Abstract
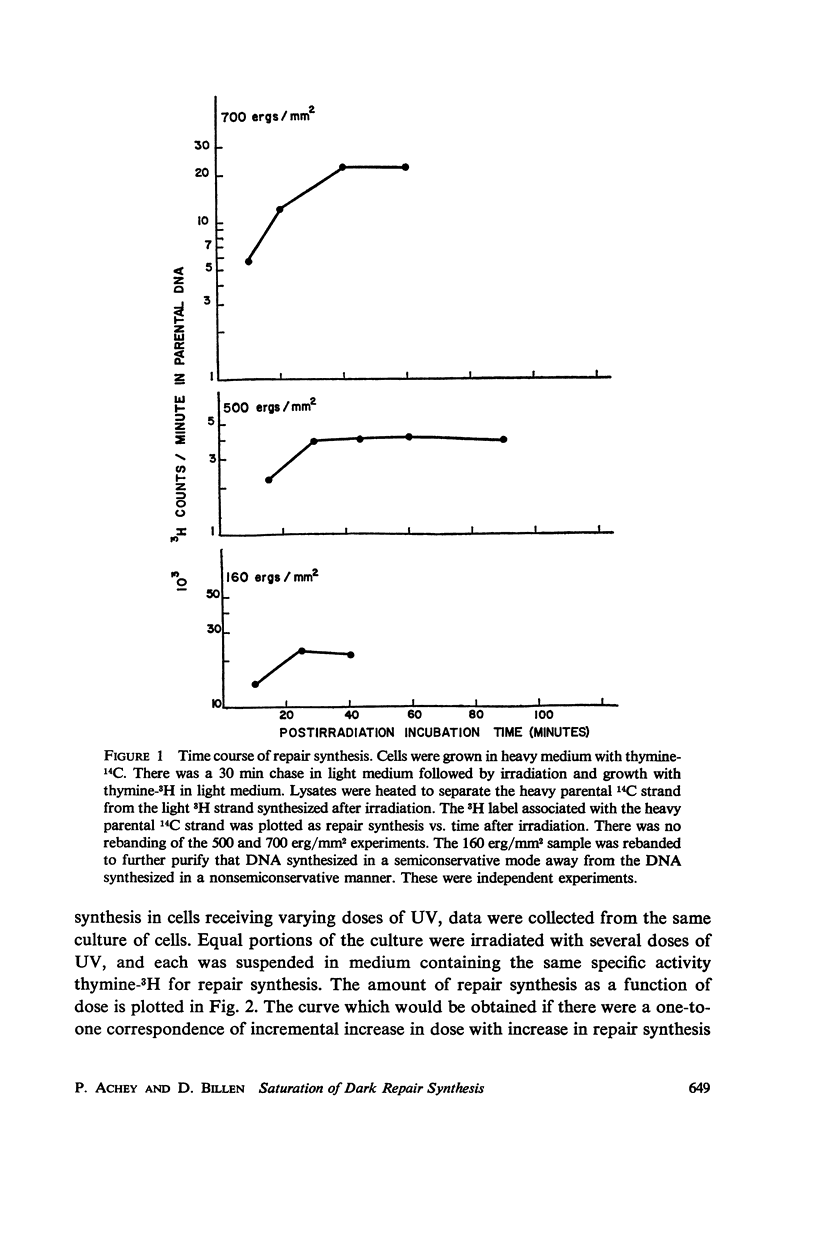
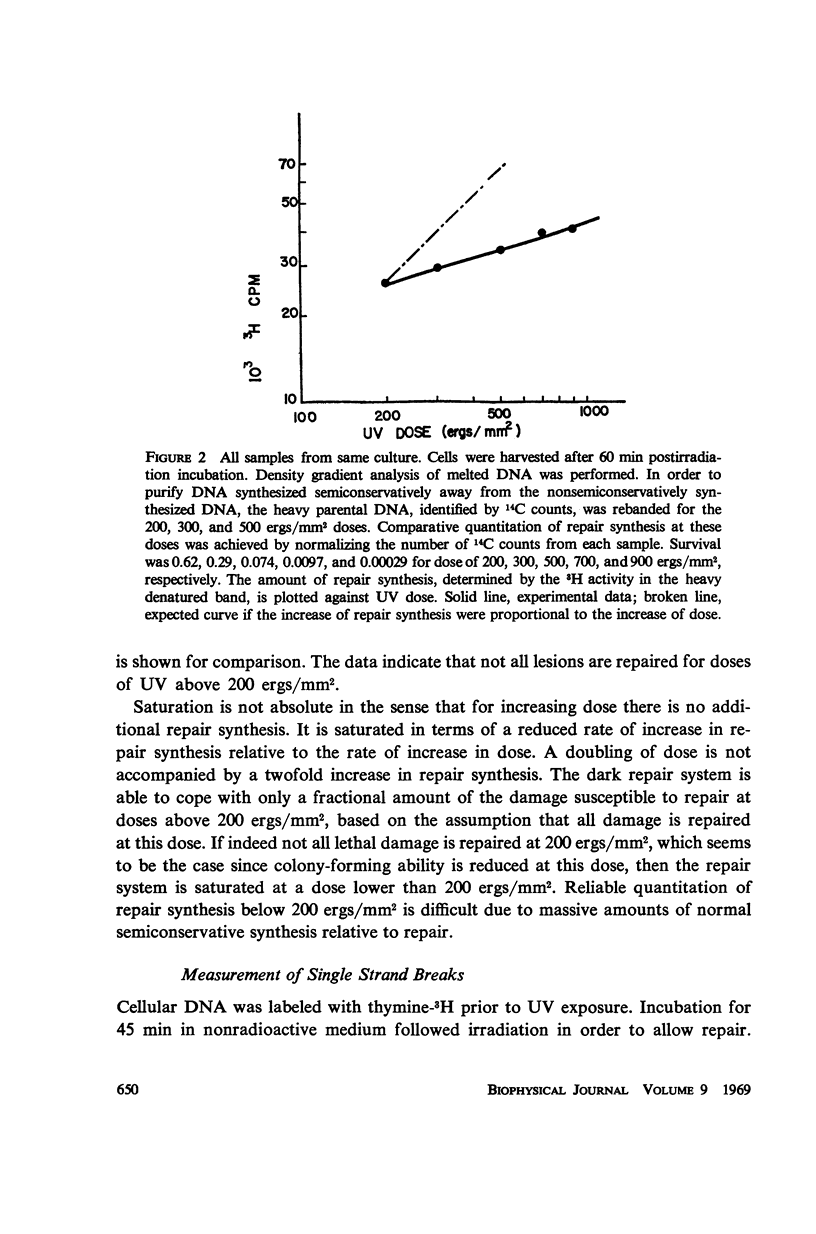
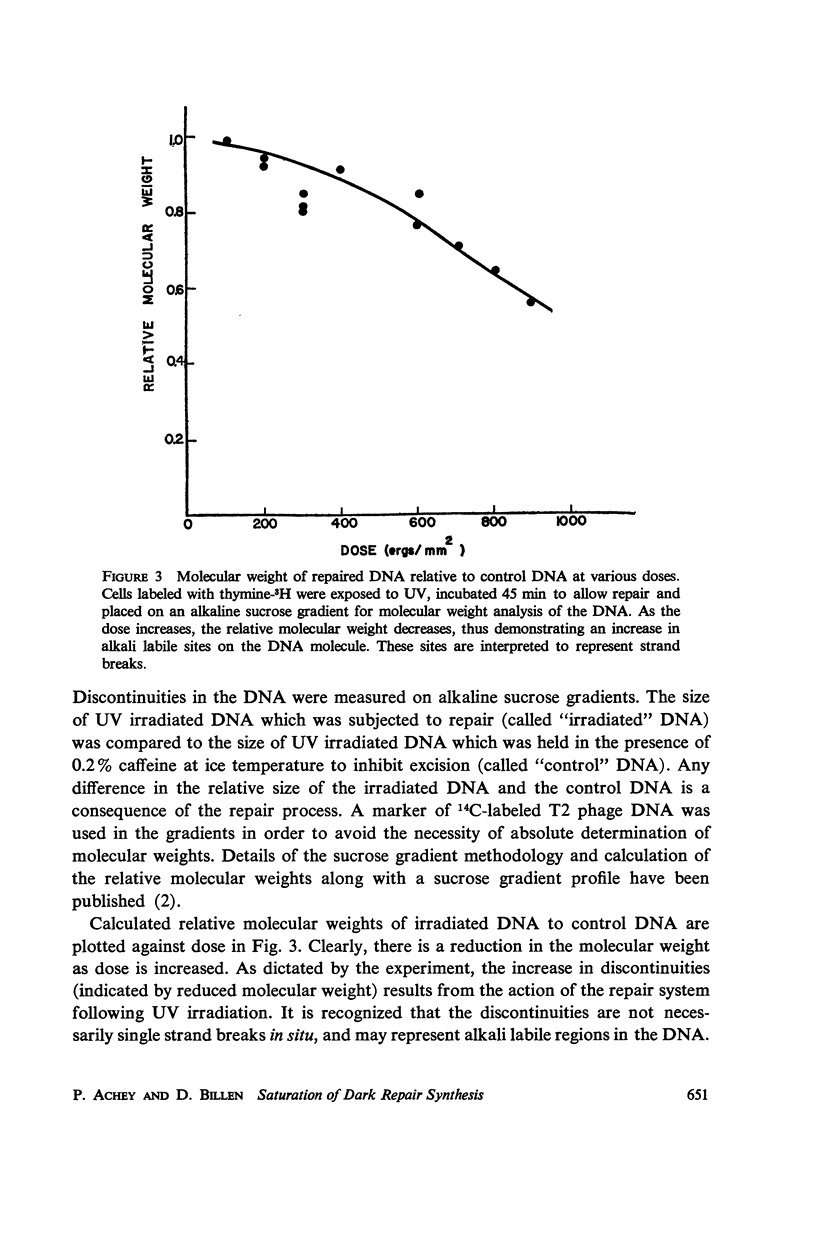
Reversal of ultraviolet light damage to DNA by the dark repair system is limited. Experiments utilizing density and radioactive labels demonstrated that repair synthesis is not proportional to dose at doses above 200 ergs/mm2. In addition, the number of residual excision induced gaps in Escherichia coli B/r hcr+ DNA increases with higher UV doses. The extent of repair is apparently limited by saturation of the repair synthesis step.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achey P. M., Whitfield V. G. Influence of anoxia on radiation-induced breaks in the Escherichia coli chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):1180–1181. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.1180-1181.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billen D., Hewitt R. R., Lapthisophon T., Achey P. M. Deoxyribonucleic acid repair replication after ultraviolet light or x-ray exposure of bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1538–1545. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1538-1545.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath R. A., Williams R. W. Reconstruction in vivo of irradiated Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid; the rejoining of broken pieces. Nature. 1966 Oct 29;212(5061):534–535. doi: 10.1038/212534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


