Abstract
1. L-Noradrenaline (NA), dopamine, 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) and lysergide were administered iontophoretically to neurones in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat and the responses to these drugs recorded.
2. Many neurones were depressed by the monoamines and lysergide.
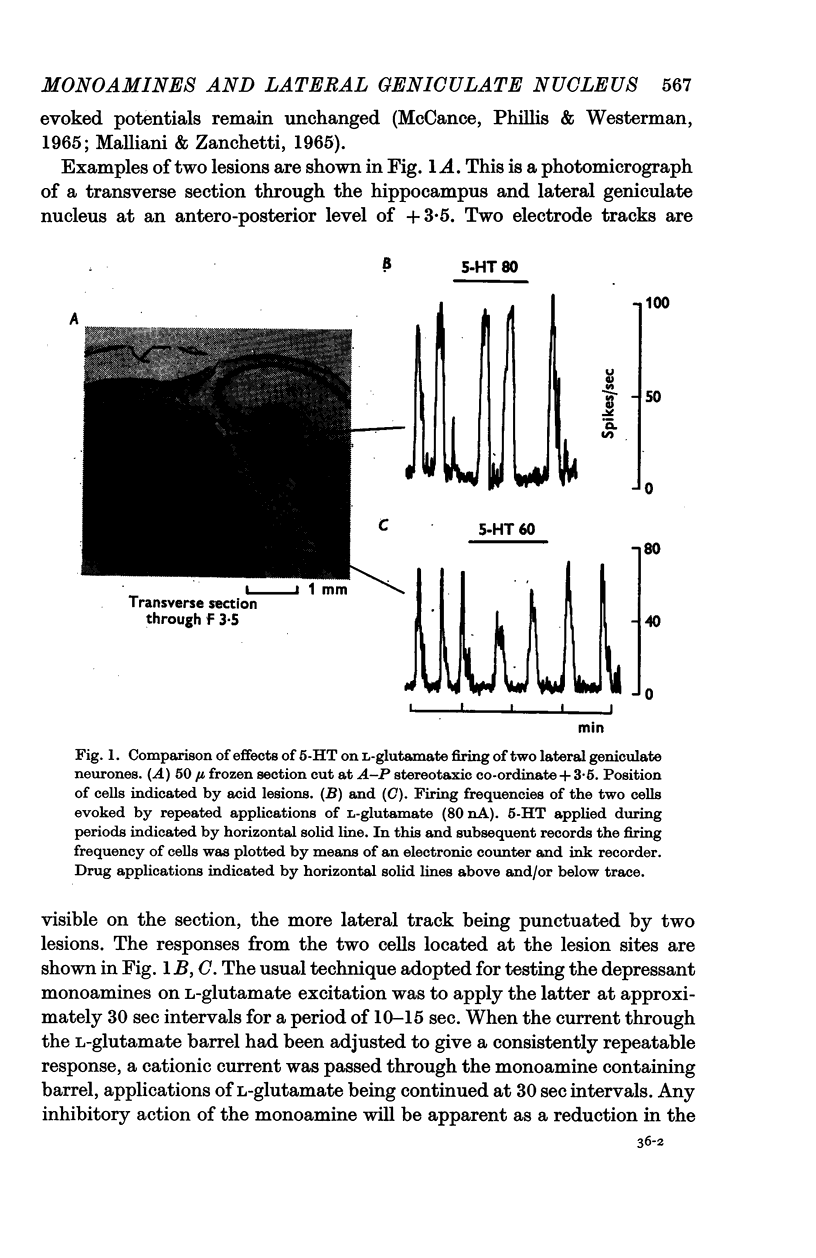
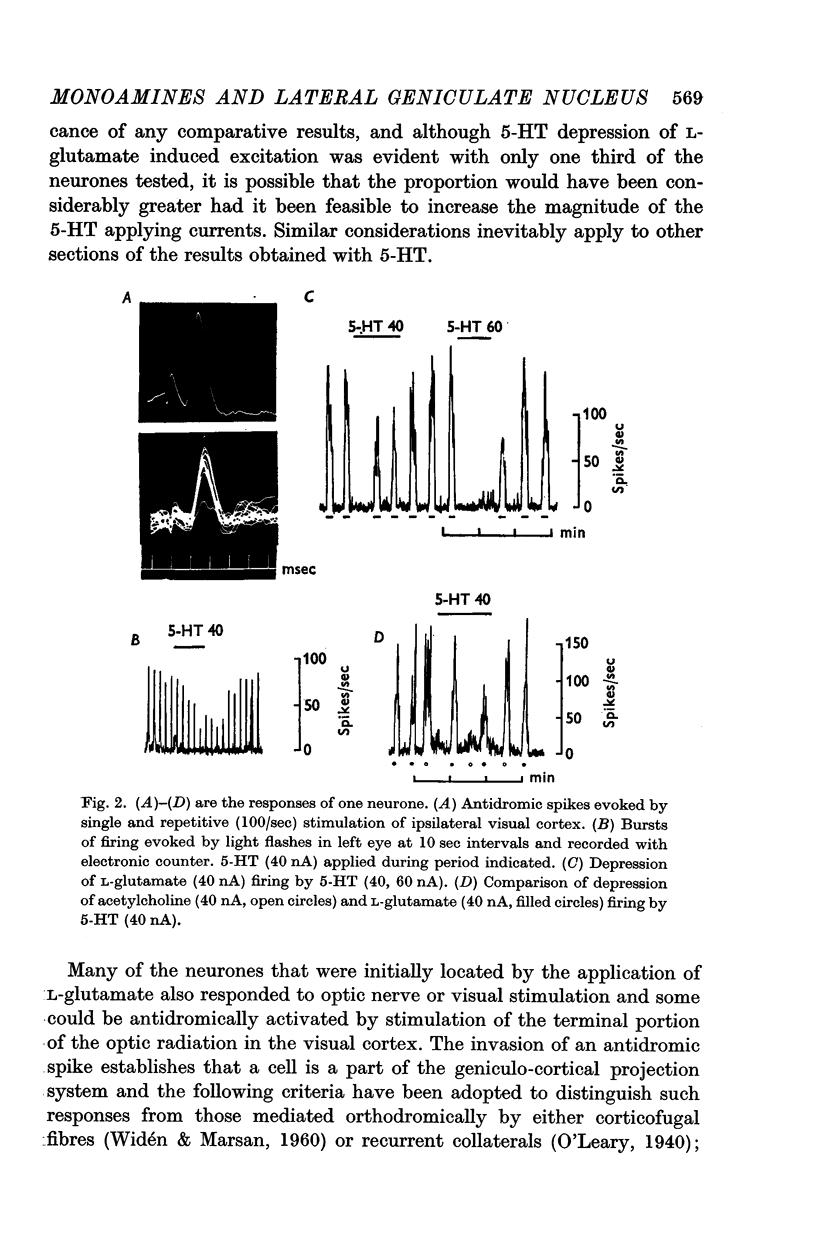
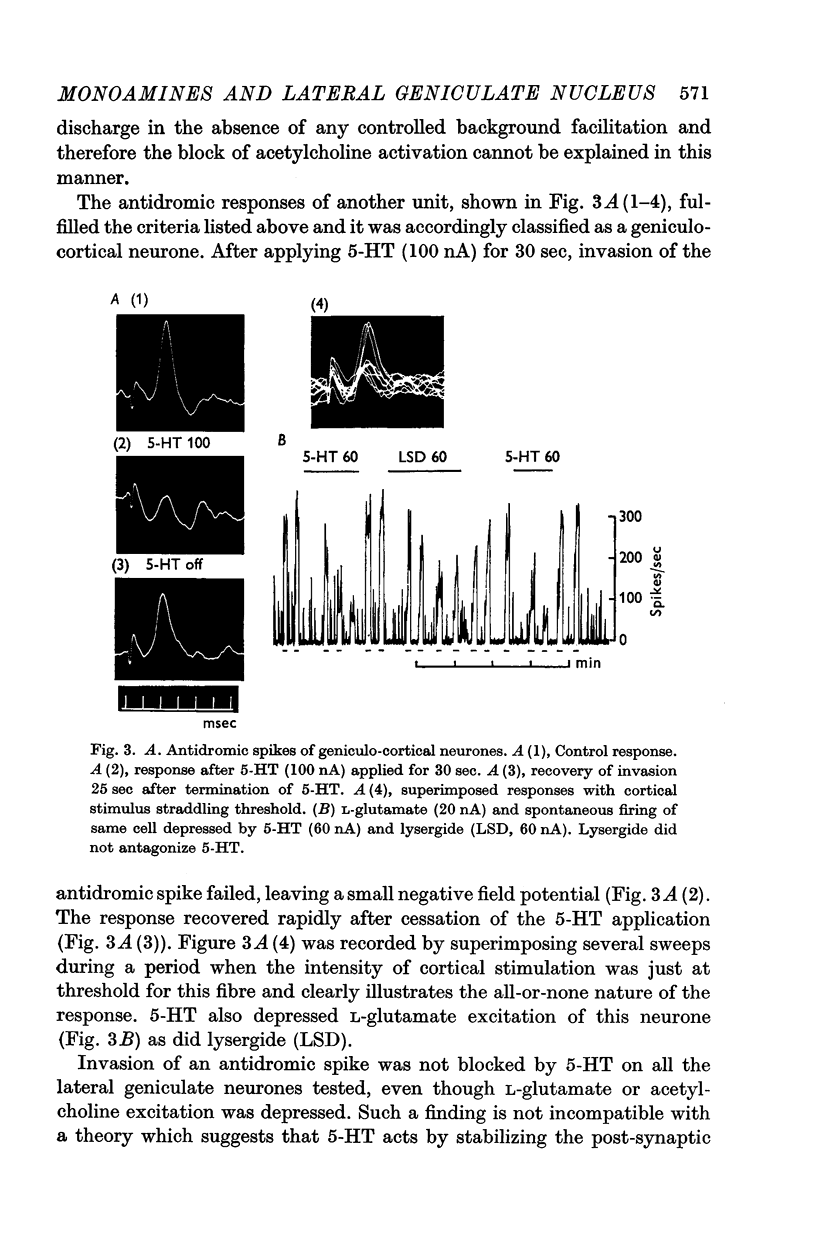
3. This depression was manifested by a reduction or abolition of the effects of optic nerve or visual