Abstract
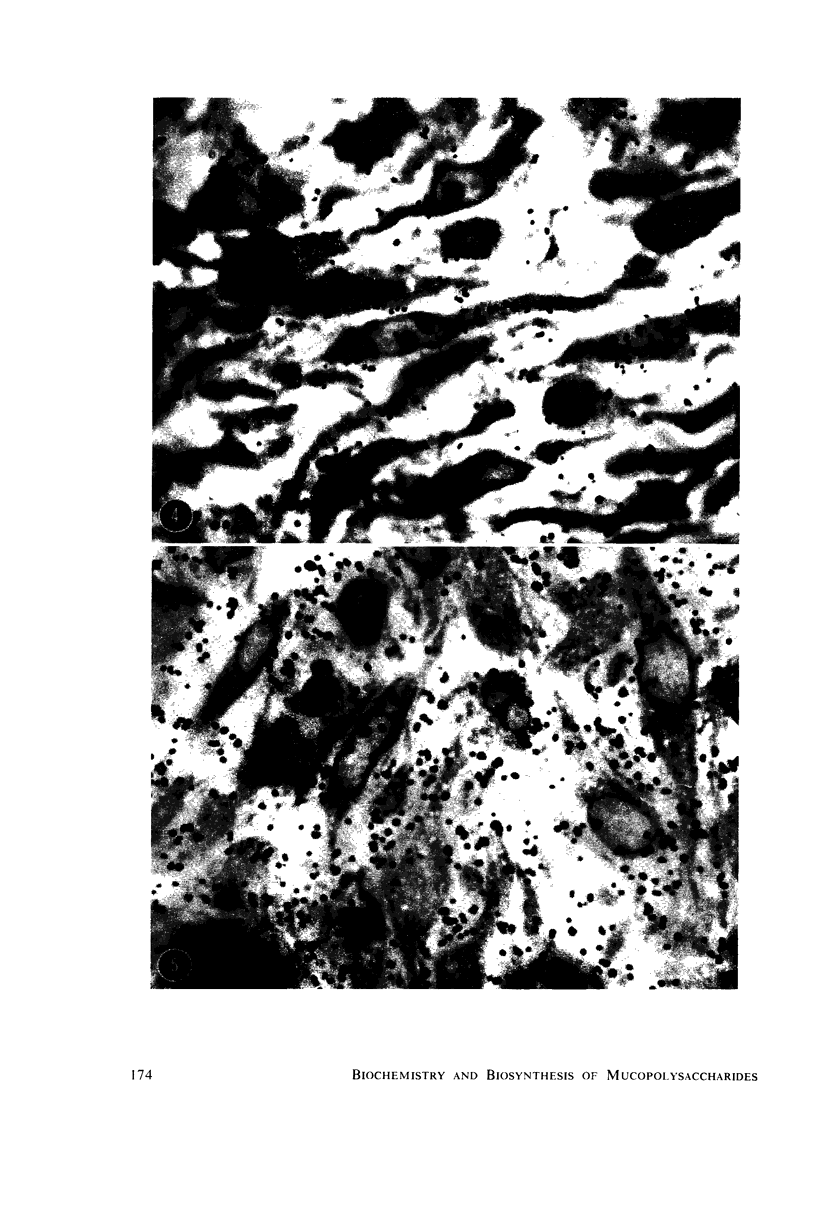
Fibroblasts active in collagen production show a rich development of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and an enlarged Golgi complex, both characteristic of cells engaged in protein synthesis. The relatively quiescent fibrocyte, on the other hand, is deficient in these same cytoplasmic systems. When fibroblasts (or chondroblasts) are provided with tritiated (H3) proline, the label shows, by autoradiography, incorporation first into materials (collagen) in the cisternae of the ER, transfer thence in time to the Golgi, and eventual secretion into the extracellular environment. Sulfur25 incorporation into chondroitin sulfate appears to involve only structural elements of the Golgi complex. There is increasing evidence of intimate fibroblast (or cell) involvement in the initiation and orientation of unit collagen fibrils. This question is reexamined in relation to the development of the prominent basement lamella of young adult lampreys.
