Abstract
1. Depolarizing currents were applied to motor nerve terminals in the rat phrenic nerve—diaphragm muscle preparation in vitro.
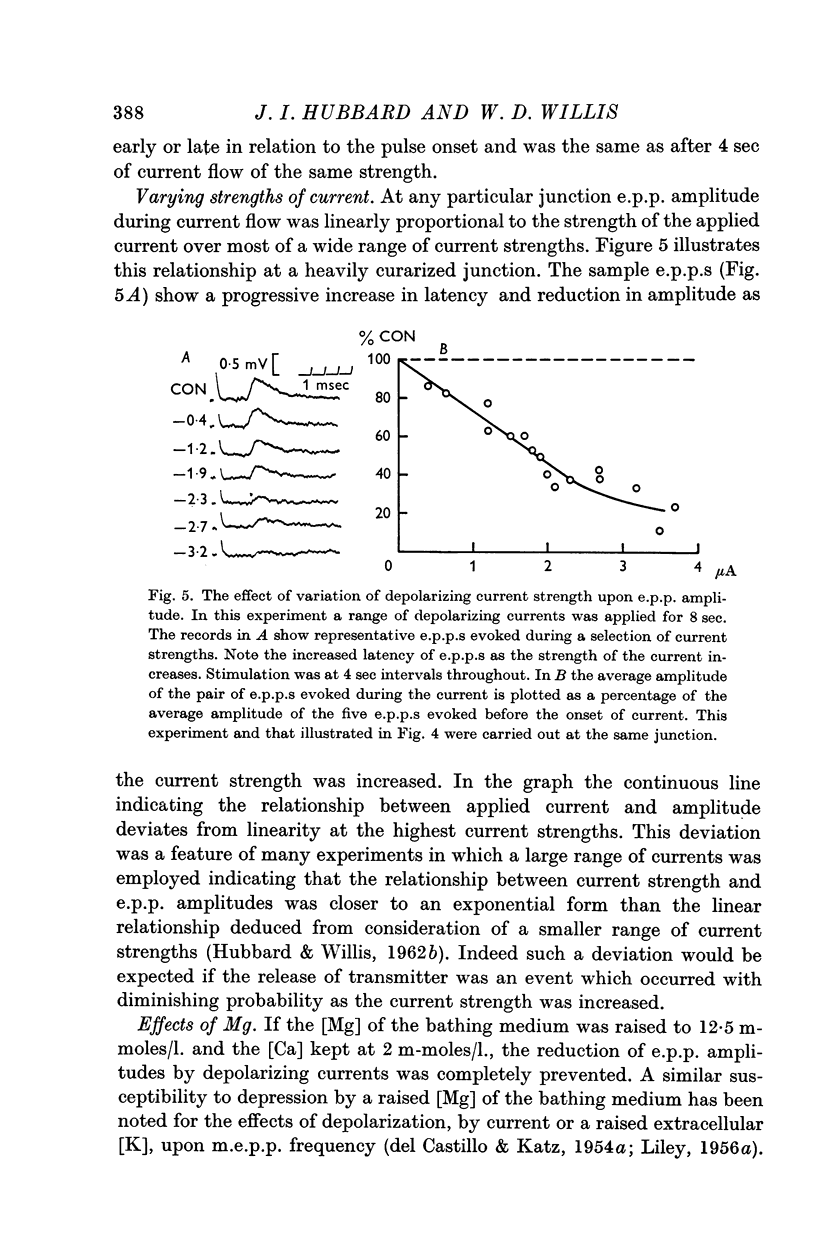
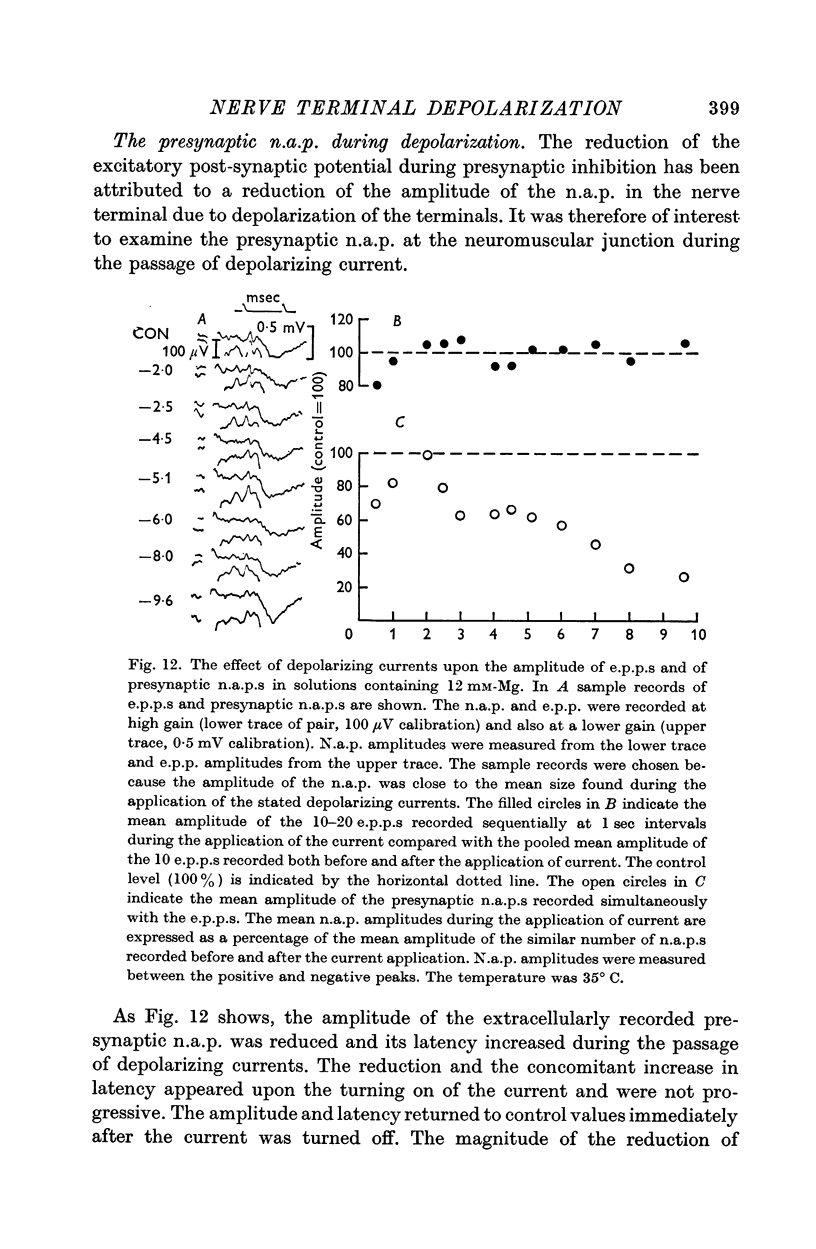
