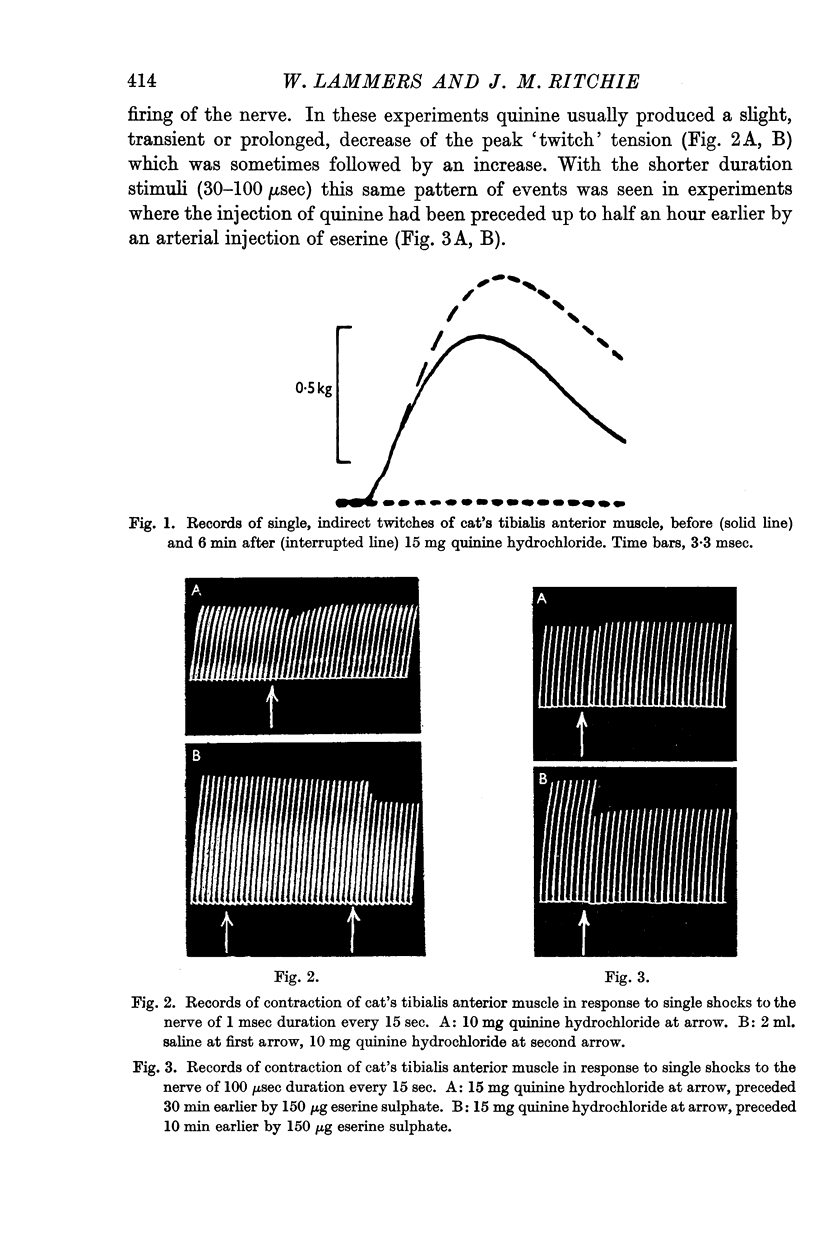
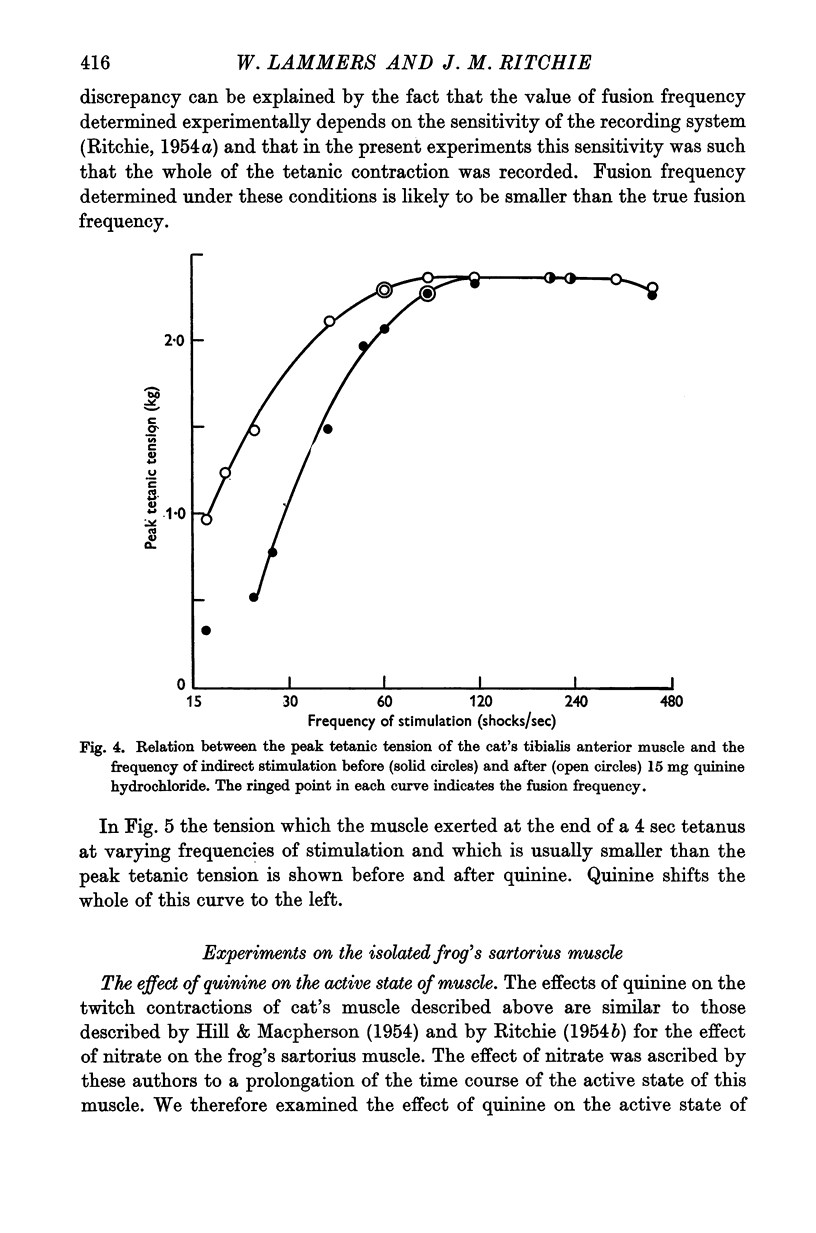
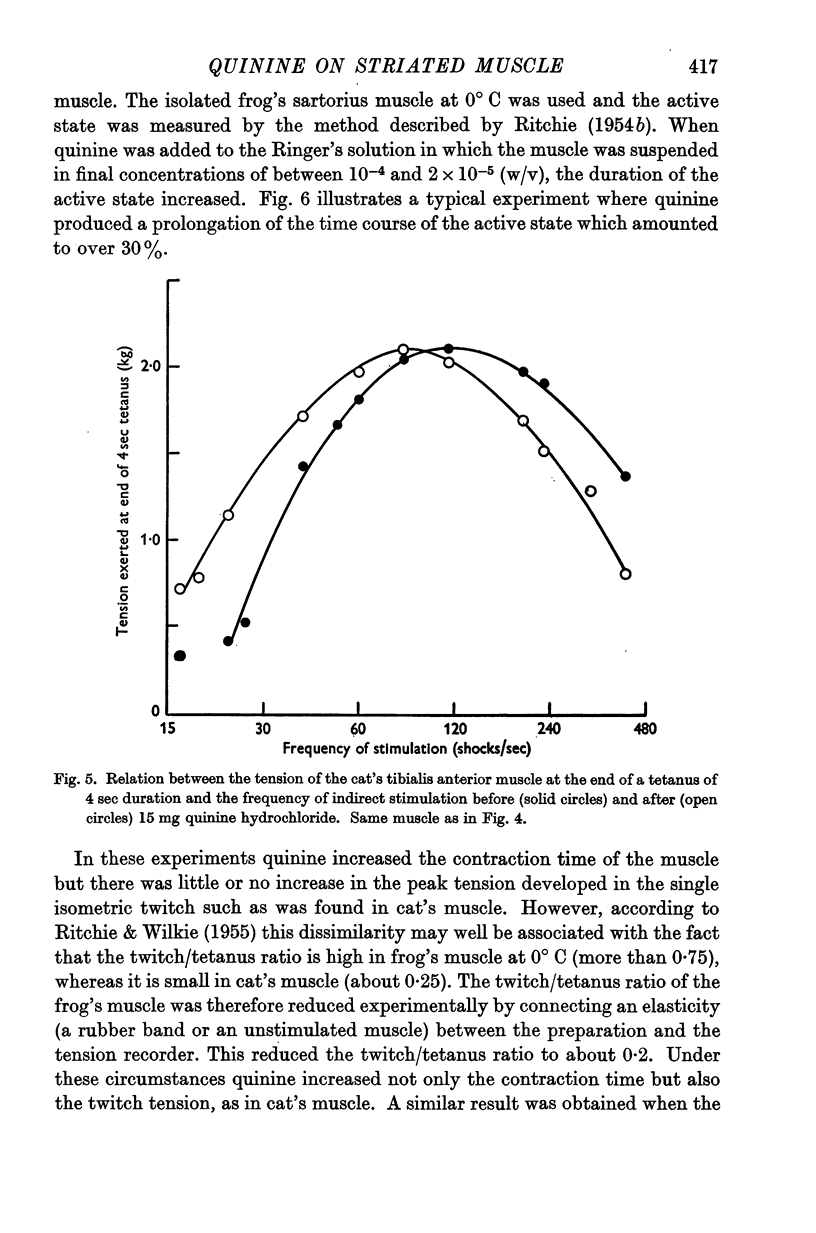
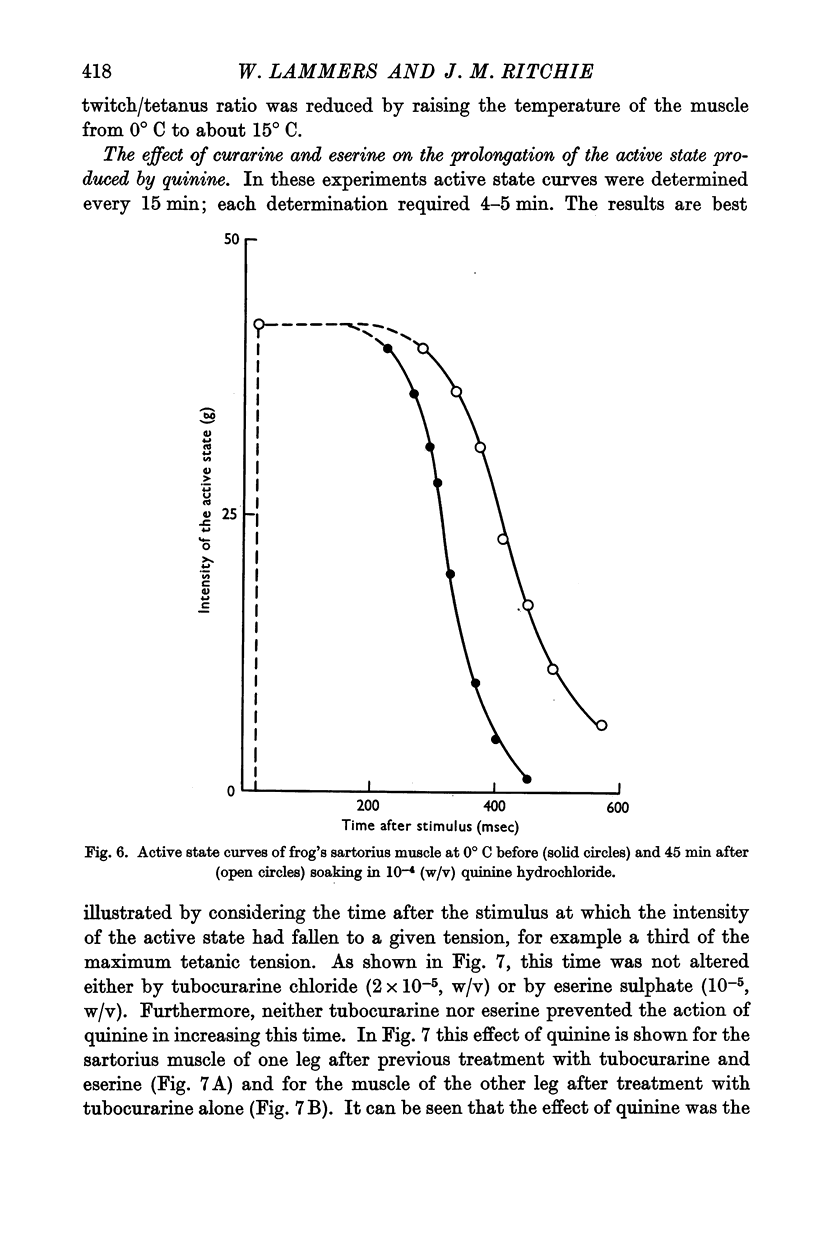
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown G. L., Burns B. D., Feldberg W. The effect of diisopropyl fluorophosphonate on neuromuscular transmission in cats. J Physiol. 1948 Jun 25;107(3):346–354. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1948.sp004279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOFFART M., RITCHIE J. M. The effect of adrenaline on the contraction of mammalian skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1952 Mar;116(3):357–371. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey A. M. The actions of quinine on skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1939 Feb 14;95(1):45–67. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1939.sp003710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RITCHE J. M. The duration of the plateau of full activity in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):605–612. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZAIMIS E. J. Motor end-plate differences as a determining factor in the mode of action of neuromuscular blocking substances. J Physiol. 1953 Nov 28;122(2):238–251. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