Full text
PDF




















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CAMERON D. A. The fine structure of osteoblasts in the metaphysis of the tibia of the young rat. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Mar;9:583–595. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.3.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARO L. G. Electron microscopic radioautography of thin sections: the Golgi zone as a site of protein concentration in pancreatic acinar cells. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 May;10:37–45. doi: 10.1083/jcb.10.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAPMAN J. A. Fibroblasts and collagen. Br Med Bull. 1962 Sep;18:233–237. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a069985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAPMAN J. A. Morphological and chemical studies of collagen formation. I. The fine structure of guinea pig granulomata. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Mar;9:639–651. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.3.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERRIS W., WEISS P. The basement lamelia of amphibian skin; its reconstruction after wounding. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1956 Jul 25;2(4 Suppl):275–282. doi: 10.1083/jcb.2.4.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GODMAN G. C., PORTER K. R. Chondrogenesis, studied with the electron microscope. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Dec;8:719–760. doi: 10.1083/jcb.8.3.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSSFELD H., MEYER K., GODMAN G., LINKER A. Mucopolysaccharides produced in tissue culture. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1957 May 25;3(3):391–396. doi: 10.1083/jcb.3.3.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
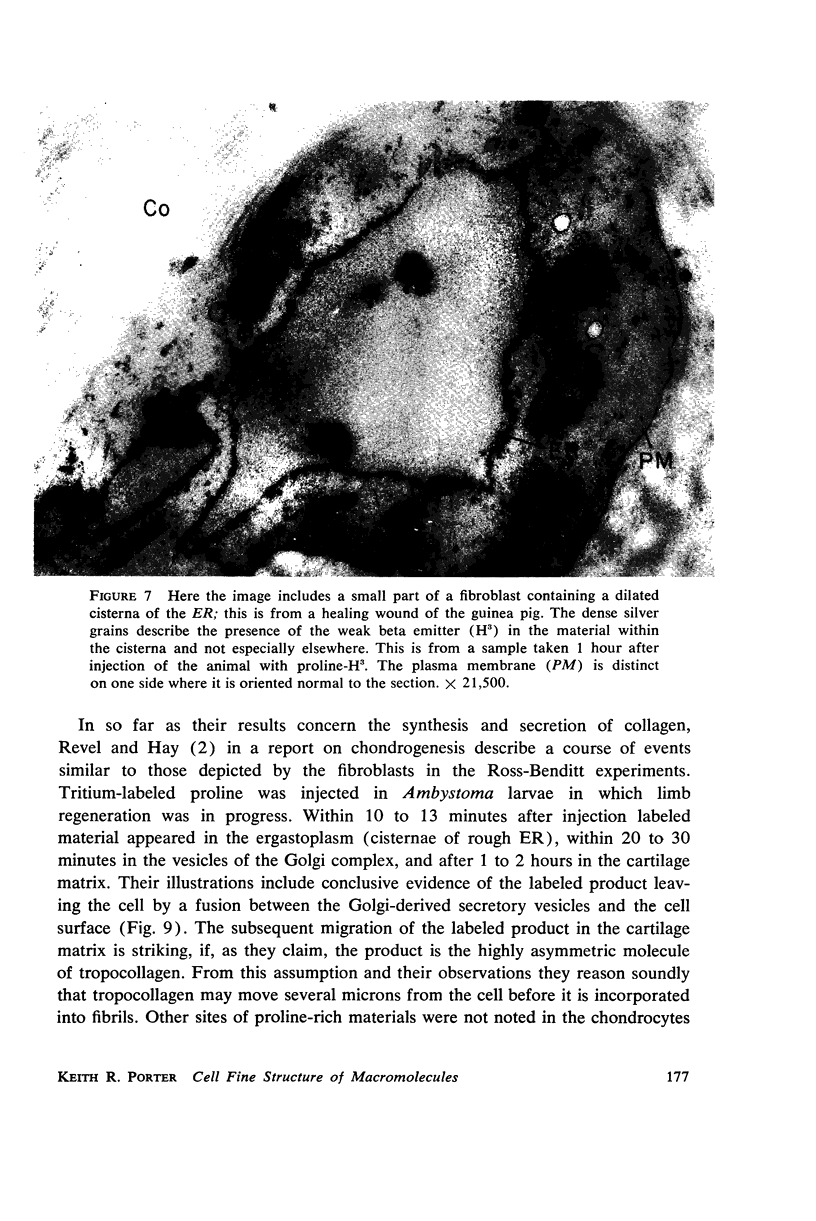
- HAY E. D., REVEL J. P. Autoradiographic studies of the origin of the basement lamella in Ambystoma. Dev Biol. 1963 Mar;6:152–168. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(63)90114-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON D. S., BENTLEY J. P. On the significance of the extractable collagens. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Feb;7:37–42. doi: 10.1083/jcb.7.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON D. S. Connective tissue growth stimulated by carrageenin. I. The formation and removal of collagen. Biochem J. 1957 Feb;65(2):277–284. doi: 10.1042/bj0650277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON S. F., SMITH R. H. Studies on the biosynthesis of collagen. I. The growth of fowl osteoblasts and the formation of collagen in tissue culture. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1957 Nov 25;3(6):897–912. doi: 10.1083/jcb.3.6.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON S. F. The morphogenesis of avian tendon. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1956 Mar 13;144(917):556–572. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1956.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWTHER D. A., GREEN N. M., CHAPMAN J. A. Morphological and chemical studies of collagen formation. II. Metabolic activity of collagen associated with subcellular fractions of guinea pig granulomata. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Jul;10:373–388. doi: 10.1083/jcb.10.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
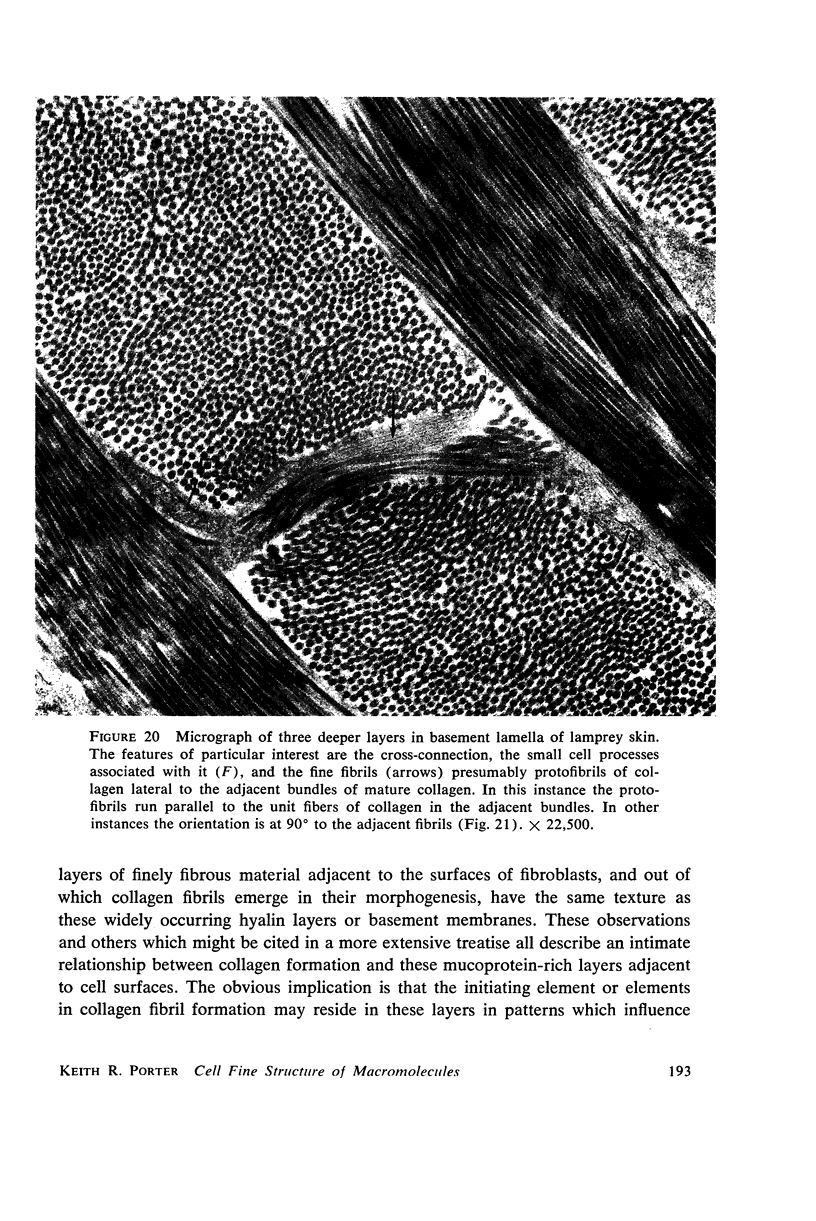
- MOVAT H. Z., FERNANDO N. V. The fine structure of connective tissue. I. The fibroblast. Exp Mol Pathol. 1962 Dec;1:509–534. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(62)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