2. During the passage of depolarizing currents the amplitude of the presynaptic nerve action potentials and of end-plate potentials (e.p.p.s) was reduced in proportion to the current strength.
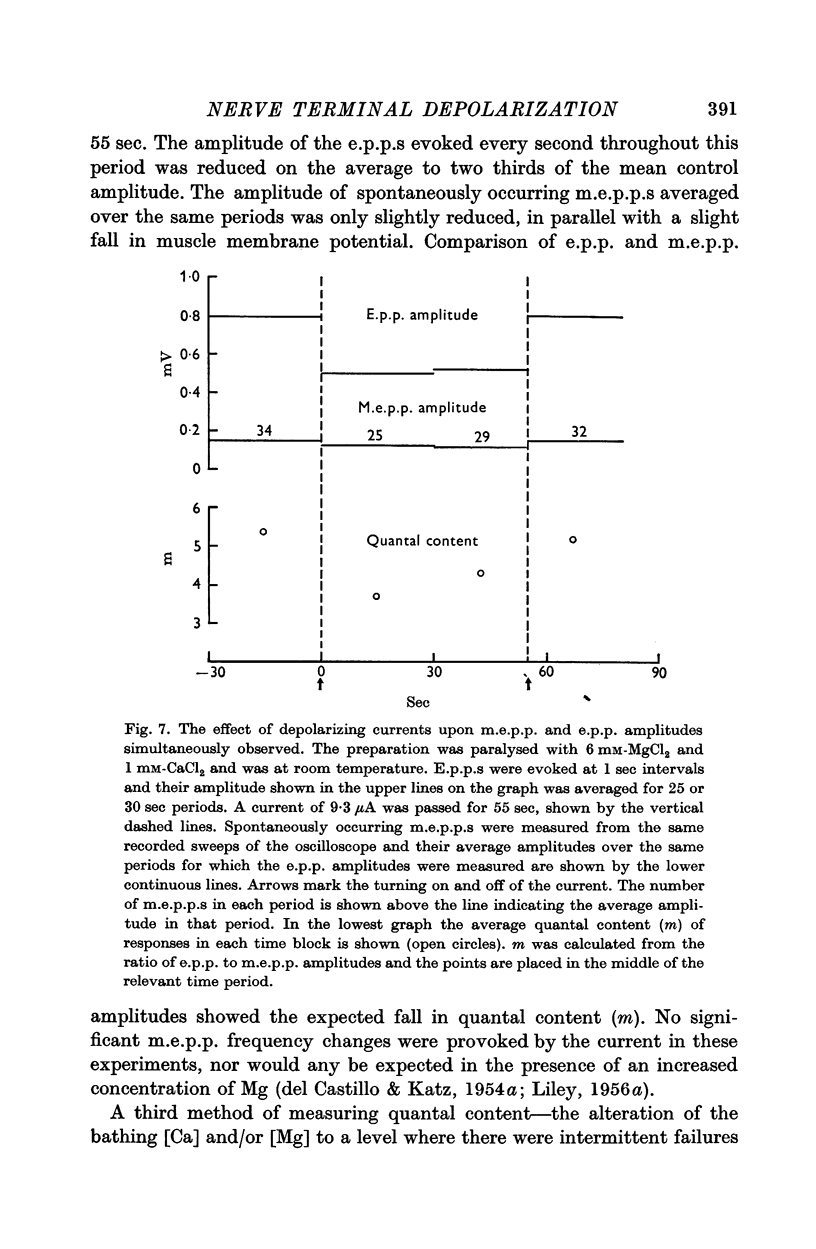
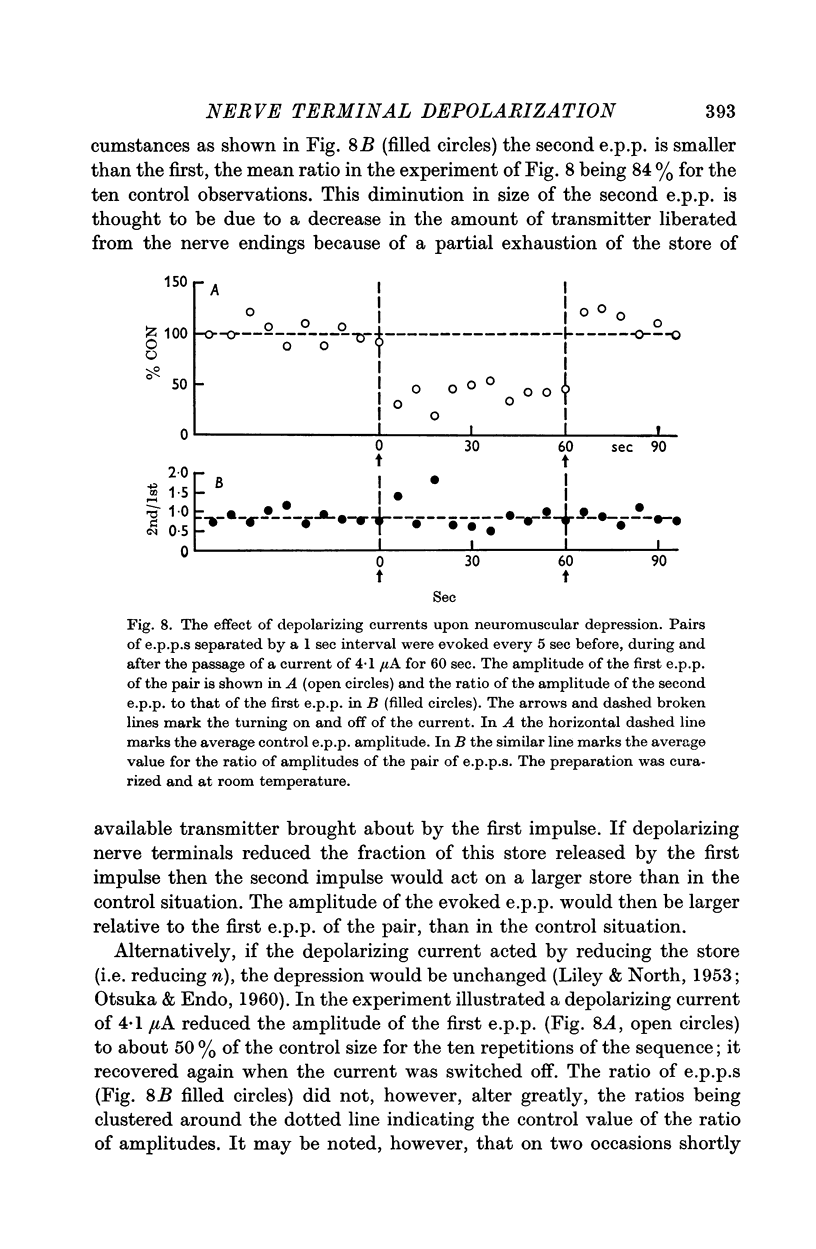
3. The reduction in e.p.p. amplitudes was shown to be due to a reduction in the number of quanta released.
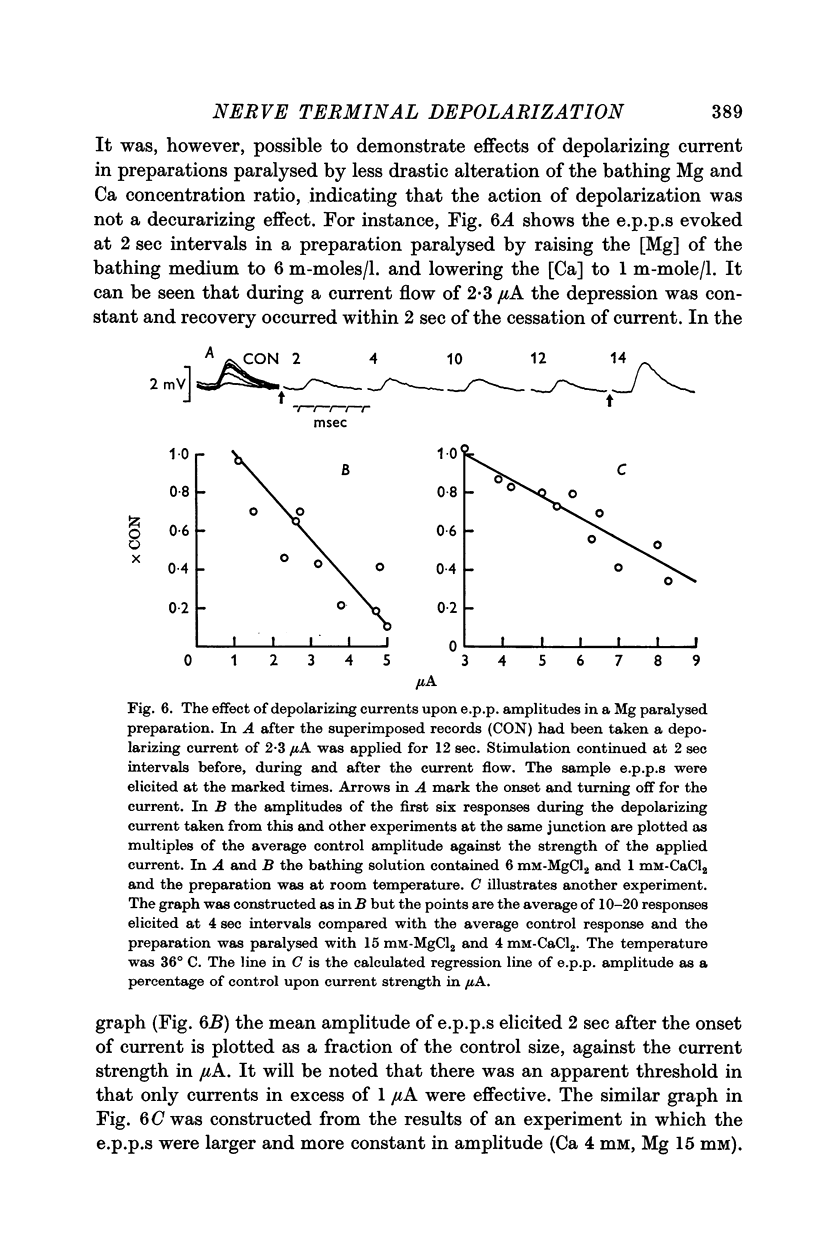