stimulation, by a failure in some instances of an antidromically propagating spike to invade the cell soma, and by a depression of the excitant effects of L-glutamate and acetylcholine.
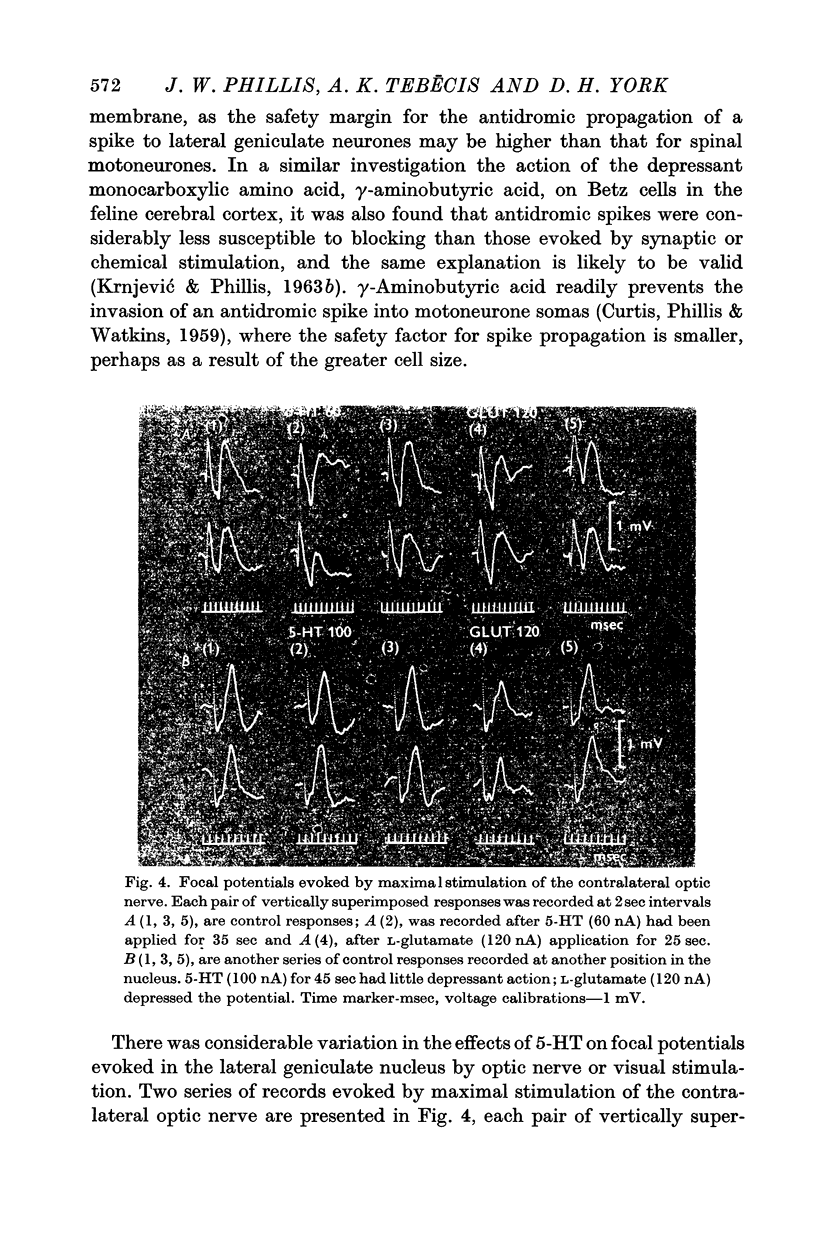
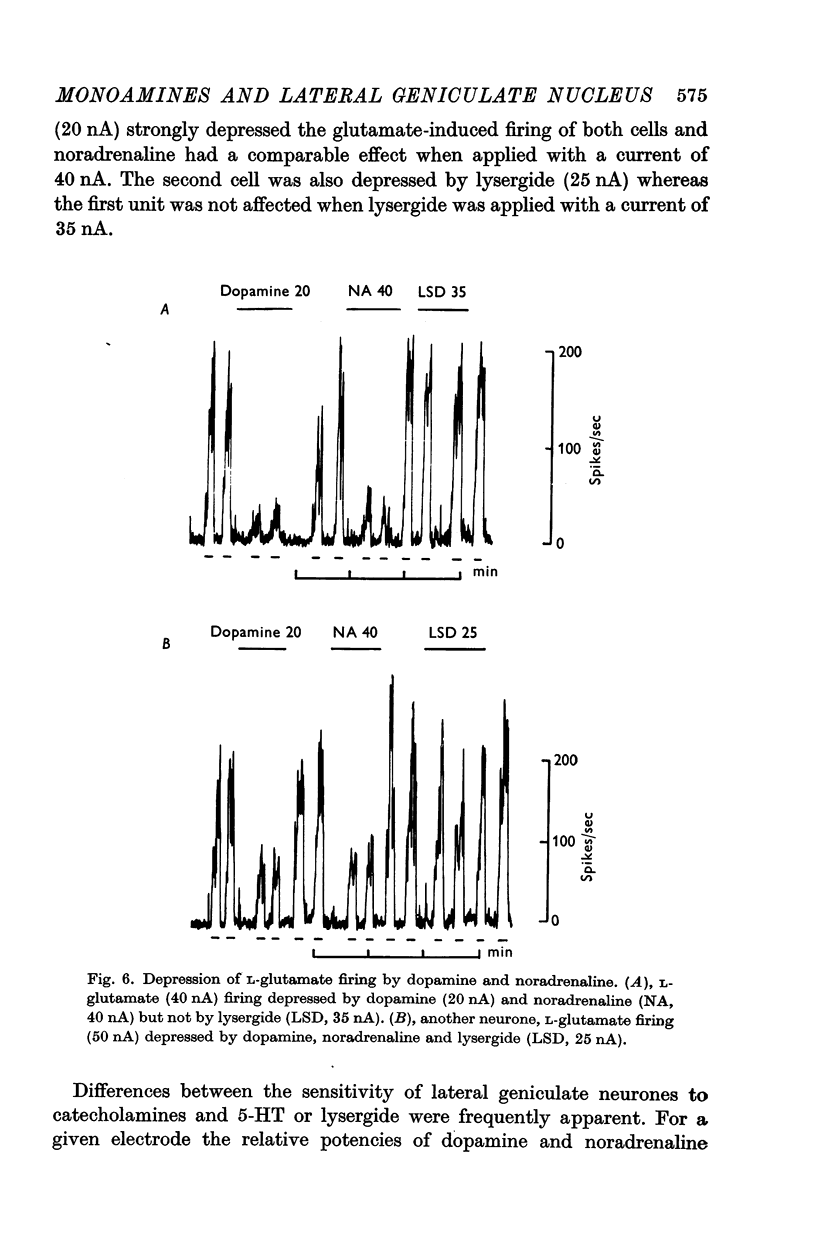
4. Although there was considerable variation in the magnitude of the depressant effects of the monoamines, dopamine was found to be slightly more potent than 5-HT and NA. Neurones which were inhibited by catecholamines did not always respond to 5-HT and lysergide and vice versa.
