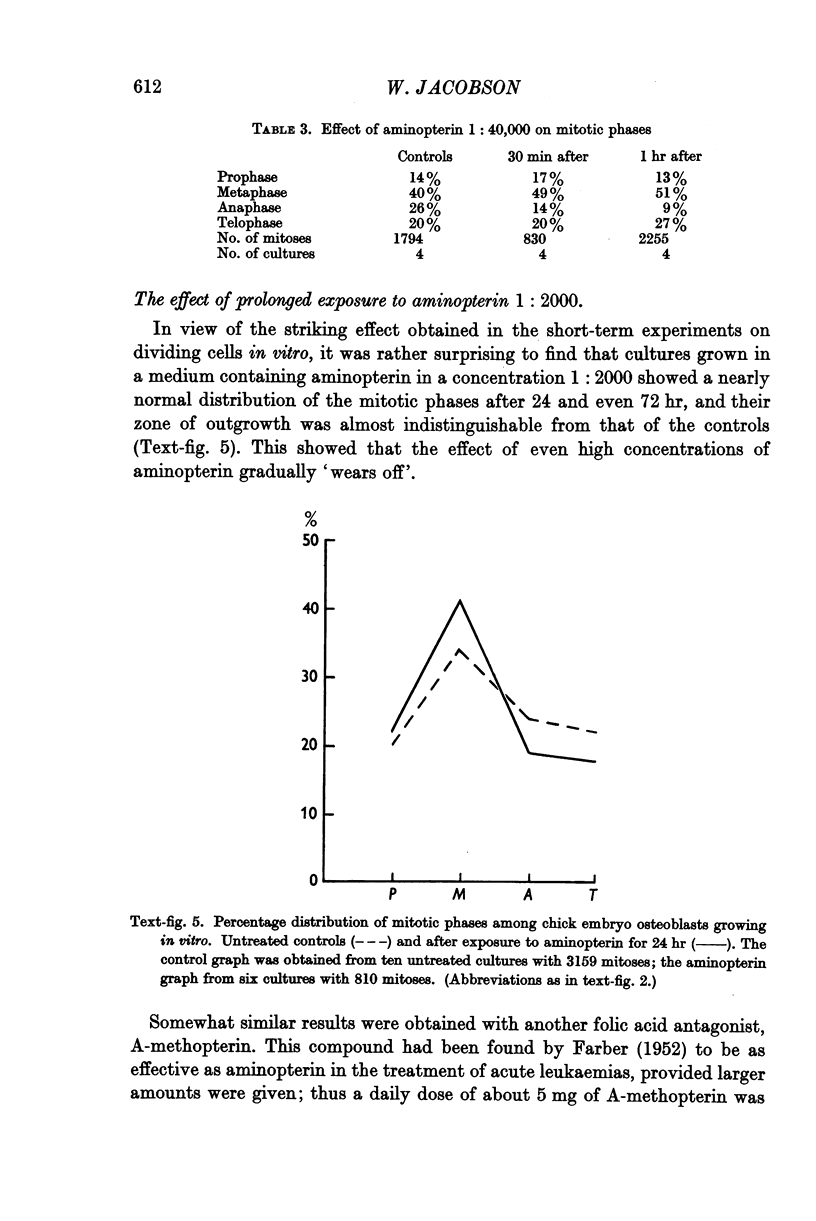
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DUSTIN P., Jr Lésions cellulaires provoquées par les acides 4-aminoptéroylglutamiques chez la souris. Rev Hematol. 1950;5(5-6):603–617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAMPA G., DUSTIN P., Jr Analyse, par la colchicine, des effets radiomimétiques de l'acide 4-amino-ptéroylglutamique (aminoptérine). Rev Belg Pathol Med Exp. 1952 Sep;22(2):113–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBSON W. The role of the Leuconostoc citrovorum factor (LCF) in cell division and the mode of action of folic-acid antagonists on normal and leukaemic cells. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1952 Jan;64(1):245–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBSON W., WEBB M. The two types of nucleic acid during mitosis. J Physiol. 1951 Jan;112(1-2):2p–4p. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERING H. G. Folic acid antagonists. Physiol Rev. 1952 Apr;32(2):197–213. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1952.32.2.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PROCEEDINGS of the Second Conference on Folic Acid Antagonists in the treatment of leukemia. Blood. 1952 Jan;7(Suppl):97–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODS D. D. Folic acid and related compounds in the metabolism of microorganisms. Br Med Bull. 1953;9(2):122–125. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a074326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]