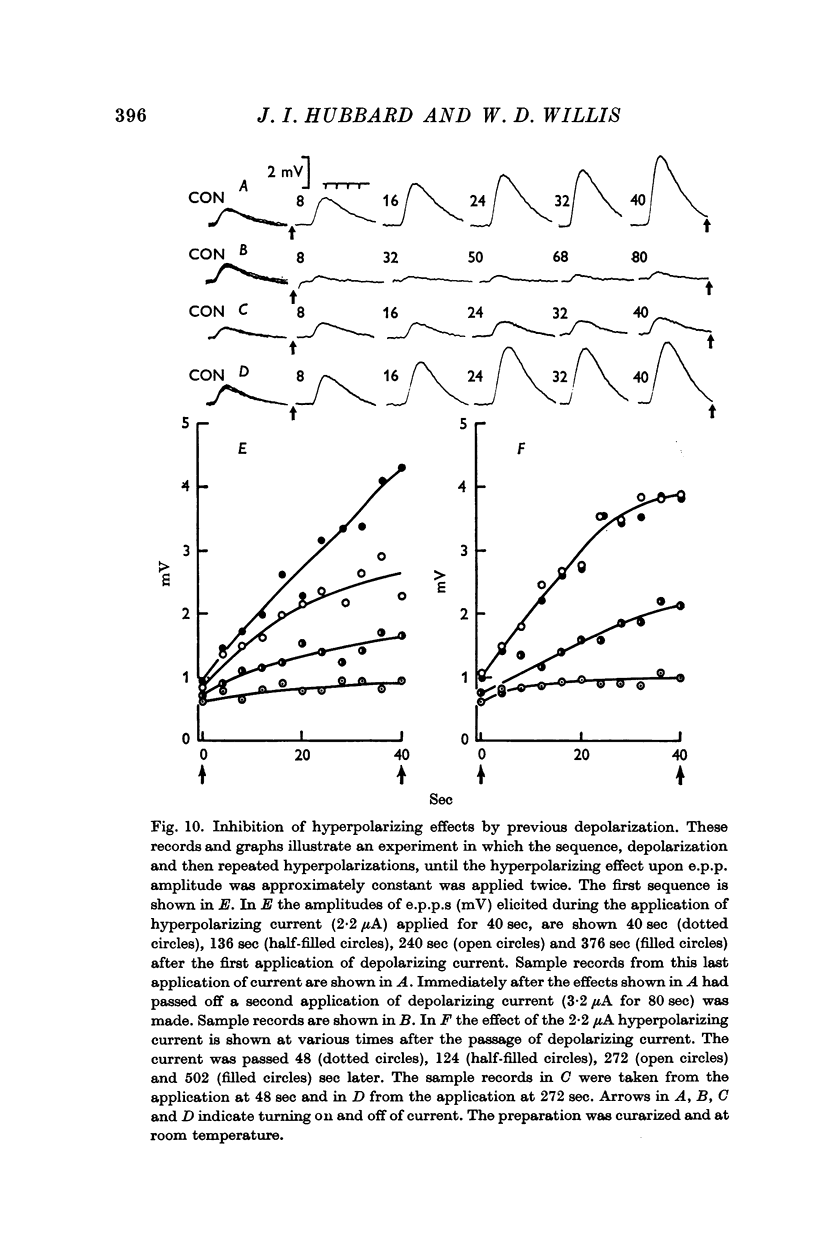
4. An excess of Mg ions or the previous application of a hyperpolarizing current could prevent the reduction of e.p.p. amplitudes and quantal contents by depolarizing current.
