Abstract
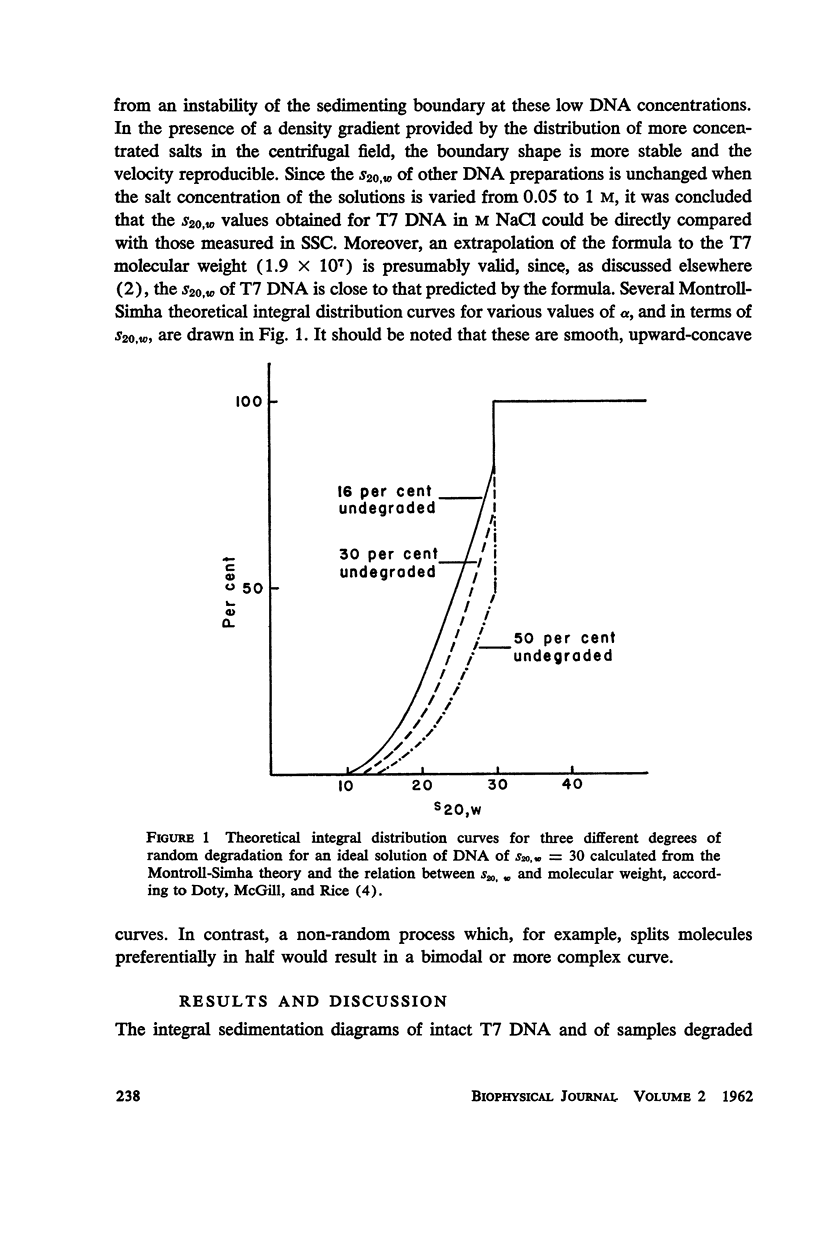
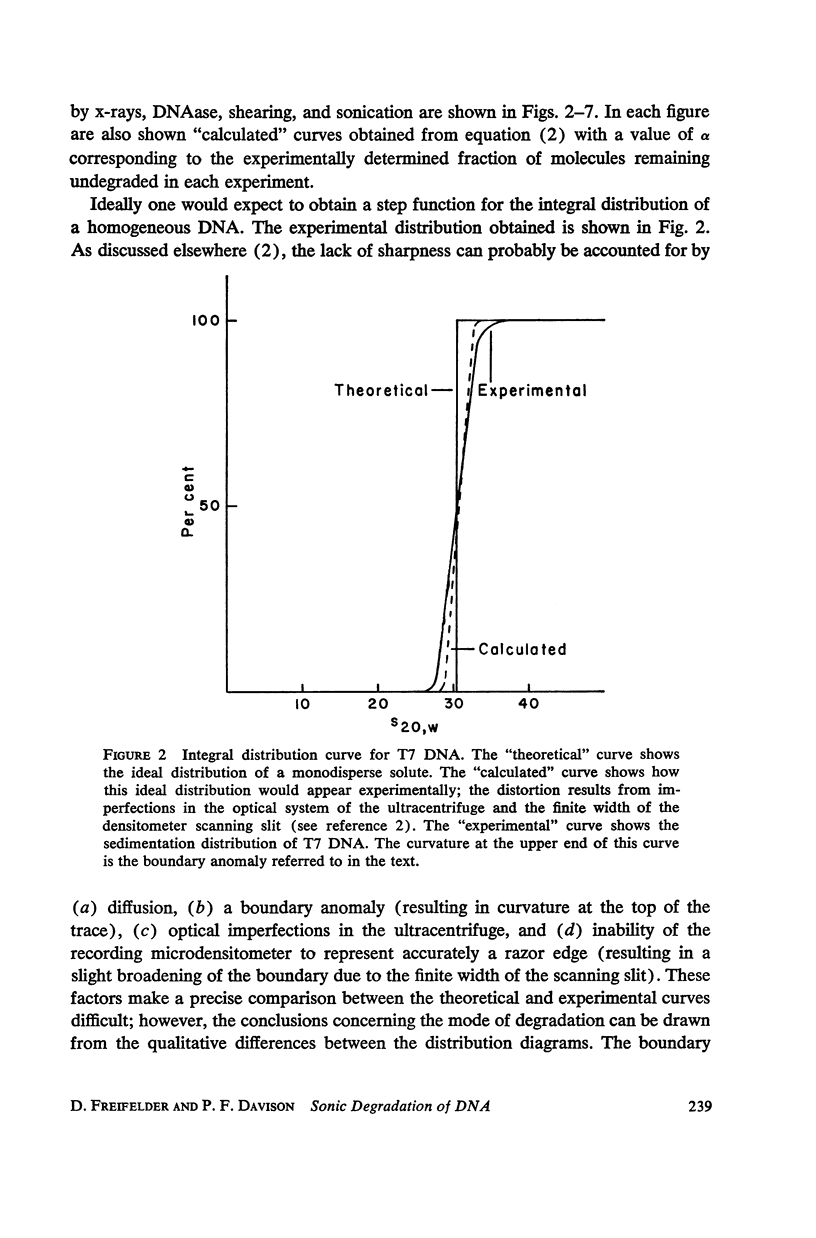
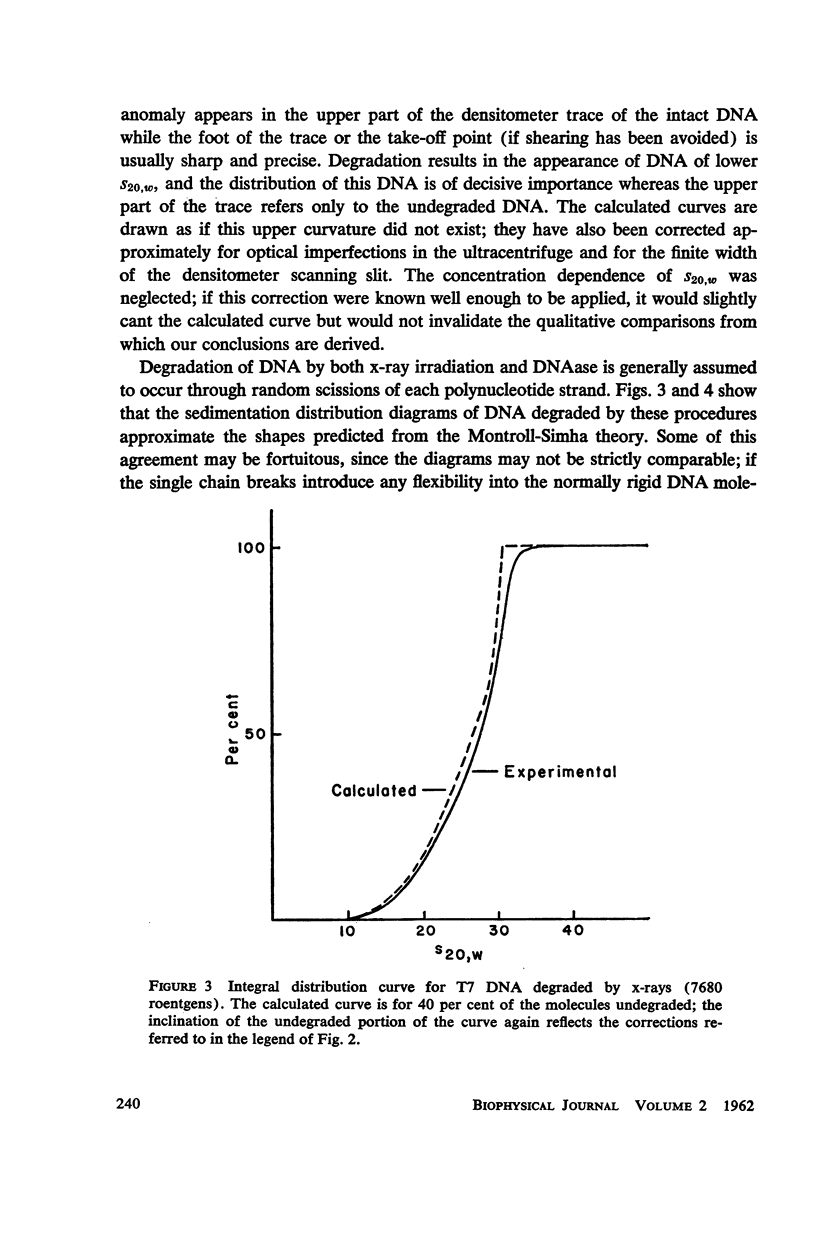
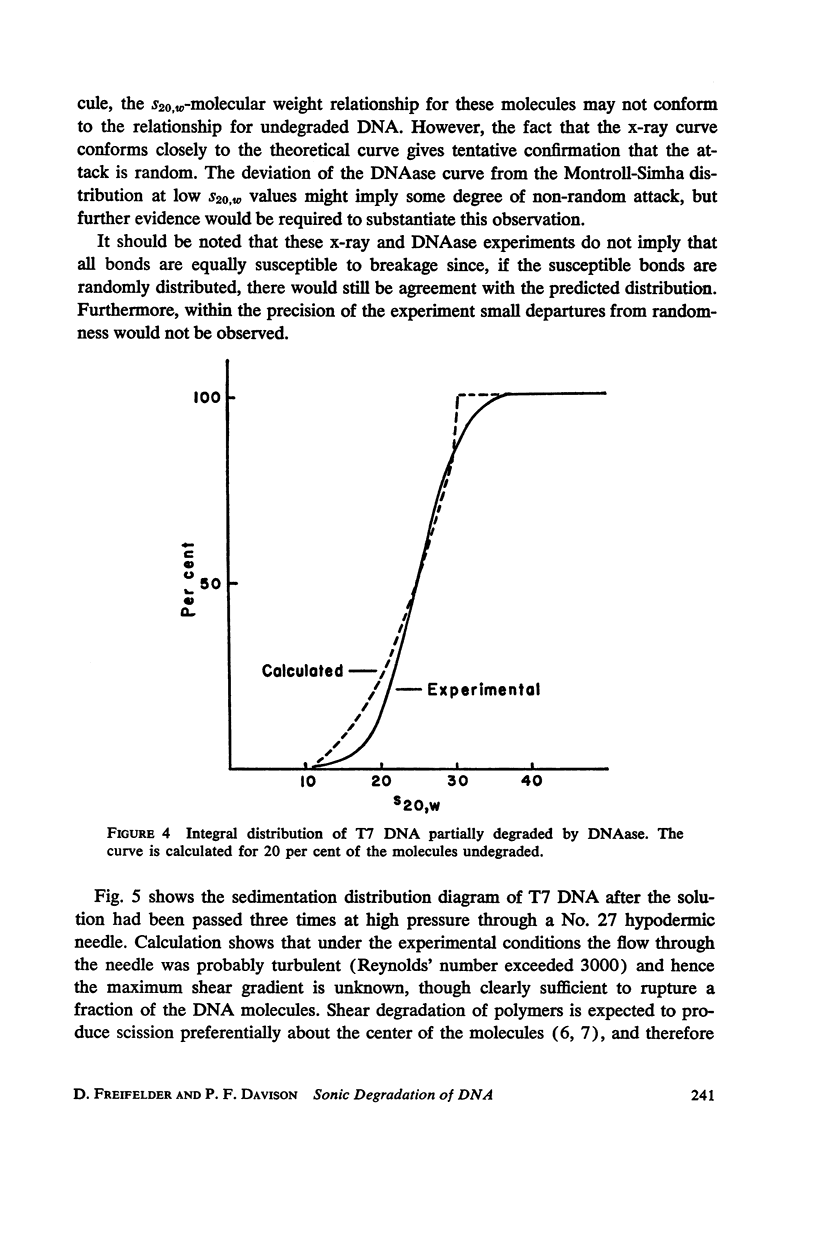
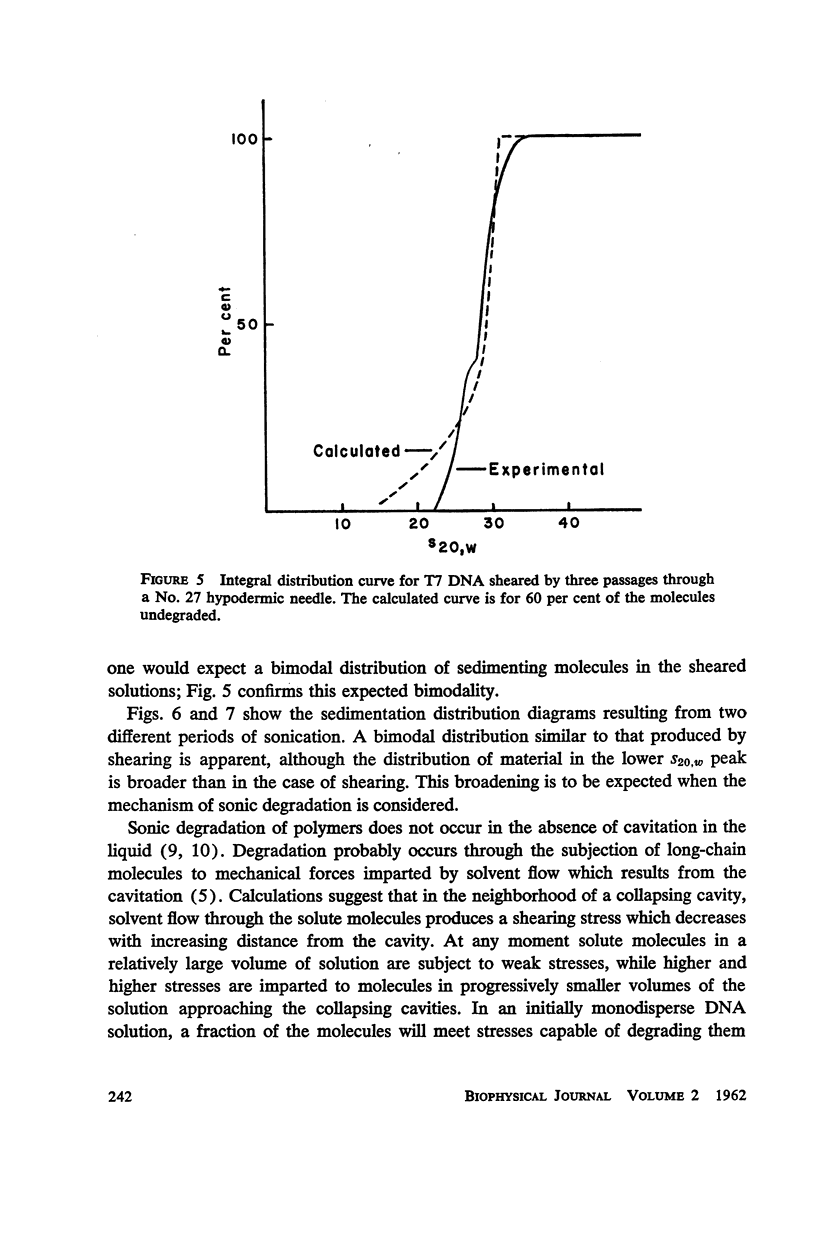
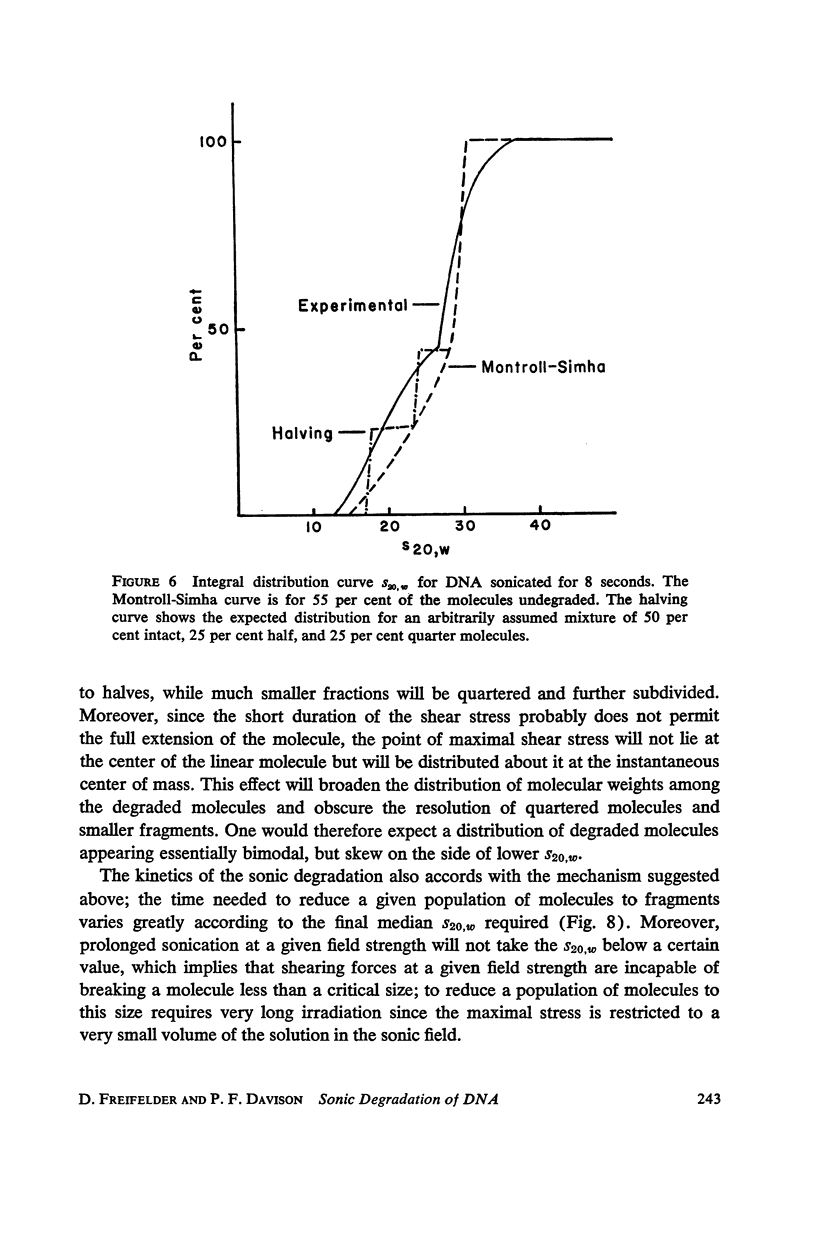
