Abstract
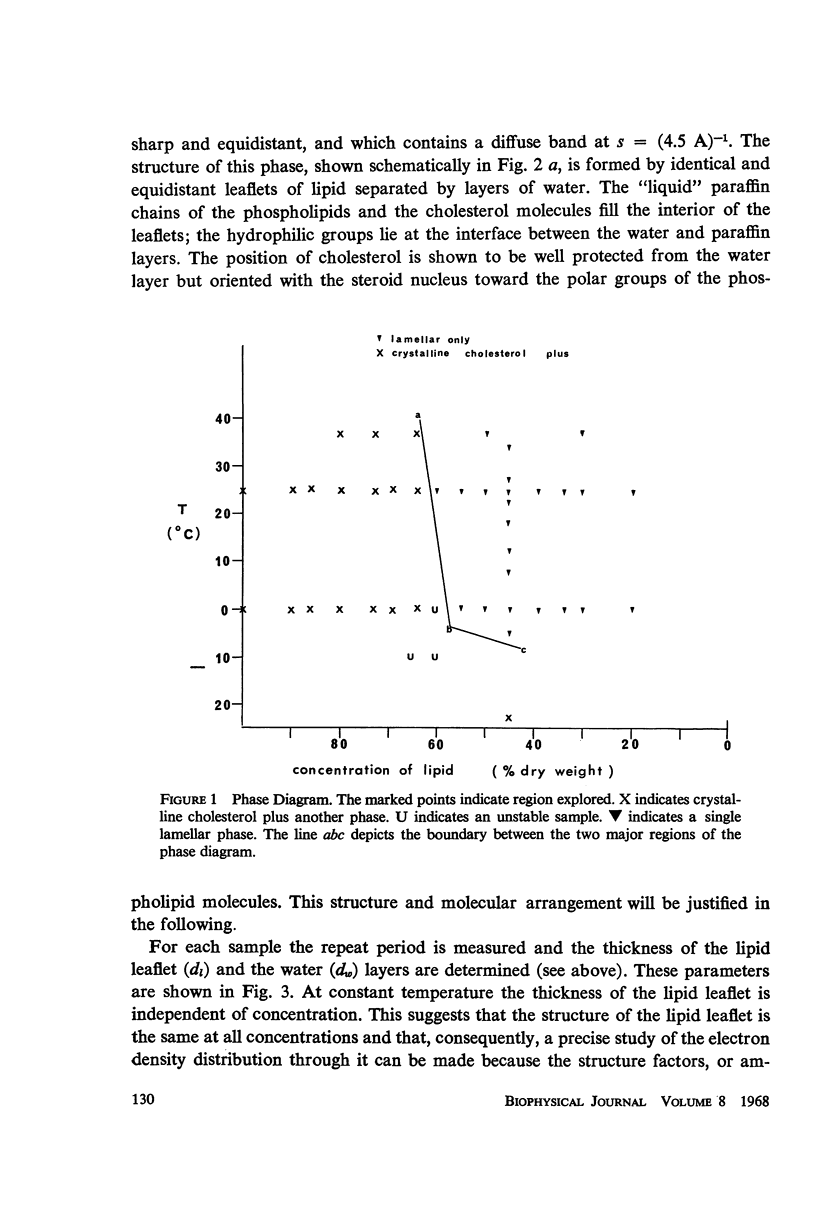
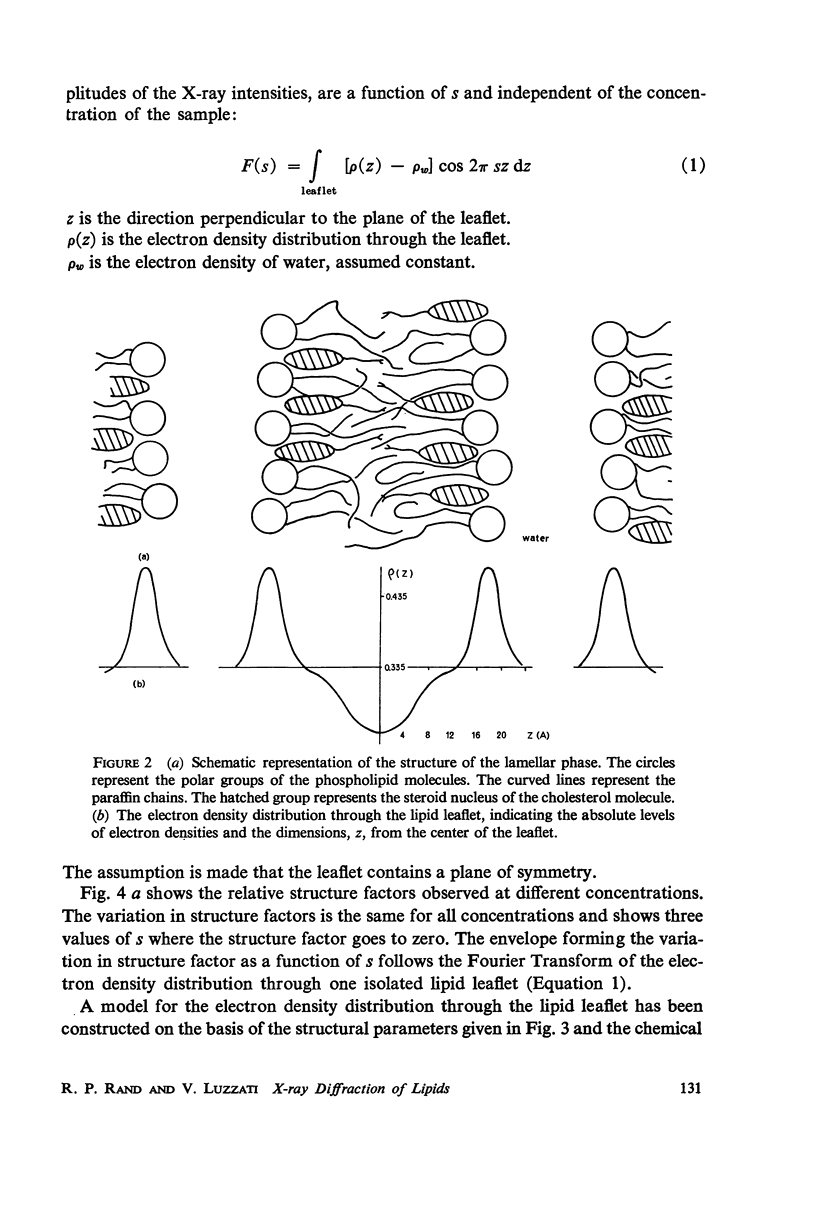
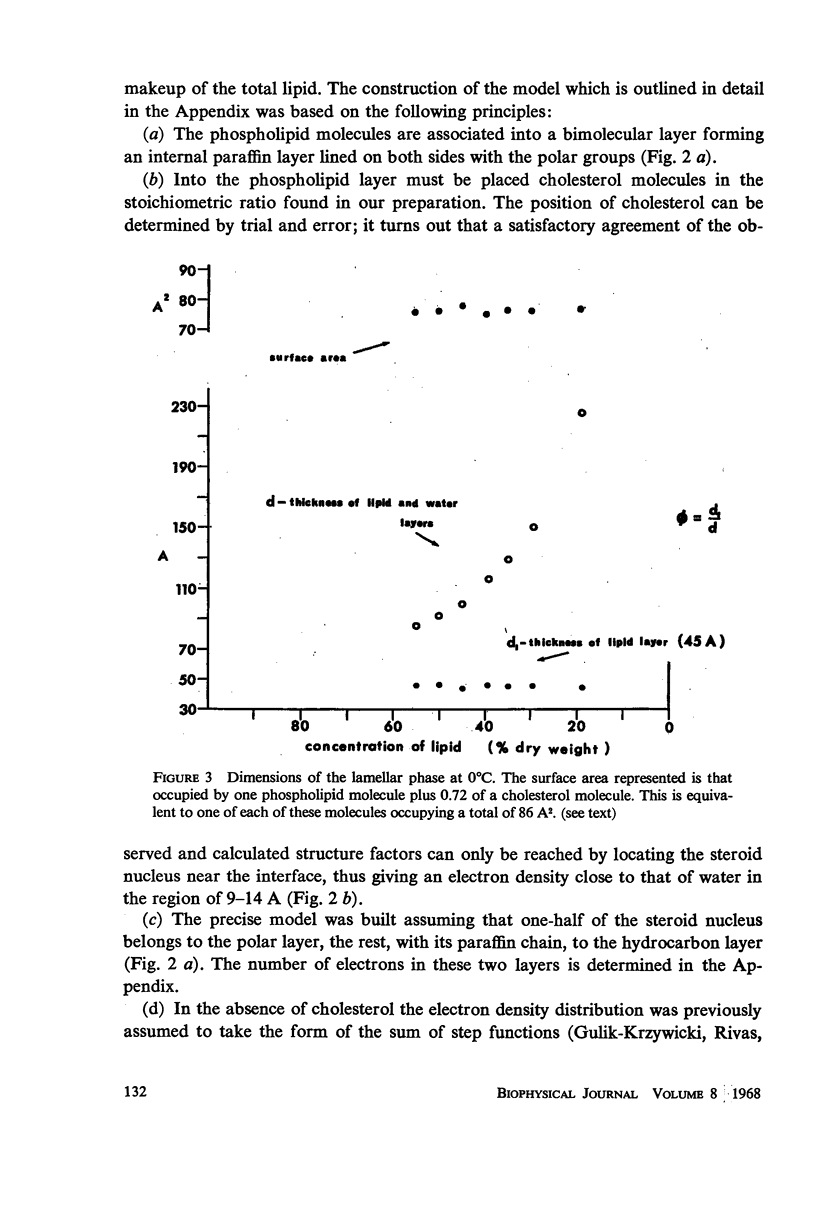
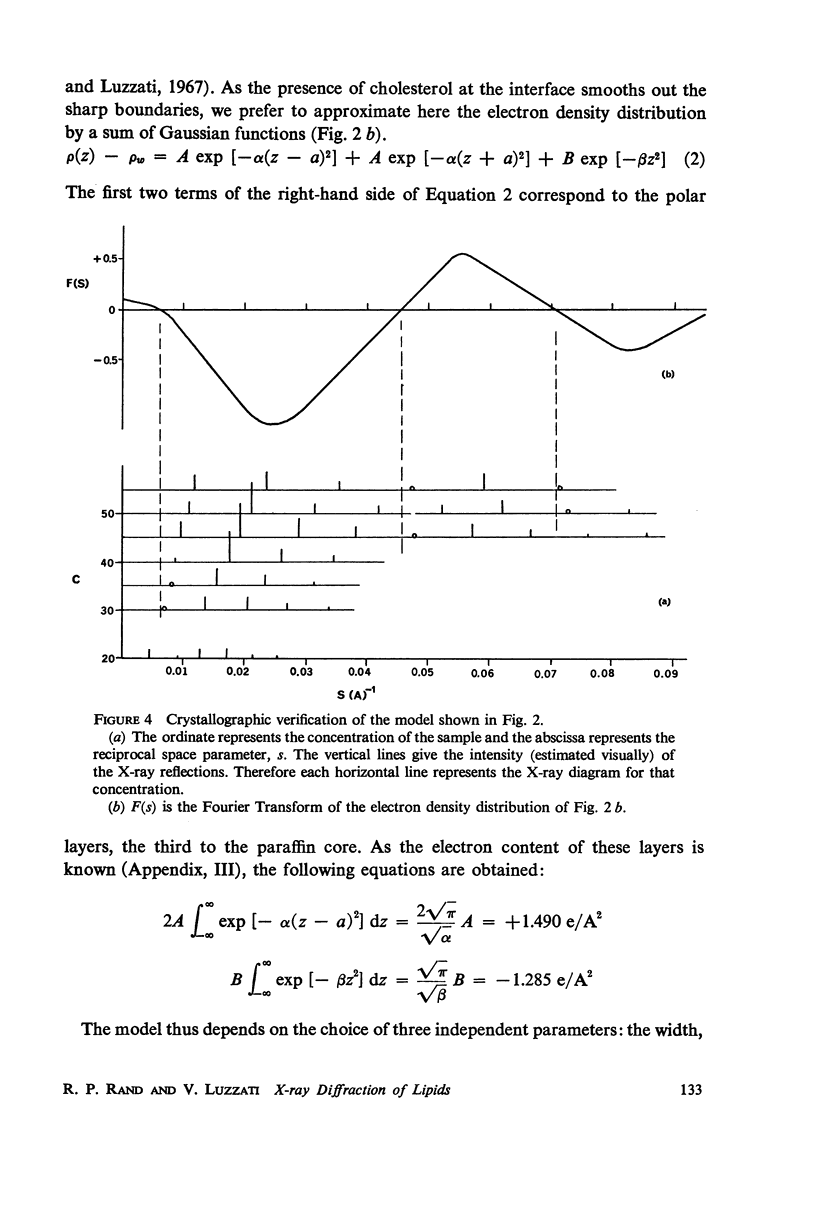
Lipids, carefully extracted from fresh human erythrocytes, form liquid-crystalline structures in water. A phase diagram of this system was constructed, characterizing, by X-ray diffraction, the structures which form as a function of concentration of lipid and temperature. One extended range of concentration of the phase diagram, in which a single lamellar phase exists, permitted further analysis of the diffraction data. This phase consists of lipid layers of constant thickness separated by water layers of varying thickness according to the water content of the system. The distribution of the electron density is precisely analyzed and the amplitude of the reflections is, at all concentrations, proportional to the Fourier Transform of an isolated lipid layer. This