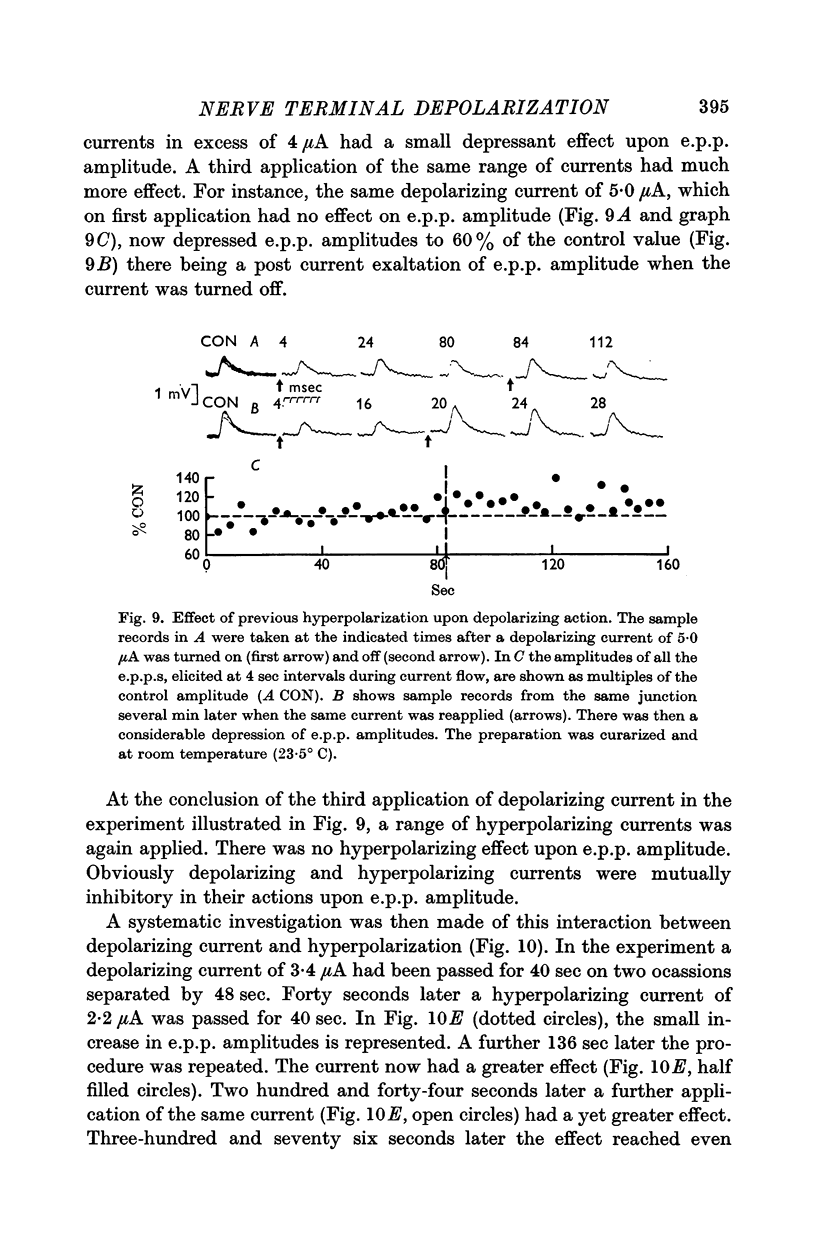
5. Depolarizing current application prevented later hyperpolarizing currents affecting e.p.p. amplitudes.
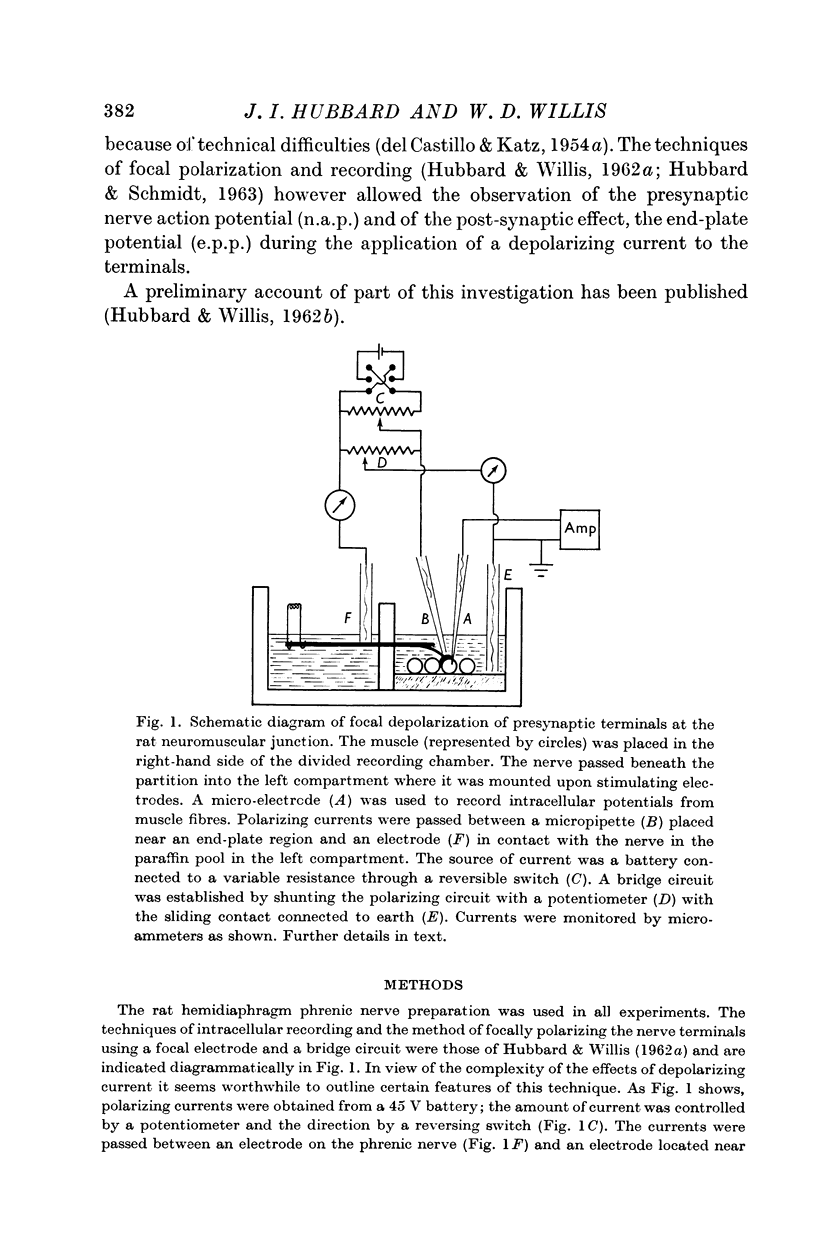
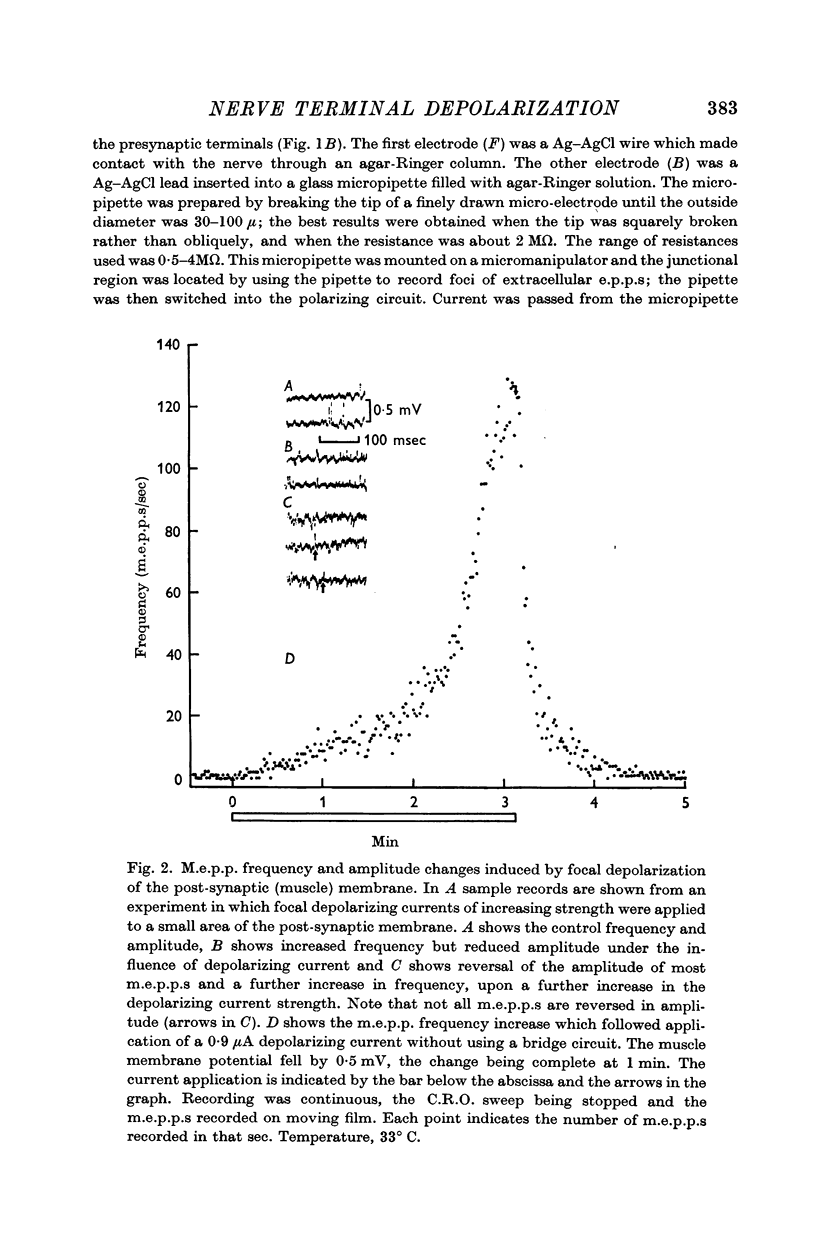
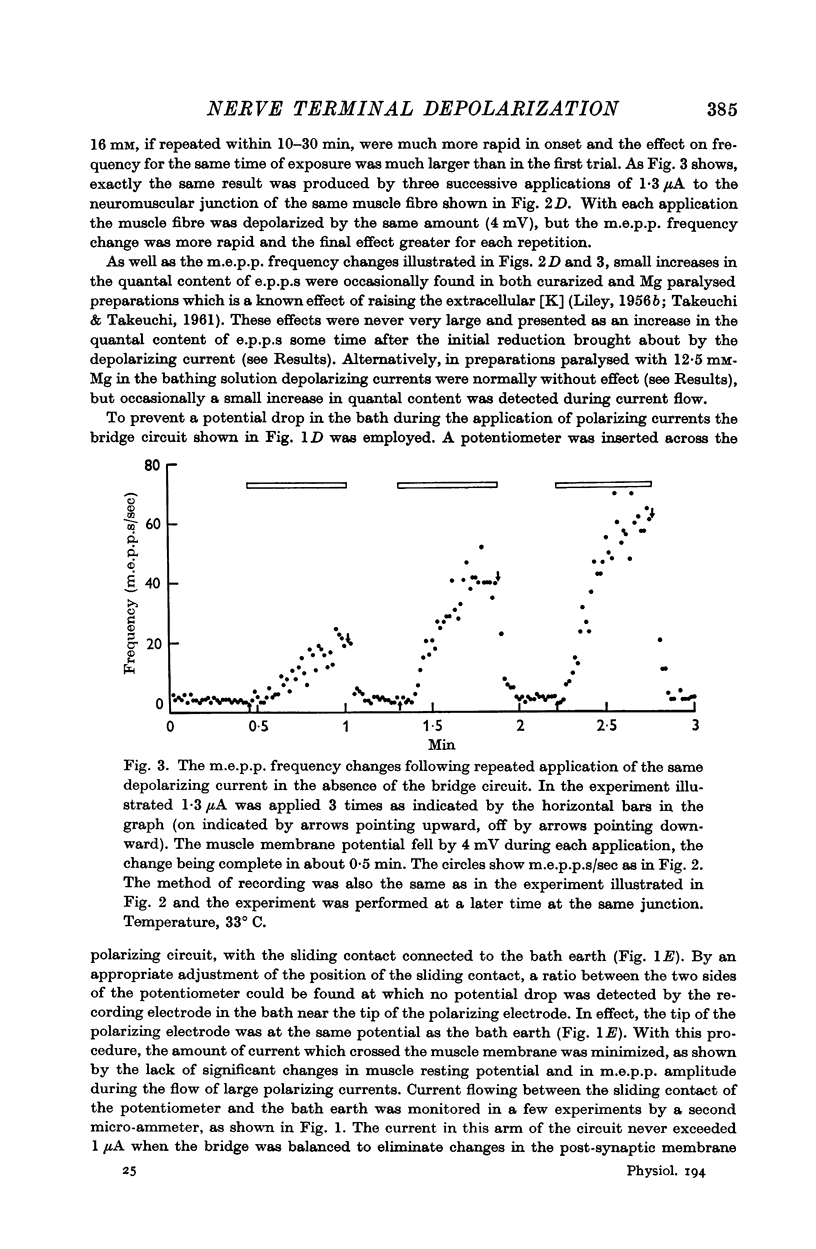
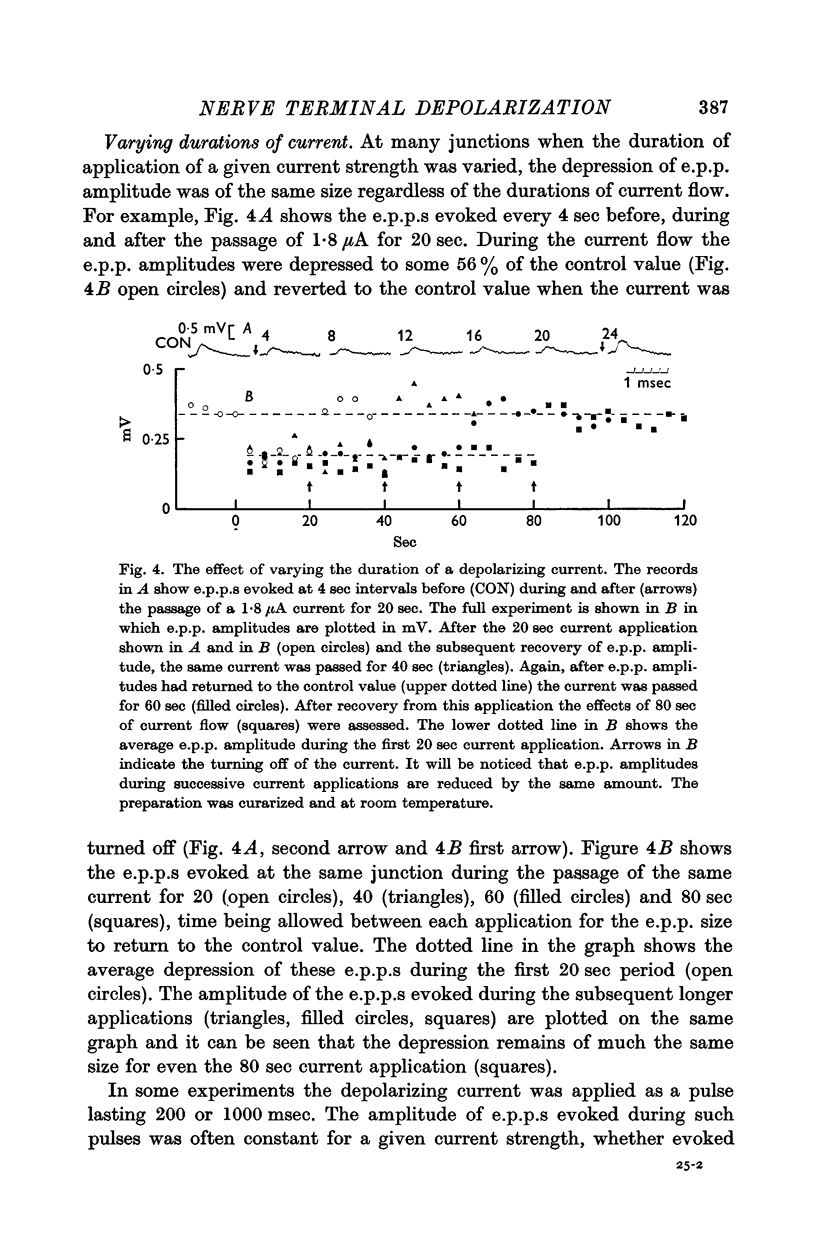
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloedel J., Gage P. W., Llinás R., Quastel D. M. Transmitter release at the squid giant synapse in the presence of tetrodotoxin. Nature. 1966 Oct 1;212(5057):49–50. doi: 10.1038/212049a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Changes in end-plate activity produced by presynaptic polarization. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):586–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Quantal components of the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):560–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Statistical factors involved in neuromuscular facilitation and depression. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):574–585. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., JAEGER J. C. The relationship between the mode of operation and the dimensions of the junctional regions at synapses and motor end-organs. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1958 Jan 1;148(930):38–56. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1958.0003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., KOSTYUK P. G., SCHMIDT R. F. The effect of electric polarization of the spinal cord on central afferent fibres and on their excitatory synaptic action. J Physiol. 1962 Jun;162:138–150. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmqvist D., Quastel D. M. A quantitative study of end-plate potentials in isolated human muscle. J Physiol. 1965 Jun;178(3):505–529. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elul R. Dependence of synaptic transmission on protein metabolism of nerve cells: a possible electrokinetic mechanism of learning? Nature. 1966 Jun 11;210(5041):1127–1131. doi: 10.1038/2101127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Quastel D. M. Dual effect of potassium on transmitter release. Nature. 1965 May 8;206(984):625–626. doi: 10.1038/206625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGIWARA S., TASAKI I. A study on the mechanism of impulse transmission across the giant synapse of the squid. J Physiol. 1958 Aug 29;143(1):114–137. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBBARD J. I., SCHMIDT R. F. An electrophysiological investigation of mammalian motor nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:145–167. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBBARD J. I., WILLIS W. D. Hyperpolarization of mammalian motor nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;163:115–137. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBBARD J. I., WILLIS W. D. Reduction of transmitter output by depolarization. Nature. 1962 Mar 31;193:1294–1295. doi: 10.1038/1931294a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. I., Kwanbunbumpen S. Evidence for the vesicle hypothesis. J Physiol. 1968 Feb;194(2):407–420. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINSON D. H. The nature of the antagonism between calcium and magnesium ions at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1957 Oct 30;138(3):434–444. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. PROPAGATION OF ELECTRIC ACTIVITY IN MOTOR NERVE TERMINALS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Feb 16;161:453–482. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. THE EFFECT OF CALCIUM ON ACETYLCHOLINE RELEASE FROM MOTOR NERVE TERMINALS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Feb 16;161:496–503. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNO M. MECHANSIM OF FACILITATION AND DEPRESSION OF THE EXCITATORY SYNAPTIC POTENTIAL IN SPINAL MOTONEURONES. J Physiol. 1964 Dec;175:100–112. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The release of acetylcholine from nerve endings by graded electric pulses. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1967 Jan 31;167(1006):23–38. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1967.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W., NORTH K. A. An electrical investigation of effects of repetitive stimulation on mammalian neuromuscular junction. J Neurophysiol. 1953 Sep;16(5):509–527. doi: 10.1152/jn.1953.16.5.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W. The effects of presynaptic polarization on the spontaneous activity at the mammalian neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):427–443. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W. The quantal components of the mammalian end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1956 Sep 27;133(3):571–587. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN A. R. A further study of the statistical composition on the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1955 Oct 28;130(1):114–122. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRELL F. Effect of anodal polarization on the firing pattern of single cortical cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1961 Jul 28;92:860–876. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1961.tb40962.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRELL F. Electrophysiological contributions to the neural basis of learning. Physiol Rev. 1961 Jul;41:443–494. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1961.41.3.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OTSUKA M., ENDO M. The effect of guanidine on neuromuscular transmission. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1960 Mar;128:273–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons R. L., Hofmann W. W., Feigen G. A. Presynaptic effects of potassium ion on the mammalian neuromuscular junction. Nature. 1965 Nov 6;208(5010):590–591. doi: 10.1038/208590a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIKER W. K. EFFECTS OF TETRAETHYLAMMONIUM CHLORIDE ON ELECTRICAL ACTIVITIES OF FROG SYMPATHETIC GANGLION CELLS. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1964 Sep;145:317–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A., TAKEUCHI N. Changes in potassium concentration around motor nerve terminals, produced by current flow, and their effects on neuromuscular transmission. J Physiol. 1961 Jan;155:46–58. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A., TAKEUCHI N. Electrical changes in pre- and postsynaptic axons of the giant synapse of Loligo. J Gen Physiol. 1962 Jul;45:1181–1193. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.6.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