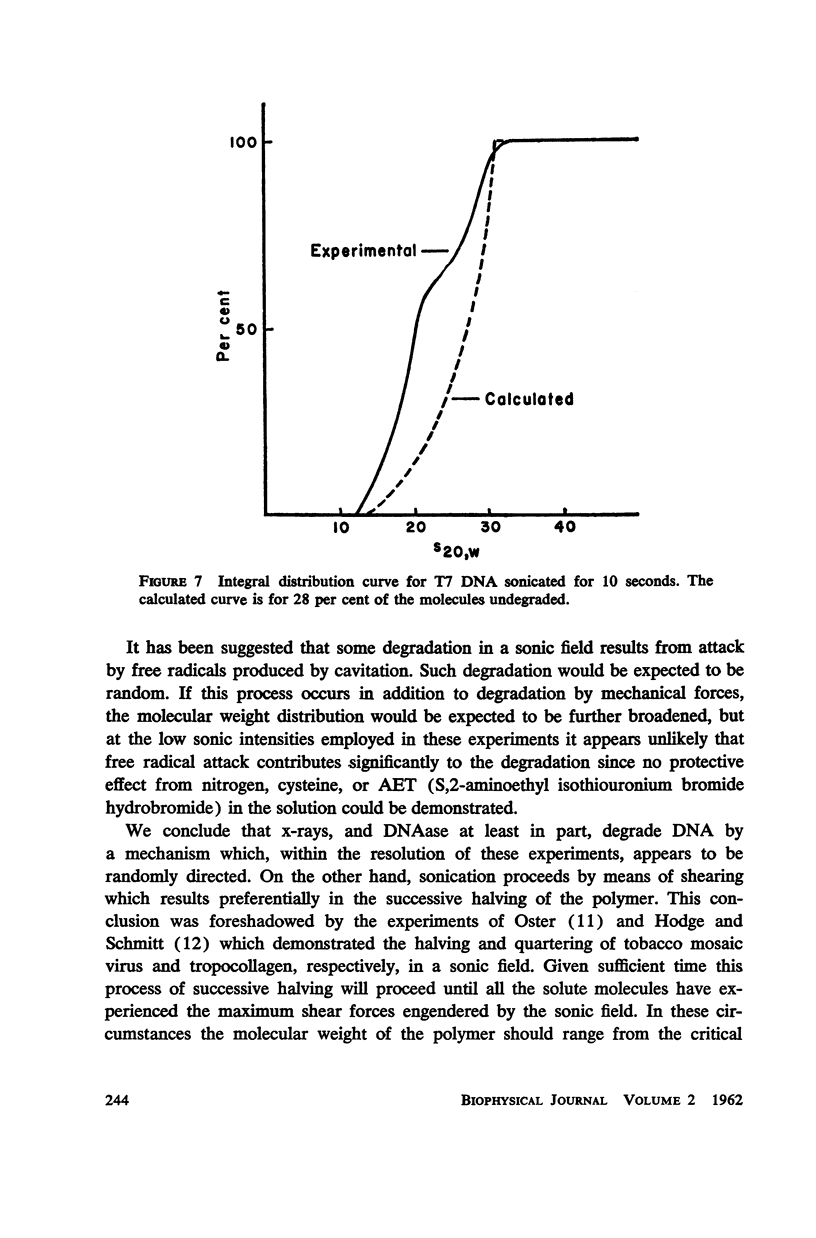
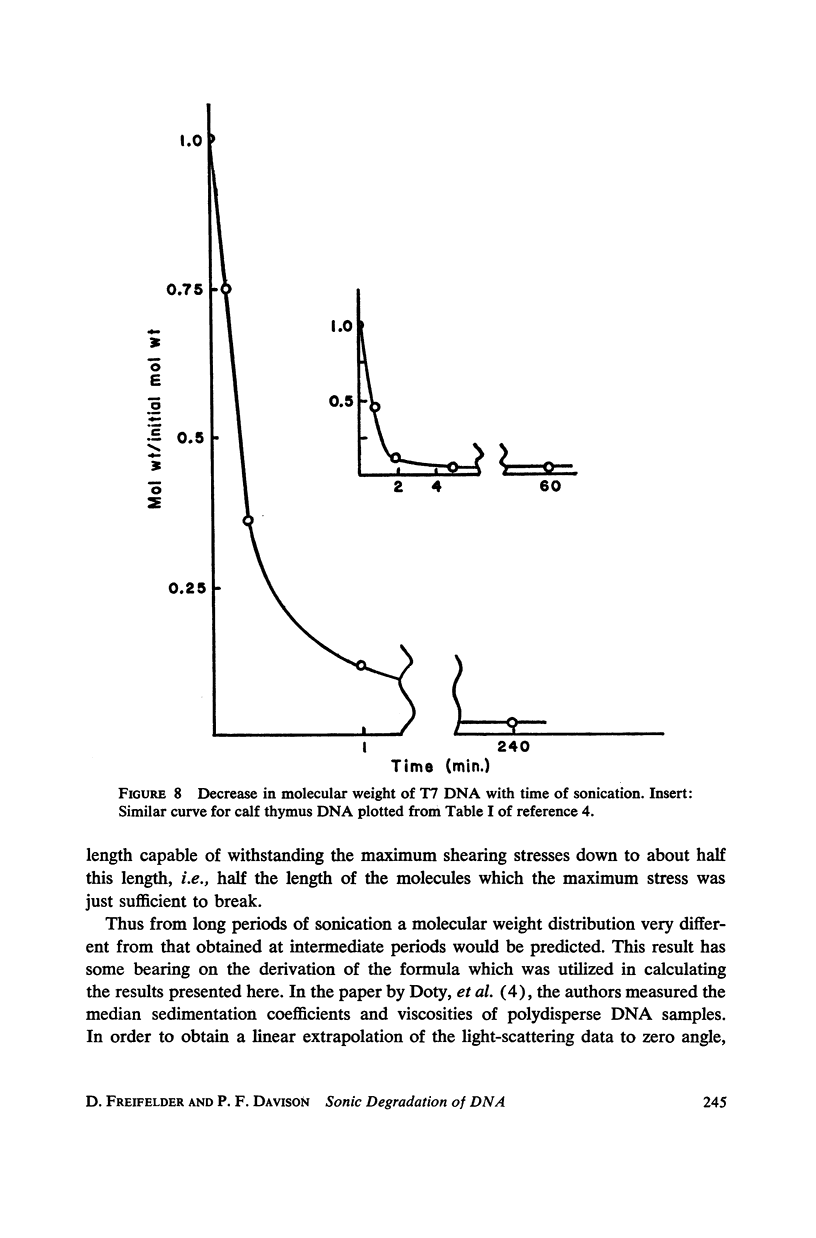
T7 DNA was partially degraded by x-rays, DNAase, and sonic irradiation. The molecular weight distributions were calculated from sedimentation velocity studies on the resulting preparations. Comparison with the theoretical curve derived by Montroll and Simha showed that the first two degradative methods act grossly at random, whereas sonication is a non-random process resulting in the preferential halving of the DNA molecules in solution.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURGI E., HERSHEY A. D. A relative molecular weight series derived from the nucleic acid of bacteriophage T2. J Mol Biol. 1961 Aug;3:458–472. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVISON P. F. Sedimentation of deoxyribonucleic acid isolated under low hydrodynamic shear. Nature. 1960 Mar 26;185:918–920. doi: 10.1038/185918a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doty P., McGill B. B., Rice S. A. THE PROPERTIES OF SONIC FRAGMENTS OF DEOXYRIBOSE NUCLEIC ACID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 May;44(5):432–438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.5.432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ S. Low-angle light scattering and the molecular weight of deoxyribonucleic acid. Nature. 1961 Jul 15;191:280–281. doi: 10.1038/191280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINTHAL C., DAVISON P. F. Degradation of deoxyribonucleic acid under hydrodynamic shearing forces. J Mol Biol. 1961 Oct;3:674–683. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