shows that the lipid layer is filled with the hydro-carbon chains of the phospholipids and is covered on both sides by their hydrophilic groups. Cholesterol, present in high concentration in erythrocyte membranes, is located so that part of its steroid nucleus is between the polar groups of the phospholipid molecules while the rest of the molecule extends into the inner hydrocarbon layer.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourgès M., Small D. M., Dervichian D. G. Biophysics of lipidic associations. II. The ternary systems: cholesterol-lecithin-water. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 14;137(1):157–167. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulik-Krzywicki T., Rivas E., Luzzati V. Structure et polymorphisme des lipides: étude par diffraction des rayons X du systéme formé de lipides de mitochondries de coeur de boeuf et d'eau. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 28;27(2):303–322. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUZZATI V., HUSSON F. The structure of the liquid-crystalline phasis of lipid-water systems. J Cell Biol. 1962 Feb;12:207–219. doi: 10.1083/jcb.12.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzati V., Reiss-Husson F., Rivas E., Gulik-Krzywicki T. Structure and polymorphism in lipid-water systems, and their possible biological implications. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jul 14;137(2):409–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb50172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REED C. F., SWISHER S. N., MARINETTI G. V., ENEN E. G. Studies of the lipids of the erythrocyte. I. Quantitative analysis of the lipids of normal human red blood cells. J Lab Clin Med. 1960 Aug;56:281–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROELOFSEN B., DE GIER J., VAN DEENENL BINDING OF LIPIDS IN THE RED CELL MEMBRANE. J Cell Physiol. 1964 Apr;63:233–243. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030630214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSE H. G., OKLANDER M. IMPROVED PROCEDURE FOR THE EXTRACTION OF LIPIDS FROM HUMAN ERYTHROCYTES. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:428–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss-Husson F. Structure des phases liquide-cristallines de différents phospholipides, monoglycérides, sphingolipides, anhydres ou en présence d'eau. J Mol Biol. 1967 May 14;25(3):363–382. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90192-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van DEENEN L., HOUTSMULLERUM, de HASS G., MULDER E. Monomolecular layers of synthetic phosphatides. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1962 Jul;14:429–444. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1962.tb11121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


