Abstract
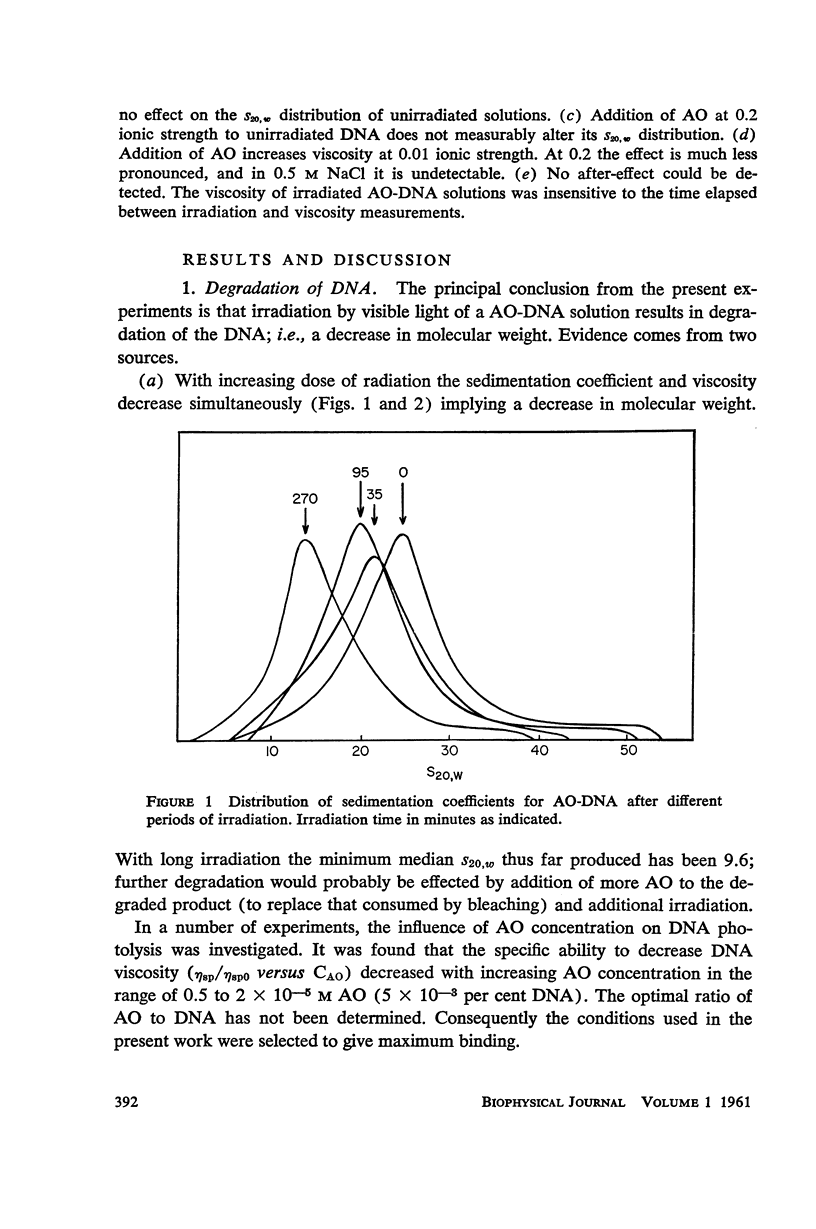
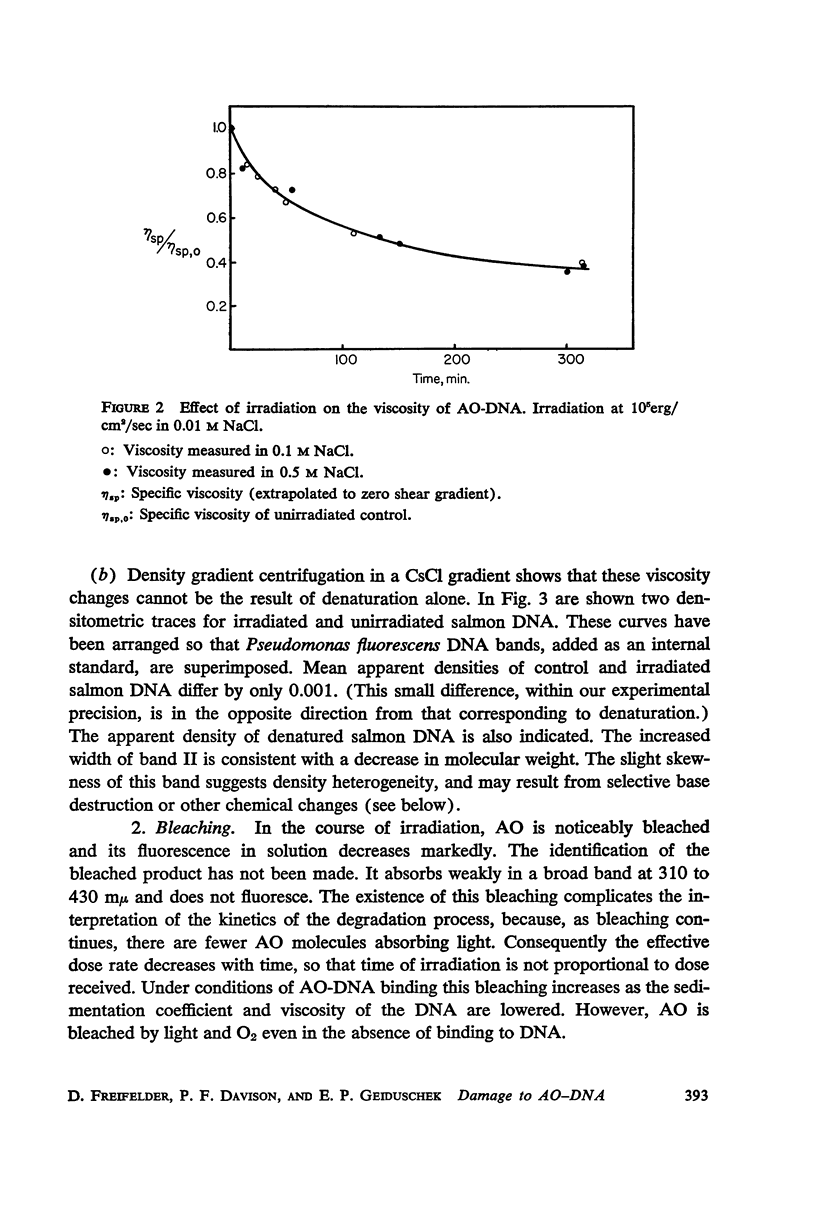
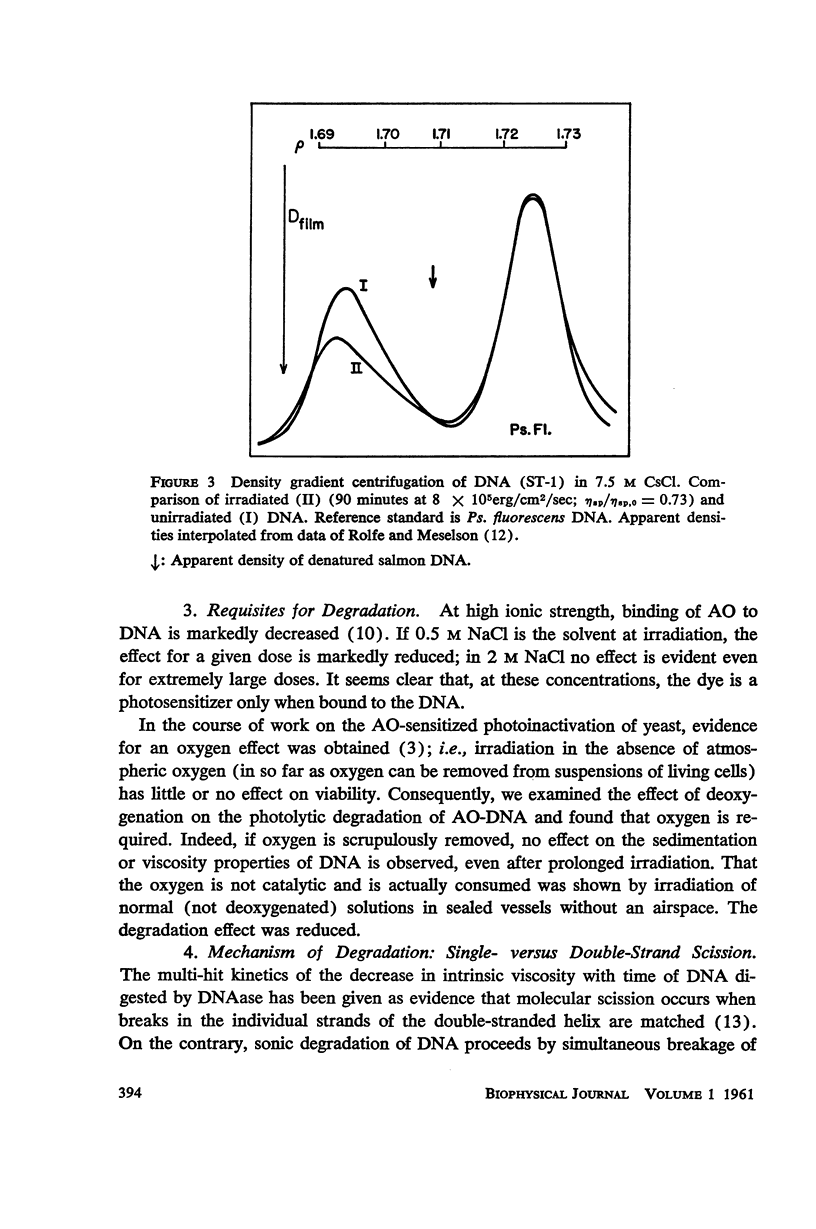
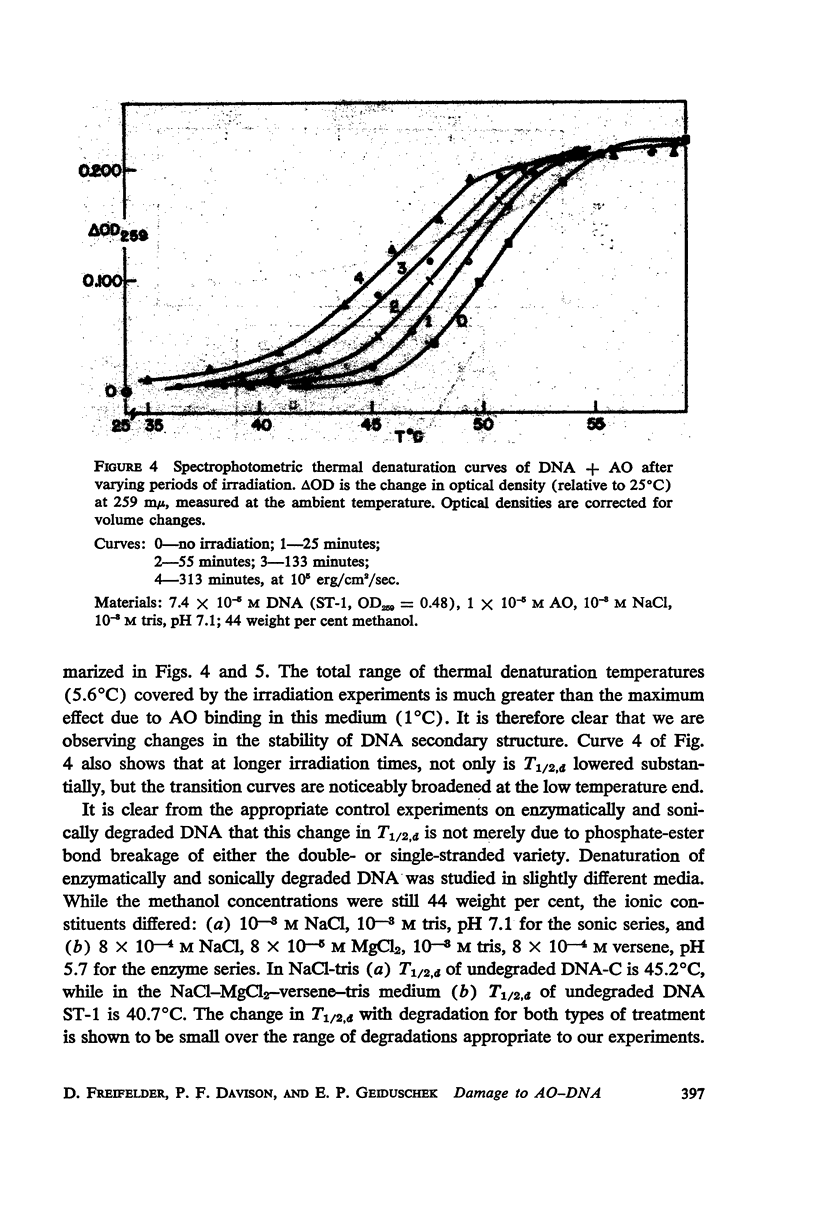
Salmon DNA has been irradiated with visible light in the presence of acridine orange. If the dye is bound to the DNA, there results: (a) a decrease in sedimentation coefficient, (b) a lowering of viscosity, and (c) a decrease in the thermal denaturation temperature. CsCl banding experiments show that the first two effects reflect depolymerization of the DNA. Depolymerization apparently occurs by single-strand scission although some double-strand scission is not excluded. The destabilization of secondary structure results probably from chemical attack on the components of the individual strands.