5. The inhibitory actions of monoamines on lateral geniculate neurones are comparable with those that have been recorded in other structures of the central nervous system.
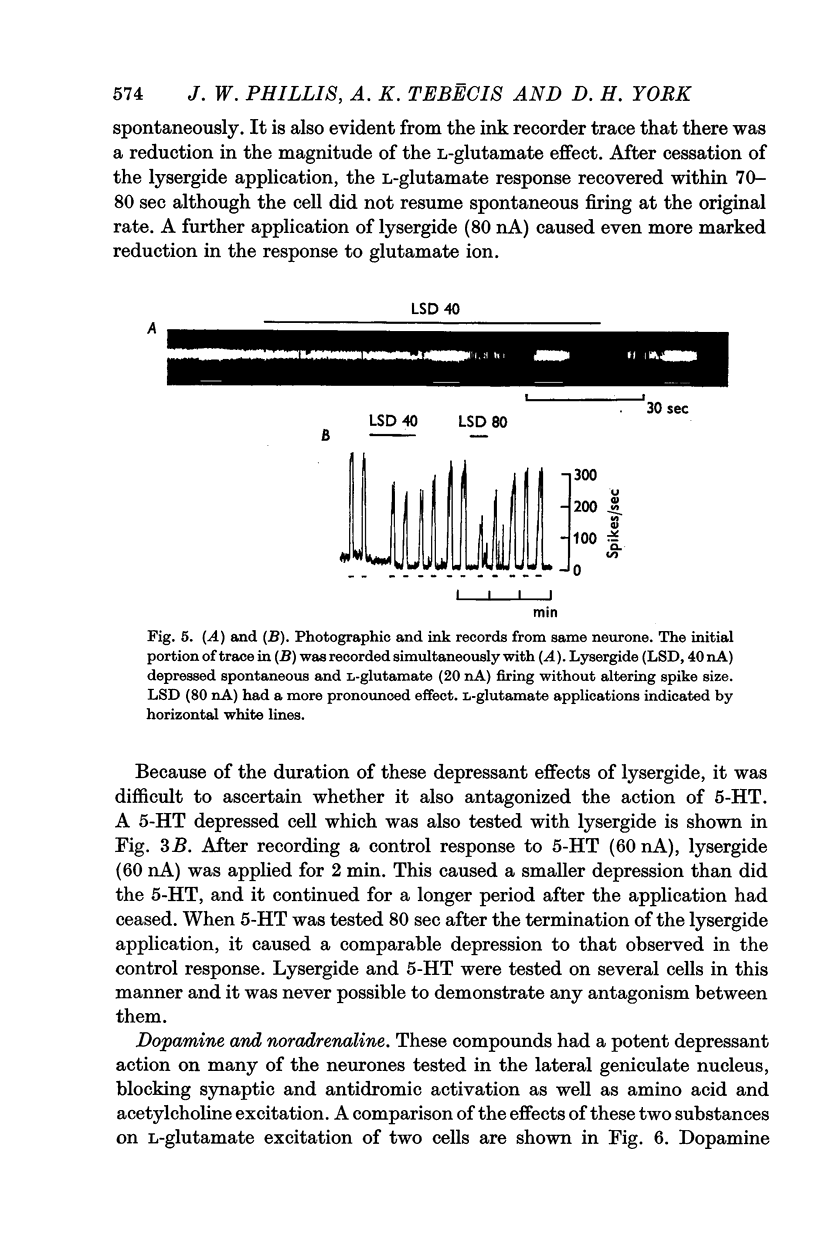
6. Lysergide did not antagonize the action of 5-HT.
7. Catecholamines and 5-HT are present in nerve terminals in the lateral geniculate nucleus and the findings of this study suggest that they act as inhibitory transmitters.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMIN A. H., CRAWFORD T. B., GADDUM J. H. The distribution of substance P and 5-hydroxytryptamine in the central nervous system of the dog. J Physiol. 1954 Dec 10;126(3):596–618. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSEN P., CURTIS D. R. THE PHARMACOLOGY OF THE SYNAPTIC AND ACETYLCHOLINE-INDUCED EXCITATION OF VENTROBASAL THALAMIC NEURONES. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 May-Jun;61:100–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1964.tb02946.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BISHOP P. O., BURKE W., HAYHOW W. R. Lysergic acid diethylamide block of lateral geniculate synapses and relief by repetitive stimulation. Exp Neurol. 1959 Dec;1:556–568. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(59)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BISHOP P. O., FIELD G., HENNESSY B. L., SMITH J. R. Action of d-lysergic acid diethylamide on lateral geniculate synapses. J Neurophysiol. 1958 Nov;21(6):529–549. doi: 10.1152/jn.1958.21.6.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOGDANSKI D. F., WEISSBACH H., UDENFRIEND S. The distribution of serotonin, 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase, and monoamine oxidase in brain. J Neurochem. 1957;1(3):272–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1957.tb12082.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY P. B., WOLSTENCROFT J. H. ACTIONS OF DRUGS ON SINGLE NEURONES IN THE BRAIN-STEM. Br Med Bull. 1965 Jan;21:15–18. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biscoe T. J., Straughan D. W. Micro-electrophoretic studies of neurones in the cat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1966 Mar;183(2):341–359. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bito L. Z., Davson H. Local variations in cerebrospinal fluid composition and its relationship to the composition of the extracellular fluid of the cortex. Exp Neurol. 1966 Mar;14(3):264–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(66)90114-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom F. E., Costa E., Salmoiraghi G. C. Anesthesia and the responsiveness of individual neurons of the caudate nucleus of the cat to acetylcholine, norepinephrine and dopamine administered by microelectrophoresis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 Nov;150(2):244–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., DAVIS R. Pharmacological studies upon neurones of the lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1962 Apr;18:217–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1962.tb01404.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., DAVIS R. The excitation of lateral geniculate neurones by quaternary ammonium derivatives. J Physiol. 1963 Jan;165:62–82. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., ECCLES R. M. The excitation of Renshaw cells by pharmacological agents applied electrophoretically. J Physiol. 