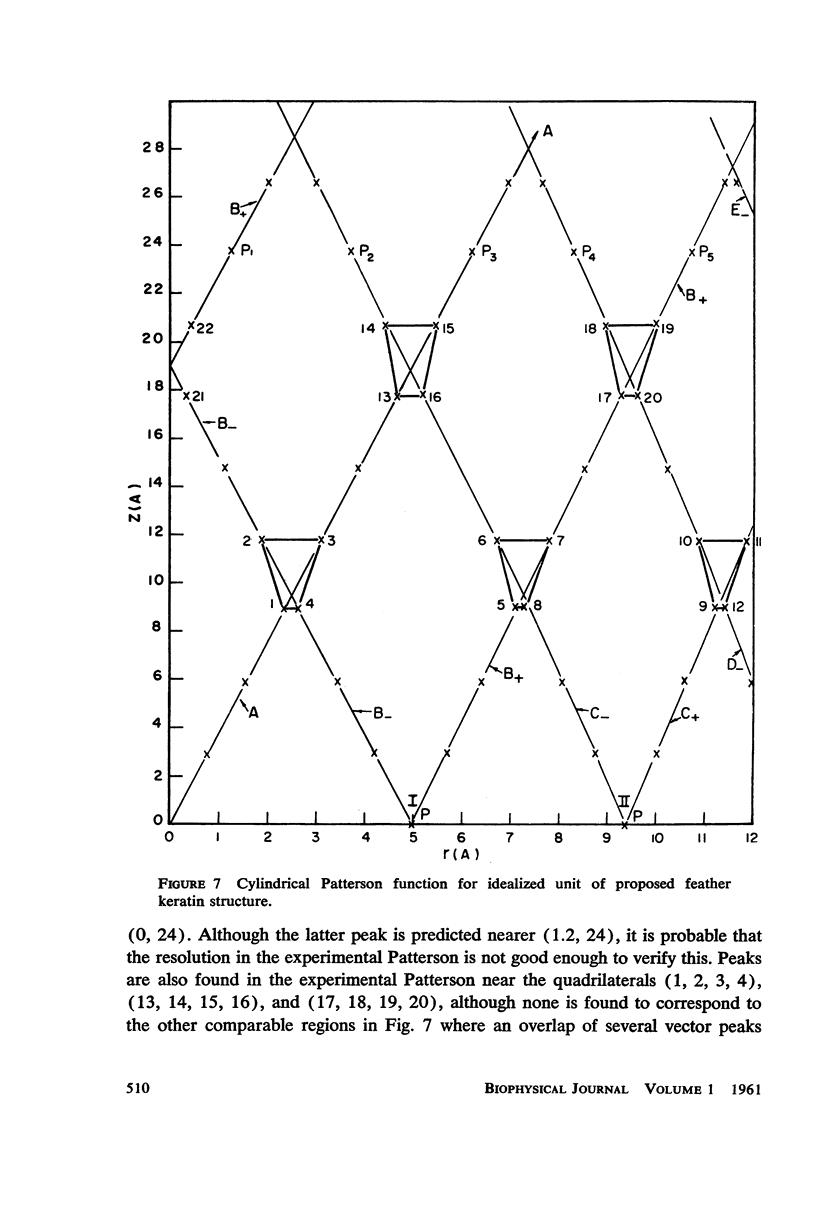
Abstract
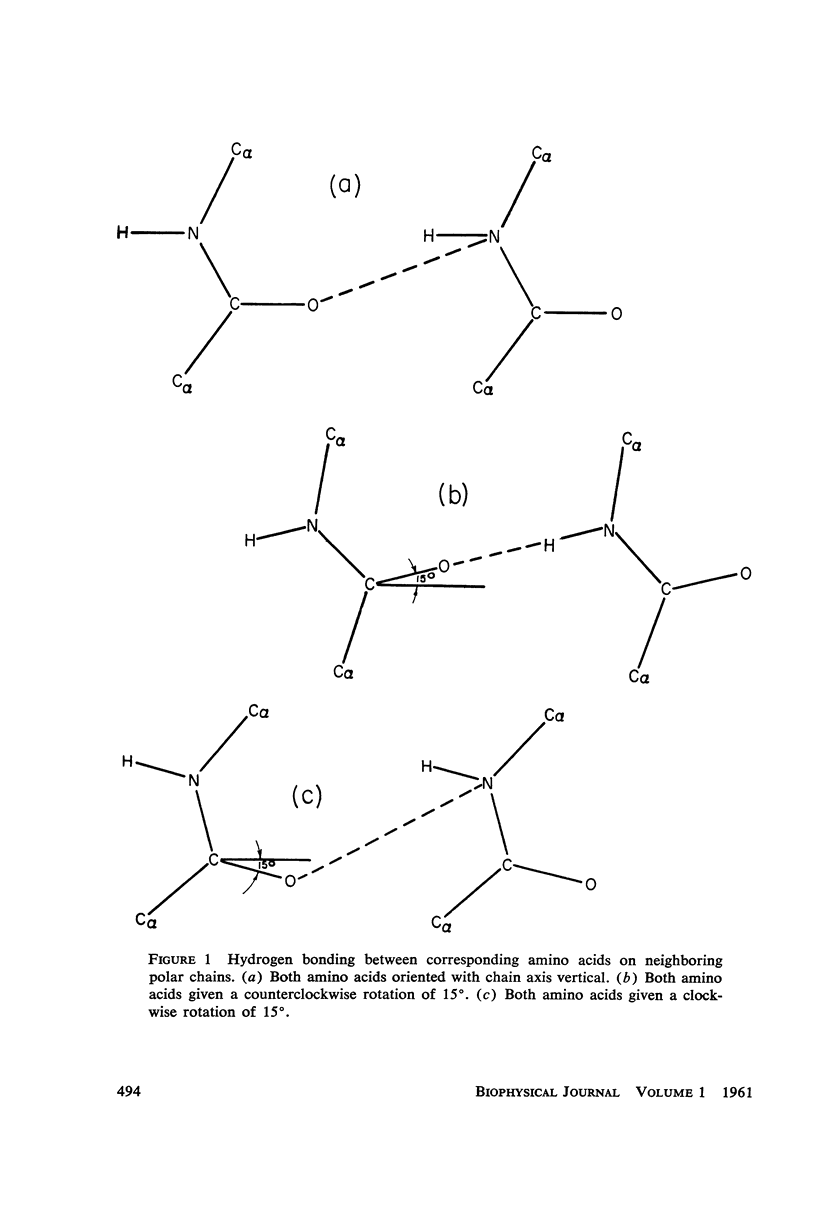
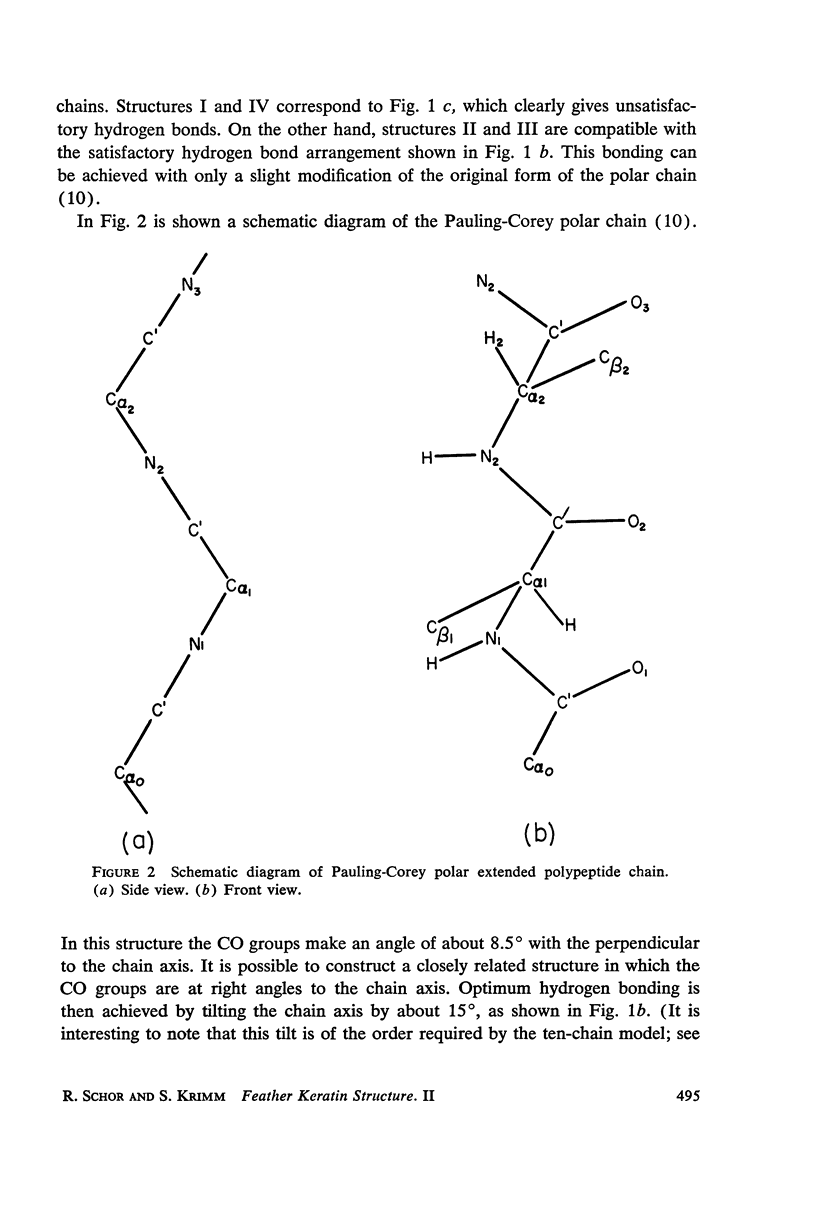
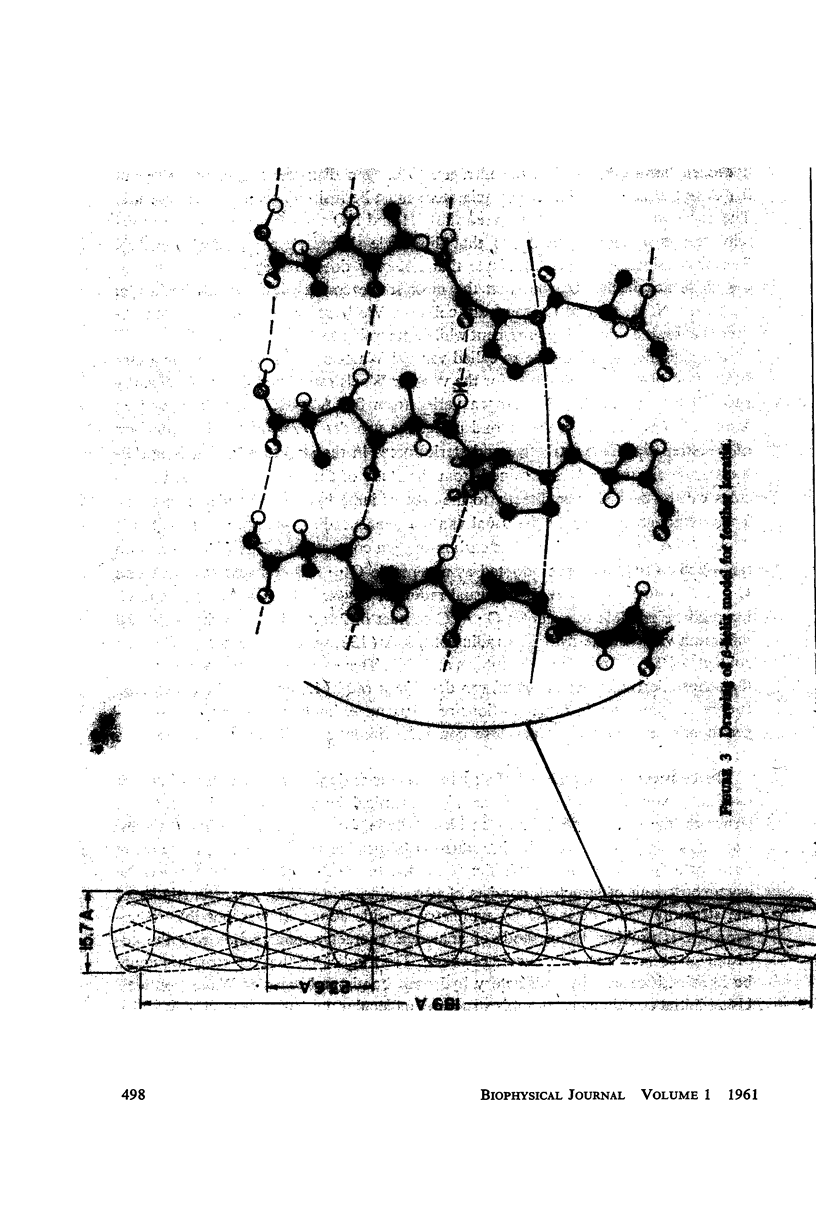
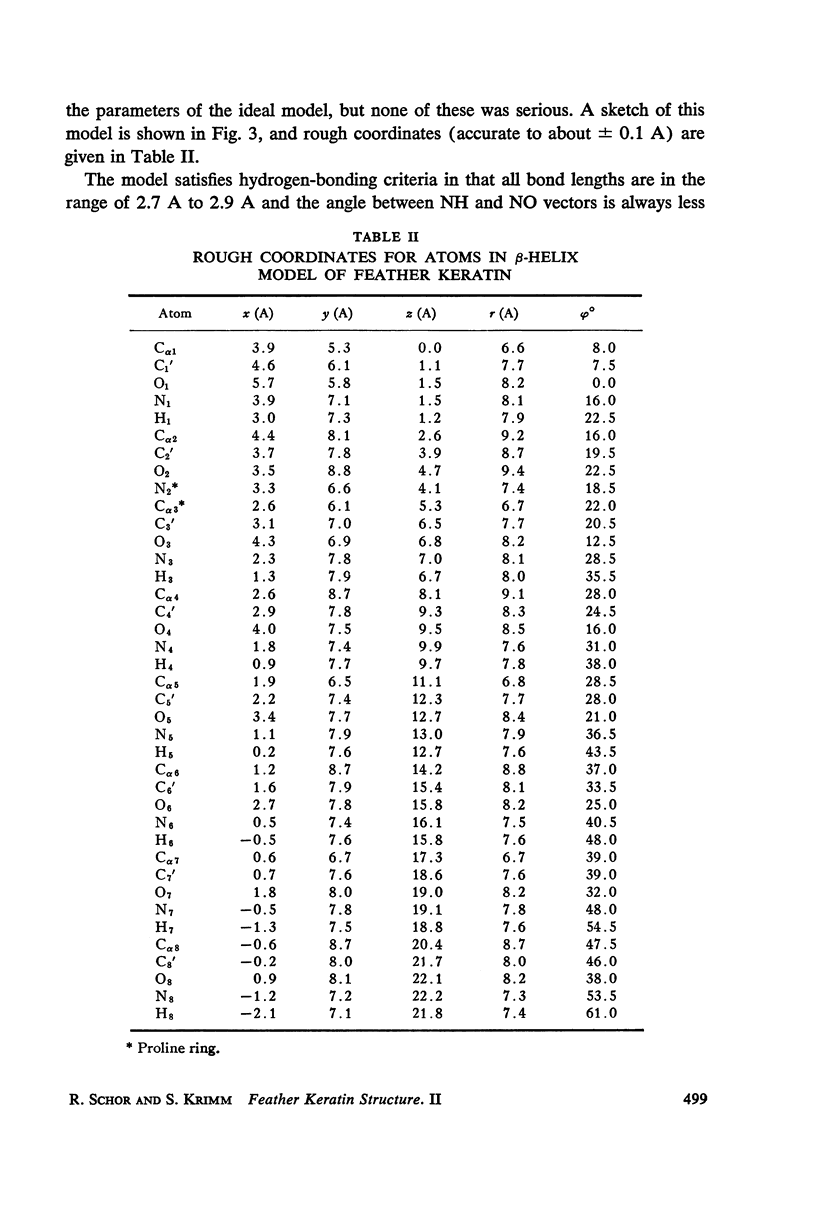
The assumption that the proline residues in feather keratin, which comprise 12 per cent of the total, are periodically located along the polypeptide chain is shown to lead to an essentially unique structure for this fibrous protein. The structure is based on a β-helix; i.e., an extended chain which coils slowly to form a helix of relatively large pitch. Such helices tend to aggregate by hydrogen bonding to form cylindrical units, which in turn can aggregate further into cable-like structures. This model has been tested with respect to its predictions concerning the x-ray diffraction pattern, infrared spectrum, mechanical properties, and chemical behavior of feather keratin. Preliminary results indicate that it is better capable of accounting for the data than previously proposed structures.
Full text