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEERS R. F., Jr, HENDLEY D. D., STEINER R. F. Inhibition and activation of polynucleotide phosphorylase through the formation of complexes between acridine orange and polynucleotides. Nature. 1958 Jul 26;182(4630):242–244. doi: 10.1038/182242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRENNER S., BENZER S., BARNETT L. Distribution of proflavin-induced mutations in the genetic fine structure. Nature. 1958 Oct 11;182(4641):983–985. doi: 10.1038/182983a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doty P., Marmur J., Eigner J., Schildkraut C. STRAND SEPARATION AND SPECIFIC RECOMBINATION IN DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACIDS: PHYSICAL CHEMICAL STUDIES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Apr;46(4):461–476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.4.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doty P., McGill B. B., Rice S. A. THE PROPERTIES OF SONIC FRAGMENTS OF DEOXYRIBOSE NUCLEIC ACID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 May;44(5):432–438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.5.432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREIFELDER D., URETZ R. B. Inactivation by visible light of yeast sensitized by a nucleic acid fluorochrome. Nature. 1960 May 28;186:731–732. doi: 10.1038/186731b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMILTON L. D., BARCLAY R. K., WILKINS M. H., BROWN G. L., WILSON H. R., MARVIN D. A., EPHRUSSI-TAYLOR H., SIMMONS N. S. Similarity of the structure of DNA from a variety of sources. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 May 25;5(3):397–404. doi: 10.1083/jcb.5.3.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIHLMAN B. A. Effect of nitric oxide on the production of chromosomal aberrations by x-rays. Exp Cell Res. 1959 Jun;17(3):588–590. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(59)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIPSETT M. N., HEPPEL L. A., BRADLEY D. F. Complex formation between adenine oligonucleotides and polyuridylic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jun 17;41:175–177. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90394-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolfe R., Meselson M. THE RELATIVE HOMOGENEITY OF MICROBIAL DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Jul;45(7):1039–1043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.7.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


