., LEWIS D. H., LUNDGREN O., MELLANDER S., WALLENTIN I. THE EFFECT OF GRADED VASOCONSTRICTOR FIBRE STIMULATION ON THE INTESTINAL RESISTANCE AND CAPACITANCE VESSELS. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 Aug;61:445–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLKOW B., LEWIS D. H., LUNDGREN O., MELLANDER S., WALLENTIN I. THE EFFECT OF THE SYMPATHETIC VASOCONSTRICTOR FIBRES ON THE DISTRIBUTION OF CAPILLARY BLOOD FLOW IN THE INTESTINE. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 Aug;61:458–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMAN M. E., JOWETT A. SOME ACTIONS OF CATECHOLAMINES ON THE SMOOTH MUSCLE OF THE GUINEA-PIG VAS DEFERENS. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1964 Feb;42:40–53. doi: 10.1038/icb.1964.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KURIYAMA H. ELECTROPHYSIOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS ON THE MOTOR INNERVATION OF THE SMOOTH MUSCLE CELLS IN THE GUINEA-PIG VAS DEFERENS. J Physiol. 1963 Nov;169:213–228. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCGREGOR D. D. THE EFFECT OF SYMPATHETIC NERVE STIMULATION OF VASOCONSTRICTOR RESPONSES IN PERFUSED MESENTERIC BLOOD VESSELS OF THE RAT. J Physiol. 1965 Mar;177:21–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. The response of the guineapig ileum to electrical stimulation by coaxial electrodes. J Physiol. 1955 Feb 28;127(2):40–1P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGERS L. A., ATKINSON R. A., LONG J. P. RESPONSES OF ISOLATED PERFUSED ARTERIES TO CATECHOLAMINES AND NERVE STIMULATION. Am J Physiol. 1965 Aug;209:376–382. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.2.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