PDF

















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANFINSEN C. B., REDFIELD R. R. Protein structure in relation to function and biosynthesis. Adv Protein Chem. 1956;11:1–100. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60420-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEAR R. S., RUGO H. J. The results of x-ray diffraction studies on keratin fibers. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1951 Mar;53(3):627–648. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1951.tb31964.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donohue J. Hydrogen Bonded Helical Configurations of the Polypeptide Chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1953 Jun;39(6):470–478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.39.6.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRASER R. D., MACRAE T. P., SIMMONDS D. H. Models of alpha-keratin sturcture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Sep;25(3):654–655. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90546-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAULING L., COREY R. B., BRANSON H. R. The structure of proteins; two hydrogen-bonded helical configurations of the polypeptide chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1951 Apr;37(4):205–211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.37.4.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAULING L., COREY R. B. Compound helical configurations of polypeptide chains: structure of proteins of the alpha-keratin type. Nature. 1953 Jan 10;171(4341):59–61. doi: 10.1038/171059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAULING L., COREY R. B. The pleated sheet, a new layer configuration of polypeptide chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1951 May;37(5):251–256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.37.5.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauling L., Corey R. B. Two Rippled-Sheet Configurations of Polypeptide Chains, and a Note about the Pleated Sheets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1953 Apr;39(4):253–256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.39.4.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMACHANDRAN G. N., SASISEKHARAN V. Cylindrical lattice structure of collagen. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Jul;63(1):255–257. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZENT-GYORGYI A. G., COHEN C. Role of proline in polypeptide chain configuration of proteins. Science. 1957 Oct 11;126(3276):697–698. doi: 10.1126/science.126.3276.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schor R., Krimm S. Studies on the Structure of Feather Keratin: I. X-Ray Diffraction Studies and Other Experimental Data. Biophys J. 1961 Jul;1(6):467–487. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(61)86903-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODIN A. M. Structure and composition of soluble feather keratin. Biochem J. 1956 Aug;63(4):576–581. doi: 10.1042/bj0630576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


