Abstract
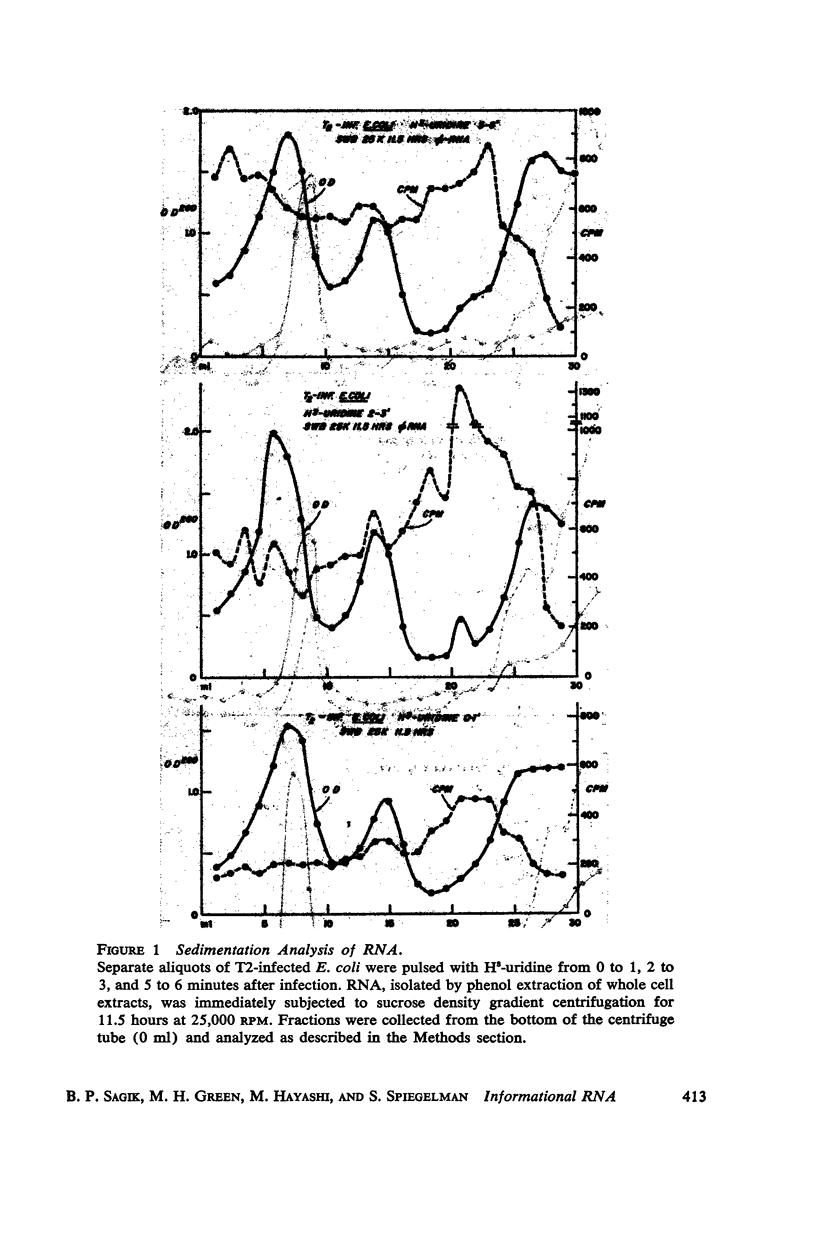
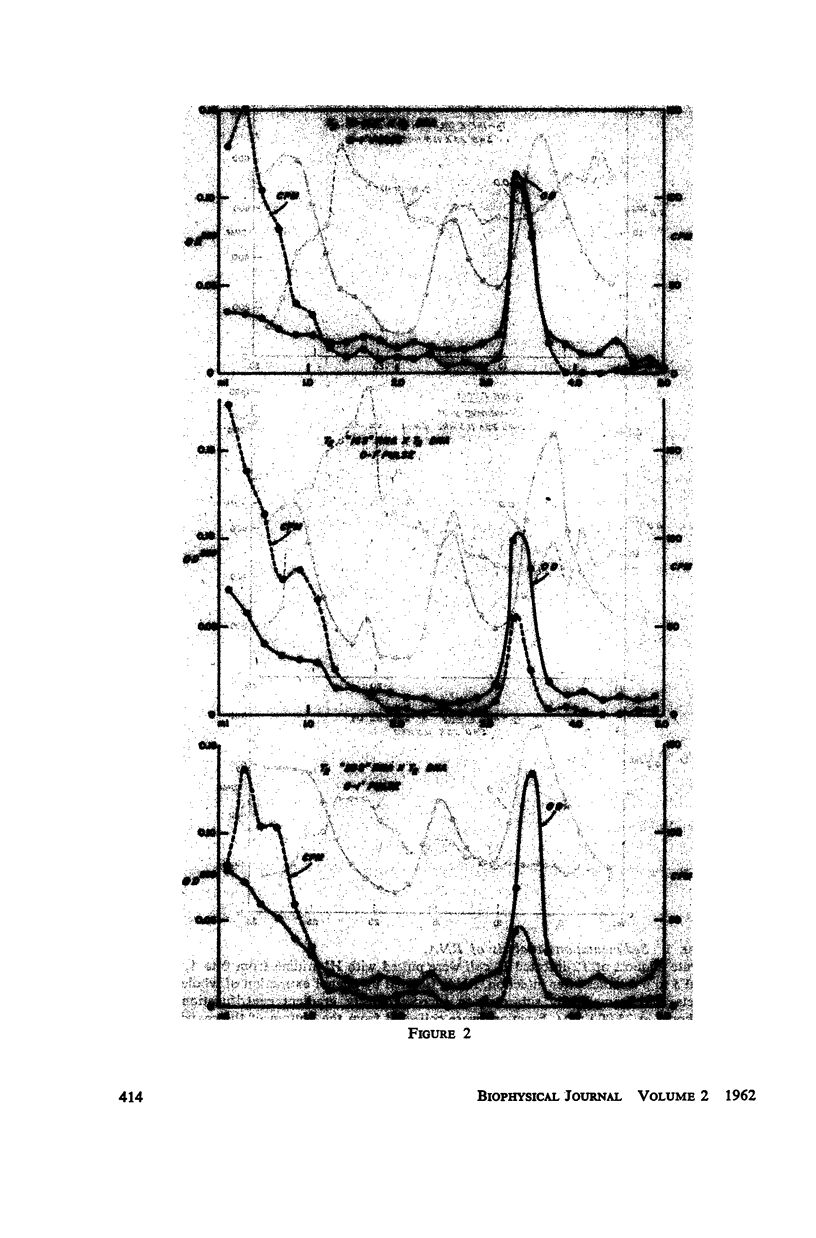
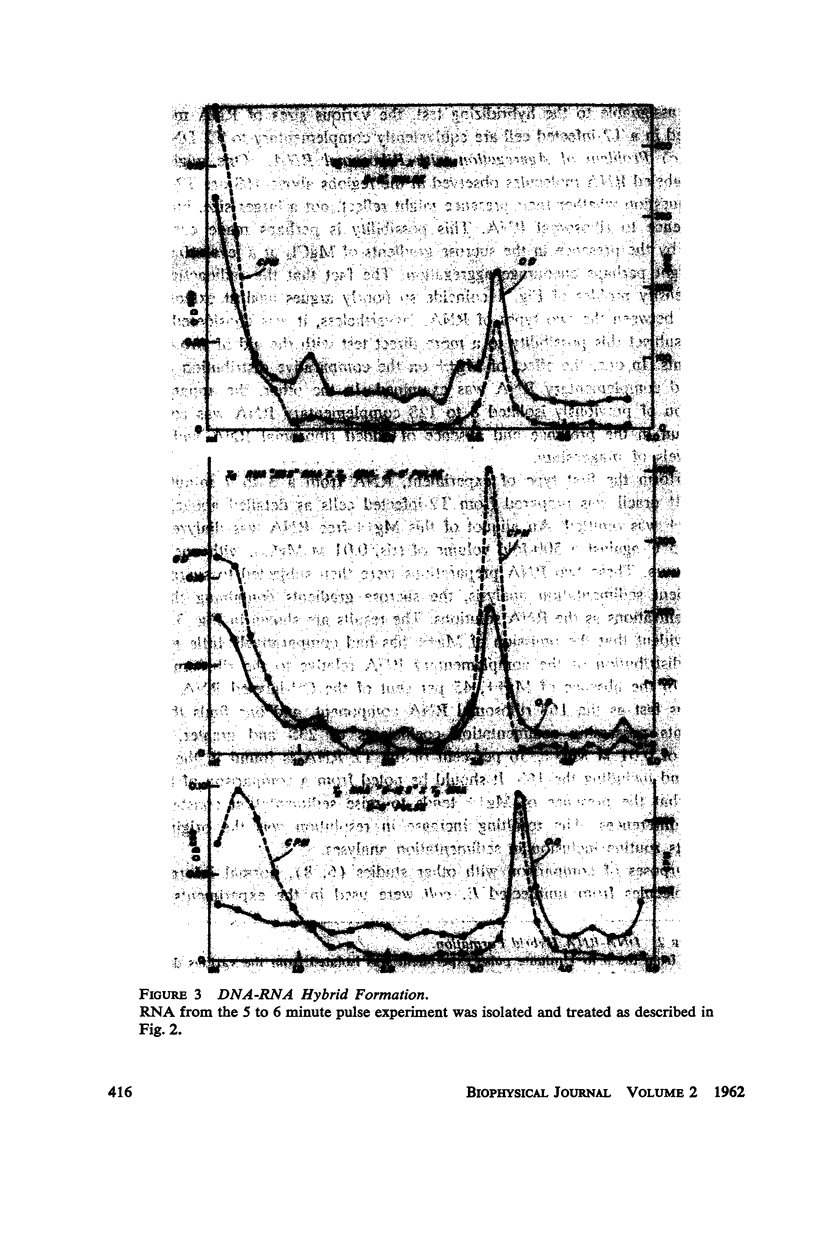
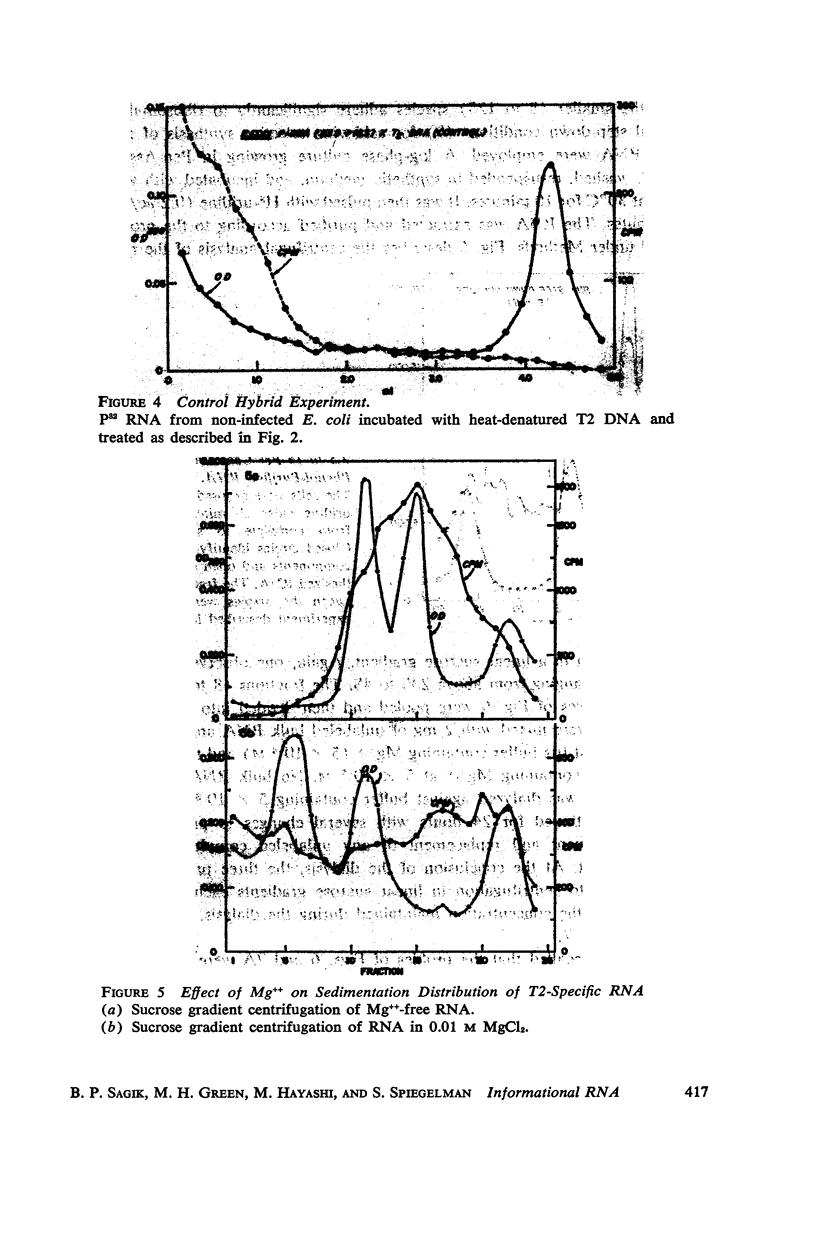
Previous investigations suggested that the size of “informational” or “messenger” RNA was confined to sedimentation rates lying between 8 and 14S. These involved procedures permitting extended contact of the RNA with enzymatically active extracts. The present study re-examined the size distribution of T2-complementary RNA isolated by a method which minimized enzymatic degradation. A much greater diversity in size distribution (4S to 25S) was observed. Experiments are described indicating that 8 to 12S informational RNA does not readily attach to the 16S and 23S ribosomal components under the conditions used for sedimentation analysis.
