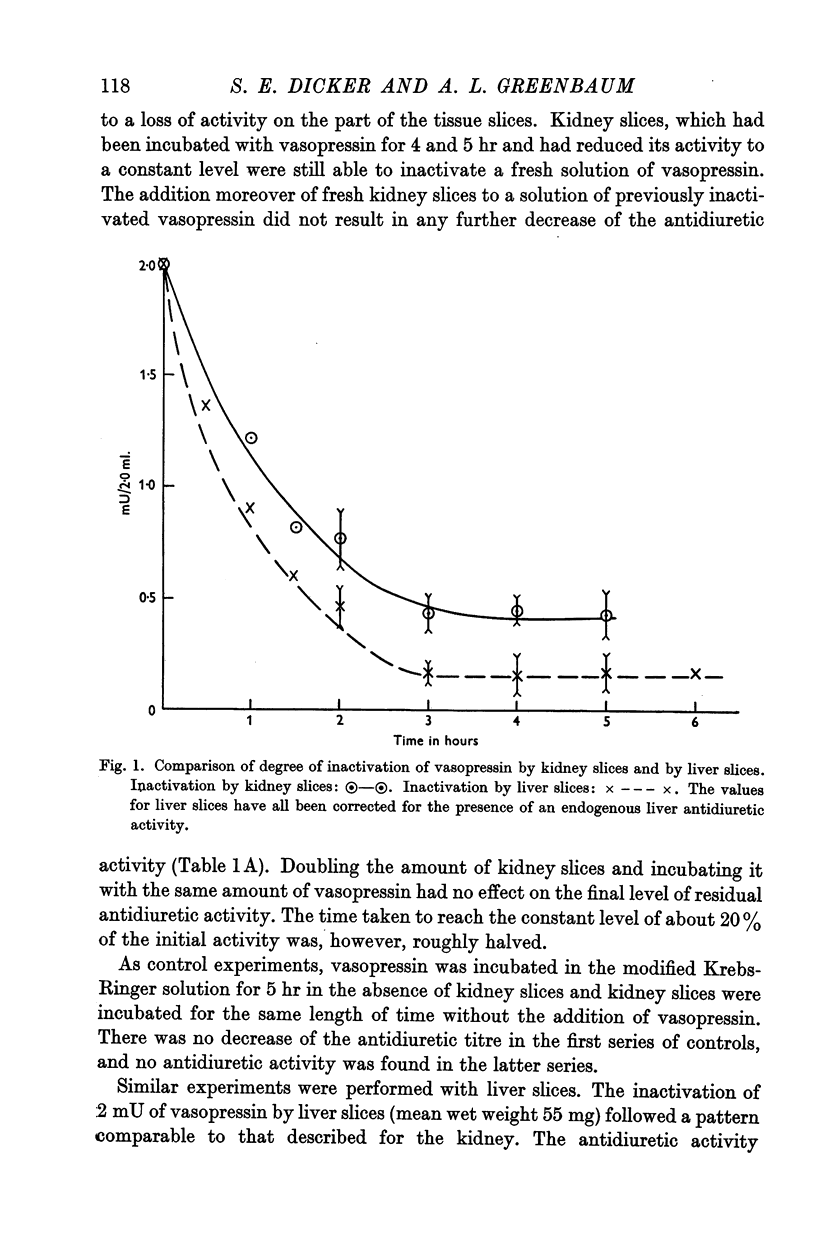
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIRNIE J. H. The inactivation of posterior pituitary antidiuretic hormone by liver extracts. Endocrinology. 1953 Jan;52(1):33–38. doi: 10.1210/endo-52-1-33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOURA A., DICKER S. E. An apparatus for the maintenance of a constant water load and the recording of urine flow in rats. J Physiol. 1953 Oct;122(1):144–148. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICKER S. E. A method for the assay of very small amounts of antidiuretic activity with a note on the antidiuretic titre of rat's blood. J Physiol. 1953 Oct;122(1):149–157. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICKER S. E., GINSBURG M. Some observations on the antidiuretic activity of rat serum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1950 Dec;5(4):497–504. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1950.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICKER S. E., GREENBAUM A. L. The degree of inactivation of vasopressin by the kidney and the liver of rats. J Physiol. 1954 May 28;124(2):35–6P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICKER S. E. The fate of the antidiuretic activity of pitressin in rats. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):464–475. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINSBURG M., HELLER H. The clearance of injected vasopressin from the circulation and its fate in the body. J Endocrinol. 1953 Jul;9(3):283–291. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0090283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELLER H., BLACKMORE K. E. The assay of small amounts of antidiuretic activity by intravenous injections into mice. J Endocrinol. 1952 Jul;8(3):224–228. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0080224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller H. The state in the blood and the excretion by the kidney of the antidiuretic principle of posterior pituitary extracts. J Physiol. 1937 Feb 19;89(1):81–95. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1937.sp003464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller H., Urban F. F. The fate of the antidiuretic principle of postpituitary extracts in vivo and in vitro. J Physiol. 1935 Dec 16;85(4):502–518. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1935.sp003334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOBLE R. L., TAYLOR N. B. Antidiuretic substances in human urine after haemorrhage, fainting, dehydration and acceleration. J Physiol. 1953 Nov 28;122(2):220–237. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


