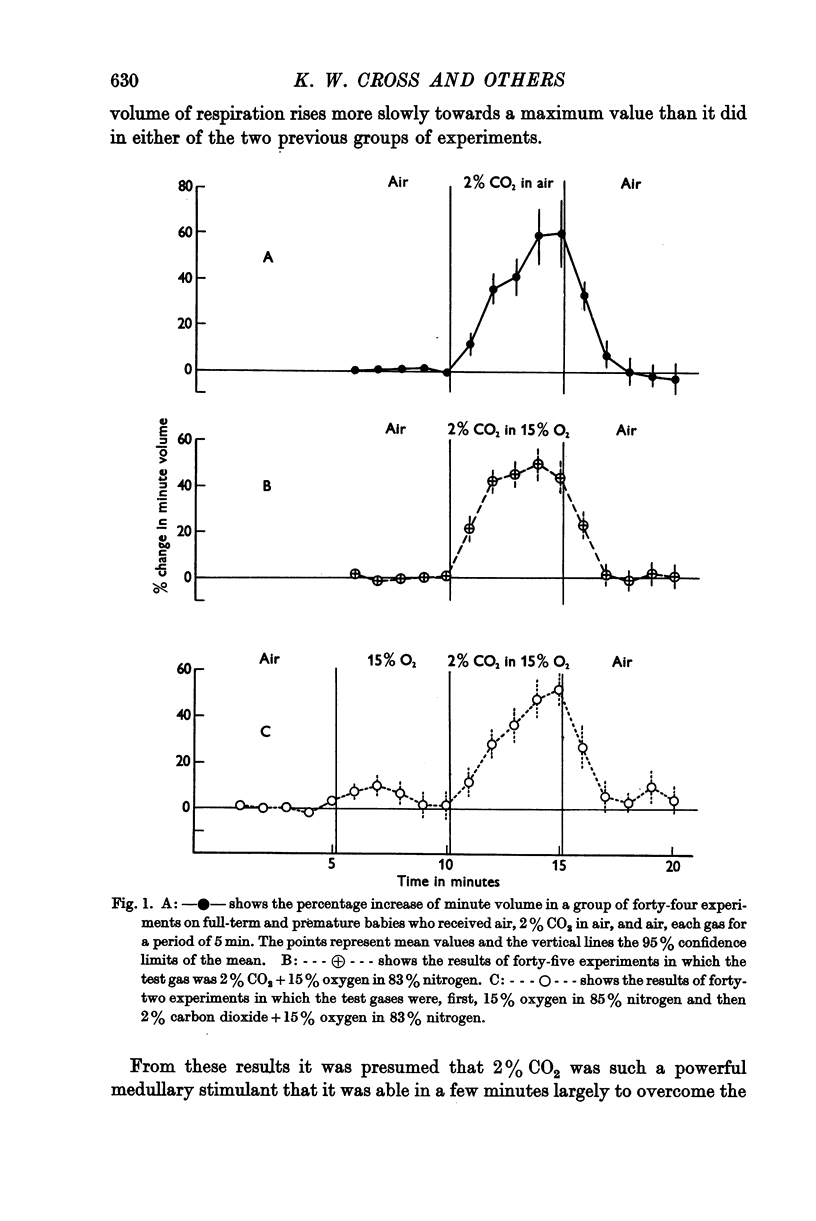
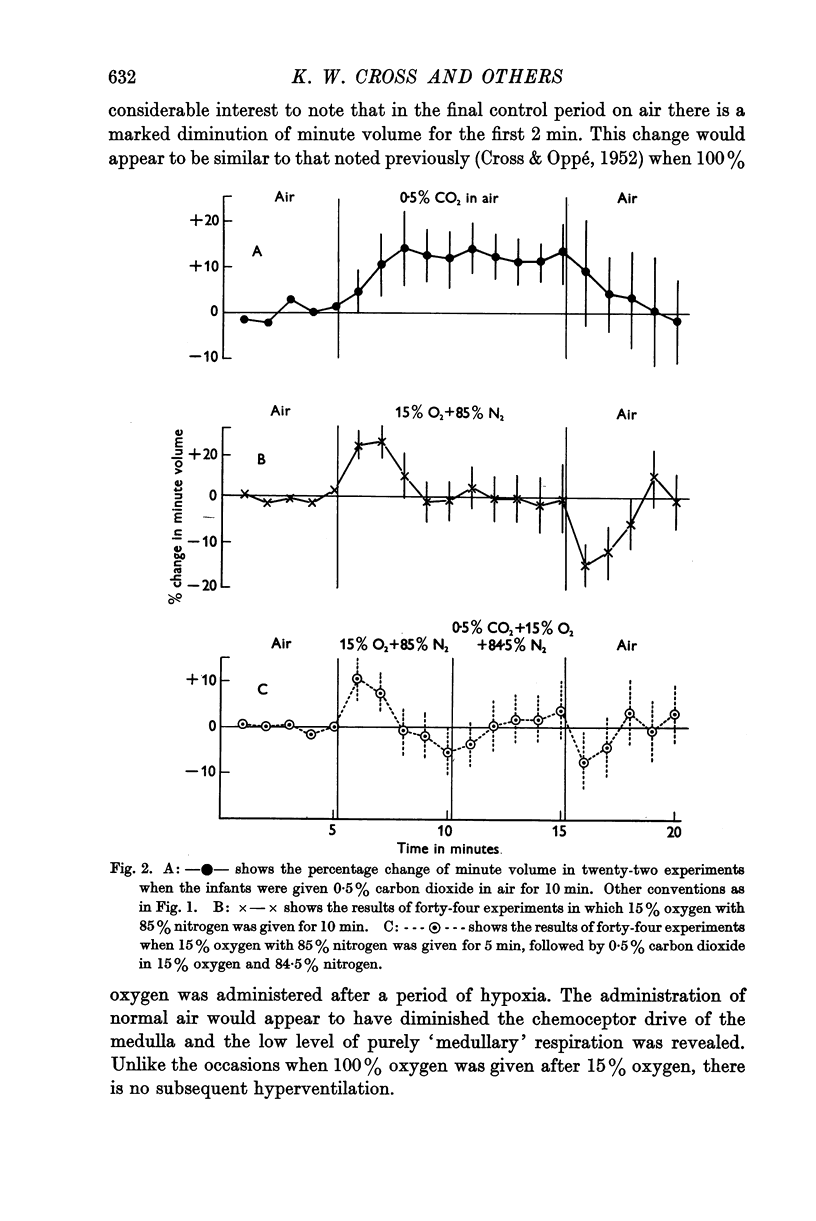
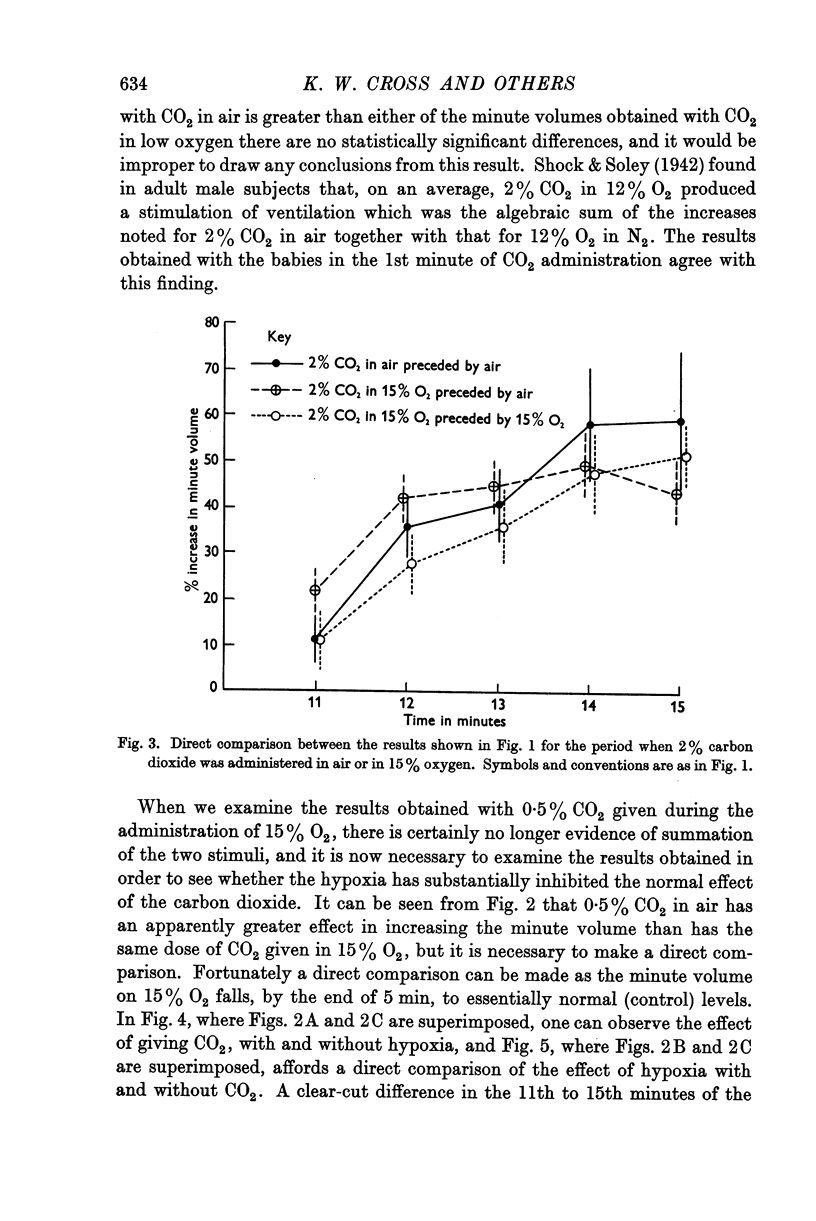
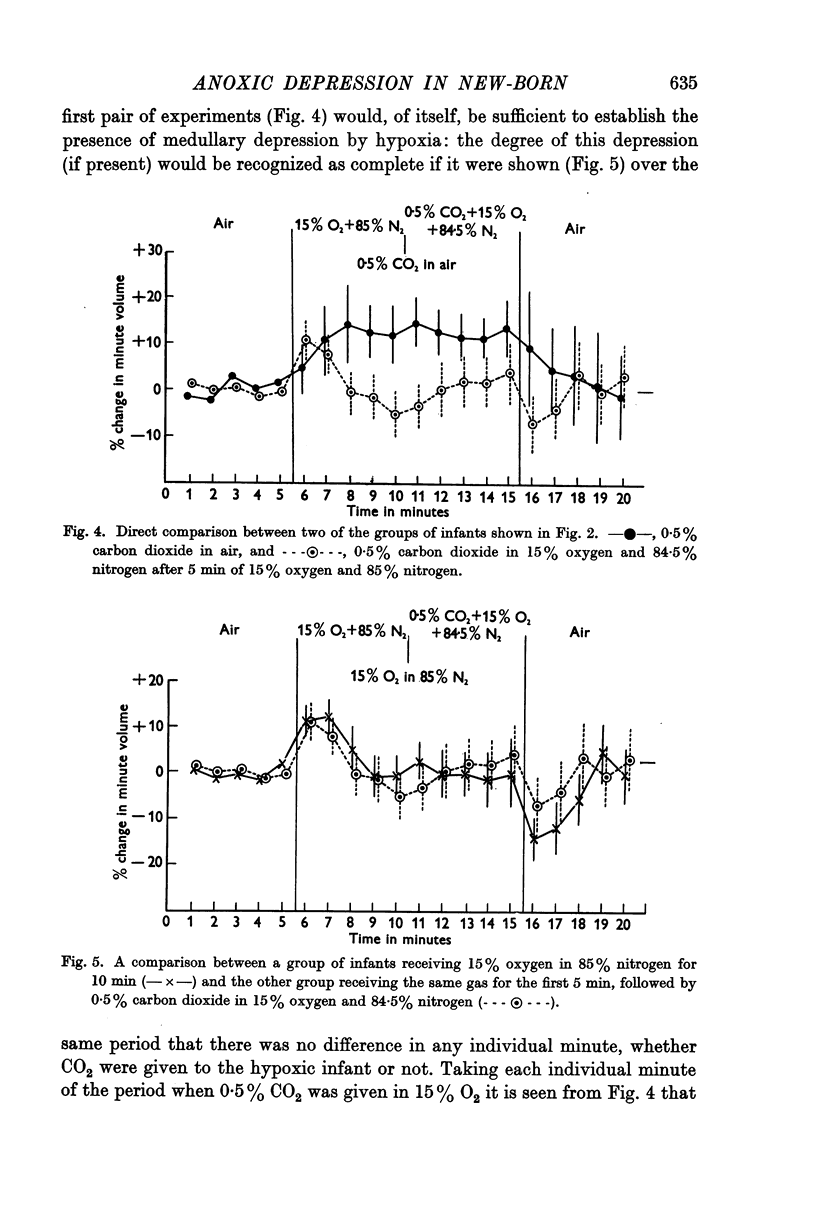
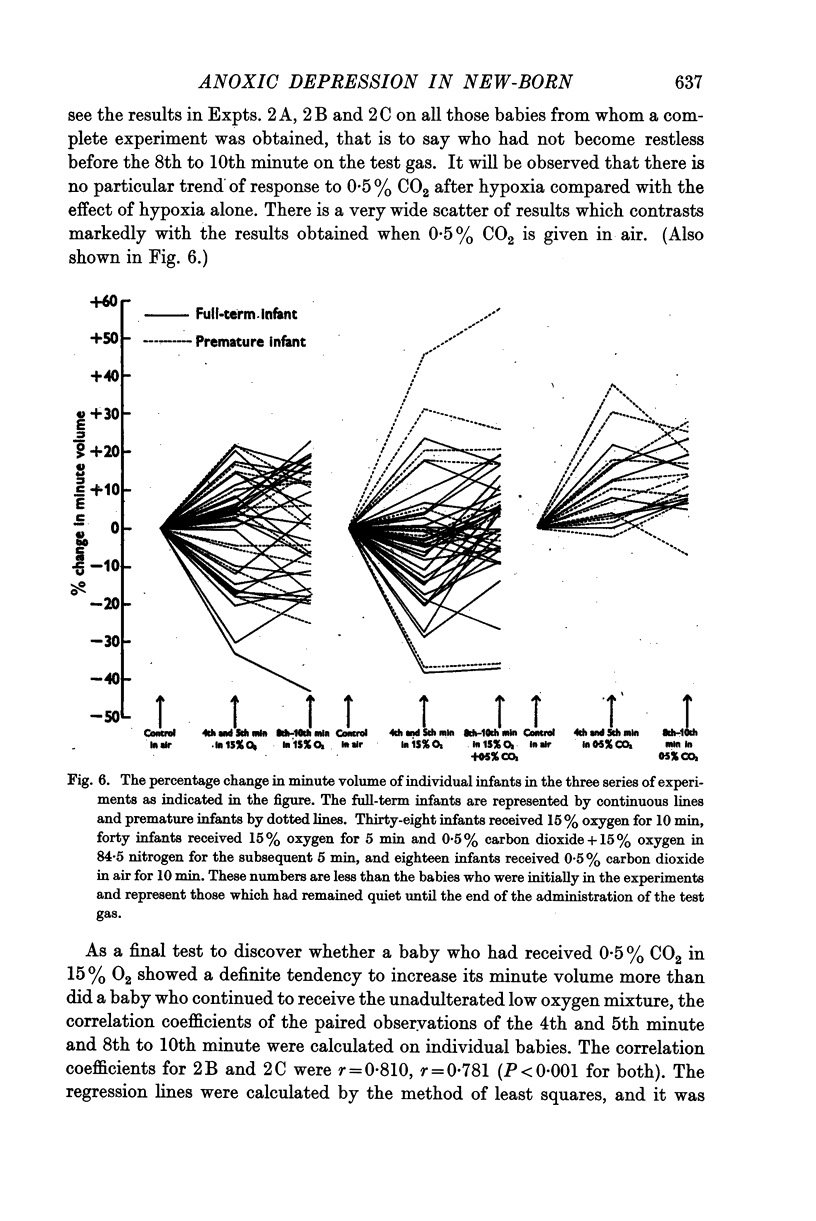
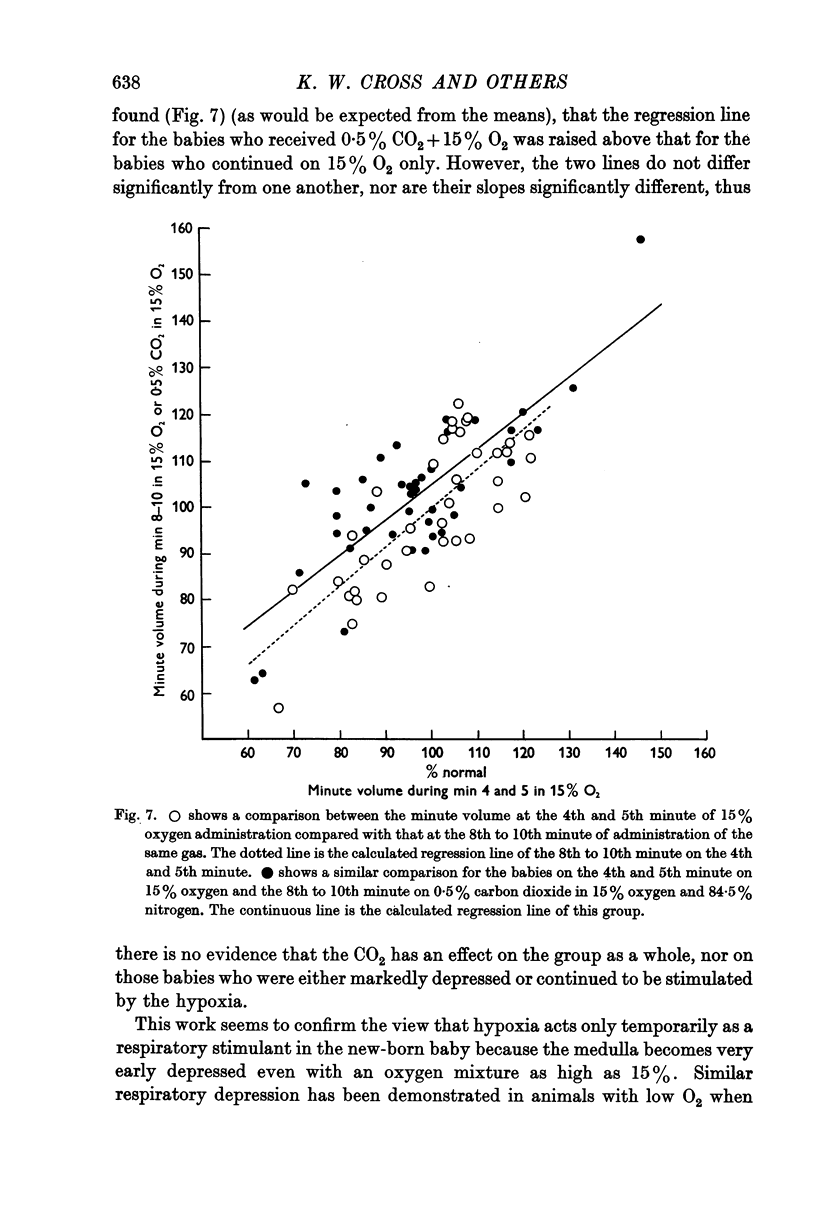
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CROSS K. W., HOOPER J. M., OPPE T. E. The effect of inhalation of carbon dioxide in air on the respiration of the full-term and premature infant. J Physiol. 1953 Nov 28;122(2):264–273. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSS K. W., OPPE T. E. The effect of inhalation of high and low concentrations of oxygen on the respiration of the premature infant. J Physiol. 1952 May;117(1):38–55. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSS K. W. The respiratory rate and ventilation in the newborn baby. J Physiol. 1949 Sep;109(3-4):459–474. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSS K. W., WARNER P. The effect of inhalation of high and low oxygen concentrations on the respiration of the newborn infant. J Physiol. 1951 Jul;114(3):283–295. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIELSEN M., SMITH H. Studies on the regulation of respiration in acute hypoxia; with a appendix on respiratory control during prolonged hypoxia. Acta Physiol Scand. 1952 Feb 12;24(4):293–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1952.tb00847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