Full text
PDF




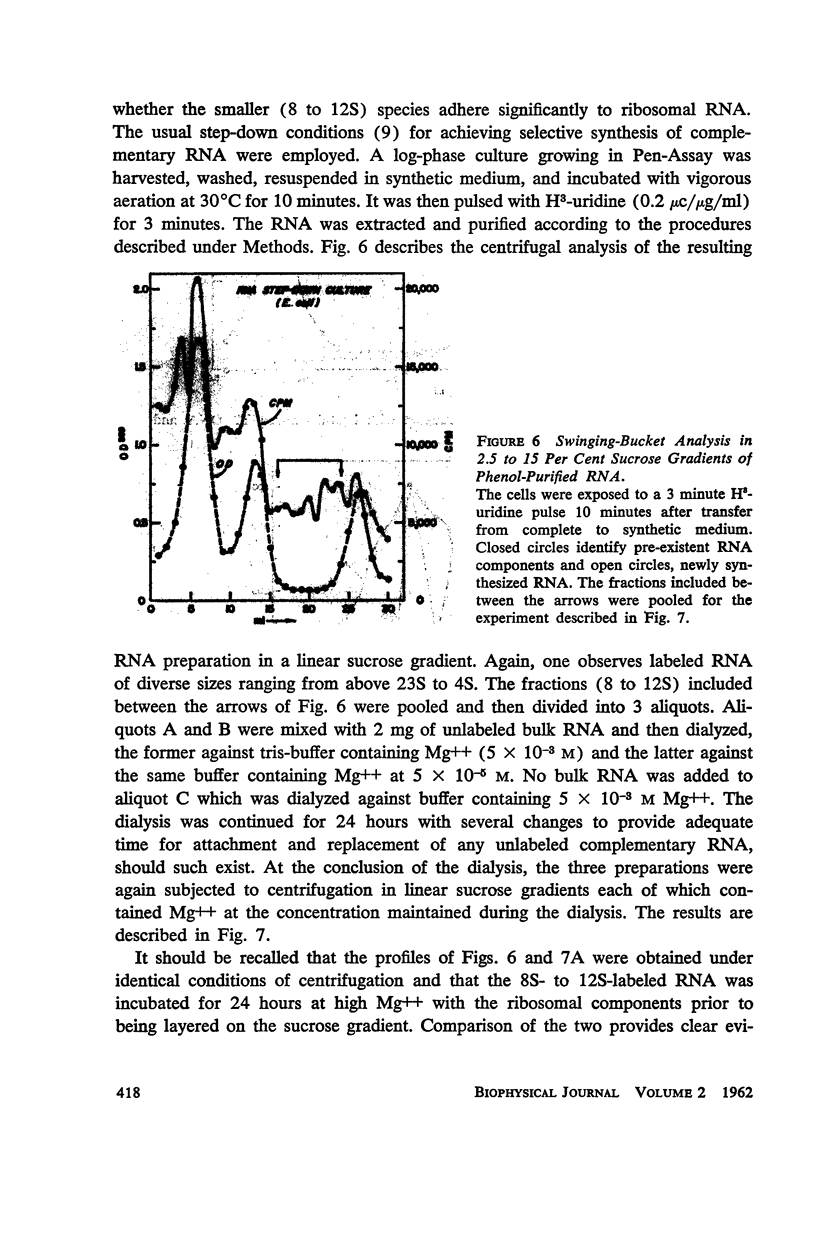


Selected References
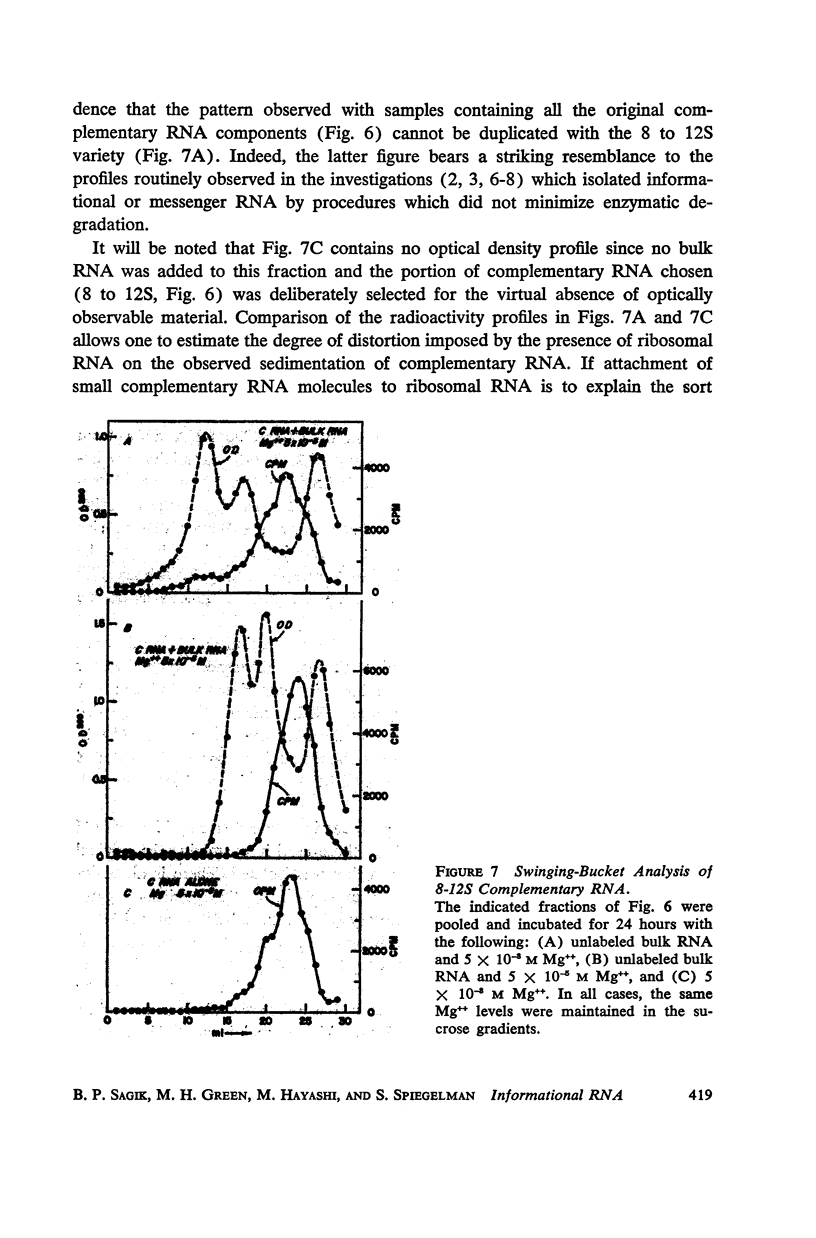
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GEIDUSCHEK E. P., NAKAMOTO T., WEISS S. B. The enzymatic synthesis of RNA: complementary interaction with DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Sep 15;47:1405–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.9.1405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIERER A., SCHRAMM G. Infectivity of ribonucleic acid from tobacco mosaic virus. Nature. 1956 Apr 14;177(4511):702–703. doi: 10.1038/177702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROS F., HIATT H., GILBERT W., KURLAND C. G., RISEBROUGH R. W., WATSON J. D. Unstable ribonucleic acid revealed by pulse labelling of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1961 May 13;190:581–585. doi: 10.1038/190581a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSSMAN L., LEVINE S. S., ALLISON W. S. The reaction of formaldehyde with nucleotides and T2 bacteriophage DNA. J Mol Biol. 1961 Feb;3:47–60. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL B. D., SPIEGELMAN S. Sequence complementarity of T2-DNA and T2-specific RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Feb 15;47:137–163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.2.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYASHI M., SPIEGELMAN S. The selective synthesis of informational RNA in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Oct 15;47:1564–1580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.10.1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., MONOD J. Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J Mol Biol. 1961 Jun;3:318–356. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KITAZUME Y., YCAS M., VINCENT W. S. Metabolic properties of a ribonucleic acid fraction in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Feb;48:265–282. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPIEGELMAN S. The relation of informational RNA to DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1961;26:75–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1961.026.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TISSIERES A., HOPKINS J. W. Factors affecting amino acid incorporation into proteins by Escherichia coli ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Dec 15;47:2015–2023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.12.2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOLKIN E., ASTRACHAN L. Phosphorus incorporation in Escherichia coli ribo-nucleic acid after infection with bacteriophage T2. Virology. 1956 Apr;2(2):149–161. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(56)90016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