1958 May 28;141(3):435–445. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., PHILLIS J. W., WATKINS J. C. Actions of aminoacids on the isolated hemisected spinal cord of the toad. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1961 Jun;16:262–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1961.tb01086.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., PHILLIS J. W., WATKINS J. C. Cholinergic and non-cholinergic transmission in the mammalian spinal cord. J Physiol. 1961 Sep;158:296–323. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., PHILLIS J. W., WATKINS J. C. The chemical excitation of spinal neurones by certain acidic amino acids. J Physiol. 1960 Mar;150:656–682. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., PHILLIS J. W., WATKINS J. C. The depression of spinal neurones by gamma-amino-n-butyric acid and beta-alanine. J Physiol. 1959 Apr 23;146(1):185–203. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobbin L. B., Leeder S., Pollard J. Smooth muscle stimulants in extracts of optic nerves, optic tracts and lateral geniculate bodies of sheep. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1965 Oct;25(2):295–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1965.tb02050.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVARTS E. V., LANDAU W., FREYGANG W., Jr, MARSHALL W. H. Some effects of lysergic acid diethylamide and bufotenine on electrical activity in the cat's visual system. Am J Physiol. 1955 Sep;182(3):594–598. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1955.182.3.594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engberg I., Ryall R. W. The inhibitory action of noradrenaline and other monoamines on spinal neurones. J Physiol. 1966 Jul;185(2):298–322. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUXE K. EVIDENCE FOR THE EXISTENCE OF MONOAMINE NEURONS IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. IV. DISTRIBUTION OF MONOAMINE NERVE TERMINALS IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1965:SUPPL 247–247:37+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GADDUM J. H., HAMEED K. A. Drugs which antagonize 5-hydroxytryptamine. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1954 Jun;9(2):240–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1954.tb00848.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLETT R. C., PHILLIS J. W., VEALE J. L. A SPIKE INTENSIFIER AND SINGLE TRIGGER GENERATOR FOR IDENTIFICATION OF VENTRAL ROOT AXONS. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1965 Jan;18:82–84. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(65)90150-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., LAVERTY R., SHARMAN D. F. Iontophoretic release of adrenaline, noradrenaline and 5-hydroxytryptamine from micropipettes. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Jun;20:491–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb01485.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., MITCHELL J. F., SZERB J. C. Determination of iontophoretic release of acetylcholine from micropipettes. J Physiol. 1963 Mar;165:421–436. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., PHILLIS J. W. Actions of certain amines on cerebral cortical neurones. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Jun;20:471–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb01484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., PHILLIS J. W. Iontophoretic studies of neurones in the mammalian cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1963 Feb;165:274–304. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOCKARD I., REERS B. L. Staining tissue of the central nervous system with luxol fast blue and neutral red. Stain Technol. 1962 Jan;37:13–16. doi: 10.3109/10520296209114562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legge K. F., Randic M., Straughan D. W. The pharmacology of neurones in the pyriform cortex. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1966 Jan;26(1):87–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1966.tb01814.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCANCE I., PHILLIS J. W. DISCHARGE PATTERNS OF ELEMENTS IN CAT CEREBELLAR CORTEX, AND THEIR RESPONSES TO IONTOPHORETICALLY APPLIED DRUGS. Nature. 1964 Nov 28;204:844–846. doi: 10.1038/204844a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCANCE I., PHILLIS J. W. THE LOCATION OF MICROELECTRODE TIPS IN NERVOUS TISSUES. Experientia. 1965 Feb 15;21:108–109. doi: 10.1007/BF02144771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCLENNAN H. THE RELEASE OF ACETYLCHOLINE AND OF 3-HYDROXYTYRAMINE FROM THE CAUDATE NUCLEUS. J Physiol. 1964 Oct;174:152–156. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malliani A., Zanchetti A. Local tissue lesions as a means of assessing the local or remote origin of evoked potentials within the brain. Nature. 1965 May 8;206(984):627–629. doi: 10.1038/206627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCance I., Phillis J. W., Westerman R. A. Responses of thalamic neurones to iontophoretically applied drugs. Nature. 1966 Feb 12;209(5024):715–716. doi: 10.1038/209715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUZUKI H., TAIRA N. Effect of reticular stimulation upon synaptic transmission in cat's lateral geniculate body. Jpn J Physiol. 1961 Dec 15;11:641–655. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.11.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmoiraghi G. C., Stefanis C. N. Patterns of central neurons responses to suspected transmitters. Arch Ital Biol. 1965 Dec 10;103(4):705–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGT M. The concentration of sympathin in different parts of the central nervous system under normal conditions and after the administration of drugs. J Physiol. 1954 Mar 29;123(3):451–481. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIDEN L., AJMONE MARSAN C. Effects of corticipetal and corticifugal impulses upon single elements of the dorsolateral geniculate nucleus. Exp Neurol. 1960 Oct;2:468–502. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(60)90028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C. Pharmacological receptors and general permeability phenomena of cell membranes. J Theor Biol. 1965 Jul;9(1):37–50. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(65)90055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weight F. F., Salmoiraghi G. C. Responses of spinal cord interneurons to acetylcholine, norepinephrine and serotonin administered by microelectrophoresis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 Sep;153(3):420–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]