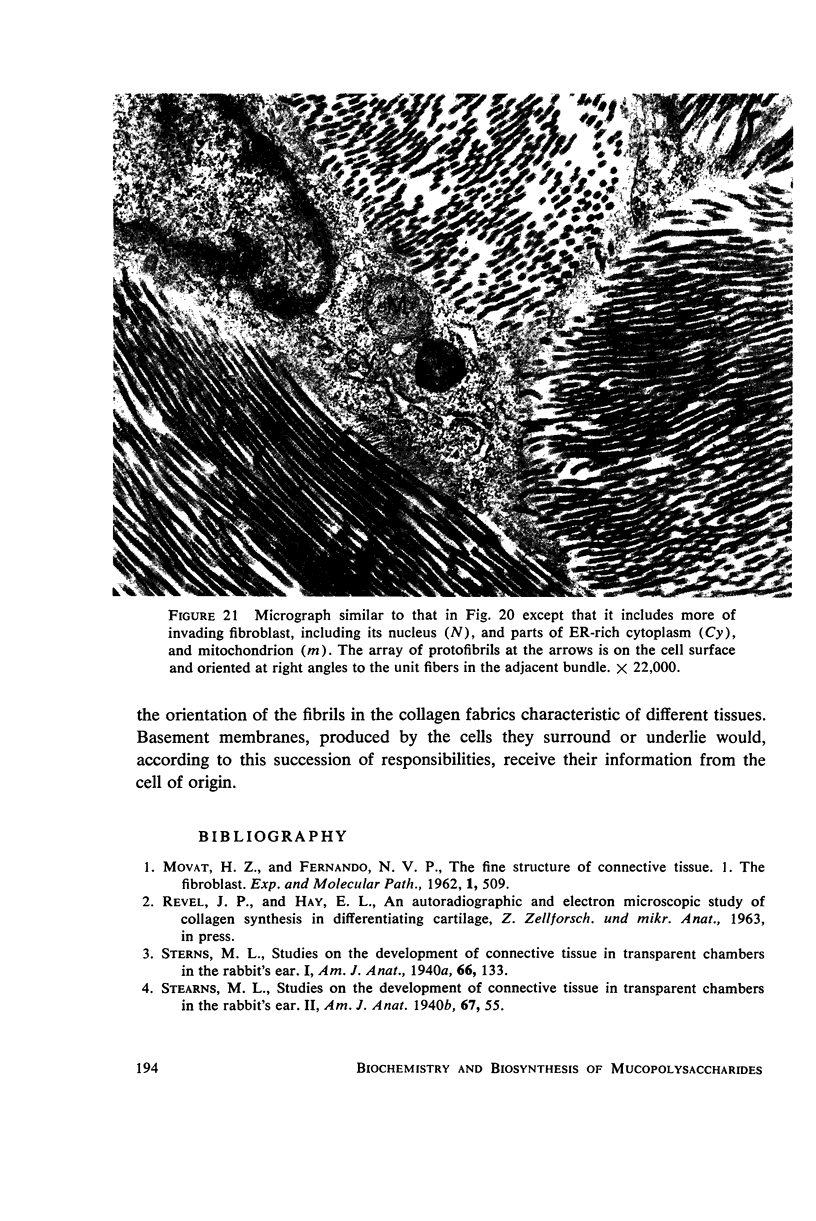
- PARKS H. F. Morphological study of the extrusion of secretory materials by the parotid glands of mouse and rat. J Ultrastruct Res. 1962 Jun;6:449–465. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(62)80002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEACH R., WILLIAMS G., CHAPMAN J. A. Alight and electron optical study of regenerating tendon. Am J Pathol. 1961 Apr;38:495–513. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER K. R., PAPPAS G. D. Collagen formation by fibroblasts of the chick embryo dermis. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 Jan 25;5(1):153–166. doi: 10.1083/jcb.5.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS W. C., WATSON R. F., PAPPAS G. D., PORTER K. R. Some effects of anti-collagen serum on collagen formation in tissue culture: a preliminary report. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1955 Jul 25;1(4):381–384. doi: 10.1083/jcb.1.4.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSS R., BENDITT E. P. Wound healing and collagen formation. III. A quantitative radioautographic study of the utilization of proline-H3 in wounds from normal and scorbutic guinea pigs. J Cell Biol. 1962 Oct;15:99–108. doi: 10.1083/jcb.15.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARNER J. R., KNOPF P. M., RICH A. A multiple ribosomal structure in protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jan 15;49:122–129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YARDLEY J. H., HEATON M. W., GAINES L. M., Jr, SHULMAN L. E. Collagen formation by fibroblasts: preliminary electron microscopic observations using thin sections of tissue cultures. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1960 Jun;106:381–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]